 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 APOD: 2026 January 25 – Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: 2026 January 25 – Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
This moon is doomed.
Mars,
the red planet named for the
Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos, whose
names are derived from the Greek for Fear and
Panic.
These Martian moons may well be captured
asteroids
originating in the main
asteroid belt between Mars and
Jupiter
or perhaps from even more distant reaches of
our Solar System.
The larger moon, Phobos, is indeed seen
to be a cratered, asteroid-like object in this
stunning color image from the robotic
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter,
which can image objects as small as 10 meters.
But Phobos orbits
so close to Mars - about 5,800 kilometers above the
surface compared to 400,000 kilometers
for our Moon - that gravitational
tidal forces are dragging it down.
In perhaps 50 million years,
Phobos is expected to disintegrate
into a ring of debris.
 APOD: 2025 December 30 – An Artificial Comet
APOD: 2025 December 30 – An Artificial Comet
Explanation:
Yes, but can your comet tail do this?
No, and what you are seeing is not the
tail of a
comet.
The picture features a
cleverly overlayed time-lapse
sequence of a
group of satellites orbiting
Earth together in June.
Specifically, these are
Starlink communications satellites in
low Earth orbit reflecting back sunlight before sunrise to
Inner Mongolia,
China.
Although the satellites appear to the
human eye as points,
the 20-second-long camera exposures caused them to appear as short
streaks.
Currently there are over 9000
Starlinks in orbit,
with more being
launched nearly every week.
Other
satellite constellations are also being planned.
 APOD: 2025 December 1 – 3I ATLAS: Tails of an Interstellar Comet
APOD: 2025 December 1 – 3I ATLAS: Tails of an Interstellar Comet
Explanation:
How typical is our Solar System?
Studying 3I/ATLAS, a comet just passing through, is providing clues.
Confirmed previous interstellar visitors include an
asteroid,
a comet,
a meteor, and a
gas wind dominated by hydrogen and helium.
Comet 3I/ATLAS
appears
relatively normal when compared to
Solar
System
comets,
therefore providing more evidence that
our Solar System is a somewhat typical star system.
For example, Comet 3I/ATLAS has a broadly similar
chemical composition and
ejected dust.
The featured image
was captured last week from
Texas and shows a
green coma, a wandering
blue-tinted ion tail likely deflected by our
Sun's wind, and a slight
anti-tail, all typical cometary attributes.
The comet, visible with
a telescope, passed its closest to the Sun in late October and will pass its closest to the Earth in mid-December,
after which it will return to
interstellar space and never return.
 APOD: 2025 November 10 – Micro Moon vs Super Moon
APOD: 2025 November 10 – Micro Moon vs Super Moon
Explanation:
What was so super about Wednesday's supermoon?
Last week, a full moon occurred that appeared
slightly larger and brighter than usual.
The reason is that
the Moon's fully illuminated
phase
occurred within a short time from
perigee - when the Moon was its closest to the Earth in its
elliptical orbit.
Although the precise conditions that define a supermoon vary, last
Wednesday's supermoon was surely the closest, largest, and brightest
full moon this year.
One reason
supermoons
are popular is because they are so easy to see -- just go outside at
sunset and watch an impressive full moon rise!
Pictured here, Wednesday's supermoon is compared to April's micro moon --
when a
full Moon occurs near the furthest part of the Moon's orbit --
so that it appears slightly smaller and dimmer than usual.
Given many definitions, at least one
supermoon occurs each year, with another one coming next month (moon-th).
 APOD: 2025 November 4 – Comet Lemmon Beyond Lomnický Peak
APOD: 2025 November 4 – Comet Lemmon Beyond Lomnický Peak
Explanation:
Comet Lemmon has been putting on a show for cameras around the globe.
Passing nearest to Earth in late October, the
photogenic comet
C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) sprouted
two long and
picturesque tails:
a blue ion tail and a white dust tail.
The ion tail is pushed away from the
coma by the ever-present but ever-changing
solar wind, at one point extending over 20 times the diameter of the
full Moon --
as captured in this long-duration exposure.
The shorter and wider
dust tail is pushed away from the
coma and shines by reflecting sunlight.
The featured picture, captured two weeks ago, framed the
comet behind
Lomnický Peak of the
High Tatra Mountains,
home to the
Slovakian
Lomnický Stit Observatory.
Comet Lemmon is now fading as it
heads away from planet Earth.
The huge
shedding
snowball will
round the Sun later this week.
 APOD: 2025 October 17 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
APOD: 2025 October 17 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
Explanation:
This asteroid has a moon.
The
robot spacecraft Galileo
enroute to explore the
Jovian system in 1993,
encountered and photographed two
asteroids during its long interplanetary voyage.
The second minor planet it photographed,
243 Ida,
was discovered to have a moon.
The tiny moon,
named Dactyl,
is only about 1.6 kilometers across and seen as a
small dot to the right
in the image.
In contrast, Ida is much larger,
measuring about 60 kilometers long and 25 km wide.
In fact,
Dactyl is the
first moon of an asteroid ever discovered.
But now many asteroids
are known to have moons.
Minor planet names
Ida and Dactyl were taken from
Greek mythology.
 APOD: 2025 September 16 – New Comet SWAN25B over Mexico
APOD: 2025 September 16 – New Comet SWAN25B over Mexico
Explanation:
A newly discovered comet is already visible with binoculars.
The comet,
C/2025 R2 (SWAN) and nicknamed SWAN25B,
is brightening significantly as it emerges from the
Sun's direction and might soon become visible on your smartphone --
if not
your eyes.
Although the brightnesses of
comets are notoriously hard to predict,
many comets appear brighter as they approach the Earth, with
SWAN25B reaching only a quarter of the Earth-Sun distance near October 19.
Nighttime skygazers
will also be watching for a
SWAN25B-spawned meteor shower around
October 5 when our Earth passes through the plane of the
comet's orbit.
The unexpectedly
bright comet was discovered by an
amateur astronomer in images of the
SWAN instrument on
NASA's
SOHO satellite.
The comet is currently best observed in southern skies but is slowly moving north.
The featured image was captured at sunset three days ago
just above the western horizon in
Zacatecas,
Mexico.
 APOD: 2025 January 28 – Comet G3 ATLAS over Uruguay
APOD: 2025 January 28 – Comet G3 ATLAS over Uruguay
Explanation:
Comets can be huge.
When far from the Sun, a comet's size usually refers to its
hard nucleus of ice and rock,
which typically spans a few kilometers -- smaller than even a
small moon.
When
nearing the Sun, however, this
nucleus can
eject dust and gas and leave a
thin tail that can spread to an
enormous length --
even greater than the distance between the
Earth and the
Sun.
Pictured,
C/2024 G3 (ATLAS) sports a
tail of sunlight-reflecting dust and glowing gas that
spans several times the apparent size of a full
moon, appearing
even larger on
long duration camera images
than to the unaided eye.
The
featured image shows impressive Comet ATLAS over trees and a grass field in
Sierras de Mahoma,
San Jose,
Uruguay
about a week ago.
After being
prominent in the sunset skies of
Earth's southern hemisphere,
Comet G3 ATLAS is
now fading
as it moves away from the Sun,
making its impressive tails increasingly hard to see.
 APOD: 2025 January 15 – Wolf Moon Engulfs Mars
APOD: 2025 January 15 – Wolf Moon Engulfs Mars
Explanation:
Does the Moon ever engulf Mars?
Yes, but only in the sense that it moves in front, which happens on
rare occasions.
This happened just yesterday, though, as seen from some locations in
North America and western Africa.
This occultation was notable
not only because the Moon was a fully lit
Wolf Moon, but because Mars was near its largest and brightest, moving to
opposition -- the closest to the Earth in its orbit -- only tomorrow.
The engulfing, more formally called an
occultation, typically lasts about an hour.
The featured image was taken from near
Chicago,
Illinois,
USA just as
Earth's largest satellite
was angularly moving away from the much more distant
red planet.
Our
Moon
occasionally moves in front of all of the
Solar System's planets.
Given the temporary alignment of
orbital planes, the
next time our
Moon eclipses Mars
will be a relatively soon February 9.
 APOD: 2024 November 27 – The Meteor and the Comet
APOD: 2024 November 27 – The Meteor and the Comet
Explanation:
How different are these two streaks?
The streak on the upper right is
Comet Tsuchinshan-Atlas showing an
impressive dust tail.
The comet is a large and dirty iceberg that entered the inner
Solar System and is
shedding gas and dust
as it is warmed by the Sun's light.
The streak on the lower left is a
meteor showing an impressive
evaporation trail.
The meteor is a small and cold rock that entered the
Earth's atmosphere and is shedding gas and dust as it is
warmed by molecular collisions.
The meteor was likely once part of a comet or
asteroid -- perhaps later composing part of its tail.
The meteor was
gone in a flash
and was only caught by coincidence during a
series of exposures documenting the
comet's long tail.
The featured image was captured just over a month ago from
Sichuan Province in
China.
 APOD: 2024 October 17 - The Clipper and the Comet
APOD: 2024 October 17 - The Clipper and the Comet
Explanation:
NASA's Europa Clipper
is now headed toward an ocean world beyond Earth.
The large spacecraft is tucked into the payload fairing atop the
Falcon Heavy rocket in this
photo, taken at Kennedy Space Center
the day before the mission's successful October 14 launch.
Europa Clipper's interplanetary voyage will first take it to Mars,
then back to Earth, and then on to Jupiter on
gravity assist trajectories
that will allow it to enter orbit around Jupiter in April 2030.
Once orbiting Jupiter, the spacecraft will fly past Europa 49 times,
exploring a Jovian moon
with a global subsurface ocean that may have conditions to support life.
Posing in the background next to the floodlit rocket
is Comet Tsuchinsan-ATLAS, about a day after the comet's closest approach to
Earth.
A current darling of evening skies,
the naked-eye comet is a
visitor from the distant Oort cloud
 APOD: 2024 October 4 - Comet at Moonrise
APOD: 2024 October 4 - Comet at Moonrise
Explanation:
Comet C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS)
is growing brighter in planet Earth's sky.
Fondly known as comet A3,
this new visitor to the inner Solar System is traveling from the
distant Oort cloud.
The comet reached perihelion,
its closest approach to the Sun,
on September 27 and will reach perigee, its
closest to our fair planet, on October 12,
by then becoming an evening sky apparition.
But comet A3
was an early morning riser on September 30
when this image was made.
Its bright coma and already long tail share a pre-dawn skyscape from
Praia Grande, Santa Catarina in southern Brazil with
the waning crescent Moon just peeking above the eastern horizon.
While the behaviour of comets is
notoriously
unpredictable, Tsuchinshan–ATLAS could become a
comet visually rivaling
C/2020 F3 (NEOWISE).
Comet NEOWISE
wowed skygazers in the summer of 2020.
 APOD: 2024 April 29 – Comet, Planet, Moon
APOD: 2024 April 29 – Comet, Planet, Moon
Explanation:
Three bright objects satisfied seasoned stargazers of the western sky just after sunset earlier this month.
The most familiar was
the Moon,
seen on the upper left in a crescent
phase.
The rest of the Moon was
faintly visible by sunlight first reflected by
the Earth.
The bright planet
Jupiter,
the largest planet in
the Solar System,
is seen to the upper left.
Most unusual was
Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks, below the Moon and showing a
stubby dust tail on the right but an
impressive ion
tail extending upwards.
The featured image, a composite of several images taken consecutively at the same location and with the same camera, was taken near the village of
Llers, in
Spain's
Girona province.
Comet Pons-Brooks passed its closest to
the Sun
last week and is now dimming as it
moves into southern skies
and returns to the outer Solar System.
 APOD: 2024 April 8 – The Changing Ion Tail of Comet Pons Brooks
APOD: 2024 April 8 – The Changing Ion Tail of Comet Pons Brooks
Explanation:
How does a comet tail change?
It depends on the comet.
The ion tail of
Comet 12P/Pons–Brooks has been changing markedly,
as detailed in the featured image sequenced over nine days
from March 6 to 14 (top to bottom).
On some days, the comet's
ion tail was relatively long and complex,
but not every day.
Reasons for tail changes include the rate of
ejection of material from the
comet's nucleus,
the strength and complexity of the
passing solar wind, and the
rotation rate of the
comet.
Over the course of a week, apparent changes even include a
change of perspective from the Earth.
In general, a comet's
ion tail will point away from the Sun,
as gas expelled is pushed out by the
Sun's wind.
Today,
Pons-Brooks may become a rare comet
suddenly visible in the middle of the day for those able to see the
Sun totally eclipsed by the Moon.
 APOD: 2024 March 18 – Comet Pons Brooks Swirling Coma
APOD: 2024 March 18 – Comet Pons Brooks Swirling Coma
Explanation:
A bright comet will be visible during next month's total solar eclipse.
This very
unusual coincidence occurs because
Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks's
return to the inner Solar System places it by chance only
25 degrees away from the Sun during Earth's
April 8 total solar eclipse.
Currently the comet
is just on the
edge of visibility
to the unaided eye,
best visible with binoculars in the early evening sky toward the
constellation
of the Fish
(Pisces).
Comet Pons-Brooks,
though, is putting on quite a show for deep camera images even now.
The featured image is a
composite of three very specific colors, showing the comet's ever-changing
ion tail in light blue, its outer
coma in green,
and highlights some red-glowing gas around the coma in a
spiral.
The spiral is thought to be caused by gas being expelled by the slowly
rotating nucleus of the giant iceberg comet.
Although it is always difficult to predict the future brightness of comets,
Comet Pons-Brook
has been particularly prone to
outbursts, making it even more difficult
to predict how bright it will actually be as the
Moon moves in front of the Sun on
April 8.
 APOD: 2024 March 11 – A Full Plankton Moon
APOD: 2024 March 11 – A Full Plankton Moon
Explanation:
What glows in the night?
This night
featured a combination of usual and unusual glows.
Perhaps the most usual glow was from
the Moon, a potentially familiar object.
The full Moon's nearly
vertical descent results from the observer being near
Earth's equator.
As the Moon sets,
air and
aerosols in
Earth's atmosphere preferentially scatter out blue light, making
the
Sun-reflecting satellite appear reddish when
near the horizon.
Perhaps the most
unusual glow
was from the bioluminescent
plankton, likely less familiar objects.
These microscopic creatures glow blue, it is thought, primarily to
surprise
and
deter predators.
In this case, the glow was caused primarily by
plankton-containing waves crashing onto the beach.
The image was taken on
Soneva Fushi Island,
Maldives just over
one year ago.
 APOD: 2024 February 13 – A January Wolf Moon
APOD: 2024 February 13 – A January Wolf Moon
Explanation:
Did you see the full moon last month?
During every month, on average, a
full moon occurs in the skies over
planet Earth.
This is because
the Moon takes a
month
to complete another orbit around our
home planet,
goes through all of its
phases, and once
again has its entire
Earth-facing half lit by reflected sunlight.
Many indigenous cultures give each full moon a name, and this past full moon's
names include the Ice Moon, the Stay at Home Moon, and the Quiet Moon.
Occurring in January on the
modern western calendar,
several cultures have also named the most recent full moon the
Wolf Moon, in honor of the
famous howling animal.
Featured here above the Italian
Alps mountains,
this past
Wolf Moon was captured in combined long and short exposure images.
The image is
striking because, to some,
the surrounding clouds appear as a wolf's mouth ready to swallow the
Wolf Moon, while others see the Moon as a wolf's eye.
 APOD: 2024 January 24 – Earth and Moon from Beyond
APOD: 2024 January 24 – Earth and Moon from Beyond
Explanation:
What do the Earth and Moon look like from beyond the Moon?
Although
frequently
photographed
together, the familiar duo was captured with this unusual perspective in late 2022 by the robotic
Orion spacecraft of
NASA's
Artemis I
mission as it looped around Earth's most massive satellite and
looked back toward its home world.
Since our
Earth
is about four times the diameter of the
Moon, the satellite’s
seemingly large size was caused by the capsule
being closer to the smaller body.
Artemis II,
the next launch in NASA’s Artemis series,
is currently scheduled to take people around the Moon in 2025, while
Artemis III
is planned to return humans to
lunar surface in late 2026.
Last week,
JAXA's robotic
SLIM
spacecraft, launched from
Japan,
landed on the Moon and released two hopping rovers.
 APOD: 2023 November 4 - Dinkinesh Moonrise
APOD: 2023 November 4 - Dinkinesh Moonrise
Explanation:
Last Wednesday the
voyaging Lucy spacecraft
encountered
its first asteroid,
152830
Dinkinesh, and discovered the inner-main belt asteroid has a moon.
From a distance of just over 400 kilometers, Lucy's Long-Range
Reconnaissance Imager
captured this close-up
of the binary system during
a flyby at 4.5 kilometer per second or around 10,000 miles per hour.
A marvelous world, Dinkinesh
itself is small, less than 800 meters (about 0.5 miles) across at its widest.
Its satellite is seen from the spacecraft's perspective
to emerge from behind the primary asteroid.
The asteroid moon is estimated to be only about 220 meters wide.
 APOD: 2023 August 27 – Three Galaxies and a Comet
APOD: 2023 August 27 – Three Galaxies and a Comet
Explanation:
Diffuse starlight and dark nebulae
along the southern
Milky Way arc over the
horizon and sprawl diagonally through this
gorgeous nightscape.
The breath-taking mosaic spans a wide
100 degrees, with the rugged
terrain of the
Patagonia,
Argentina
region in the foreground.
Along with the
insider's view of
our own galaxy, the image
features our outside perspective on two irregular satellite galaxies -
the Large and
Small Magellanic Clouds.
The scene also captures the
broad tail
and bright coma of
Comet McNaught, the
Great Comet of 2007.
 APOD: 2023 July 14 - Comet C/2023 E1 ATLAS near Perihelion
APOD: 2023 July 14 - Comet C/2023 E1 ATLAS near Perihelion
Explanation:
Comet C/2023 E1 (ATLAS)
was just spotted in March,
another comet found by the NASA funded Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last
Alert System.
On July 1 this Comet ATLAS reached perihelion,
its closest approach to the Sun.
Days later the telescopic comet was
captured in this frame
sporting a pretty greenish coma
and faint, narrow ion tail against a background of stars in the
far northern constellation Ursa Minor.
This comet's closest approach to Earth is still to come though.
On August 18 this
visitor to the inner Solar System
will be a mere 3 light-minutes or so from our fair planet.
Based on its
inclination to the ecliptic plane
and orbital
period of about 85 years C/2023 E1 (ATLAS) is
considered a
Halley-type comet.
 APOD: 2023 June 3 - Charon: Moon of Pluto
APOD: 2023 June 3 - Charon: Moon of Pluto
Explanation:
A darkened and mysterious north polar region
known to some as
Mordor Macula caps this premier high-resolution view.
The
portrait of Charon, Pluto's largest moon,
was captured by New Horizons near the spacecraft's closest
approach on July 14, 2015.
The combined blue, red,
and infrared data was processed to enhance colors
and follow variations in Charon's surface properties
with a resolution of about 2.9 kilometers (1.8 miles).
A stunning image of Charon's Pluto-facing hemisphere, it also
features a clear view of an apparently
moon-girdling belt of
fractures and canyons that seems to
separate smooth southern plains from varied northern terrain.
Charon is 1,214 kilometers (754 miles) across.
That's about 1/10th the size of planet Earth
but a whopping 1/2 the diameter of
Pluto
itself, and makes it the largest satellite relative to its
parent body in the Solar System.
Still, the moon appears as a small bump at about the 1 o'clock position
on Pluto's disk in the grainy, negative,telescopic picture inset
at upper left.
That view was used by James Christy and Robert Harrington
at the U.S. Naval Observatory in Flagstaff to
discover
Charon in June of 1978.
 APOD: 2023 May 28 – Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
APOD: 2023 May 28 – Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
Explanation:
This asteroid has a moon.
The robot spacecraft Galileo on route to
Jupiter
in 1993 encountered and photographed two
asteroids during its long interplanetary voyage.
The second minor planet it photographed,
243 Ida, was
unexpectedly
discovered to have a moon.
The tiny moon, Dactyl, is only about 1.6 kilometers across and seen as a
small dot on the right of the sharpened
featured image.
In contrast, the
potato-shaped Ida is much larger,
measuring about 60 kilometers long and 25 km wide.
Dactyl is the first moon of an asteroid ever discovered --
now many asteroids are
known to have moons.
The names Ida and Dactyl are from
Greek mythology.
 APOD: 2023 February 7 – A Comet and Two Dippers
APOD: 2023 February 7 – A Comet and Two Dippers
Explanation:
Can you still see the comet?
Yes. Even as C/2022 E3 (ZTF) fades, there is still time to see it if you know
where and when to look.
Geometrically,
Comet ZTF has passed its closest to both the
Sun and the
Earth
and is now headed back to the outer
Solar System.
Its orbit around the Sun has it gliding across the northern sky all month, after passing
near Polaris and both the
Big and
Little Dippers
last month.
Pictured,
Comet ZTF was photographed between the two dippers in late January
while sporting an
ion tail that extended over 10
degrees.
Now below naked-eye visibility,
Comet ZTF can be found with binoculars or a small telescope and a
good sky map.
A good time to
see the comet over the next week is after the Sun sets -- but before
the Moon rises.
The comet will move
nearly in front of Mars in a few
days
 APOD: 2022 September 29 - DART Asteroid Impact from Space
APOD: 2022 September 29 - DART Asteroid Impact from Space
Explanation:
Fifteen days
before impact,
the DART spacecraft deployed a small companion satellite
to document its historic
planetary defense technology
demonstration.
Provided by the Italian Space Agency, the Light Italian CubeSat for
Imaging Asteroids, aka LICIACube,
recorded this image of the event's
aftermath.
A cloud of ejecta is seen near the right edge of the frame
captured only minutes
following DART's impact with
target asteroid Dimorphos while LICIACube was about 80
kilometers away.
Presently about 11 million kilometers from Earth,
160 meter diameter Dimorphos is a moonlet orbiting 780 meter diameter
asteroid Didymos.
Didymos is seen off center in the LICIACube image.
Over the coming weeks, ground-based telescopic observations will look for a
small change in Dimorphos' orbit
around Didymos
to
evaluate
how effectively the DART impact deflected its target.
 APOD: 2022 July 3 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: 2022 July 3 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
This moon is doomed.
Mars,
the red planet named for the
Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos, whose
names are derived from the Greek for Fear and
Panic.
These martian moons may well be captured
asteroids
originating in the main
asteroid belt between Mars and
Jupiter
or perhaps from even more distant reaches of
our Solar System.
The larger moon, Phobos, is indeed seen
to be a cratered, asteroid-like object in this
stunning color image from the robotic
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter,
with objects as small as 10 meters visible.
But Phobos orbits
so close to Mars - about 5,800 kilometers above the
surface compared to 400,000 kilometers
for our Moon - that gravitational
tidal forces are dragging it down.
In perhaps 50 million years,
Phobos is expected to disintegrate
into a ring of debris.
 APOD: 2022 January 28 - Western Moon, Eastern Sea
APOD: 2022 January 28 - Western Moon, Eastern Sea
Explanation:
The Mare Orientale,
Latin for Eastern Sea, is one of the most striking
large scale lunar features.
The youngest of the large lunar impact basins it's
very difficult to see from an
earthbound perspective.
Still, taken during a period of favorable tilt, or libration of the lunar
nearside, the Eastern Sea can be found near top center in this sharp
telescopic view, extremely foreshortened
along the Moon's western edge.
Formed by the impact of an asteroid over 3 billion years
ago and nearly 1000 kilometers across, the
impact basin's
concentric circular features are ripples in the lunar crust.
But they are a little easier to spot in
more direct images of the region taken from
lunar orbit.
So why is the Eastern Sea at the Moon's western edge?
The Mare Orientale lunar feature was named before 1961.
That's when the convention labeling
east and west on lunar maps
was reversed.
 APOD: 2021 November 28 - A High Cliff on Comet Churyumov Gerasimenko
APOD: 2021 November 28 - A High Cliff on Comet Churyumov Gerasimenko
Explanation:
This high cliff occurs not on a planet, not on a moon, but on a comet.
It was discovered to be part of the dark nucleus of
Comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko (CG) by
Rosetta,
a robotic spacecraft
launched by
ESA that rendezvoused with the Sun-orbiting comet in 2014.
The ragged cliff, as featured
here, was imaged by Rosetta in 2014.
Although towering about one kilometer high, the low surface gravity of
Comet CG would likely make it an
accessible climb -- and even a
jump from the
cliff survivable.
At the foot of the cliff is relatively smooth terrain dotted with
boulders as large as 20 meters across.
Data from
Rosetta indicates that the ice in
Comet CG
has a significantly different
deuterium
fraction -- and hence likely a different origin -- than the water in Earth's oceans.
Rosetta ended its mission with a controlled impact onto Comet CG in 2016.
Comet CG has just completed
another close approach to Earth and
remains visible through a small telescope.
 APOD: 2021 October 10 - Full Moon Silhouettes
APOD: 2021 October 10 - Full Moon Silhouettes
Explanation:
Have you ever watched the Moon rise?
The slow rise of a nearly full moon over a clear horizon can be an impressive sight.
One impressive moonrise was imaged in early 2013 over
Mount Victoria
Lookout in
Wellington,
New Zealand.
With detailed planning, an
industrious astrophotographer
placed a camera about two kilometers away and pointed it across the lookout to where
the Moon
would surely soon be making its nightly debut.
The
featured single shot sequence is unedited and
shown in real time -- it is not a time lapse.
People on
Mount Victoria Lookout
can be seen in silhouette
themselves admiring the dawn of Earth's largest satellite.
Seeing a moonrise yourself is not difficult:
it happens every day, although only half the time at night.
Each day the
Moon rises about
fifty minutes later
than the previous day, with a full moon
always rising at sunset.
This Saturday, October 16, is
International Observe the Moon Night,
where you observe a
first-quarter Moon along with
other lunar enthusiasts.
 APOD: 2021 September 5 - Earth and Moon
APOD: 2021 September 5 - Earth and Moon
Explanation:
The Earth and Moon are rarely photographed together.
One of most spectacular times this occurred was about 30 years ago when the Jupiter-bound
Galileo spacecraft
zoomed past our home planetary system.
Then, robotic Galileo watched from about 15-times the
Earth-Moon separation as
our only natural satellite glided past our home world.
The featured video combines 52 historic
color-enhanced images.
Although our Moon may
appear small next to the
Earth,
no other planet in our Solar System has a
satellite
so
comparable
in
size
.
The Sun, far off to the right, illuminated about half of each sphere,
and shows the spinning Earth's
white clouds,
blue oceans, and tan continents.
 APOD: 2021 February 3 - Found on the Moon: Candidate for Oldest Known Earth Rock
APOD: 2021 February 3 - Found on the Moon: Candidate for Oldest Known Earth Rock
Explanation:
Was the oldest known rock on Earth found on the Moon?
Quite possibly.
The story opens with the
Apollo 14 lunar mission.
Lunar sample
14321, a large rock found in
Cone crater by astronaut
Alan Shepard, when analyzed back on Earth,
was found to have a fragment that was a much
better match to Earth rocks than other Moon rocks.
Even more surprising,
that rock section has recently been dated back
4 billion years,
making it older, to within measurement uncertainty, than
any rock ever found on Earth.
A leading hypothesis now holds that an ancient comet or
asteroid impact launched
Earth rocks into the Solar System, some of which fell back to
the Moon,
became mixed with heated lunar soil and other rocks, cooled, and re-fragmented.
The video features an internal
X-ray scan of
14321
showing multiple sections with markedly different chemistries.
Moon rocks
will continue to be
studied to learn a more complete history of the
Moon,
the Earth, and the
early Solar System.
Friday marks the
50th Anniversary of the
Apollo 14
landing on the Moon.
 APOD: 2020 November 12 - Comet ATLAS and Orion's Belt
APOD: 2020 November 12 - Comet ATLAS and Orion's Belt
Explanation:
With its closest approach to planet Earth scheduled for November 14,
this Comet ATLAS (C/2020 M3) was discovered just this summer,
another comet found by the NASA funded
Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System.
It won't get as bright
as Comet NEOWISE
but it can still be spotted using binoculars, as it
currently sweeps through the familiar constellation of Orion.
This telephoto field from November 8,
blends exposures registered on the comet with exposures
registered on Orion's stars.
It creates an effectively deep skyview that shows colors and details you
can't quite see though, even in binoculars.
The comet's telltale greenish coma is toward the upper left, above
Orion's three belt stars lined-up across the frame below center.
You'll also probably spot the Orion Nebula, and famous Horsehead Nebula
in the stunning field of view.
Of course one of
Orion's belt stars is nearly 2,000 light-years away.
On November 14,
this comet ATLAS
will fly a mere 2.9 light-minutes from Earth.
 APOD: 2020 November 11 - Colors of the Moon
APOD: 2020 November 11 - Colors of the Moon
Explanation:
What color is the Moon?
It depends on the night.
Outside of the Earth's atmosphere, the
dark Moon,
which shines by reflected sunlight, appears a
magnificently brown-tinged gray.
Viewed from inside the
Earth's atmosphere, though, the moon can appear quite different.
The featured image highlights a collection of apparent colors of the full moon documented by one astrophotographer over 10 years from
different locations across
Italy.
A
red or yellow colored moon usually indicates a moon seen near the horizon.
There, some of the
blue light has been scattered away
by a long path through the
Earth's atmosphere,
sometimes laden with fine dust.
A blue-colored moon is more rare and
can indicate a moon seen through an atmosphere carrying larger dust particles.
What created the purple moon is
unclear --
it may be a combination of several effects.
The last image captures the
total lunar eclipse of 2018 July --
where the moon,
in Earth's shadow, appeared a
faint red -- due to light
refracted through
air around the
Earth.
The next full moon will occur at the end of this month
(moon-th)
and is known in some cultures as the
Beaver Moon.
 APOD: 2020 November 8 - Martian Moon Phobos from Mars Express
APOD: 2020 November 8 - Martian Moon Phobos from Mars Express
Explanation:
Why is Phobos so dark?
Phobos, the largest and innermost of two
Martian moons, is the darkest moon in the entire
Solar System.
Its unusual orbit and color indicate that it may be a captured
asteroid composed of a mixture of ice and dark rock.
The featured picture
of Phobos near the limb of
Mars
was captured in 2010 by the robot spacecraft
Mars Express currently orbiting Mars.
Phobos is a heavily cratered and
barren moon, with its
largest crater located on the far side.
From images like this,
Phobos has been determined
to be covered by perhaps a meter of
loose dust.
Phobos orbits
so close to Mars that from some places it would appear to rise and
set twice a day, but from other places
it would not be visible at all.
Phobos' orbit around Mars is
continually decaying -- it will likely
break up with pieces crashing to the Martian surface in about 50 million years.
 APOD: 2020 September 25 - Moon over Andromeda
APOD: 2020 September 25 - Moon over Andromeda
Explanation:
The Great Spiral Galaxy
in Andromeda (also known
as M31),
a mere 2.5 million light-years
distant,
is the closest large spiral to our own Milky Way.
Andromeda is visible to the unaided eye as a small, faint, fuzzy patch,
but because its surface brightness is so low, casual
skygazers
can't appreciate the galaxy's impressive extent in
planet Earth's sky.
This entertaining composite image compares the
angular size
of the nearby galaxy
to a brighter, more familiar celestial sight.
In it, a
deep
exposure of Andromeda, tracing beautiful blue star
clusters in spiral arms far beyond the bright yellow core,
is combined with a typical view of a nearly full Moon.
Shown at the same
angular scale, the Moon covers
about 1/2 degree on the
sky, while the galaxy is clearly several times that size.
The deep Andromeda exposure also includes two bright satellite
galaxies, M32 and
M110 (below and right).
 APOD: 2020 September 5 - A Falcon 9 Moon
APOD: 2020 September 5 - A Falcon 9 Moon
Explanation:
Illuminating planet Earth's night, full moons can have many names.
This year the last full moon of northern hemisphere summer was on
September 2, known to some as the
Full Corn Moon.
A few days earlier on August 30 this almost full moon rose just before sunset
though, shining through cloudy skies over
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Florida's
Space Coast.
A well-timed snapshot
caught the glare
of rocket engines firing
below the lunar disk,
a Falcon 9 rocket's first stage successfully
returning to Cape Canaveral's landing zone 1.
About 9 minutes earlier, the same SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket
had launched
the SAOCOM 1B satellite toward polar orbit.
The fourth launch for this reusable Falcon 9 first stage, it
was the first launch to a
polar orbit
from Cape Canaveral since 1969.
 APOD: 2020 July 27 – Comet and Lightning Beyond Bighorn Mountains
APOD: 2020 July 27 – Comet and Lightning Beyond Bighorn Mountains
Explanation:
Normally, Steamboat Point looks cool -- but not this cool.
Every day, the iconic peak of the Bighorn Mountains is an interesting sight, in particular from
US Highway 14 in
Wyoming.
On some rare days, the
rocky vertical ridges
look even more incredible when seen in front of a
distant lightning storm.
Earlier this month, though,
something even more unusual happened -- the naked-eye
Comet NEOWISE rose above it in the middle of the night.
Just as a distant
lightning storm was occurring in the background.
Recognizing a rare opportunity, a determined astrophotographer
spent a sleepless night capturing
over 1400 images of this unusual
triple conjunction.
The featured image is among the best of them, with the foreground lit by the
Moon off to the right.
Comet C/2020 F3 (NEOWISE) is now
headed back to the outer
Solar System, destined to return only in about 6700
years.
 APOD: 2020 July 19 - Rotating Moon from LRO
APOD: 2020 July 19 - Rotating Moon from LRO
Explanation:
No one, presently, sees the Moon rotate like this.
That's because the Earth's moon is tidally locked to the Earth, showing us
only one side.
Given modern digital technology, however, combined with many detailed images returned by the
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), a high resolution virtual
Moon rotation movie has been composed.
The featured time-lapse video
starts with the standard Earth
view of the Moon.
Quickly, though,
Mare Orientale, a large crater with a dark center
that is difficult to see from the Earth, rotates into view just below the equator.
From an entire
lunar month condensed into 24 seconds,
the video clearly shows that the Earth side of
the Moon contains an abundance of
dark lunar maria,
while the lunar far side is dominated by bright
lunar highlands.
Currently, over 19 new missions to the Moon are under active development from eight different countries, most of which have expected launch dates in the next three years.
 APOD: 2020 July 14 - Comet NEOWISE over Stonehenge
APOD: 2020 July 14 - Comet NEOWISE over Stonehenge
Explanation:
Have you ever seen a comet?
Tonight -- and likely the next few nights -- should be a
good chance.
Go outside just at sunset and look to your northwest.
The lower your horizon, the better.
Binoculars may help,
but if your sky is cloudless and dark,
all you should need is your unaided eyes and patience.
As the Sun sets, the sky will darken,
and there will be an unusual faint streak
pointing diagonally near the horizon.
That is Comet NEOWISE.
It is a 5-kilometer-wide
evaporating dirty iceberg visiting from --
and returning to -- the outer
Solar System.
As the
Earth turns,
the comet will soon set, so you might want to take a picture.
In the
featured image,
Comet
C/2020 F3 (NEOWISE)
was captured two mornings ago rising over
Stonehenge in the
UK.
Discovered with the NASA satellite
NEOWISE toward the end of March,
Comet NEOWISE has
surprised many by surviving its closest approach to the Sun, brightening dramatically, and developing impressive (blue) ion and (white) dust tails.
 APOD: 2020 March 21 - Comet ATLAS and the Mighty Galaxies
APOD: 2020 March 21 - Comet ATLAS and the Mighty Galaxies
Explanation:
Comet ATLAS C/2019 Y4
was discovered by the NASA funded
Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System,
the last comet discovery reported in 2019.
Now growing brighter in northern night skies, the comet's pretty
greenish coma is at the upper left of
this telescopic skyview
captured from a remotely operated observatory
in New Mexico on March 18.
At lower right are M81 and M82, well-known as
large, gravitationally interacting galaxies.
Seen through faint dust clouds above the Milky Way,
the galaxy pair lies about 12 million light-years distant, toward
the constellation Ursa Major.
In bound Comet ATLAS is about 9 light-minutes from Earth, still beyond the
orbit of Mars.
The comet's elongated orbit is similar to
orbit of the
Great
Comet of 1844
though, a trajectory that will return
this comet to the inner Solar System in about 6,000 years.
Comet ATLAS
will reach a perihelion
or closest approach to the Sun on May 31 inside the orbit of Mercury and
may become a naked-eye comet
in
the coming days.
 APOD: 2019 December 13 - Full Moon Geminids
APOD: 2019 December 13 - Full Moon Geminids
Explanation:
The dependable annual Geminid meteor shower
will be near its peak tonight
(December 13/14) and before tomorrow's dawn.
As Earth crosses through the
dusty trail of active asteroid 3200 Phaethon
the meteors will flash through the sky from the shower's
radiant in Gemini.
Gemini will be pretty easy for skygazers to find too as it won't be far
from a nearly full waning gibbous Moon.
You don't have look at the shower's radiant to see meteors though.
The almost full moonlight won't hide the brightest of the Geminids
from view either,
but it will substantially reduce the rate of visible
meteors for those who are counting.
In fact, the 2019 Geminids
should look a lot like the 2016 meteor shower.
This composite image from the 2016 Geminids aligns individual
short exposures to capture many of the brighter Geminid meteors,
inspite of a Full Moon shining near the constellation of the Twins.
Along the horizon are the Teide Observatory's
Solar Laboratory (right) and the
Teide volcano on the Canary Island of Tenerife.
 APOD: 2019 September 13 - A Harvest Moon
APOD: 2019 September 13 - A Harvest Moon
Explanation:
Famed in festival, story, and song the best known full moon is
the
Harvest Moon.
For northern hemisphere dwellers that's a traditional name of the
full moon nearest the September equinox.
In most North America time zones
this
year's Harvest Moon
will officially rise on Friday, September 13.
In fact the same Harvest Moon will rise on September 14
for much of the planet though.
Of course the Moon will look almost full in the surrounding days.
Regardless of your time zone the Harvest Moon,
like any other full moon, will rise just opposite the setting Sun.
Near the horizon, the
Moon
Illusion might make it
appear bigger and brighter to you
but this Harvest Moon will be near
lunar apogee.
That's the farthest point in its orbit, making it the most distant,
and so the smallest, full moon of the year.
On August 15 a wheat field harvested in south central France
made this
a harvest moon
scene too, the
full
moon shining on
with beautiful iridescent clouds at sunset.
 APOD: 2018 December 7 - December's Comet Wirtanen
APOD: 2018 December 7 - December's Comet Wirtanen
Explanation:
Coming close in mid-December,
Comet 46P Wirtanen
hangs in this starry sky over the bell tower of a Romanesque church.
In the constructed vertical panorama, a series of digital exposures
capture its greenish coma
on December 3 from Sant Llorenc de la Muga, Girona, Catalonia, Spain,
planet Earth.
With an orbital period that is now about 5.4 years, the
periodic comet's perihelion, its closest approach,
to the Sun will be on December 12.
On December 16 it will be closest to Earth, passing at a distance of
about 11.6 million kilometers or 39 light-seconds.
That's close
for a comet, a mere 30 times the Earth-Moon distance.
A good binocular target
for comet watchers,
Wirtanen could be visible to the unaided eye from a dark sky site.
To spot it after dusk on December 16, look close
on
the sky to the Pleiades star cluster in Taurus.
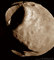 APOD: 2018 November 25 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: 2018 November 25 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
This moon is doomed.
Mars,
the red planet named for the
Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos, whose
names are derived from the Greek for Fear and
Panic.
The origin of the Martian moons is unknown, though, with a leading
hypothesis holding that they are captured
asteroids.
The larger moon, at 25-kilometers across, is Phobos,
and is indeed seen to be a cratered, asteroid-like object in this
false-colored image mosaic taken by the robotic
Viking 1 mission in 1978.
A recent analysis of the unusual long grooves seen on
Phobos indicates that they may result from
boulders rolling away from the giant impact that created the crater on the upper left:
Stickney Crater.
Phobos
orbits so close to Mars - about 5,800 kilometers above the surface compared to 400,000 kilometers
for our Moon - that gravitational
tidal forces
are dragging it down.
The ultimate result will be for
Phobos to break up in orbit and then crash down
onto the Martian surface in about 50 million years.
Well before that -- tomorrow, in fact, if everything
goes according to plan -- NASA's robotic
InSight lander will touch down on Mars
and begin investigating its internal structure.
 APOD: 2018 November 16 - The Hill, The Moon, and Saturn
APOD: 2018 November 16 - The Hill, The Moon, and Saturn
Explanation:
Last Sunday when the Moon was young
its sunlit crescent hung low near the western horizon at sunset.
With strong earthshine it was joined by
Saturn shining in the early
evening sky for a beautiful
conjunction visible to skygazers around our fair planet.
On that clear evening on a hill near
Veszprem, Hungary
mother, daughter, bright planet, and young Moon
are framed in this quiet night skyscape taken with a telephoto lens.
Of course
the Moon ages
too quickly for some,
and by tonight the sunlit part has reached its first quarter phase.
This weekend skygazers spending quality time under
Moon and stars
might expect to see the annual rain of comet dust otherwise
known as the Leonid meteor
shower.
 APOD: 2018 November 15 - Comet 46P Wirtanen
APOD: 2018 November 15 - Comet 46P Wirtanen
Explanation:
Periodic
Comet 46P/Wirtanen is now the brightest comet in the night sky,
but too faint to be seen by eye.
From dark sky sites it could just become naked-eye visible
though, as its 5.4 year long looping orbit takes it
closest to Earth and
the Sun in mid December.
Fluorescing in sunlight,
its spherical coma is about half the
angular size of a full moon in this southern hemisphere telescopic
view from November 7.
Then the comet was about 2 light-minutes away or 35 million kilometers
from Earth-bound telescopes, so the pretty greenish coma seen here is
around 150,000 kilometers across.
That makes it about the size of Jupiter.
The stack of digital images also reveals a very faint tail
extending toward 4 o'clock with a distant background galaxy
notable at the upper left.
As a regular visitor to the inner Solar System, comet 46P/Wirtanen was
once the favored rendezvous target for ESA's comet exploring
Rosetta mission.
 APOD: 2018 November 13 - Rotating Asteroid Bennu from OSIRIS REx
APOD: 2018 November 13 - Rotating Asteroid Bennu from OSIRIS REx
Explanation:
Could this close-by asteroid ever hit the Earth?
Eventually yes -- but probably not for a very long time, even though the asteroid is expected to pass inside the orbit of the Moon next century.
However, to
better understand
the nature and orbit of all near-Earth asteroids, NASA sent the robotic
Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security, Regolith Explorer
(OSIRIS-REx) to investigate this one: the 500-meter across asteroid
101955 Bennu.
Launched in 2016,
OSIRIS-REx
is now approaching Bennu, and is first scheduled to map the
minor planet's rough surface.
The
featured time-lapse video taken earlier this month compacts
Bennu's 4.25-hour rotation period into about 7 seconds.
Bennu's diamond-like appearance is similar to
asteroid Ryugu currently being visited by the
Japanese spacecraft
Hayabusa2.
The exact future orbit of
Bennu is a
bit uncertain due to close passes near the Earth and the
Yarkovsky effect:
a slight force
created by an object's rotationally-induced, asymmetric
infrared glow.
If all goes
according to plan,
ORISIS-Rx will actually touch the asteroid in 2020, collect soil samples, and
return them to Earth in 2023 for detailed analyses.
 APOD: 2018 November 10 - The Old Moon in the Young Moon's Arms
APOD: 2018 November 10 - The Old Moon in the Young Moon's Arms
Explanation:
Tonight the Moon is
young again,
but this stunning image of a young Moon near the western horizon
was taken just after sunset on October 10.
On the lunar disk
Earthshine, earthlight
reflected from the Moon's night side,
is embraced by
the slim, sunlit crescent just over 2 days old.
Along the horizon fading colors of twilight silhouette
the radio telescope dish antennas of the
Very Large Array,
New Mexico, planet Earth.
The view from the Moon would be stunning, too.
When the Moon appears in Earth's sky as a slender crescent,
a dazzlingly bright, nearly full Earth would be seen
from the lunar surface.
A description of earthshine, in terms of sunlight
reflected by Earth's oceans in turn illuminating
the Moon's dark surface, was written 500 years ago by
Leonardo da Vinci.
 APOD: 2018 October 8 - Comet 21P Between Rosette and Cone Nebulas
APOD: 2018 October 8 - Comet 21P Between Rosette and Cone Nebulas
Explanation:
Small bits of this greenish-gray comet are expected to streak across Earth's atmosphere tonight.
Specifically, debris from the
eroding nucleus of
Comet 21P / Giacobini-Zinner, pictured,
causes the annual Draconids meteor shower, which peaks this evening.
Draconid meteors are easy to enjoy this year because meteor rates will likely peak soon after sunset with the
Moon's glare nearly absent.
Patience may be needed, though, as last month's
passing of 21P near the Earth's orbit is
not expected to increase the Draconids' normal meteor rate this year of (only) a few meteors per hour.
Then again, meteor rates are notoriously hard to predict, and
the Draconids were quite impressive in
1933, 1946, and 2011.
Featured, Comet 21P gracefully posed between the
Rosette (upper left) and
Cone (lower right)
nebulas two weeks ago before
heading back out to near the orbit of
Jupiter, to return again in about
six and a half years.
 APOD: 2018 July 6 - Charon: Moon of Pluto
APOD: 2018 July 6 - Charon: Moon of Pluto
Explanation:
A darkened and mysterious north polar region
known to some as
Mordor Macula caps this premier high-resolution view.
The
portrait of Charon, Pluto's largest moon,
was captured by New Horizons near the spacecraft's closest
approach on July 14, 2015.
The combined blue, red,
and infrared data was processed to enhance colors
and follow variations in Charon's surface properties
with a resolution of about 2.9 kilometers (1.8 miles).
A stunning image of Charon's Pluto-facing hemisphere, it also
features a clear view of an apparently
moon-girdling belt of
fractures and canyons that seems to
separate smooth southern plains from varied northern terrain.
Charon is 1,214 kilometers (754 miles) across.
That's about 1/10th the size of planet Earth
but a whopping 1/2 the diameter of
Pluto
itself, and makes it the largest satellite relative to its
parent body in the Solar System.
Still, the moon appears as a small bump at about the 1 o'clock position
on Pluto's disk in the grainy, negative,telescopic picture inset
at upper left.
That view was used by James Christy and Robert Harrington
at the U.S. Naval Observatory in Flagstaff to
discover
Charon 40 years ago in June of 1978.
 APOD: 2018 January 20 - Old Moon in the New Moon's Arms
APOD: 2018 January 20 - Old Moon in the New Moon's Arms
Explanation:
Also known as the Moon's "ashen glow" or the "Old Moon in the
New Moon's arms",
earthshine
is earthlight reflected from the Moon's night side.
This stunning image of earthshine from a young crescent moon
was taken from Las Campanas Observatory, Atacama Desert, Chile,
planet Earth
near moonset on January 18.
Dramatic atmospheric inversion
layers appear above the Pacific
Ocean, colored by the sunset at the planet's western horizon.
But the view from the Moon would have been stunning, too.
When the Moon appears in Earth's sky as a slender crescent,
a dazzlingly bright, nearly full Earth would be seen
from the lunar surface.
A description of earthshine, in terms of sunlight
reflected by Earth's oceans in turn illuminating
the Moon's dark surface, was written 500 years ago by
Leonardo da Vinci.
 APOD: 2018 January 14 - Three Galaxies and a Comet
APOD: 2018 January 14 - Three Galaxies and a Comet
Explanation:
Diffuse starlight and dark nebulae
along the southern
Milky Way arc over the
horizon and sprawl diagonally through this
gorgeous nightscape.
The breath-taking mosaic spans a wide
100 degrees, with the rugged
terrain of the
Patagonia,
Argentina
region in the foreground.
Along with the
insider's view of
our own galaxy, the image
features our outside perspective on two irregular satellite galaxies -
the Large and
Small Magellanic Clouds.
The scene also captures the
broad tail
and bright coma of
Comet McNaught, the
Great Comet of 2007.
 APOD: 2017 December 4 - Earth and Moon
APOD: 2017 December 4 - Earth and Moon
Explanation:
On rare occasions, the Earth and Moon are photographed together.
One of most spectacular times this occurred was 25 years ago this month when the Jupiter-bound
Galileo spacecraft
zoomed past our home planetary system.
Then, robotic Galileo watched from about 15-times the
Earth-Moon separation as
our only natural satellite
glided past our home world.
The featured video combines 52 historic
color-enhanced images.
Although our Moon may
appear small next to the
Earth,
no other planet in our Solar System has a
satellite
so
comparable
in
size
.
The Sun,
far off to the right, illuminated about half of each sphere, and shows the spinning Earth's
white clouds,
blue oceans, and tan continents.
Tonight, a nearly full
Oak
supermoon will be visible from all of Earth from sunset to sunrise.
 APOD: 2017 December 3 - Full Moon Silhouettes
APOD: 2017 December 3 - Full Moon Silhouettes
Explanation:
Have you ever watched the Moon rise?
The slow rise of a nearly full moon over a clear horizon can be an impressive sight.
One impressive moonrise was imaged in early 2013 over
Mount Victoria Lookout in
Wellington,
New Zealand.
With detailed planning, an
industrious astrophotographer
placed a camera about two kilometers away and pointed it across the lookout to where
the Moon
would surely soon be making its nightly debut.
The
featured single shot sequence is unedited and
shown in real time -- it is not a time lapse.
People on
Mount Victoria Lookout
can be seen in silhouette themselves admiring the dawn of Earth's largest satellite.
Seeing a moonrise yourself is not difficult:
it happens every day, although only half the time at night.
Each day the
Moon rises about
fifty minutes later
than the previous day, with a full moon
always rising at sunset.
A good time to see a full moonrise
will occur tonight at sunset as
the Moon's relative closeness to Earth during a full phase -- called a
supermoon -- will cause it to appear slightly larger and brighter than usual.
 APOD: 2017 July 17 - Moon Shadow versus Sun Reflection
APOD: 2017 July 17 - Moon Shadow versus Sun Reflection
Explanation:
What are those lights and shadows crossing the Earth?
As the featured five-second
time-lapse video
progresses, a full day on planet Earth is depicted as seen from
Japan's
Himawari-8 satellite in
geostationary orbit high above the
Pacific Ocean.
The Sun rises to the right and sets to the left,
illuminating the
half of Earth that is most directly below.
A reflected image of the Sun -- a
Sun glint --
is visible as a bright spot that moves from right to left.
More unusual, though, is the
dark spot that moves from the lower left to upper right
That is the
shadow of the Moon,
and it can only appear when the Moon goes
directly between the Earth and the Sun.
Last year, on the day these images were taken, the most deeply shadowed
region experienced a
total eclipse of the Sun.
Next month
a similarly dark shadow will sweep
right across the USA.
 APOD: 2017 April 20 - Asteroid 2014 JO25
APOD: 2017 April 20 - Asteroid 2014 JO25
Explanation:
A day before its closest approach, asteroid 2014 JO25
was imaged by radar with the 70-meter antenna of NASA's
Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex in California.
This
grid of 30 radar images, top left to lower right,
reveals the two-lobed shape
of the asteroid that rotates about once every five hours.
Its largest lobe is about 610 meters across.
On the list of Potentially Hazardous Asteroids, this space rock
made its close approach to our fair planet on April 19,
flying safely past
at a distance of 1.8 million kilometers.
That's over four times the distance from the Earth to the Moon.
The asteroid was a faint and fast moving speck visible in
backyard
telescopes.
Asteroid 2014 JO25 was discovered in May 2014 by A. D. Grauer of the
Catalina Sky Survey,
a project of NASA's Near-Earth Objects Observations Program in
collaboration with the University of Arizona.
 APOD: 2017 January 26 - GOES-16: Moon over Planet Earth
APOD: 2017 January 26 - GOES-16: Moon over Planet Earth
Explanation:
Launched last November 19 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station,
the satellite now known as
GOES-16 can now
observe planet Earth from a
geostationary orbit
22,300 miles above the equator.
Its Advanced Baseline Imager captured this contrasting view of Earth and
a gibbous Moon on January 15.
The stark and airless Moon is not really the focus of GOES-16, though.
Capable of providing a high resolution full disk image of Earth
every 15 minutes in 16 spectral channels,
the new generation satellite's instrumentation is geared to
provide sharper, more detailed
views
of Earth's dynamic weather systems
and enable more accurate weather forecasting.
Like previous GOES weather satellites, GOES-16 will use the moon
over our fair planet as a calibration target.
 APOD: 2016 November 13 - Super Moon vs Micro Moon
APOD: 2016 November 13 - Super Moon vs Micro Moon
Explanation:
What is so super about tomorrow's supermoon?
Tomorrow, a full moon will occur that appears slightly larger and brighter than usual.
The reason is that the
Moon's fully illuminated phase occurs within a short time from perigee - when the Moon is its closest to the Earth in its elliptical orbit.
Although the precise conditions that define a
supermoon vary,
tomorrow's supermoon will undoubtedly qualify because it will be the
closest, largest, and brightest full moon in
over 65 years.
One reason
supermoons are popular is because they are so easy to see --
just go outside at sunset and watch an impressive full moon rise!
Since perigee actually occurs tomorrow morning, tonight's
full moon, visible starting at
sunset, should also be impressive.
Pictured here, a
supermoon from 2012 is compared to a micromoon -- when a full Moon occurs near the furthest part of the Moon's orbit -- so that it appears smaller and dimmer than usual.
Given
many definitions, at least one
supermoon
occurs each year, with another one coming next month (moon-th).
However, a full moon will not come this close to Earth again until 2034.
 APOD: 2016 October 12 - Penumbral Lunar Eclipse
APOD: 2016 October 12 - Penumbral Lunar Eclipse
Explanation:
Does this Moon look a little different to you?
Although shown in spectacular detail, the full face of Earth's
most familiar satellite appears slightly darker than usual, in particular on the upper left, because it is undergoing a
penumbral lunar eclipse.
The image was captured in
Hong Kong,
China, on
September 16 when the Moon
crossed through part of
Earth's shadow --
but not the darkest where the Earth shades the entire Sun.
A lunar eclipse can only occur during a full moon,
and many know this particular full moon as the
Harvest moon for its proximity to northern harvests.
The next full moon
will occur this coming Sunday.
Some cultures
refer to it
as a Leaf Falling Moon, named for its proximity to northern autumn.
The second full moon of the same month ("moonth") is sometimes called a
Blue moon;
meanwhile, this month features a rare second new moon, an event known to some as a
Black moon.
 APOD: 2016 August 7 - Io: Moon over Jupiter
APOD: 2016 August 7 - Io: Moon over Jupiter
Explanation:
How big is Jupiter's moon Io?
The most volcanic body in the Solar System,
Io (usually pronounced "EYE-oh") is
3,600 kilometers in diameter, about the size of
planet Earth's single large
natural satellite.
Gliding
past Jupiter
at the turn of the millennium, the Cassini spacecraft captured this
awe
inspiring view of active Io
with the
largest gas giant as a backdrop,
offering a
stunning demonstration of the ruling planet's
relative size.
Although in the featured picture Io appears
to be located just in front of the
swirling Jovian clouds,
Io hurtles around its orbit once every 42 hours
at a distance of 420,000 kilometers or so from the center
of Jupiter.
That puts
Io
nearly 350,000 kilometers above
Jupiter's cloud tops,
roughly equivalent to the distance between
Earth and Moon.
In July, NASA's
Juno
satellite began orbiting
Jupiter
and will sometimes swoop to within 5,000 kilometers of Jupiter's cloud tops.
 APOD: 2016 June 17 - Comet PanSTARRS in the Southern Fish
APOD: 2016 June 17 - Comet PanSTARRS in the Southern Fish
Explanation:
Now approaching
our fair planet this Comet PanSTARRS (C/2013 X1)
will come closest on June 21-22, a mere 5.3
light-minutes away.
By then its appearance
low in northern hemisphere predawn skies (high in the south),
will be affected by the light of a nearly Full Moon, though.
Still the comet's pretty green coma is about the apparent
size of the Full Moon in
this
telescopic portrait,
captured on June 12 from the southern hemisphere's Siding Spring Observatory.
The deep image
also follows a broad, whitish dust tail
up and toward the left in the frame, sweeping away from the Sun
and trailing behind the comet's orbit.
Buffeted by the solar wind, a fainter, narrow ion tail
extends horizontally toward the right.
On the left edge, the brightest star is bluish Iota Piscis Austrini.
Shining at about fourth magnitude, that star is visible to
the unaided eye in the constellation of the
Southern Fish.
 APOD: 2016 March 17 - Close Comet and Large Magellanic Cloud
APOD: 2016 March 17 - Close Comet and Large Magellanic Cloud
Explanation:
Sporting
a surprisingly bright, lovely
green coma
Comet 252P/Linear poses next to the
Large Magellanic Cloud
in this southern skyscape.
The stack of telephoto exposures was captured on March 16 from
Penwortham, South Australia.
Recognized as a Jupiter family
periodic
comet, 252P/Linear will come
close to our fair planet on March 21, passing a mere 5.3 million
kilometers away.
That's about 14 times the Earth-Moon distance.
In fact, it is one of two comets that will make remarkably close
approaches in the next few days as a much fainter
Comet Pan-STARRS
(P/2016 BA14) comes within 3.5 million
kilometers (9 times the Earth-Moon distance) on March 22.
The two have extremely
similar
orbits,
suggesting they may have originally been part of the same comet.
Sweeping quickly across the sky because of their proximity to Earth,
both comets will soon move into northern skies.
 APOD: 2015 December 12 - Comet Meets Moon and Morning Star
APOD: 2015 December 12 - Comet Meets Moon and Morning Star
Explanation:
A
crescent Moon and brilliant Venus met in predawn
skies on December 7, a
beautiful conjunction of planet
Earth's two brightest celestial beacons after the Sun.
Harder to see but
also
on the scene was Comet Catalina
(C/2013 US10).
The fainter comet clearly sporting two tails,
lunar night side, bright sunlit lunar crescent, and brilliant morning star,
are all recorded here by combining short and long exposures
of the same field of view.
Pointing down and right, Catalina's dust tail
tends to trail behind the comet's orbit.
Its ion tail, angled toward
the top left of the frame, is blowing away from the Sun.
Discovered in 2013, the new visitor from the
Oort cloud
was closest to the Sun on November 15 and is now outbound,
headed for its closest approach to Earth in mid-January.
 APOD: 2015 December 7 - Comet Catalina Emerges
APOD: 2015 December 7 - Comet Catalina Emerges
Explanation:
Comet Catalina is ready for its close-up.
The giant snowball from the outer Solar System, known formally as
C/2013 US10 (Catalina),
rounded the Sun last month and is now
headed for
its closest approach to Earth in January.
With the glow of the Moon now also out of the way,
morning observers in Earth's northern hemisphere are getting their best ever view of the new comet.
And Comet Catalina is
not disappointing.
Although not as bright as early predictions, the comet is sporting both
dust (lower left) and
ion (upper right)
tails,
making it an impressive object for binoculars and long-exposure cameras.
The featured image was taken last week from the
Canary Islands, off the northwest coast of
Africa.
Sky enthusiasts around the world will surely be
tracking the comet over the next few months to see how it evolves.
 APOD: 2015 November 22 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: 2015 November 22 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
This moon is doomed.
Mars,
the red planet named for the
Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos, whose
names are derived from the Greek for Fear and
Panic.
These martian moons may well be captured
asteroids
originating in the main asteroid belt between Mars and
Jupiter
or perhaps from even more distant reaches of the Solar System.
The larger moon, Phobos, is indeed seen
to be a cratered, asteroid-like object in this
stunning color image from the robotic
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter,
recorded at a resolution of about seven meters per pixel.
But Phobos
orbits so close to Mars - about 5,800 kilometers above the surface compared to 400,000 kilometers
for our Moon - that gravitational
tidal forces
are dragging it down.
A recent analysis
of the long grooves indicates that they may result from global stretching caused by
tides --
the differing force of Mars' gravity on different sides of
Phobos.
These grooves may then be an early phase in the
disintegration of
Phobos into a ring of debris around Mars.
 APOD: 2015 November 12 - Kenya Morning Moon, Planets and Taurid
APOD: 2015 November 12 - Kenya Morning Moon, Planets and Taurid
Explanation:
On November 8, a waning crescent Moon joined the continuing
parade of planets
in Earth's early morning skies.
Captured here from
Amboseli National Park, Kenya, even
the overexposed moonlight can't washout brilliant Venus
though, lined up near the ecliptic plane with faint Mars and
bright Jupiter above.
As if
Moon and planets
aren't enough, a comparably bright Taurid meteor also
streaks through the scene.
In fact November's
Taurid meteor showers
have had a high proportion of bright fireballs.
Apparently streaming from radiants in Taurus, the meteors
are caused by our fair planet's
annual passage through
debris from Comet 2P/Encke.
The comet's dust grains are
catching up with Earth's atmosphere at a relatively low
speed of about 27 kilometers per second.
 APOD: 2015 July 23 - Comet PanSTARRS, Moon, and Venus
APOD: 2015 July 23 - Comet PanSTARRS, Moon, and Venus
Explanation:
It is the object to the left of the big tree that's generating much recent excitement.
If you look closely, there you can see
Comet PanSTARRS, complete with
two tails.
During July, this comet has
increased markedly in brightness and has just
passed its closest approach to Earth.
The statuesque tree in the center is a
Norfolk Island Pine,
and to either side of this tree are
New
Zealand Pohutukawa trees.
Over the trees, far in the distance, are
bright Venus and an even brighter crescent
Moon.
If you look even more closely, you can find
Jupiter hidden in the branches of the pine.
The featured image was taken a few days ago in
Fergusson Park,
New Zealand, looking over
Tauranga Harbour Inlet.
In the coming days and weeks,
Comet C/2014 Q1 (PANSTARRS)
will slowly move away from the Sun and the Earth,
drift deep into southern skies, and fade.
 APOD: 2015 July 20 - Comet PanSTARRS and a Crescent Moon
APOD: 2015 July 20 - Comet PanSTARRS and a Crescent Moon
Explanation:
A comet has brightened quickly and unexpectedly.
Discovered last year,
Comet C/2014 Q1 (PanSTARRS) is expected to be
visible now for a few days to the unaided eye,
just after sunset, from some locations.
The comet rounded the Sun on July 6 and apparently has shed quite a bit of gas and dust.
Today it is now as close as it will ever get to the Earth, which is another factor in its
recent great apparent brightness
and the large angular extent of its tails.
In the featured image taken two days ago,
Comet PanSTARRS is seen sporting a short white dust
tail fading to the right, and a long blue
ion tail pointing away from the recently set Sun.
A crescent moon dominates the image center.
Tomorrow,
Comet PannSTARRS will pass only 7 degrees away from a bright
Jupiter, with even brighter Venus nearby.
Due to its proximity to the Sun, the
comet
and its tails may best be seen in the sunset din with binoculars or cameras using long-duration exposures.
 APOD: 2015 February 18 - Dark Craters and Bright Spots Revealed on Asteroid Ceres
APOD: 2015 February 18 - Dark Craters and Bright Spots Revealed on Asteroid Ceres
Explanation:
What are those bright spots on asteroid Ceres?
As the robotic spacecraft Dawn approaches the largest asteroid in the
asteroid belt, the puzzle only deepens.
Sharper new images taken last week and released yesterday indicate, as expected, that most of the surface of
dwarf planet Ceres is dark and heavily cratered like our
Moon and the planet
Mercury.
The new images do not clearly indicate, however,
the nature of comparatively bright spots -- although more of them are seen to exist.
The enigmatic spots were first noticed on
Texas-sized
Ceres a few weeks ago during Dawn's approach.
The intriguing
mystery might well be solved quickly as Dawn continues to advance toward
Ceres, being
on schedule to enter orbit on March 6.
 APOD: 2015 January 17 - Comet Lovejoy's Tail
APOD: 2015 January 17 - Comet Lovejoy's Tail
Explanation:
Sweeping north
in planet Earth's sky, Comet Lovejoy's greenish coma
and blue tinted ion tail stretched across this
field of stars in
the constellation Taurus on January 13.
The inset at the upper left shows the 1/2 degree angular size of
the full moon for scale.
So Lovejoy's coma appears only a little smaller (but much fainter)
than a full moon on the sky, and its tail is visible
for over 4 degrees across the frame.
That corresponds to over 5 million kilometers
at the comet's estimated distance of 75 million kilometers
from Earth.
Blown by the solar wind, the comet's tenuous, structured
ion tail streams
away from the Sun, growing as
this Comet Lovejoy
heads toward perihelion, its closest approach to the Sun, on January 30.
While diatomic carbon
(C2) gas fluorescing in sunlight
produces the coma's green color, the fainter bluish tail is tinted by
emission from ionized carbon monoxide (CO+).
 APOD: 2014 October 17 - Messier 6 and Comet Siding Spring
APOD: 2014 October 17 - Messier 6 and Comet Siding Spring
Explanation:
This looks like
a near miss but the greenish coma and tail of
Comet
Siding Spring (C/2013 A1) are really
2,000 light-years or so away from the stars of open cluster
Messier 6.
They do appear close together though,
along the same line-of-sight in this gorgeous October 9th
skyscape toward the constellation
Scorpius.
Still, on Sunday, October 19th this comet really will be involved in
a near miss, passing within only
139,500
kilometers of planet Mars.
That's about 10 times closer than any known comet flyby of planet Earth,
and nearly one third the Earth-Moon distance.
While an impact with the nucleus is not a threat
the comet's dust, moving with a speed of about 56 kilometers per second
relative to the Red Planet, and outskirts of its
gaseous coma could interact with the thin Martian atmosphere.
Of course, the comet's close encounter will be followed
intently by spacecraft in
Martian orbit and rovers on the surface.
 APOD: 2014 September 8 - Super Moon vs Micro Moon
APOD: 2014 September 8 - Super Moon vs Micro Moon
Explanation:
What is so super about tomorrow's supermoon?
Tomorrow, a full moon will occur that appears slightly larger and brighter than usual.
The reason is that the Moon's fully illuminated phase occurs within a short time from perigee - when the Moon is its closest to the Earth in its elliptical orbit.
Although the precise conditions that define a
supermoon vary, given one definition, tomorrow's will be the third supermoon of the year -- and the third consecutive month that a supermoon occurs.
One reason
supermoons are popular is because they are so easy to see --
just go outside and sunset and watch an impressive full moon rise!
Since perigee actually occurs today, tonight's sunset
moonrise should also be impressive.
Pictured above, a
supermoon from 2012 is compared to a micromoon -- when a full Moon occurs near the furthest part of the Moon's orbit -- so that it appears smaller and dimmer than usual.
Given many definitions, at least one
supermoon
occurs each year, with the next being 2015 August 30.
 APOD: 2014 September 7 - Full Moon Silhouettes
APOD: 2014 September 7 - Full Moon Silhouettes
Explanation:
Have you ever watched the Moon rise?
The slow rise of a nearly full moon over a clear horizon can be an impressive sight.
One impressive moonrise was imaged in early 2013 over
Mount Victoria Lookout in
Wellington,
New Zealand.
With detailed planning, an
industrious astrophotographer
placed a camera about two kilometers away and pointed it across the lookout to where
the Moon
would surely soon be making its nightly debut.
The
above single shot sequence is unedited and
shown in real time -- it is not a time lapse.
People on
Mount Victoria Lookout
can be seen in silhouette themselves admiring the dawn of Earth's largest satellite.
Seeing a moonrise yourself is not difficult:
it happens every day, although only half the time at night.
Each day the
Moon rises about
fifty minutes later
than the previous day, with a full moon
always rising at sunset.
A good time to see a moonrise will occur at sunset on Tuesday as
the Moon's relative closeness to Earth during a full phase -- called a
supermoon -- will cause it to appear slightly larger and brighter than usual.
 APOD: 2014 September 4 - Cloud, Clusters and Comet Siding Spring
APOD: 2014 September 4 - Cloud, Clusters and Comet Siding Spring
Explanation:
On October 19th, a good place to watch
Comet Siding Spring
will be from Mars.
Then, this inbound
visitor (C/2013 A1) to the
inner solar system, discovered in January 2013 by
Robert McNaught at Australia's Siding Spring Observatory,
will pass within 132,000 kilometers of the Red Planet.
That's a near miss,
equivalent to just over 1/3 the Earth-Moon distance.
Great views of the comet for denizens of planet Earth's
southern hemisphere are possible now, though.
This telescopic snapshot
from August 29 captured the comet's
whitish coma and arcing dust tail sweeping through southern skies.
The fabulous
field of view includes,
the Small Magellanic Cloud
and globular star clusters 47 Tucanae (right) and NGC 362 (upper left).
Worried about all those spacecraft in Martian orbit?
Streaking dust particles from the comet could pose a danger and
controllers
plan to position Mars orbiters on the opposite side of the
planet during the comet's close flyby.
 APOD: 2014 August 22 - Comet Jacques, Heart and Soul
APOD: 2014 August 22 - Comet Jacques, Heart and Soul
Explanation:
On July 13th, a good place to watch
Comet
Jacques was from Venus.
Then, the recently discovered visitor (C/2014 E2) to the
inner solar system
passed within about 14.5 million kilometers
of our sister planet.
But the outbound comet will pass only 84 million kilometers
from our fair planet on August 28 and is
already
a fine target for telescopes and binoculars.
Two days ago Jacques' greenish coma and straight and narrow ion tail
were captured in this telescopic snapshot, a single 2 minute long
exposure with a modified digital camera.
The comet is flanked by IC 1805 and IC 1848, also known as Cassiopeia's
Heart and Soul Nebulae.
If you're stuck on planet Earth this weekend you can
hunt for Comet Jacques
in evening skies, or spot a Venus, Jupiter, crescent Moon triangle
before the dawn.
 APOD: 2014 July 16 - The Moon Eclipses Saturn
APOD: 2014 July 16 - The Moon Eclipses Saturn
Explanation:
What happened to half of Saturn?
Nothing other than Earth's Moon getting in the way.
As pictured above on the far right,
Saturn is partly eclipsed by a dark edge of a Moon itself only
partly illuminated by the Sun.
This year the orbits of the
Moon and Saturn have led to an
unusually high number of alignments of the ringed giant behind Earth's largest satellite.
Technically termed an
occultation, the
above image captured one such
photogenic juxtaposition from
Buenos Aires,
Argentina that occurred early last week.
Visible to the
unaided eye
but best viewed with binoculars, there are still four
more eclipses of Saturn by our Moon left in 2014.
The next one will be on August 4 and
visible from Australia,
while the one after will occur on
August 31 and be visible from western Africa at night but
simultaneously from much of eastern North America during the day.
 APOD: 2014 June 6 - Comet PanSTARRS with Galaxy
APOD: 2014 June 6 - Comet PanSTARRS with Galaxy
Explanation:
Sweeping slowly through northern skies, the comet
PanSTARRS C/2012 K1
posed for this telescopic portrait on June 2nd in the constellation
Ursa Major.
Now within the inner solar system, the icy body
from
the Oort cloud sports two tails, a lighter broad dust tail and
crooked ion tail extending below and right.
The comet's condensed greenish coma makes a nice contrast with
the spiky yellowish background star above.
NGC
3319 appears at the upper left of the frame that spans almost
twice the apparent diameter of the full Moon.
The spiral galaxy is
about 47 million light-years away, far beyond the stars in
our own Milky Way.
In comparison, the comet was a mere 14 light-minutes from our
fair planet.
This comet PanSTARRS will slowly grow brighter in the
coming
months remaining a good target for telescopic comet watchers and
reaching perihelion, its closest approach to the Sun, while just
beyond Earth's orbit in late August.
 APOD: 2014 January 21 - Micro Moon over Super Moon
APOD: 2014 January 21 - Micro Moon over Super Moon
Explanation:
Did you see the big, bright, beautiful Full Moon last Wednesday night?
That was actually a
Micro Moon!
On that night, the smallest Full Moon of 2014 reached its full phase only
a few hours from lunar
apogee,
the time of its the most distant point from Earth in the
Moon's
elliptical orbit.
Of course, last year on the night of June 22,
a Full Super Moon was near perigee, the closest
point
in its orbit.
The relative apparent size of January 15's
Micro Moon is compared to the
June 22 Super Moon in the above
composite image digitally
superimposing
telescopic images from
Perugia, Italy.
The difference
in apparent size represents a difference in distance
of just under 50,000 kilometers between apogee and perigee, given
the Moon's average distance of about 385,000 kilometers.
How long do you have to wait to see another
Full Micro Moon?
Until March 5, 2015, when the lunar full phase will again occur within a few hours of lunar
apogee.
 APOD: 2013 December 4 - Comet Lovejoy through Morby Castle Ruins
APOD: 2013 December 4 - Comet Lovejoy through Morby Castle Ruins
Explanation:
This new comet is quite photogenic.
Comet Lovejoy, discovered only three months ago, was
imaged through
ruins of ancient
M�rby
Castle in
Sweden
last week sporting a green-glowing
coma and tails trailing several degrees.
The past few weeks have been an unusually active time for
comet watchers
as four comets were
visible simultaneously with binoculars:
ISON,
Lovejoy,
Encke, and
LINEAR.
C/2013 R1 (Lovejoy) comet is
currently visible
to the unaided eye from a dark location.
As Monday's new Moon will provide little glare, the next few days provide a
good time to see
Comet Lovejoy
as it reaches its
peak brightness.
In two and a half weeks,
Comet Lovejoy will reach its closest approach to the Sun at a
distance just inside the orbital distance of the Earth.
 APOD: 2013 October 20 - Three Galaxies and a Comet
APOD: 2013 October 20 - Three Galaxies and a Comet
Explanation:
Diffuse starlight and dark nebulae
along the southern
Milky Way
arc over the
horizon and sprawl diagonally through this
gorgeous nightscape.
The breath-taking mosaic spans a wide
100 degrees, with the rugged
terrain
of the Patagonia, Argentina region in the foreground.
Along with the insider's view of our own galaxy, the image
features our outside perspective on two irregular satellite galaxies -
the Large and
Small Magellanic Clouds.
The scene also captures the
broad tail
and bright coma of Comet McNaught, the
Great Comet of 2007.
Currently, many
sky
enthusiasts are following the development of
Comet ISON, a comet which might become the
Great Comet of 2013.
 APOD: 2013 October 7 - Comet ISON Approaches
APOD: 2013 October 7 - Comet ISON Approaches
Explanation:
How impressive will Comet ISON become?
No one is sure, but unfortunately, as
the comet
approaches the inner Solar System, it is
brightening
more slowly than many early predictions.
Pictured above, Comet ISON is
seen about two weeks ago as it continued to develop a tail.
Last week the comet passed relatively close to Mars, and was
directly imaged by the
Mars
Reconnaissance Orbiter.
When Comet
ISON dives to within a few solar radii of the Sun's surface
in late November, it
may become brighter
than the Moon and sport a long and
flowing tail -- or it may appear somewhat less spectacular.
Either way, sky
enthusiasts hope that whatever comet parts survive will put on quite an
impressive show, as viewed from Earth, through at least the rest of the year.
 APOD: 2013 August 1 - Moon Over Andromeda
APOD: 2013 August 1 - Moon Over Andromeda
Explanation:
The Great Spiral Galaxy
in Andromeda (aka M31), a mere 2.5 million
light-years distant,
is the closest
large spiral to our own Milky Way.
Andromeda is visible to the unaided eye as a small, faint, fuzzy patch,
but because its surface brightness is so low, casual
skygazers
can't appreciate the galaxy's impressive extent in
planet Earth's sky.
This entertaining composite image compares the
angular size
of the nearby galaxy
to a brighter, more familiar celestial sight.
In it, a
deep
exposure of Andromeda, tracing beautiful blue star
clusters in spiral arms far beyond the bright yellow core,
is combined with a typical view of a nearly full Moon.
Shown at the same
angular scale, the Moon covers
about 1/2 degree on the
sky, while the galaxy is clearly several times that size.
The deep Andromeda exposure also includes two bright satellite
galaxies, M32 and
M110 (bottom).
 APOD: 2013 July 20 - Comet Lemmon and the Deep Sky
APOD: 2013 July 20 - Comet Lemmon and the Deep Sky
Explanation:
Now sweeping
high above the ecliptic plane,
Comet Lemmon
has faded dramatically in
planet Earth's night sky
as it heads for the outer solar system.
Some 16 light-minutes (2 AU) from the Sun, it still sports a
greenish coma though, posing on the right
in this 4 degree wide
telescopic view from
last Saturday with deep sky star clusters and nebulae
in Cassiopeia.
In fact, the rich background skyscape is
typical within the boundaries of the
boastful northern
constellation that lie along the crowded starfields of the Milky Way.
Included near center is open
star cluster M52
about 5,000 light-years away.
Around 11,000 light-years distant, the red glowing nebula NGC 7635
below and left of M52 is well-known for its appearance in close-up
images as the Bubble Nebula.
But the fading Comet Lemmon is not the only foreground object on
the scene.
A faint streak on the right is an orbiting satellite
caught crossing through the field during the long exposure, glinting
in the sunlight and winking out as it
passes into Earth's shadow.
 APOD: 2013 July 16 - The Moon from Zond 8
APOD: 2013 July 16 - The Moon from Zond 8
Explanation:
Which moon is this?
Earth's.
Our Moon's unfamiliar appearance is due partly to an
unfamiliar viewing angle as captured by a little-known spacecraft --
the Soviet Union's
Zond 8 that circled the
Moon in October of 1970.
Pictured above,
the dark-centered circular feature that stands out near the top of the image is
Mare Orientale,
a massive impact basin formed by an ancient collision with an
asteroid.
Mare Orientale
is surrounded by light colored and highly textured highlands.
Across the image bottom lies the dark and expansive
Oceanus Procellarum,
the largest of the dark (but dry) maria that dominate the
side of the Moon
that always
faces toward the Earth.
Originally designed to carry humans, robotic
Zond 8
came within 1000 km of the
lunar surface, took about 100
detailed photographs on film,
and returned them safely to Earth within a week.
 APOD: 2013 March 15 - CME, Comet, and Planet Earth
APOD: 2013 March 15 - CME, Comet, and Planet Earth
Explanation:
After appearing in a popular photo
opportunity with a young crescent Moon near sunset, naked-eye
Comet PanSTARRS
continues to rise in northern hemisphere skies.
But this
remarkable
interplanetary perspective from March 13,
finds the comet posing with our fair planet
itself - as seen from the STEREO Behind spacecraft.
Following in Earth's
orbit, the spacecraft is nearly opposite the Sun and
looks back toward the comet
and Earth, with the Sun just off the left side of the frame.
At the left an enormous
coronal mass ejection (CME) is
erupting from a solar active region.
Of course, CME, comet, and planet Earth are all at different
distances
from the spacecraft.
(The comet is closest.)
The processed digital image is the difference between two consecutive
frames from the spacecraft's SECCHI Heliospheric Imager, causing the
strong shadowing effect for objects that move between frames.
Objects that are too bright create the sharp vertical lines.
The processing reveals
complicated feather-like structures in Comet PanSTARRS's
extensive dust tail.
 APOD: 2013 March 14 - Clouds, Comet, and Crescent Moon
APOD: 2013 March 14 - Clouds, Comet, and Crescent Moon
Explanation:
In silhouette against the
colorful evening twilight, clouds part for this much
anticipated magic moment.
The scene
captures naked-eye
Comet PanSTARRS peeking into
northern hemisphere skies on March 12.
The comet stands
over the western horizon
after sunset, joined by the thin,
flattened
crescent of a day old Moon.
Posing for its own beauty shot, the subtly lit dome of the
4.2 meter William
Herschel Telescope is
perched above cloud banks on the
Canary Island of La Palma.
While PanSTARRS has not quite developed into the spectacular comet
once hoped for, it is still growing
easier to see in the north.
In coming days it will steadily climb north, farther from the Sun into
darker
western evening skies.
 APOD: 2013 February 17 - Asteroid 2012 DA14 Passes the Earth
APOD: 2013 February 17 - Asteroid 2012 DA14 Passes the Earth
Explanation:
There it goes.
That small spot moving in front of background stars in the
above video is a
potentially dangerous asteroid passing above the Earth's atmosphere.
This past Friday, the 50-meter wide asteroid
2012 DA14 just missed the Earth,
passing not only inside the orbit of the Moon, which is
unusually close
for an asteroid of this size, but also inside the orbit of
geosynchronous satellites.
Unfortunately, asteroids this big or
bigger
strike the Earth
every 1000 years or so.
Were 2012 DA14
to have hit the Earth, it could have devastated a
city-sized landscape,
or stuck an ocean and raised
dangerous tsunamis.
Although finding and tracking potentially dangerous asteroids is a primary concern of modern astronomy,
these small bodies or ice and rock are typically so dim that only a
few percent of them have been found, so far.
Even smaller chunks of ice and rock, like the (unrelated) spectacular meteors that
streaked over Russia and
California over the past few days, are even harder to find --
but pose less danger.
 APOD: 2013 January 30 - Full Moon Silhouettes
APOD: 2013 January 30 - Full Moon Silhouettes
Explanation:
Have you ever watched the Moon rise?
The slow rise of a nearly full moon over a clear horizon can be an impressive sight.
One impressive moonrise was imaged two nights ago over
Mount Victoria Lookout in
Wellington,
New Zealand.
With detailed planning, an
industrious astrophotographer
placed a camera about two kilometers away and pointed it across the lookout to where
the Moon
would surely soon be making its nightly debut.
The
above single shot sequence is unedited and
shown in real time -- it is not a time lapse.
People on
Mount Victoria Lookout
can be seen in silhouette themselves admiring the dawn of Earth's largest satellite.
Seeing a moonrise yourself is not difficult:
it happens every day, although only half the time at night.
Each day the
Moon rises about
fifty minutes later
than the previous day, with a full moon
always rising at sunset.
 APOD: 2013 January 27 - Comet McNaught Over Chile
APOD: 2013 January 27 - Comet McNaught Over Chile
Explanation:
Comet McNaught of 2007 has been, so far, the most photogenic comet of our time.
After making
quite a show in the northern hemisphere
in early 2007 January,
the comet moved south and developed a
long and unusual dust tail that
dazzled southern hemisphere observers.
In this image,
Comet McNaught was captured above
Santiago,
Chile.
The bright comet dominates on the left while
part of its magnificent tail spreads across the entire frame.
From this vantage point in the Andes Mountains, one looks up toward
Comet
McNaught and a magnificent sky,
across at a crescent moon, and down on clouds, atmospheric
haze,
and the city lights.
The current year -- 2013 -- holds promise to be even better
for comets than 2007.
In early March,
Comet PANSTARRS
is on track to become visible to the unaided eye,
while at the end of the year Comet ISON
shows possibilities that include casting a
tail that spreads across the sky,
breaking up, and even becoming one of the
brightest comets in recorded history.
 APOD: 2012 November 29 - Super Moon vs Micro Moon
APOD: 2012 November 29 - Super Moon vs Micro Moon
Explanation:
Did
you see the big, bright, beautiful Full Moon Wednesday night?
That was actually a Micro Moon!
On that night, the smallest Full Moon of 2012 reached its full phase only
about 4 hours before
apogee, the most distant point from Earth in the
Moon's elliptical orbit.
Of course, earlier this year on May 6,
a Full Super Moon was near perigee, the closest
point
in its orbit.
The relative apparent size of November 28's
Micro Moon (right) is compared to the famous
May 6 Super Moon in these two panels,
matching
telescopic images from Bucharest, Romania.
The difference
in apparent size represents a difference in distance
of just under 50,000 kilometers between apogee and perigee, given
the Moon's average distance of about 385,000 kilometers.
How long do you have to wait to see another Full Micro Moon?
Until January 16, 2014, when the lunar full phase will occur within
about 3 hours of apogee.
 APOD: 2012 November 6 - Methone: Smooth Egg Moon of Saturn
APOD: 2012 November 6 - Methone: Smooth Egg Moon of Saturn
Explanation:
Why is this moon shaped like a smooth egg?
The robotic Cassini spacecraft completed the first flyby ever of Saturn's small moon
Methone
in May and discovered that the moon has no obvious craters.
Craters, usually caused by impacts, have been seen on every
moon,
asteroid, and comet nucleus
ever imaged in detail -- until now.
Even the Earth and
Titan have
craters.
The smoothness and egg-like shape of the
3-kilometer diameter moon might be caused by
Methone's
surface being able to shift --
something that might occur were the moon coated by a deep
pile of sub-visual
rubble.
If so, the most similar objects in our Solar System would include Saturn's moons
Telesto,
Pandora,
Calypso, as well as asteroid
Itokawa,
all of which show sections that are unusually smooth.
Methone
is not entirely featureless, though, as some surface sections
appear darker than others.
Although flybys of Methone are
difficult, interest in the nature and
history of this unusual moon is sure to continue.
 APOD: 2012 October 28 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: 2012 October 28 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
This moon is doomed.
Mars,
the red planet named for the
Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos, whose
names are derived from the Greek for Fear and
Panic.
These martian moons may well be captured
asteroids
originating in the main asteroid belt between Mars and
Jupiter
or perhaps from even more distant reaches of the Solar System.
The larger moon, Phobos, is indeed seen
to be a cratered, asteroid-like object in this
stunning color image from the
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter,
recorded at a resolution of about
seven meters per pixel.
But Phobos
orbits so close to Mars - about 5,800 kilometers above the surface compared to 400,000 kilometers
for our Moon - that gravitational
tidal forces
are dragging it down.
In 100 million years or so Phobos
will likely be shattered by stress caused by the
relentless
tidal forces, the debris forming a decaying ring around Mars.
 APOD: 2012 October 1 - Introducing Comet ISON
APOD: 2012 October 1 - Introducing Comet ISON
Explanation:
Could this dim spot brighten into one of the
brightest comets ever?
It's possible.
Alternatively,
the comet could break up
when it gets closer to the Sun, or brighten much
more modestly.
Sky enthusiasts the world over are all
abuzz, though, from the more
optimistic speculations -- that the newly discovered
C/2012 S1 (ISON) could develop a
spectacular tail or briefly approach the
brightness of the full Moon toward the end of 2013.
Comet ISON currently is very faint but is just visible at
magnitude 18 in the above image.
The comet, discovered just over a week ago from
Russia by
Vitali Nevski (Belarus)
and Artyom Novichonok (Russia), is currently falling toward the Sun
from between the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn.
In early 2013 October it will pass very near Mars and possibly be visible to rovers and orbiting spacecraft.
Comet ISON appears on course to achieve
sungrazer status as it passes within a solar diameter of Sun's surface in late 2013 November.
Whatever survives will then pass nearest the Earth in late 2013 December.
Astronomers around the world will be tracking this large dirty snowball closely to
better understand its nature and how it
might evolve
during the next 15 months.
 APOD: 2012 April 24 - Rosetta Approaches Asteroid Lutetia
APOD: 2012 April 24 - Rosetta Approaches Asteroid Lutetia
Explanation:
What would it look like to approach an asteroid in a spaceship?
In 2010, ESA's robotic
Rosetta spacecraft zipped past the asteroid 21 Lutetia
taking data and snapping images in an effort to better
determine the history of the asteroid and the origin of its
unusual colors.
Recently, many images from a camera always facing
the asteroid were compiled into the
above video.
Although of unknown composition,
Lutetia is not massive enough for gravity to pull it into a sphere.
The 100-kilometer across
Lutetian was at that time the largest asteroid or comet nucleus that
had been visited by a human-launched spacecraft.
Orbiting in the main asteroid belt,
Lutetia
shows itself to be a heavily cratered remnant of the early Solar System.
Now well past Lutetia, the Rosetta spacecraft is
continuing onto
comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko where a landing is planned for 2014.
 APOD: 2012 March 24 - The New Moon in the Old Moon's Arms
APOD: 2012 March 24 - The New Moon in the Old Moon's Arms
Explanation:
Also known as the Moon's ashen glow,
Earthshine is
Earthlight illuminating the Moon's night side.
Taken on
Nowruz,
the March 20 equinox, from Esfahan, Iran, planet Earth,
this telescopic image captures strong Earthshine from
an old Moon.
The darker earthlit disk is in the arms of a bright sunlit crescent.
But the
view
from the Moon would have been enchanting too.
When the Moon appears in Earth's sky as a slender crescent,
a dazzlingly bright, nearly full Earth would be seen
from the lunar surface.
The Earth's brightness due to reflected sunlight
is known to be strongly influenced by cloud cover.
Still, a description of Earthshine, in
terms of sunlight reflected by Earth's oceans in turn illuminating
the Moon's dark surface, was written 500 years ago by
Leonardo
da Vinci.
 APOD: 2011 November 9 - Asteroid 2005 YU55 Passes the Earth
APOD: 2011 November 9 - Asteroid 2005 YU55 Passes the Earth
Explanation:
Asteroid 2005 YU55 passed by the Earth yesterday, posing no danger.
The space rock,
estimated to be about 400 meters across, coasted by just inside the orbit of Earth's Moon.
Although the passing of smaller rocks near the Earth is
not very unusual -- in fact small rocks from space strike Earth daily -- a rock this large hasn't passed this close since 1976.
Were YU55 to have struck land,
it might have caused a
magnitude seven
earthquake
and left a city-sized crater.
A perhaps larger danger would have occurred were
YU55
to have struck the ocean and raised a large
tsunami.
The above radar image was taken two days ago by the
Deep Space Network
radio telescope in
Goldstone,
California,
USA.
YU55
was discovered only in 2005, indicating that other
potentially hazardous asteroids might lurk in
our Solar System currently undetected.
Objects like YU55 are hard to detect because they are so faint and
move so fast.
However, humanity's ability to scan the sky to detect, catalog, and analyze such objects has
increased notably in recent years.
 APOD: 2011 October 5 - Comet and CME on the Sun
APOD: 2011 October 5 - Comet and CME on the Sun
Explanation:
Did a sun-diving comet just cause a solar explosion?
Probably not.
This past weekend a comet dove toward the Sun and was followed very quickly by a
Coronal Mass Ejection (CMEs) from the other side of the Sun.
The first two sequences in the
above video shows the spectacular unfolding of events as seen by the Sun-orbiting
SOHO satellite, while the same events were
also
captured by both Sun-orbiting
STEREO satellites.
Now sungrazer comets that break up as they pass near the Sun are not all that rare --
hundreds have been cataloged over the past few years.
CMEs are even more common, with perhaps three lesser events occurring even during the eight hours of the above time-lapse movie.
Therefore, the
best bet of solar scientists is that the two events were
unrelated.
Another basis for this judgment is that CMEs are caused by rapid changes in the Sun's magnetic field, changes that a
small comet seem unlikely to make.
Such coincidences are even more likely during periods of high activity on the Sun's surface -- like
now.
 APOD: 2011 September 19 - The South Pole of Asteroid Vesta
APOD: 2011 September 19 - The South Pole of Asteroid Vesta
Explanation:
What created the circular structure around the south pole of asteroid Vesta?
Pictured above, the bottom of the second largest object in the asteroid belt
was recently imaged for the first time by the robotic
Dawn satellite that arrived last month.
A close inspection of the 260-meter resolution image shows not only hills and
craters and
cliffs and
more craters, but ragged circular features that cover most of the lower right of the 500-kilometer sized object.
Early speculation posits that the structure might have been created by a
collision and coalescence with a smaller asteroid.
Alternatively, the features might have originated in an
internal process soon after the asteroid formed.
New clues might come in the next few months as
Dawn spirals down toward the rocky world and obtains images of increasingly high resolution.
 APOD: 2010 December 1 - Martian Moon Phobos from Mars Express
APOD: 2010 December 1 - Martian Moon Phobos from Mars Express
Explanation:
Why is Phobos so dark?
Phobos, the largest and innermost of two
Martian moons, is the darkest moon in the entire
Solar System.
Its unusual orbit and color indicate that it may be a captured
asteroid composed of a mixture of ice and dark rock.
The above picture
of Phobos near the limb of Mars was
captured
last month by the robot spacecraft
Mars Express currently orbiting Mars.
Phobos is a heavily cratered and
barren moon, with its
largest crater located on the far side.
From images like this,
Phobos has been determined
to be covered by perhaps a meter of
loose dust.
Phobos orbits
so close to Mars that from some places it would appear to rise and
set twice a day, but from other places
it would not be visible at all.
Phobos' orbit around Mars is
continually decaying -- it will likely
break up with pieces crashing to the Martian surface in about 50 million years.
 APOD: 2010 July 26 - Lutetia: The Largest Asteroid Yet Visited
APOD: 2010 July 26 - Lutetia: The Largest Asteroid Yet Visited
Explanation:
As humans explore the universe, the record for largest asteroid
visited by a spacecraft has increased yet again.
Earlier this month, ESA's robotic
Rosetta spacecraft zipped past the asteroid 21 Lutetia
taking data and snapping images in an effort to better
determine the history of the asteroid and the origin of its
unusual colors.
Although of unknown composition,
Lutetia is not massive enough for gravity to pull it into a sphere.
Pictured above on the upper right, the 100-kilometer across
Lutetia is shown in comparison with the other nine asteroids and four comets that have been visited, so far, by human-launched spacecraft.
Orbiting in the main asteroid belt,
Lutetia
shows itself to be a heavily cratered remnant of the early Solar System.
The Rosetta spacecraft is
now continuing onto
comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko where a landing is planned for 2014.
 APOD: 2010 February 3 - P2010 A2: Unusual Asteroid Tail Implies Powerful Collision
APOD: 2010 February 3 - P2010 A2: Unusual Asteroid Tail Implies Powerful Collision
Explanation:
What is this strange object?
First discovered on ground based
LINEAR
images on January 6, the object appeared unusual
enough to investigate further with the
Hubble Space Telescope last week.
Pictured above, what Hubble saw indicates that P/2010 A2 is unlike any object ever seen before.
At first glance, the object appears to have the
tail of a comet.
Close inspection, however, shows a 140-meter
nucleus offset from the tail center, very unusual structure near the nucleus, and no discernable gas in the tail.
Knowing that the
object orbits in the
asteroid belt
between Mars and
Jupiter, a preliminary hypothesis that appears to explain all of the known clues is that
P/2010 A2
is the debris left over from a recent
collision
between two small asteroids.
If true,
the collision likely occurred at over 15,000 kilometers per hour -- five times the speed of a
rifle bullet --
and liberated energy in excess of a
nuclear bomb.
Pressure from sunlight would then spread out the debris into a trailing tail.
Future
study of P/2010 A2 may better indicate the nature of the progenitor collision and may help humanity better understand the
early years of our Solar System, when many similar collisions occurred.
 APOD: 2009 November 18 - Water Discovered in Moon Shadow
APOD: 2009 November 18 - Water Discovered in Moon Shadow
Explanation:
Why is there water on the Moon?
Last month, the
LCROSS mission crashed a large
impactor into a
permanently shadowed crater near the
Moon's South Pole.
A plume of dust rose that was visible to
the satellite,
although hard to discern from Earth.
The plume is shown above in visible light.
Last week, the results of a preliminary chemical analysis gave a clear indication that the
dust plume contained water.
Such water is of importance not only for understanding the
history of the Moon,
but as a possible reservoir for future astronauts trying to
live on the Moon for long periods.
The source of the
lunar water
is now a topic of debate.
Possible origins include many small meteorites,
a comet, or primordial
moon soil.
 APOD: 2009 September 28 - Water Discovered on the Moon
APOD: 2009 September 28 - Water Discovered on the Moon
Explanation:
Water has been discovered on the surface of the Moon.
No lakes have been found, but rather NASA's
Moon Mineralogy Mapper aboard India's new
Chandrayaan-1
lunar orbiter radios back that parts of the Moon's surface absorb a very specific color of light identified previously only with water.
Currently, scientists are trying to fit this with other facts about the
Moon to figure out how much water is there, and even what form this water takes.
Unfortunately, even the
dampest scenarios leave our moon dryer than the
driest of Earth's deserts.
A fascinating clue being debated is whether the
water signal rises and falls during a single lunar day.
If true, the signal might be explainable by hydrogen flowing
out from the Sun and interacting with
oxygen in the lunar soil.
This could leave an extremely thin
monolayer
of water, perhaps only a few molecules thick.
Some of the resulting water might subsequently evaporate away in bright sunlight.
Pictured above, the area near a crater on the
far side of the Moon shows a
relatively high abundance of water-carrying minerals in false-color blue.
Next week, the new LCROSS satellite will release an
impactor that will strike a
permanently shadowed crater
near the lunar south pole to see if any hidden water or ice sprays free there.
 APOD: 2009 June 22 - Atlas 5 Rocket Launches to the Moon
APOD: 2009 June 22 - Atlas 5 Rocket Launches to the Moon
Explanation:
This rocket is headed for the Moon.
Pictured above, a huge
Altas V rocket
roared off the
launch pad last week to start NASA's
first missions to Earth's
Moon in 10 years.
The rocket is carrying two robotic spacecraft.
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
(LRO)
is scheduled to orbit and better map the Moon, search for buried and hidden ice, and return many high resolution images.
Some images will be below one-meter in resolution and include images of historic
Apollo landing sites.
Exploratory data and images should allow a more informed choice of possible future astronaut landing sites.
The Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS) is scheduled to
monitor the controlled
impact of the rocket's
upper stage into a permanently shadowed crater near the
Moon's south pole.
This impact, which should occur in about three months, might be visible on Earth through small telescopes.
 APOD: 2009 February 21 - The Swift View of Comet Lulin
APOD: 2009 February 21 - The Swift View of Comet Lulin
Explanation:
Now growing brighter, Comet Lulin is headed for its
closest approach to planet Earth early next week.
But the comet's greenish glow,
familiar to
earthbound skygazers, is replaced
by false colors in
this
premier view from the
orbiting
Swift
satellite.
Image data from the Swift detectors, normally intended to
follow cosmic
gamma-ray bursts, were recorded on January 28.
The data are
combined here, along with a sky survey image of background stars,
to show optical and ultraviolet light in green-blue hues
and x-rays from the comet in red.
The result maps remarkable
x-ray emission on the comet's sunward
side as incoming solar wind ions interact
with gases in the swollen
coma.
It also shows substantial ultraviolet emission opposite the Sun,
in the direction of motion and the comet's tail.
The ultraviolet emission is from the OH molecule derived
from the breakup of water, an indicator of the copius amounts of water
produced by this extremely
active comet.
In fact, astronomers estimate Lulin was releasing about
800 gallons of water each second, enough to fill an Olympic-size
swimming pool in less than 15 minutes.
 APOD: 2008 September 8 - Rosetta Spacecraft Passes Asteroid Steins
APOD: 2008 September 8 - Rosetta Spacecraft Passes Asteroid Steins
Explanation:
What's that
diamond in the sky?
Cruising though space, sometimes you'll come across an unusual object.
Such was the case on Friday for
ESA's Rosetta spacecraft
on its way to comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko in 2014.
Robotic Rosetta buzzed right by the main belt asteroid
2867 �teins, taking many pictures, some of which have been compiled
into a
short video.
At first glance, Steins looked like a 5-kilometer wide
diamond,
but as Rosetta shot by, craters and a more extended shape become evident.
In the
above sequence of six images, a notable
chain of craters
is evident vertically on the asteroid's surface, most probably caused by a
chance collision with a stream of meteors.
Space scientists
will now study the data taken by
Rosetta of asteroid Steins in an effort to better
understand its composition, origin, and why the asteroid reflects light so
well.
As the Earth-bound scientists toil,
Rosetta itself will continue to zoom across our
Solar System, next swooping again by the Earth in 2009 November,
flying by asteroid
21 Lutetia in 2010
July,
and finally landing on
comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko in 2014 November.
 APOD: 2008 April 14 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: 2008 April 14 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
This moon is doomed.
Mars,
the red planet named for the
Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos, whose
names are derived from the Greek for Fear and
Panic.
These martian moons may well be captured
asteroids
originating in the main asteroid belt between Mars and
Jupiter
or perhaps from even more distant reaches of the Solar System.
The larger moon, Phobos, is indeed seen
to be a cratered, asteroid-like object in this
stunning color image from the
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter,
recorded at a resolution of about
seven meters per pixel.
But Phobos
orbits so close to Mars - about 5,800 kilometers above the surface compared to 400,000 kilometers
for our Moon - that gravitational
tidal forces
are dragging it down.
In 100 million years or so Phobos
will likely be shattered by stress caused by the
relentless
tidal forces, the debris forming a decaying ring around Mars.
 APOD: 2008 January 30 - Asteroid 2007 TU24 Passes the Earth
APOD: 2008 January 30 - Asteroid 2007 TU24 Passes the Earth
Explanation:
Asteroid 2007 TU24 passed by the Earth yesterday, posing no danger.
The space rock,
estimated to be about 250 meters across, coasted by just outside the orbit of Earth's Moon.
The passing was
not very unusual -- small rocks strike Earth daily,
and in 2003 a rock the size of a bus passed inside the orbit of the Moon,
being detected only after passing.
TU24 was notable partly because it was so large.
Were TU24 to have struck land,
it might have caused a
magnitude seven
earthquake
and left a city-sized crater.
A perhaps larger danger would have occurred were
TU24
to have struck the ocean and raised a large
tsunami.
This radar image was taken two days ago.
The Arecibo Radio Telescope in
Puerto Rico
broadcast radar that was reflected by the asteroid and then recorded by the
Byrd Radio Telescope in
Green Bank,
West Virginia.
The resulting image shows TU24 to have an oblong and irregular shape.
TU24 was discovered only three months ago, indicating that other
potentially hazardous asteroids might lurk in
our Solar System currently undetected.
Objects like TU24 are hard to detect because they are so faint and
move so fast.
Humanity's ability to scan the sky to detect, catalog, and analyze such objects has
increased notably in recent years.
 APOD: 2008 January 20 - Comet McNaught Over Chile
APOD: 2008 January 20 - Comet McNaught Over Chile
Explanation:
Comet McNaught was perhaps the most photogenic comet of our time.
After making
quite a show in the northern hemisphere
in early January,
the comet moved south and developed a
long and unusual dust tail that
dazzled southern hemisphere observers.
In this image, Comet McNaught was captured one year ago above
Chile.
The bright comet dominates on the left while
part of its magnificent tail
spreads across the entire picture.
From this vantage point in the Andes Mountains, one looks up toward
Comet
McNaught and a magnificent sky,
across at a crescent moon,
and down on clouds, atmospheric
haze,
and the city lights of
Santiago.
Comet McNaught
has glided into the outer Solar System and is now only visible as a speck
in a large telescope.
The other spectacular comet of 2007,
Comet Holmes, has also faded from easy view.
 APOD: 2007 November 3 - Golden Comet Holmes
APOD: 2007 November 3 - Golden Comet Holmes
Explanation:
Surprising Comet Holmes remains easily visible
as a round, fuzzy cloud in the northern constellation
Perseus.
Skywatchers with telescopes, binoculars, or those that
just decide to look up
can
enjoy the solar system's latest
prodigy as it glides
about 150 million kilometers from Earth, beyond the orbit of Mars.
Still expanding,
Holmes now appears to be about 1/3 the
size of the Full Moon, and many observers report a
yellowish tint to the dusty
coma.
A golden color does dominate this
telescopic view recorded on November 1,
showing variations across the coma's bright central region.
But where's the comet's tail?
Like any good
comet, Holmes'
tail would tend to point away from the Sun.
That direction is nearly along our line-of-sight behind the comet,
making its tail very difficult to see.
 APOD: 2007 October 25 - Apogee Moon, Perigee Moon
APOD: 2007 October 25 - Apogee Moon, Perigee Moon
Explanation:
Tonight, those blessed with clear skies can enjoy
a glorious Full Moon,
(exact full phase at 0452 UT, October 26).
In fact, the Moon will
reach its full phase within a few hours of
perigee,
the closest point in its
elliptical orbit,
making it the largest Full Moon of 2007.
On April 3, the Full Moon was within hours of apogee,
the farthest point in the lunar orbit,
corresponding to the smallest Full Moon of 2007.
The difference in apparent size between the largest and smallest Full
Moon is quite dramatic and similar to
this
side by side comparison of the lunar
apogee/perigee
apparitions from 2006.
But seen in the sky many months apart, the change is difficult to notice.
Skygazers should
also enjoy the Moon on Saturday, October 27, as
it encounters the lovely
Pleiades star cluster.
Because the Moon will be so bright, it will be easiest to spot the
Pleiades stars near the Moon with binoculars or a small telescope.
 APOD: 2007 April 5 - Asteroid and Galaxy
APOD: 2007 April 5 - Asteroid and Galaxy
Explanation:
Apollo class
asteroid
2006 VV2
flashed past planet Earth
in late March, approaching to within 3.4 million kilometers
or about 8.8 times the Earth-Moon distance.
Due to the proximity of its orbit to Earth and its estimated
diameter of over 1 kilometer, 2006 VV2 is
classified
as a Potentially
Hazardous Asteroid.
Telescopes large and small were trained on the much
anticipated flyby,
the closest for a known asteroid of comparable
size until the year 2036.
This
composite telescopic view is from a series
of images recorded over a period of about an hour
on Mar. 28 from Vado, New Mexico.
The asteroid begins near the center of the field and tracks
down and to the left, apparently passing very near galaxy M81.
Of course,
along with
its companion galaxy M82 on the right,
M81 is really 12 million light years
away, compared to
the
asteroid's range of a mere 15 light seconds.
 APOD: 2007 March 30 - Three Galaxies and a Comet
APOD: 2007 March 30 - Three Galaxies and a Comet
Explanation:
Diffuse starlight and dark nebulae
along the southern
Milky Way
arc over the horizon and sprawl diagonally through this
gorgeous nightscape.
The breath-taking mosaic spans a wide
100 degrees, with the rugged
terrain
of the Patagonia, Argentina region in the foreground.
Along with the insider's view of our own galaxy, the image
features our outside perspective on two irregular satellite galaxies -
the Large and
Small Magellanic Clouds.
Recorded on January 28, the scene also captures the
broad tail
and bright coma of Comet McNaught, The
Great Comet of 2007.
 APOD: 2007 March 4 - Triton: Neptunes Largest Moon
APOD: 2007 March 4 - Triton: Neptunes Largest Moon
Explanation:
In October of 1846,
William Lassell
was observing the newly discovered planet
Neptune.
He was attempting to confirm his observation, made just the previous week,
that Neptune had a ring.
But this time he discovered that Neptune had a satellite as well.
Lassell soon proved that the ring was a product of his new
telescope's distortion, but the satellite
Triton
remained.
The above picture of
Triton
was taken in 1989 by the only spacecraft ever to pass
Triton:
Voyager 2.
Voyager 2 found fascinating terrain,
a thin atmosphere, and even evidence for
ice volcanoes
on this world of peculiar orbit and spin.
Ironically, Voyager 2 also confirmed the existence of
complete thin rings around Neptune
- but these would have been quite
invisible
to Lassell!
 APOD: 2007 January 17 - Comet McNaught from New STEREO Satellite
APOD: 2007 January 17 - Comet McNaught from New STEREO Satellite
Explanation:
The brightest comet of recent decades was a surprising first sight for a new camera in space.
The Sun Earth Connection Coronal
and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) instrument onboard the
Solar TErrestrial
RElations Observatory (STEREO) satellite had just opened up
on January 11 when it snapped the above image of
Comet McNaught.
Visible was a spectacular view of the
ion tail of
Comet McNaught
being swept away from the Sun by the
solar wind
in filamentary rays.
The comet tail is seen to extend at least seven degrees across the
above image, while the
central coma is so bright it saturates.
Comet McNaught is now reportedly so bright that it is visible
even in broad daylight by blocking out the Sun with your hand.
Comet McNaught
has rounded the Sun and will slowly
fade away for observers in
Earth's Southern Hemisphere
as it recedes from the Sun.
 APOD: 2006 December 28 - Moon Over Andromeda
APOD: 2006 December 28 - Moon Over Andromeda
Explanation:
The Great Spiral Galaxy
in Andromeda (aka M31), a mere 2.5 million
light-years distant,
is the closest
large spiral to our own Milky Way.
Andromeda is visible to the unaided eye as a small, faint, fuzzy patch,
but because its surface brightness is so low, casual
skygazers can't
appreciate the galaxy's impressive extent in planet Earth's sky.
This entertaining composite image compares the
angular size
of the nearby galaxy
to a brighter, more familiar celestial sight.
In it, a
deep
exposure of Andromeda, tracing beautiful blue star
clusters in spiral arms far beyond the bright yellow core,
is combined with a typical view of a nearly full Moon.
Shown at the same angular scale, the Moon covers about 1/2 degree on the
sky, while the galaxy is clearly several times that size.
The deep Andromeda exposure also includes two bright satellite
galaxies, M32 and
M110 (bottom).
 APOD: 2006 December 3 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: 2006 December 3 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
This moon is doomed.
Mars,
the red planet named for the
Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos, whose
names are derived from the Greek for Fear and Panic.
These martian moons may well be captured
asteroids
originating in the main asteroid belt between Mars
and Jupiter or perhaps from even more distant reaches
of the Solar System.
The larger moon, Phobos, is indeed seen
to be a cratered, asteroid-like object in this
stunning color image
from the Mars Express spacecraft, recorded at a resolution of about
seven meters per pixel.
But Phobos orbits so close to Mars -
about 5,800 kilometers above the surface compared to 400,000 kilometers
for our Moon - that
gravitational tidal forces are dragging it down.
In 100 million years or so it will likely crash into the
surface or be shattered by stress caused by the
relentless
tidal forces, the debris forming a ring around Mars.
 APOD: 2006 August 13 - The Comet and the Galaxy
APOD: 2006 August 13 - The Comet and the Galaxy
Explanation:
The Moon almost ruined this photograph.
During late March and early April 1997,
Comet Hale-Bopp
passed nearly in front of the
Andromeda Galaxy.
Here the Great Comet
of 1997 and the
Great Galaxy in Andromeda were
photographed together
on 1997 March 24th.
The problem was the brightness of the
Moon. The Moon was full that night and so bright that long
exposures meant to capture the
tails of Hale-Bopp and the disk of
M31 would capture instead
only moonlight reflected off the Earth's atmosphere.
By the time the Moon would set, this opportunity would be gone.
That's why this picture was taken during a total
lunar eclipse.
 APOD: 2006 May 23 - Comet Schwassmann Wachmann 3 Passes the Earth
APOD: 2006 May 23 - Comet Schwassmann Wachmann 3 Passes the Earth
Explanation:
Rarely does a comet pass this close to Earth.
Last week, dedicated astrofilmographers were able to take advantage
of the close approach of crumbling
73P / Comet Schwassmann-Wachmann 3 to make time-lapse movies of the fast-moving comet.
Large comet fragments passed about 25 times the Moon's distance from the Earth.
The above time lapse movie of
Fragment B of
Comet Schwassmann-Wachmann 3 over
Colorado,
USA was taken during a single night, May 16, with 83
consecutive 49-second exposures.
Some observers report being able to perceive the slight motion of
the comet with respect to the background stars using only their
binoculars and without resorting to the creation of fancy digital time-lapse movies.
Fragment B of
Comet Schwassmann-Wachmann 3 became just barely visible to the
unaided eye two weeks ago but now is appearing to fade as the comet
has moved past the Earth and nears the Sun.
Many sky enthusiasts will be
on the watch for a particularly active meteor shower tonight as the
Earth made its closest approach to orbit of
Comet Schwassmann-Wachmann 3 late yesterday.
 APOD: 2006 April 26 - Crumbling Comet Schwassmann Wachmann 3 Approaches
APOD: 2006 April 26 - Crumbling Comet Schwassmann Wachmann 3 Approaches
Explanation:
A crumbling comet will soon pass near the Earth.
Comet 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 3 is brightening and may even be visible to the unaided
eye when the
fragmented comet zooms past Earth during the middle of next month.
Still, the small comet poses no
Earth hazard, since it will pass the Earth at about 25 times the
distance of the Moon.
Exactly how bright
Comet Schwassman-Wachmann 3 will get is unknown.
It is even possible, althought unlikely, that debris from
the comet
will have spread out enough to cause a notable
meteor shower.
Pictured above,
Fragment B of
Comet Schwassman-Wachmann 3 was photographed two nights ago by a 8.2-meter
Very Large Telescope in
Chile.
Visible to the lower right of the large B fragment are many mini-comets
that have broken off and now orbit the Sun separately.
Each mini-comet itself sheds gas and dust and so appears to have its own hazy coma.
The comet will pass closest to the Sun on June 7.
 APOD: 2006 March 11 - Colors of Comet Pojmanski
APOD: 2006 March 11 - Colors of Comet Pojmanski
Explanation:
Comet Pojmanski flew by planet Earth
last weekend on a surprise trip through
the inner solar system.
Then an easy binocular target for morning
skygazers,
Pojmanski ultimately showed off a
long tail,
but it also presented some lovely green-blue hues
as gas molecules in its tenuous coma and tail
fluoresced
in the sunlight.
Astronomers Adam Block and Jay GaBany recorded
this
colorful high-resolution view on March 3rd in the
darkness just before twilight.
The picture spans about one full moon on the sky.
Comet
Pojmanski (C/2006 A1) is outward bound and fading now,
still visible in binoculars for northern hemisphere observers.
 APOD: 2006 March 6 - Unexpected Comet Pojmanski Now Visible
APOD: 2006 March 6 - Unexpected Comet Pojmanski Now Visible
Explanation:
Have you ever seen a comet?
Comets bright enough to be visible to the unaided eye appear only
every few years.
Right now, however, a new comet has brightened unexpectedly and is
visible as a faint streak to the unaided northern observer in the eastern morning sky just before sunrise.
Binoculars may help.
Comet Pojmanski, officially designated C/2006 A1 and discovered only in January, now sports a turquoise tail several times longer than the full moon.
Comet Pojmanski's
ion tail is due to gas particles expelled by the comet being pushed away from the Sun by the
solar wind,
the same wind that ionizes gas in the tail causing its blue tint.
Pictured above as it appeared only last week,
Comet Pojmanski has now begun to fade as its
orbit around the Sun takes
it further from the Earth.
 APOD: 2006 February 12 - Phoebe: Comet Moon of Saturn
APOD: 2006 February 12 - Phoebe: Comet Moon of Saturn
Explanation:
Was Saturn's moon Phoebe once a comet?
Images from the robotic
Cassini spacecraft taken two years ago when entering
the neighborhood of
Saturn indicate that
Phoebe
may have originated in the outer
Solar System.
Phoebe's
irregular surface,
retrograde orbit, unusually dark surface,
assortment of large and small craters, and low average density
appear consistent with the
hypothesis that Phoebe was once part of the
Kuiper belt of icy comets beyond Neptune before being
captured by Saturn.
Visible in the
above image of Phoebe are craters, streaks, and
layered deposits of light and dark material.
The image was taken from around 30,000 kilometers out from this
200-kilometer diameter moon.
Two weeks after taking the
above image,
Cassini fired its engines
to decelerate into orbit around Saturn.
 APOD: 2005 September 19 - Approaching Asteroid Itokawa
APOD: 2005 September 19 - Approaching Asteroid Itokawa
Explanation:
What are asteroids made of?
To help find out,
Japan's
JAXA space agency launched the
Hayabusa mission to
rendezvous with
asteroid Itokawa.
Last week, the small robotic Hayabusa spacecraft arrived at asteroid
Itokawa and stationed itself only 20 kilometers away.
Although a long term goal is to find out how much ice, rock and trace
elements reside on the asteroid's surface, a shorter term goal is to
determine the mass of the asteroid by measuring the attraction of the drifting
Hayabusa spacecraft.
During the next few months,
Hayabusa will also image and map asteroid Itokawa as it orbits the Sun.
The above time-lapse image sequence was taken by Hayabusa upon final approach,
showing the general oblong shape of the
asteroid.
In November, a small coffee-can sized robot dubbed
MINERVA is scheduled for release and is expected to hop around the asteroid taking pictures.
Also in November, Hayabusa will fire pellets into
asteroid Itokawa
and collect some of the debris in a return capsule.
In December, Hayabusa
will fire its rockets toward Earth and drop the
return capsule to Earth in 2007 June.
 APOD: 2005 April 23 - Eclipsed Moon in Infrared
APOD: 2005 April 23 - Eclipsed Moon in Infrared
Explanation:
In September of 1996,
the Midcourse
Space Experiment (MSX) satellite had a spectacular view of
a total lunar eclipse
from Earth orbit.
SPIRIT III, an on board infrared telescope, was used to
repeatedly image the moon
during the eclipse.
Above is one of
the images taken during the 70 minute totality, the Moon completely
immersed in the Earth's shadow.
Infrared light
has wavelengths
longer than visible light - humans can not see it but
feel it as heat.
So, the bright spots correspond to the warm areas on
the lunar surface,
and dark areas are cooler.
The brightest spot below and left of center is the
crater Tycho, while
the dark region at the upper right is
the Mare Crisium.
Of course, this
Sunday's lunar eclipse
will not be a total, or even a partial one.
Instead, the Moon will glide
through the subtle outer portion
of the Earth's shadow in a penumbral
eclipse
of the Moon.
 APOD: 2004 November 19 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: 2004 November 19 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
This moon is doomed.
Mars,
the red planet named for the
Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos, whose
names are derived from the Greek for Fear and Panic.
These martian moons may well be captured
asteroids
originating in the main asteroid belt between Mars
and Jupiter or perhaps from even more distant reaches
of the Solar System.
The largest moon, Phobos, is indeed seen
to be a cratered, asteroid-like object in this
stunning new color image
from the Mars Express spacecraft, recorded at a resolution of about
seven meters per pixel.
But Phobos orbits so close to Mars -
about 5,800 kilometers above the surface compared to 400,000 kilometers
for our Moon - that
gravitational tidal forces are dragging it down.
In 100 million years or so it will likely crash into the
surface or be shattered by stress caused by the
relentless
tidal forces, the debris forming a ring around Mars.
 APOD: 2004 October 21 - Apogee Moon, Perigee Moon
APOD: 2004 October 21 - Apogee Moon, Perigee Moon
Explanation:
Why don't these pieces fit?
This third quarter Moon (left) and first quarter Moon were
both photographed during the last lunar cycle or
lunation with the
same telescope and camera.
But, simply combining the pictures into one sharp, full
surface view
would clearly be a problem.
In fact, on October 6th the Moon's third quarter phase
happened to occur near
lunar
apogee, the farthest point in the Moon's
orbit.
On September 21st, the first quarter phase fell close to
lunar
perigee, the Moon's closest approach to planet Earth.
Viewed two weeks apart,
the resulting difference in apparent sizes would not be
noticed by casual skygazers, but the
simultaneous side by side comparison makes it hard to ignore.
Skygazers will likely
notice the Moon
next week though,
as it slides through Earth's shadow during October 27th's
total lunar eclipse.
 APOD: 2004 October 2 - Toutatis Nears Planet Earth
APOD: 2004 October 2 - Toutatis Nears Planet Earth
Explanation:
On Wednesday, September 29,
asteroid
Toutatis came within one million miles of Earth -- the
closest predicted aproach of a sizable asteroid or comet to our
fair planet in this century.
Coming within
one million miles or about 4 times the Earth-Moon
distance, Earth would have appeared to be nearly the size of the full
moon in the asteroid's sky.
In Earth's sky,
Toutatis appeared
only as a faint, starlike, but rapidly moving object.
Even so,
asteroid 4179 Toutatis
was still bright enough to see in small telescopes.
Astronomers John Chumack, observing near Dayton Ohio, and
Juergen Wolf from near Palo Alto, California, offer these
composite images showing the progress of the asteroid
(seen as a series of dots) against a background of distant stars.
Their multiple exposures span a two hour period on two different days
about a week before the asteroid's record
close
approach, which tracked through night
skies south of the celestial
equator.
 APOD: 2004 October 1 - Earth Nears Asteroid Toutatis
APOD: 2004 October 1 - Earth Nears Asteroid Toutatis
Explanation:
On Wednesday, September 29, the Earth came within one million
miles of the
asteroid
Toutatis -- the closest predicted
aproach of our fair planet to a sizable asteroid or comet in this
century.
Coming within
one million miles or about 4 times the Earth-Moon
distance, Earth would appear to be nearly the size of the full
moon in the asteroid's sky, as suggested in this illustration.
In Earth's sky,
Toutatis appeared
only as a faint object rapidly moving against a
background of stars.
Also known as Earth-crossing
asteroid 4179,
Toutatis is in an eccentric 4 year orbit
which moves it from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter to just
inside Earth's orbit.
When the Earth passed near it
in 1992 Toutatis was imaged
by radar and seen to be two irregularly shaped lumps,
perhaps joined by a narrow neck.
This bizarre object is up to 1.5 miles wide, 3 miles long, and is
tumbling through space.
Studies of Toutatis and other
Earth-crossing asteroids help reveal
connections between the
Solar System's
meteorites, main-belt asteroids and comets.
These asteroids also offer tantalizing
targets for robotic
exploration and, over time, represent
potential collision hazards
for planet Earth!
 APOD: 2004 August 30- Announcing Comet C 2003 K4 LINEAR
APOD: 2004 August 30- Announcing Comet C 2003 K4 LINEAR
Explanation:
A comet discovered last year has brightened unexpectedly and now may become visible to the unaided eye within the next month.
Designated Comet C/2003 K4 (LINEAR), the comet was discovered in
2003 May by project
LINEAR.
Many reports already place the comet as brighter than
magnitude 7, meaning that it can now be seen with binoculars.
Reports also indicate the comet already has a
visible tail nearly the length of a
full Moon.
Since predicting the
future brightness of comets is a very
tricky business, there remains the possibility that
K4 might never become very bright.
Current
predictions, however, estimate the comet may
approach fifth magnitude in October.
K4 passes
closest to the Sun on October 12 and then closest to the Earth
on December 23.
Comet K4 was photographed above from Van Buren,
Arkansas,
USA on August 17.
 APOD: 2004 July 31 - Tonight: A Blue Moon
APOD: 2004 July 31 - Tonight: A Blue Moon
Explanation:
How often does a full moon occur twice in a single month?
Exactly once in a
Blue Moon.
In fact, the modern usage of the term "Blue Moon" refers to the
second Full Moon in a single month.
Tonight's Blue Moon will be the first since November 2001.
A Blue Moon typically occurs every few years.
The reason for the rarity of the
Blue Moon is that the 29.53 days between full moons is
just slightly shorter than the number of days in the average month.
Don't, however, expect the moon to look blue tonight!
The term "Blue Moon" has recently been traced to an error in a
magazine article in 1946.
It is possible for the
Moon to appear tinged by a blue hue, sometimes caused by fine dirt circulating in the
Earth's atmosphere, possibly from a volcanic explosion.
The above picture was taken not during a full moon but through a morning sky that appeared dark blue.
The bright crescent is the only part directly exposed to sunlight - the rest of the Moon glows from sunlight reflected from the Earth.
In this dramatic photo, however, the planet
Jupiter
is also visible along with its
four largest moons.
 APOD: 2004 June 30 - Phoebe: Comet Moon of Saturn
APOD: 2004 June 30 - Phoebe: Comet Moon of Saturn
Explanation:
Was Saturn's moon Phoebe once a comet?
Images from the robotic
Cassini spacecraft taken two weeks ago when entering
the neighborhood of
Saturn indicate that
Phoebe
may have originated in the outer
Solar System.
Phoebe's
irregular surface,
retrograde orbit, unusually dark surface,
assortment of large and small craters, and low average density
appear consistent with the
hypothesis that Phoebe was once part of the
Kuiper belt of icy comets beyond Neptune before being
captured by Saturn.
Visible in the
above image of Phoebe are craters, streaks, and
layered deposits of light and dark material.
The image was taken from around 30,000 kilometers out from this
200-kilometer diameter moon.
Late today, Cassini will begin to
fire its engines
to decelerate into orbit around Saturn.
 APOD: 2004 June 19 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
APOD: 2004 June 19 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
Explanation:
This
asteroid has a moon!
The robot
spacecraft Galileo destined to explore the Jovian system,
encountered and photographed two
asteroids
during its long interplanetary voyage to
Jupiter.
The second asteroid it photographed,
Ida,
was discovered to have
a moon which appears as a small dot to the right of Ida in
this
image from 1993.
The
tiny moon, named Dactyl, is about one mile across, while
the potato shaped Ida measures about 36 miles long and 14 miles wide.
Dactyl is the first moon of an asteroid ever discovered.
The names
Ida and
Dactyl are from Greek mythology.
Many other asteroids
are now known to
have
moons.
 APOD: 2004 April 23 - Comet C/2001 Q4 (NEAT)
APOD: 2004 April 23 - Comet C/2001 Q4 (NEAT)
Explanation:
Inbound from the distant solar system,
comet C/2001 Q4
will soon pass just inside planet Earth's orbit
and should be one of two
bright,
naked-eye comets
visible in
southern skies
in May.
First picked up nearly three years ago by the
Near Earth Asteroid Tracking
(NEAT) project
Q4 appears in both of these stunning telescopic views
recorded only a few days ago,
on April 18th (left) and 19th, from a site near Alcohuaz, Chile.
Remarkable changes in the structure of the long, graceful tail
can be seen by comparing the two photos, including the
dramatic kink
seen near the tail's midpoint on April 19th.
The apparent motion of the comet sweeping
across
the sky is evident when you compare the position of the tail
relative to background galaxy NGC 1313, visible as a smudge
near the top of each image.
Q4's closest approach to the Sun will be on May 15th while its
closest encounter with planet Earth will be on May 7th
(see animation by
L. Koehn).
 APOD: 2004 April 22 - Comet C/2002 T7 (LINEAR)
APOD: 2004 April 22 - Comet C/2002 T7 (LINEAR)
Explanation:
Discovered by the the Lincoln Near Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR)
project in October of 2002,
comet C/2002 T7 is now visiting the
inner solar system, making its closest approach
(see animation by
L. Koehn)
to the Sun tomorrow, April 23rd.
Emerging from the solar glare, the
comet is
now just visible to
the unaided eye in the constellation Pisces, near the eastern horizon
in morning twilight.
In this
gorgeous telescopic view
recorded before dawn
yesterday, the clearly active comet has developed an extensive, complex
tail extending over 2 degrees in
the anti-sunward direction, and a pronounced
anti-tail or
anomalous tail.
Later next month this comet should appear brighter,
making its closest approach to planet Earth on May 19th.
In fact, it could
share southern skies with another naked-eye comet,
also anticipated to brighten in May, designated C/2001 Q4 (NEAT).
 APOD: 2004 April 19 - Comet Bradfield Passes the Sun
APOD: 2004 April 19 - Comet Bradfield Passes the Sun
Explanation:
Today,
Comet Bradfield is passing the Sun.
The above image, taken yesterday in the direction of the
Sun by the
SOHO
LASCO
instrument, shows the comet and its
dust tail
as the elongated white streak.
The Sun
would normally be seen in the very center but has been
blocked from view.
Comet C/2004 F4 (Bradfield) was discovered
just one month ago and has brightened dramatically
as it neared the Sun.
Careful sky gazers can see
Comet Bradfield
with the unaided eye near the Sun, although
NASA's
sun-orbiting SOHO satellite has the best view.
During the day,
Comet Bradfield will continually shift inside the
LASCO frame as it rounds the Sun.
There is even the possibility that the comet will
break up.
If not, the bright comet's trajectory will carry it
outside the field of LASCO sometime tomorrow.
Along with T7 and
Q4,
Comet Bradfield is now the
third comet that is currently visible
on the sky with the unaided eye, the most ever of which we are aware
and quite possibly the most in
recorded
history.
 APOD: 2004 February 9 - Announcing Comet C 2002 T7 LINEAR
APOD: 2004 February 9 - Announcing Comet C 2002 T7 LINEAR
Explanation:
A newly discovered comet may outshine most stars in the sky by May.
Designated Comet C/2002 T7 (LINEAR), the comet was discovered in 2002 October by
project LINEAR.
Many reports already place the comet as brighter than
magnitude 7, meaning that it can now be seen with binoculars.
Reports also indicate the comet already has a visible
tail nearly the length of a
full Moon.
Since predicting the
future brightness of comets is a very
tricky business, there remains the possibility that
T7 might never become visible to the unaided eye.
Alternatively, another comet,
C/2001 Q4 (NEAT), may also
reach naked eye visibility at nearly the same time,
making 2004 April and May two of the busiest
bright-comet months in centuries.
Comet T7 can be seen on the above right on January 20,
while an airplane trail is visible on the left.
 APOD: 2004 January 31 - A Galaxy is not a Comet
APOD: 2004 January 31 - A Galaxy is not a Comet
Explanation:
This gorgeous galaxy and
comet portrait was recorded on April 5th, 2002,
in the skies over the Oriental Pyrenees near Figueres,
Spain.
From a site above 1,100 meters,
astrophotographer
Juan Carlos Casado used a guided time exposure, fast film, and
a telephoto lens to capture the predicted conjunction of
the bright Comet Ikeya-Zhang (right)
and the Andromeda Galaxy (left).
This stunning celestial scene would also have been a
rewarding one for the influential 18th century comet
hunter Charles Messier.
While Messier scanned French skies for comets,
he carefully cataloged positions of things which were
fuzzy and comet-like
in appearance but did not move against the background stars and
so were definitely not comets.
The Andromeda Galaxy,
also known as M31, is the 31st object in
his famous
not-a-comet catalog.
Not-a-comet object
number 110, a late addition to Messier's catalog, is
one of Andromeda's small satellite galaxies, and can be
seen here just below M31.
Our modern
understanding
holds that the Andromeda galaxy is a large spiral galaxy
some 2 million light-years
distant.
The photogenic
Comet
Ikeya-Zhang, then a lovely sight in
early morning skies
was about 80 million kilometers (4 light-minutes) from planet Earth.
 APOD: 2003 November 8 - Eclipsed Moon in Infrared
APOD: 2003 November 8 - Eclipsed Moon in Infrared
Explanation:
The total lunar eclipse of September 1996
disappointed many observers in North America who
were cursed with cloudy skies.
However, the
Midcourse
Space Experiment (MSX) satellite had
a spectacular view from Earth orbit and
SPIRIT III,
an on board infrared telescope, was used to
repeatedly image the moon
during the eclipse.
Above is one of
the images taken during the 70 minute totality, the Moon completely
immersed in
the Earth's shadow.
Infrared light
has wavelengths
longer than visible light - humans can not see it but feel it as heat.
The bright spots correspond to the warm areas on the
lunar surface, dark areas are cooler.
The brightest spot below and left of center is the
crater Tycho,
the dark region at the upper right is
the Mare Crisium.
The series of SPIRIT III images allow the determination of cooling
rates for geologically different areas, exploring the physical properties
of the Moon's surface.
 APOD: 2003 October 3 - Cold Comet Halley
APOD: 2003 October 3 - Cold Comet Halley
Explanation:
While this may not be the most esthetic image of
Comet Halley
that you have ever seen, it is likely the most unique.
The tiny cluster of pixels circled is the
famous
comet along its orbit over
4 billion (4,000,000,000) kilometers or 28
AU
from the Sun --
a record distance for a comet observation.
Its last passage through
our neck of the woods in 1986,
Comet Halley
presently cruises through the dim reaches of the outer solar
system, almost as far away as outermost gas giant Neptune, and shows no
sign of activity.
Captured in March, this negative image is a composite of
digital exposures made with three
of ESO's Very Large Telescopes.
The exposures are registered on the
moving comet, so the
picture shows background stars and galaxies as elongated smudges.
An earth-orbiting satellite appears as a dark streak at the top.
Comet
Halley is clearly extremely faint here, but large earthbound
telescopes will be able to
follow
it as it grows fainter still, reaching
the most distant point in its orbit, more than 5 billion kilometers
(35 AU) from the Sun, in 2023.
 APOD: 2003 August 29 - The Mineral Moon
APOD: 2003 August 29 - The Mineral Moon
Explanation:
Even
if the Moon really were made of
green cheese it probably wouldn't
look this bizarre.
Still, this
mosaic
of 53 images was recorded by the
Jupiter-bound Galileo spacecraft as
it passed near our own large
natural
satellite in 1992.
The pictures were recorded through three spectral filters and
combined in an exaggerated false-color scheme
to explore the
composition
of the lunar surface as
changes in mineral content produce subtle
color differences in
reflected light.
Familiar to earthdwellers, the lunar near side is
on the left, but the space-based view looks down on the
Moon's north pole located
in the upper half of the image near the shadow line.
Blue to orange shades indicate volcanic lava flows.
The dark blue
Mare Tranquillitatis
at the lower left is richer in
titanium bearing minerals than the green and orange maria above it.
Near the bottom of the image and to the right of Tranquillitatis
is the dark oval-shaped Mare Crisium surrounded by
shocking pink colors indicating material of the
lunar
highlands.
 APOD: 2003 April 6 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: 2003 April 6 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
This moon is doomed.
Mars,
the red planet named for the
Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos, whose names are derived from the Greek for
Fear and Panic.
These
Martian
moons may well be captured
asteroids
originating in the main asteroid belt between Mars
and Jupiter or perhaps from even more
distant reaches of the
Solar System.
In this 1978
Viking 1 orbiter image,
the largest moon, Phobos, is indeed seen to be a
heavily cratered asteroid-like object.
About 17 miles across, Phobos really zips through the
Martian sky.
Actually rising above Mars' western horizon and setting in the east,
it completes an orbit in less than 8 hours.
But Phobos orbits so close to Mars,
(about 5,800 kilometers above the surface compared to 400,000 kilometers
for our Moon) that
gravitational tidal forces are dragging it down.
In 100 million years or so it will likely crash into the
surface or be shattered by stress caused by the
relentless
tidal forces, the debris forming a ring around Mars.
 APOD: 2003 March 6 - Comet NEAT in Southern Skies
APOD: 2003 March 6 - Comet NEAT in Southern Skies
Explanation:
After last month's dramatic swoop past the
Sun, Comet NEAT (C/2002 V1)
appeared as a naked-eye comet,
emerging from the evening twilight in planet Earth's southern skies.
On March 1st,
New Zealand photographer Noel Munford captured this telephoto view of
the outbound comet close to the southwestern horizon
against the faint stars of the constellation
Sculptor.
He reports that the picture is a good representation of the comet's
visual appearance on that date and estimates the impressive tail to be
five or six degrees long.
Discovered
last November as part of the
Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking
program, there was some speculation that this comet would not
survive its close encounter with the Sun.
However, Comet NEAT is now
returning to
the outer solar system,
diving
southward and fading fast.
 APOD: 2003 February 24 - Comet NEAT Passes an Erupting Sun
APOD: 2003 February 24 - Comet NEAT Passes an Erupting Sun
Explanation:
As Comet NEAT flared last week, the
Sun roared.
Just as the comet swooped inside the orbit of
Mercury
and developed a long and flowing tail of gas and
dust,
the Sun emitted a huge
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME).
Neither the fortuitous
hot ball of solar gas
nor the intense glare of sunlight appeared to disrupt the
comet's nucleus.
The action was too close to the
Sun to be easily visible by
humans,
but the orbiting Sun-pointing
SOHO satellite had a clear view of the celestial daredevil show.
The above image was taken on February 18 when the
comet
was so bright it created an
artificial horizontal streak on the camera image.
During the encounter,
Comet NEAT, official designation (C/2002 V1),
brightened to second
magnitude.
An opaque disk blocked the Sun's image.
The now-outbound comet remains
bright but will surely fade as it moves away from the Sun.
Nevertheless, Comet NEAT will likely be visible with binoculars
to southern hemisphere observers for the next month.
 APOD: 2003 February 10 - Comet NEAT Approaches the Sun
APOD: 2003 February 10 - Comet NEAT Approaches the Sun
Explanation:
A comet
may likely become visible to the unaided eye over the
next few days above the
horizon where the Sun has just set.
Comet NEAT (C/ 2002 V1), discovered last November, has
brightened dramatically as it approached the Sun.
Over the next few days, the
quickly setting comet could
appear as bright as second
magnitude.
On February 18 it will round the Sun well within the orbit of
Mercury.
During surrounding days, the Sun's glare will effectively
hide the comet to human observers.
It is quite probable, though, that
Comet NEAT will standout prominently in
images taken by the Sun-looking
SOHO satellite.
Pictured above,
Comet NEAT's complex and developing
tail was photographed on
January 29 (top) and February 2.
Sky enthusiasts
should remember to never look directly at the Sun.
 APOD: 2002 December 9 - Moon Shadow Moves Over Africa
APOD: 2002 December 9 - Moon Shadow Moves Over Africa
Explanation:
When the
Moon's shadow reached out and touched the
Earth
last week, the result was a
solar eclipse.
Such an eclipse is total only for observers located along a
narrow path corresponding to the ground track
of the shadow's dark central portion or
umbra.
For this eclipse, racing along at nearly 2000 kilometers per hour,
the Moon's umbra obligingly crossed over land along regions of
Africa and
Australia.
Totality lasted for about two
minutes or less at a given location.
Many nearby regions fell within the lighter but much wider
outer shadow region, the
penumbra, and witnessed a
partial solar eclipse.
The above movie follows the Moon's shadow as it crossed
Africa during a
similar eclipse in June 2001.
Each frame is separated in time by about 20 minutes.
The movie was created from frames taken by the orbiting
European satellite
MeteoSat-6.
 APOD: 2002 November 16 - Tempel-Tuttle: The Leonid Comet
APOD: 2002 November 16 - Tempel-Tuttle: The Leonid Comet
Explanation:
Star trails
streak this composite time exposure of
comet
Tempel-Tuttle recorded by Tim Puckett on January 26, 1998.
Then passing through the inner solar system on its
33 year orbit around the Sun,
Tempel-Tuttle brightened unexpectedly, but
binoculars or small telescopes
were still required to visually observe it.
Tempel-Tuttle is also called "the Leonid Comet" as the yearly
Leonid meteor shower
results when the Earth crosses this comet's orbital
plane and encounters a trail of
cometary dust.
So, while not rivaling spectacular naked-eye comets like
Hyakutake or
Hale-Bopp,
Tempel-Tuttle still puts on a show.
The Earth is
now approaching relatively
dense regions
of Tempel-Tuttle's orbiting debris trail, so
in the next few days,
skywatchers will be
searching for leonid meteors.
An extremely active meteor shower
is expected to be visible
over Europe and North America
in the early morning hours of
Tuesday, November 19,
despite interference from a glaring full moon.
 APOD: 2002 November 13 - Asteroid Annefrank
APOD: 2002 November 13 - Asteroid Annefrank
Explanation:
NASA's interplanetary probe
STARDUST,
on its way to
Comet Wild 2 in January 2004, passed asteroid
5535 Annefrank earlier this month.
Annefrank, named for a
holocaust
victim who kept a
famous diary, is a member of the
main asteroid belt between
Mars and
Jupiter.
Just prior to closest approach at about 3300 km distant, the
robot spacecraft took the
above picture.
Although images obtained were not detailed enough to
resolve much of the asteroid's surface, the size, reflectivity,
and general shape of the asteroid were
recorded.
At 6 kilometers across, asteroid Annefrank turned out to be
larger -- and darker -- than expected.
 APOD: 2002 September 19 - Asteroid 1998 KY26
APOD: 2002 September 19 - Asteroid 1998 KY26
Explanation:
A day is just under 11 minutes long
on 1998 KY26, a 30 meter wide,
fast-spinning, water-rich asteroid.
This computer simulated view of its lumpy surface has a resolution of
about 3 meters and is
based
on radar and optical observations
(click on the image for a series of surface views).
The observations
were
made shortly after the discovery of the
diminutive world which passed within about 800,000 kilometers of Earth,
or about 2 times the Earth-Moon distance, in June of 1998.
Around 10 million asteroids of similar size may exist in orbits that
also come near Earth's,
but little is known about them.
However, spinning so fast, tiny 1998 KY26 can not be a
loose conglomerate held together by gravity alone.
Instead it is likely a monolithic chunk fragmented from a
larger asteroid.
As the radar and optical data suggest 1998 KY26
has a high water content, this
relatively
accessible asteroid
could be a literal oasis for
future space explorers.
 APOD: 2002 August 17 - Asteroid 2002 NY40
APOD: 2002 August 17 - Asteroid 2002 NY40
Explanation:
Asteroid 2002 NY40 will fly by planet Earth
early in the morning August 18 Universal Time (late in the evening
August 17 Eastern Daylight Time).
Approaching
to within about 530,000 kilometers or 1.3 times the
Earth-Moon distance
2002
NY40 will definitely not be close enough
to pose any danger of collision.
But it will be close enough and just bright enough for experienced
skygazers to see this 800 meter wide
space rock in a small telescope or
binoculars as it glides quickly
through northern skies past the
bright star Vega.
It will also be close enough to
ping with radar,
and asteroid hunters
using the large
Arecibo radio telescope
in Puerto Rico expect to
determine the three dimensional outline of 2002 NY40.
Similar investigations of
other near Earth asteroids have revealed some
surprising shapes.
In this five minute time exposure, recorded at
Cerro Tololo
Inter-American Observatory
on August 14, 2002 NY40 shows itself as a long smudge as it moves
against a background of faint stars in the
constellation Aquarius.
 APOD: 2002 July 6 - Io: Moon Over Jupiter
APOD: 2002 July 6 - Io: Moon Over Jupiter
Explanation:
How big is the Jovian moon Io?
The most volcanic body in the Solar System,
Io (usually pronounced "EYE-oh") is
3,600 kilometers in diameter, about the size of
planet Earth's single large
natural satellite.
Gliding
past Jupiter
at the turn of the millennium, the Cassini spacecraft captured this
awe
inspiring view of
active Io
with the
largest gas giant as a backdrop,
offering a stunning demonstration of the ruling planet's
relative size.
Although in the picture Io appears
to be located just in front of the
swirling Jovian clouds, Io hurtles around its orbit once every 42 hours
at a distance of 420,000 kilometers or so from the center
of Jupiter.
That puts it nearly 350,000 kilometers above
Jupiter's cloud tops,
roughly equivalent to the distance between
Earth and Moon.
The
Cassini
spacecraft itself was about 10 million kilometers
from Jupiter when recording the image data.
 APOD: 2002 June 30 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
APOD: 2002 June 30 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
Explanation:
This asteroid has a moon!
The robot spacecraft Galileo
currently exploring the Jovian system, encountered and photographed two asteroids
during its long journey to Jupiter.
The second asteroid it photographed,
Ida, was discovered to have
a moon which appears as a small dot to the right of Ida in
this picture.
The tiny moon, named Dactyl, is about one mile across, while
the potato shaped Ida measures about 36 miles long and 14 miles wide.
Dactyl is the first moon of an asteroid ever discovered.
The names Ida and Dactyl are based on characters in
Greek mythology.
Other asteroids are now known to
have moons.
 APOD: 2002 April 19 - The Old Moon in the New Moon's Arms
APOD: 2002 April 19 - The Old Moon in the New Moon's Arms
Explanation:
Also known as the Moon's "ashen glow" or
"the old Moon in the new Moon's arms",
Earthshine is
Earthlight reflected from the Moon's night side.
This dramatic image
of Earthshine and a young crescent
Moon was taken by
astrophotographer and
APOD translator
Laurent Laveder from the remote
Pic du
Midi Observatory on planet Earth.
But the
view
from the Moon would have been stunning too.
When the Moon appears in Earth's sky as a slender crescent,
a dazzlingly bright, nearly full Earth would be seen
from the lunar surface.
The Earth's brightness, due to reflected sunlight,
is strongly influenced by cloud cover and
recent studies
of Earthshine indicate that it is more pronounced
during April and May.
A description of Earthshine, in
terms of sunlight reflected by Earth's oceans in turn illuminating
the Moon's dark surface, was written 500 years ago by
Leonardo
da Vinci.
 APOD: 2002 April 12 - A Galaxy is not a Comet
APOD: 2002 April 12 - A Galaxy is not a Comet
Explanation:
This gorgeous galaxy and
comet portrait was recorded on April 5th
in the skies over the Oriental Pyrenees near Figueres,
Spain.
From a site above 1,100 meters,
astrophotographer
Juan Carlos Casado used a guided time exposure, fast film, and
a telephoto lens to capture the predicted conjunction of
the bright Comet Ikeya-Zhang (right)
and the Andromeda Galaxy (left).
This stunning celestial scene would also have been a
rewarding one for the influential 18th century comet
hunter Charles Messier.
While Messier scanned French skies for comets,
he carefully cataloged positions of things which were
fuzzy and comet-like
in appearance but did not move against the background stars and
so were definitely not comets.
The Andromeda Galaxy,
also known as M31, is the 31st object in
his famous
not-a-comet catalog.
Not-a-comet object
number 110, a late addition to Messier's catalog, is
one of Andromeda's small satellite galaxies, and can be
seen here just below M31.
Our modern
understanding
holds that the Andromeda galaxy is a large spiral galaxy
some 2 million light-years
distant.
The photogenic
Comet
Ikeya-Zhang, now a lovely sight in
early morning skies,
is about 80 million kilometers (4 light-minutes) from planet Earth.
 APOD: 2002 February 21 - Comet Ikeya-Zhang
APOD: 2002 February 21 - Comet Ikeya-Zhang
Explanation:
Comet
Ikeya-Zhang
is presently heading north in planet
Earth's sky,
framed by stars of the constellation Cetus.
The comet was
discovered as a faint,
telescopic
object near the western
horizon on the evening of February 1st independently by
Kaoru Ikeya of Shizuoka prefecture, Japan,
Daqing Zhang in Henan province, China, and
later by
observer Paulo Raymundo of Salvador, Brazil.
But Ikeya-Zhang
is expected to brighten significantly and in March and
April could become visible to the unaided eye.
This picture, taken near Tucson, Arizona, USA on the evening of
February 9th, covers a field a bit less than the width of the full moon
showing the comet's
condensed coma and narrow, developing
tail.
Ikeya-Zhang should pass closest to the Sun (perihelion) on March 18 at
a point roughly midway between the orbits of
Mercury and Venus.
Based on preliminary calculations of this comet's orbit,
Ikeya-Zhang is
suspected of being a periodic comet, returning to the inner
Solar System every 500 years or so.
In fact, it is speculated that Ikeya-Zhang may be directly connected
with a historic
bright comet seen in 1532.
 APOD: 2002 February 4 - Comet LINEAR WM1 Shines in the South
APOD: 2002 February 4 - Comet LINEAR WM1 Shines in the South
Explanation:
A new comet has brightened unexpectedly and is
currently visible to unaided observers of southern skies.
Comet C/2000 WM1 (LINEAR)
is now reported by some observers to be at third
magnitude, making it brighter -- although more diffuse --
than most visible stars.
A dust tail as long as
3 degrees has also been reported.
Pictured above is the center of
Comet LINEAR (WM1) taken the morning of February 1
from 300 km north of Sydney,
Australia.
A bright coma and the start of the dust tail are visible
despite a bright, nearly full Moon.
The comet has now passed its closest approach to the Sun (January) and the
Earth (December) and will
move toward northern skies as it fades.
 APOD: 2001 December 24 - Asteroid 1998 WT24 Passes Near Earth
APOD: 2001 December 24 - Asteroid 1998 WT24 Passes Near Earth
Explanation:
Last week, an asteroid approached unusually close to the Earth.
Passing well outside the orbit of our Moon,
Asteroid 1998 WT24 posed no danger,
but became
bright enough to see with binoculars and to
track with radar.
Pictured above, the kilometer-sized
asteroid was imaged crossing the sky on December 14,
two days before
closest approach.
Every few years, an asteroid will
actually pass inside the orbit of the Moon.
Large impact features on the Earth are testaments to
asteroids or comets that actually impacted the
Earth in the distant past.
Astronomers continue to discover, track, and study
potentially hazardous asteroids with a goal of
making planet
Earth a safer place.
 APOD: 2001 December 15 - Ganymede: Torn Comet Crater Chain
APOD: 2001 December 15 - Ganymede: Torn Comet Crater Chain
Explanation:
This striking line of 13 closely spaced craters
on Jupiter's moon
Ganymede
was photographed by the Galileo spacecraft in 1997.
The picture covers an area about 120 miles wide and
the chain of craters cuts across a sharp boundary between
dark and light terrain.
What caused this crater chain?
Remarkably, the
exploration
of the Solar System, has shown that
crater chains like this one are
not
unique, though
they
were considered mysterious until a
dramatic object lesson was offered by comet Shoemaker-Levy 9.
In 1994 many denizens of planet Earth
watched as huge pieces of
this torn comet
slammed into Jupiter itself in a spectacular series of
sequential impacts.
It is very likely that similar torn comets from the early history
of the Solar System are responsible for this and
other crater chains.
 APOD: 2001 September 15 - Eclipsed Moon in Infrared
APOD: 2001 September 15 - Eclipsed Moon in Infrared
Explanation:
The total lunar eclipse of September 1996
disappointed many observers in North America who
were cursed with cloudy skies.
However, the
Midcourse
Space Experiment (MSX) satellite had
a spectacular view from Earth orbit and
SPIRIT III,
an onboard infrared telescope, was used to
repeatedly image the moon
during the eclipse.
Above is one of
the images taken during the 70 minute totality, the Moon completely
immersed in
the Earth's shadow.
Infrared light
has wavelengths
longer than visible light - human's can not see it but feel it as heat.
The bright spots correspond to the warm areas on the
lunar surface, dark areas are cooler.
The brightest spot below and left of center is the
crater Tycho,
the dark region at the upper right is
the Mare Crisium.
The series of SPIRIT III images allow the determination of cooling
rates for geologically different areas, exploring the physical properties
of the Moon's surface.
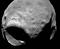 APOD: 2001 August 18 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: 2001 August 18 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
Mars,
the red planet named for
the Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos,
whose names are derived from the Greek for Fear and Panic.
These
Martian
moons may well be captured
asteroids
originating in the main asteroid belt between Mars
and Jupiter or perhaps from even more
distant reaches of the
Solar System.
In this 1978
Viking 1 orbiter image,
the largest moon, Phobos, is indeed seen to be a
heavily cratered asteroid-like object.
About 17 miles across, Phobos really
zips through the Martian sky.
Actually rising above Mars' western horizon and setting in the east,
it completes an orbit in less than 8 hours.
But Phobos is doomed.
Phobos orbits so close to Mars,
(about 3,600 miles above the surface compared to 250,000 miles for
our Moon)
that gravitational tidal forces are dragging it down.
In 100 million
years or so it will likely crash into the surface or be shattered by stress
caused by the
relentless
tidal forces, the debris forming a ring around Mars.
 APOD: 2001 June 25 - A Brighter Comet LINEAR
APOD: 2001 June 25 - A Brighter Comet LINEAR
Explanation:
Brighter than ever
expected, comet LINEAR --
you know, the one designated
C/2001 A2 -- is a sight to see
in southern skies.
This comet LINEAR first brightened
impressively in late March as its active nucleus began
to fragment, prompting some
speculation that the comet might soon
break up completely.
But still hanging together after its closest approach to
the Sun, C/2001 A2 suddenly brightened again and
was reported
last week to have reached nearly 3rd magnitude,
easily visible to the unaided eye.
This
delightful telescopic picture of the brighter
coma of comet LINEAR was recorded from Australia on June 20.
Stars seen through the tenuous coma
and filamentary tail appear as a series of short trails in
this three-color composite image registered
on the comet.
North is up and the scene covers about half the width of
the full Moon.
Now moving through the
constellation Cetus, comet LINEAR
will be
north of the celestial equator by July 4 as it
comes into view for eager northern sky-gazers.
 APOD: 2001 May 21 - Another Comet LINEAR Breaks Up
APOD: 2001 May 21 - Another Comet LINEAR Breaks Up
Explanation:
Last year, a different comet LINEAR (C/1999 S4) broke up.
This year, a comet
first imaged by the
Lincoln Near Asteroid Research (LINEAR) telescope in
New Mexico on
2001 January 3, is also breaking up.
This new Comet LINEAR
(C/2001 A2) unexpectedly brightened to the edge of naked-eye
visiblilty a few weeks ago when its nucleus broke in two.
Observations taken just last week
now indicate that one of the two remaining
nuclear fragments
has again fragmented.
The first piece to break off is visible on the upper left of the above
false-color image by a
Very Large Telescope,
while additional fragmentation is inferred
from the brightness and elongation of the
spot on the lower right.
When a
comet nucleus splits,
new surfaces are exposed and previously trapped ice and gas
are released that evaporate and brighten in the energetic sunlight.
Comet LINEAR may remain visible with little or no optical aid
into early June.
In contrast, at least two other much dimmer
Comet
LINEARs discovered recently appear stable.
 APOD: 2001 February 13 - NEAR Spacecraft Survives Landing on Asteroid Eros
APOD: 2001 February 13 - NEAR Spacecraft Survives Landing on Asteroid Eros
Explanation:
Yesterday NEAR-Shoemaker became the
first spacecraft to land on an asteroid
and send signals back from its surface.
Since the
robot spacecraft was not designed for such a
contingency,
the success of the landing on
asteroid
433 Eros was not assured.
Shown above is the last picture taken by
NEAR-Shoemaker before its touchdown.
The streaking on the lower part of the image
was caused by the loss of
telemetry as the satellite impacted the
surface.
The image was taken 130 meters above the surface and
spans 6 meters across.
Rocks as small as a human hand are visible.
As engineers
continue to try to communicate
with the beached car-sized spacecraft,
scientists will work to understand features visible in the
highest resolution photographs ever taken of an asteroid.
 APOD: 2000 November 1 - Double Asteroid 90 Antiope
APOD: 2000 November 1 - Double Asteroid 90 Antiope
Explanation:
This eight-frame animation is based on the
first
ever images of a
double
asteroid!
Formerly thought to be a single enormous chunk of rock,
asteroid
90 Antiope resides in the
solar system's
main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Now, these premier images reveal Antiope to actually consist of
two 50 mile wide asteroids separated by about 100 miles.
Like weights on each end of an elastic string,
the pair mutually orbit their center of mass, or balance
point in the space between them, once every 16.5 hours.
Binary asteroids and asteroids
with moons are believed
to be rare, but observations of their orbits allow a direct
determination of asteroid masses and densities.
Surprisingly, Antiope
and known
asteroid-moon systems are found
to have densities closer to ice than rock, despite their
relatively dark and unreflective surfaces.
These sharp images were made at the Keck Observatory
atop the Hawaiian volcano Mauna Kea
using newly developed adaptive optics technology to
overcome the
blurring effect of Earth's atmosphere.
 APOD: 2000 September 9 - X Ray Moon and X Ray Star
APOD: 2000 September 9 - X Ray Moon and X Ray Star
Explanation:
An
x-ray star winks out behind the Moon
in these before (left) and after
views of a
lunar occultation of the galactic x-ray source
designated GX5-1.
The false color images were made using data from the
ROSAT
(ROentgen SATellite), orbiting observatory.
They show high energy x-rays in yellow (mostly from
GX5-1), and lower energy x-rays in red (the
Moon reflecting x-rays from the Sun).
GX5-1 is a
binary system consisting of a
neutron star and a companion star in
mutual orbit about the system's center of mass.
The gas in the companion star's outer envelope falls
toward the neutron star
and accumulates in a disk around it.
This disk material swirls deeper in to
the neutron star's gravitational well, and is finally dumped onto
its surface - in the process creating tremendous
temperatures and generating the high energy x-rays.
 APOD: 2000 July 27 - Tails Of Comet LINEAR
APOD: 2000 July 27 - Tails Of Comet LINEAR
Explanation:
Comet C/1999 S4 LINEAR is only one of
many
comets discovered with the
Lincoln Near Earth
Asteroid Research (LINEAR) telescope
operating near Soccoro, New Mexico, USA.
Traveling steadily southward through Earth's night sky, C/1999 S4
passed perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) yesterday on what is likely
its
first trip through the
inner
solar system.
Now fading,
comet LINEAR
became no brighter than about 6th
magnitude, but is still easily visible
with binoculars in northern hemisphere skies.
While the memorable comets
Hale-Bopp and
Hyakutake were much brighter,
comet LINEAR is
displaying
delightful tails evident in this false-color composite
image
from the
Crni Vrh
Observatory in Slovenia.
The combined series of exposures made on July 22nd are
registered on the comet.
In the resulting picture, stars appear as rows of dots,
but the faint structures in
the comet's tail are beautifully recorded.
Presently seen moving from
Ursa Major to Leo this
comet LINEAR will
begin to shine in southern hemisphere skies in August.
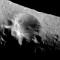 APOD: 2000 March 8 - Nearer To Asteroid Eros
APOD: 2000 March 8 - Nearer To Asteroid Eros
Explanation:
As the
robot spacecraft NEAR lowers itself toward
asteroid 433 Eros,
more surface details are becoming visible.
Last week's
maneuvers brought
NEAR
to within 204 kilometers of the floating mountain's
surface.
With increased resolution,
NEAR's camera then documented
Eros' unusual shape,
craters large and small,
boulders,
and mysterious grooves similar to
asteroid Gaspra and
Martian moon Phobos.
If you could stand on
Eros,
you would still be too small to be visible on
this recent image, which shows features as small
as 20 meters across.
However, you would feel
gravity only 1/1000 that on Earth, so that
you could easily jump over even this large 5 kilometer wide crater.
 APOD: 2000 February 14 - An Unexpected Asteroid Valentine
APOD: 2000 February 14 - An Unexpected Asteroid Valentine
Explanation:
Maybe the
Moon owns our
hearts, but this won't stop
the occasional
asteroid from sending us a
valentine.
Friday, to the surprise of many, the
NEAR mission on approach to asteroid
433 EROS photographed
what appears to be a
heart-shaped depression.
After NEAR reaches the asteroid today, NASA plans a
series of maneuvers to make the
robot spacecraft the first ever to orbit an asteroid.
More detailed
pictures
will soon be taken
of the 33 kilometer long
asteroid EROS and this 5 kilometer long depression.
Most likely, fortuitous lighting and viewing angles
accentuate the
apparent heart shape -- but don't tell the
Moon.
 APOD: December 22, 1999 - Perigee Moon, Apogee Moon
APOD: December 22, 1999 - Perigee Moon, Apogee Moon
Explanation:
Tonight, those blessed with clear skies can enjoy a
glorious full moon,
the last full moon of the "Y1.9K"s.
In fact, tonight's moon will be a full-perigee-solstice moon,
reaching its full phase and perigee (the closest point in
its orbit)
on the solstice,
the first day of northern hemisphere winter.
Anticipation of this celestial event has generated
a flood of e-mail chasing the rumor
that the full-perigee-solstice moon will be intensely bright.
However, calculations show it will only be a little brighter than usual,
and certainly not dramatically so.
Why would it be brighter?
Mostly because the moon appears bigger and brighter at perigee.
The above illustration, based on
Galileo spacecraft images,
shows the approximate difference in apparent
size between a
full moon
at perigee (left) and a full moon at apogee,
the farthest point in the lunar orbit.
The Earth and moon are also a few percent closer to the sun
during northern winter,
but the combined effects will cause tonight's full moon to appear
only about 20% brighter than an average full moon.
That difference is not even likely to be noticeable to
the human eye.
 APOD: October 14, 1999 - Moon Over Eugenia
APOD: October 14, 1999 - Moon Over Eugenia
Explanation:
Eugenia is an
asteroid with a moon!
This animation was constructed from infrared discovery images of the
Eugenia-moon system taken in November 1998 using the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT).
Main belt asteroid Eugenia, represented here as a central white patch,
is a mere 215 kilometers in diameter.
Its moon, seen at 5 separate positions around a clockwise orbit,
is estimated to be 13 kilometers wide.
An adaptive optics system was used with the CFHT,
located atop Mauna Kea, Hawaii,
to counteract the blurring effect of Earth's atmosphere making possible
this premier discovery from a ground-based
telescope.
Only one
other asteroid-moon system is known.
Dactyl, moon of the asteroid Ida, was discovered by the
Galileo spacecraft during a 1993 flyby.
Eugenia's moon has a nearly circular orbit with a radius of
1,190 kilometers which it completes once in 4.7 days.
The orbit appears oval-shaped because it is tilted
at a 45 degree angle to the line-of-sight.
Knowing the moon's orbit allows astronomers
to calculate the asteroid's mass.
Combining mass and size determines the asteroid's density,
which in this case gives a surprising result -
Eugenia is found to have a density only 20% greater than water.
The low density suggests that Eugenia itself is a porous "rubble pile"
of rocks or composed mostly of water-ice with only a little
additional rocky material.
 APOD: October 10, 1999 - Triton: Neptune's Largest Moon
APOD: October 10, 1999 - Triton: Neptune's Largest Moon
Explanation:
One hundred and fifty three years ago, on October 10th, 1846,
William Lassell
was observing the newly discovered planet
Neptune.
He was attempting to confirm his observation, made just the previous week,
that Neptune had a ring.
But this time he discovered
that Neptune had a satellite as well.
Lassell soon proved that the ring was a product of his new
telescope's distortion, but the satellite
Triton
remained.
The above picture of
Triton
was taken in 1989 by the only spacecraft ever to pass
Triton:
Voyager 2.
Voyager 2 found fascinating terrain,
a thin atmosphere, and even evidence for
ice volcanoes
on this world of peculiar orbit and spin.
Ironically, Voyager 2 also confirmed the existence of complete thin rings around Neptune
- but these would have been quite invisible to Lassell!
 APOD: August 7, 1999 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
APOD: August 7, 1999 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
Explanation:
This asteroid has a moon!
The robot spacecraft Galileo
currently exploring the Jovian system, encountered and photographed two asteroids
during its long journey to Jupiter.
The second asteroid it photographed,
Ida, was discovered to have
a moon which appears as a small dot to the right of Ida in
this picture.
The tiny moon, named Dactyl, is about one mile across, while
the potato shaped Ida measures about 36 miles long and 14 miles wide.
Dactyl is the first moon of an asteroid ever discovered.
The names Ida and Dactyl are based on characters in
Greek mythology.
Do other asteroids have moons?
 APOD: March 14, 1999 - The Comet and the Galaxy
APOD: March 14, 1999 - The Comet and the Galaxy
Explanation:
The Moon almost ruined this photograph.
During late March and early April 1997,
Comet Hale-Bopp
passed nearly in front of the
Andromeda Galaxy.
Here the Great Comet of 1997 and the
Great Galaxy in Andromeda were
photographed together
on 1997 March 24th.
The problem was the brightness of the
Moon. The Moon was full that night and so bright that long
exposures meant to capture the
tails of Hale-Bopp and the disk of
M31 would capture instead
only moonlight reflected off the Earth's atmosphere.
By the time the Moon would set, this opportunity would be gone.
That's why this picture was taken during a
lunar eclipse.
 APOD: August 5, 1998 - Ganymede: Torn Comet Crater Chain
APOD: August 5, 1998 - Ganymede: Torn Comet Crater Chain
Explanation:
This remarkable line of 13 closely spaced craters
on Jupiter's moon
Ganymede
was photographed by the Galileo spacecraft in 1997.
The picture covers an area about 120 miles wide and
the chain of craters cuts across a sharp boundary between
dark and light terrain.
What caused this crater chain?
During the
exploration of the Solar System,
crater chains like this one
have been discovered
in several places
and were considered mysterious until a
dramatic object lesson was offered by
comet Shoemaker-Levy 9.
In 1994
many denizens of planet Earth
watched as huge pieces of
this torn comet
slammed into Jupiter itself in a spectacular series of
sequential impacts.
It is very likely that
similar torn comets from the early history
of the Solar System are responsible for this and
other crater chains.
 APOD: July 9, 1998 - Hale-Bopp: The Crowd Pleaser Comet
APOD: July 9, 1998 - Hale-Bopp: The Crowd Pleaser Comet
Explanation:
In 1997, the bright
comet Hale-Bopp may have become the most viewed
comet in history -- visible even to casual skywatchers in
light polluted
cities around
the globe.
In this picture, taken by photographer
Joe Orman on the evening of May 8, 1997,
Hale-Bopp easily competes with near twilight skies and a shining,
over-exposed, crescent moon above Mobile, Arizona, USA.
Where is Hale-Bopp now?
Still visible
to telescopic observers in the Southern Hemisphere,
the comet is
outbound,
presently about 537 million miles from the Sun.
(Jupiter orbits at about 480 million miles.)
The long lead time provided by the early
discovery of Hale-Bopp has allowed
extensive observing campaigns
producing a
bonanza of information about this
primordial chunk of our Solar System.
 APOD: May 31, 1998 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: May 31, 1998 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
Phobos is doomed.
Mars, the red planet named for the Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos,
whose names are derived from the Greek for Fear and Panic.
These Martian
moons may well be captured asteroids originating
in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter
or perhaps from even more
distant reaches of the Solar System.
In this 1977 Viking orbiter image, the largest moon,
Phobos, is seen to be a heavily cratered asteroid-like object.
It is about 17 miles across and zips through the Martian sky completing an
orbit in less than 8 hours. Phobos orbits so close to Mars,
(about 3,600 miles above the surface compared to 250,000 miles for our
Moon)
that gravitational tidal forces are dragging it down. In 100 million
years or so it should crash into the surface or be shattered by stress
caused by the relentless tidal forces, the debris forming a ring around
Mars.
 APOD: March 13, 1998 - Asteroids
APOD: March 13, 1998 - Asteroids
Explanation:
No asteroid or comet is known to be on
a collision course with Earth.
The asteroid
designated 1997 XF11
had been predicted to come uncomfortably close,
but new estimates place its passing beyond the orbit of the Moon.
This earth-approaching
asteroid was discovered by
SpaceWatch astronomer Jim Scotti in December of last year.
Orbital computations using
new observations suggested that it would pass
within 30,000 miles of the Earth's center
on October 26, 2028 - a very near miss considering that
the radius of the Earth itself is about 4,000 miles.
However, more recent and further
refined calculations based on both
new and archival data
indicate that the closest approach will be 600,000 miles in 2028.
Imaged by NASA spacecraft,
the three potato-shaped objects above are
large main-belt asteroids
orbiting between Mars and Jupiter.
Shown to the same scale from left to right are
Mathilde, Gaspra,
and Ida.
Mathilde has dimensions of about 37 by 29 miles.
The asteroid 1997 XF11 is much smaller, probably a mile wide,
yet the impact of
an asteroid of this
size could have
catastrophic effects.
Over the last two decades,
teams of astronomers have just begun
to catalog and track
near-earth objects.
 APOD: March 12, 1998 - Moon Shadow
APOD: March 12, 1998 - Moon Shadow
Explanation:
When the Moon's shadow
reached out and touched the Earth last
month, the result was a Solar
Eclipse.
Such an eclipse is total only
for observers located
along
a narrow path corresponding
to the ground track of the shadow's
dark central portion or "umbra".
For this eclipse,
racing along at nearly 1,200 miles per hour, the Moon's umbra
obligingly crossed over land along
pleasant tropical locales
in South America and the Caribbean islands.
Totality lasted for about 3 minutes or less at a
given location.
Sizable fractions of North and South America fell
within the lighter but much wider outer shadow region,
the "penumbra", and witnessed a partial eclipse.
This movie gif follows the Moon's shadow from Central and South
America eastward across the Atlantic - as seen
from the vantage point of an orbiting
Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES),
22,000 miles above Earth.
The three frame animation spans about 2 hours.
GOES satellite images are
a corner stone of
U.S. weather monitoring and forecast operations.
 APOD: January 29, 1998 - The Earth-Moon System
APOD: January 29, 1998 - The Earth-Moon System
Explanation:
This evocative mosaic image of
the Earth-Moon system was recorded by
NASA's Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) spacecraft earlier this month.
The relative sizes shown are appropriate for viewing both
the Earth and
Moon
from a distance of about 250,000 miles, although the apparent
brightness of the Moon has been increased by about a factor
of five for the sake of appearances.
This space-based perspective is a unique one,
the bland and somber
Lunar Southern Hemisphere
contrasting strongly with blue oceans,
swirling clouds, and the bright icy white continent
of Antarctica on planet Earth.
Though its lack of
atmosphere
and oceans
make it relatively dull looking,
the Earth's moon is one of
the largest moons in the solar system
- even larger than the planet
Pluto.
During this
recent flyby of the Earth-Moon system,
the NEAR spacecraft
used Earth's gravity to deflect it towards its ultimate destination,
the Asteroid 433 Eros.
It is scheduled to arrive at Eros in January 1999.
 APOD: November 25, 1997 - The Comet and the Galaxy
APOD: November 25, 1997 - The Comet and the Galaxy
Explanation:
The Moon almost ruined this photograph.
During late March and early April,
Comet Hale-Bopp
passed nearly in front of the
Andromeda Galaxy.
Here the Great Comet of 1997 and the
Great Galaxy in Andromeda were
photographed together
on March 24th.
The problem was the brightness of the
Moon. The Moon was full that night and so bright that long
exposures meant to capture the
tails of Hale-Bopp and the disk of
M31 would capture instead
only moonlight reflected off the Earth's atmosphere.
By the time the Moon would set, this opportunity would be gone.
That's why this picture was taken during the
lunar eclipse.
 APOD: November 23, 1997 - Triton: Neptune's Largest Moon
APOD: November 23, 1997 - Triton: Neptune's Largest Moon
Explanation:
On October 10th, 1846,
William Lassell
was observing the newly discovered
planet Neptune. He was attempting
to confirm his observation, made just the previous week,
that Neptune had a ring.
But this time he discovered
that Neptune
had a satellite as well. Lassell soon proved that the ring
was a product of his new telescope's distortion, but the satellite
Triton
remained. The above picture of Triton
was taken in 1989 by the only spacecraft ever to pass Triton:
Voyager 2. Voyager 2 found fascinating terrain,
a thin atmosphere, and even evidence for ice volcanoes on this
world of peculiar orbit and spin. Ironically, Voyager 2 also confirmed the existence of complete thin rings around Neptune
- but these would have been quite invisible to Lassell!
 APOD: September 10, 1997 - Comet Hale-Bopp Outbound
APOD: September 10, 1997 - Comet Hale-Bopp Outbound
Explanation:
Hale-Bopp,
the Comet of the Century, is leaving the inner Solar System.
Outbound at about 12 miles per second it is presently nearing the main
asteroid belt
between Mars and
Jupiter.
This false-color image represents a recent
view from low Earth orbit showing the comet surrounded by
its shrinking coma
against a background of stars.
It was constructed from a fraction of the
data taken aboard the
Space Shuttle Discovery in
August by a small innovative telescopic camera known as
the Southwest Ultraviolet Imaging System
or SWUIS.
SWUIS (sounds like "swiss") images will be particularly
interesting to astronomers who wish to continue to follow
the Great Comet's interaction with
the Solar Wind.
The once bright Hale-Bopp
has faded below 4th
magnitude
but is still visible to Earthbound observers
south of 35 degrees north latitude.
 APOD: July 28, 1997 - Help Aldebaran Map the Moon
APOD: July 28, 1997 - Help Aldebaran Map the Moon
Explanation:
Turn on your camcorder, go outside, and become an astronomer.
How?.
Tomorrow morning, our
Moon will pass directly in front of
Aldebaran, the brightest star in this picture and in
entire constellation of Taurus.
Aldebaran
is visible to the left and below
Comet
Hale-Bopp in the
above photograph,
which was taken on April 30th in
Tenerife, Spain.
This occultation is valuable because
disappearance
times from
different locations can be used to map the height of the
lunar terrain
at the occultation points. You can help by
clicking here,
where a site will detail how to tape a familiar cable channel and then
take your still-running
camcorder
outside to tape the occultation of Aldebaran by the Moon. You can then donate your VCR tape
to science by mailing it to
this address.
Leave yourself
plenty of time
for a practice run and be sure to check the weather
before going to a lot of trouble!
 APOD: June 29, 1997 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
APOD: June 29, 1997 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
Explanation:
This asteroid has a moon!
The robot spacecraft Galileo
currently exploring the Jovian system,
encountered and photographed two
asteroids
during its long journey to Jupiter.
The second asteroid it photographed,
Ida, was discovered to have
a moon which appears as a small dot to the right of Ida in this
picture.
The tiny moon, named Dactyl, is about one mile across, while
the potato shaped Ida measures about 36 miles long and 14 miles wide.
Dactyl is the first moon of an asteroid ever discovered.
The names Ida and Dactyl are based on characters in Greek mythology.
Do other asteroids have moons?
 APOD: June 18, 1997 - Asteroid 3753: Earth's Curious Companion
APOD: June 18, 1997 - Asteroid 3753: Earth's Curious Companion
Explanation:
Earth is not alone. It orbits the Sun with a small companion:
Asteroid 3753.
First discovered in 1986 and designated 1986 OT, this five kilometer
rock was recently found to orbit the
Sun while executing a
strange dance with the
Earth. A portion of the asteroid's
complex
orbit is shown above. As the Earth orbits once,
Asteroid 3753 follows the yellow line - while also orbiting the Sun.
Each time around, however, the yellow kidney-bean traced by
Asteroid 3753 shifts slightly - eventually
going from trailing the Earth to leading the Earth.
Every 385 years the cycle repeats.
Because the plane of 3753's orbit is tilted when compared
to the Earth's orbit, the
two will never collide. In autumn 1997,
Asteroid 3753 will pass below the
Earth's South Pole at about
100 times the distance to the
Moon. It will, however, be very
faint - about 15th
magnitude - 10,000 times fainter than the dimmest star without
a telescope.
Suggestions
are being taken for a good name for this asteroid.
 APOD: January 20, 1997 - Earth Nears Asteroid Toutatis
APOD: January 20, 1997 - Earth Nears Asteroid Toutatis
Explanation:
On November 29, 1996 the Earth came within 3.3 million miles of the
asteroid Toutatis.
Above is a
computer simulated picture of this spectacle
from the surface of Toutatis
(a 2.5 degree field of view looking toward Earth).
In Earth's sky, Toutatis appeared
only as a faint object moving against a background of stars.
Also known as Earth-crossing asteroid 4179,
Toutatis is in an eccentric 4 year orbit
which moves it from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter to just
inside Earth's orbit.
When the Earth passed near it
in 1992 Toutatis was
imaged by radar
and seen to be two irregularly shaped lumps,
perhaps joined by a narrow neck.
This bizarre object is up to 1.5 miles wide, 2.9 miles long, and is
tumbling through space.
In the year 2004, on September 29, the Earth will pass
very near Toutatis, closing to within
a million miles (4 times the Earth-Moon distance) -
the closest approach predicted for any
asteroid or comet between now and 2060.
Studies of Toutatis and other
Earth-crossing asteroids help reveal
connections between the Solar System's
meteorites,main-belt asteroids
and comets.
These wayward asteroids also offer tantalizing
targets for robotic exploration and, over time, represent
potential collision hazards for planet Earth!
 APOD: January 10, 1997 - Eclipsed Moon in Infrared
APOD: January 10, 1997 - Eclipsed Moon in Infrared
Explanation:
Last September's total lunar eclipse
disappointed many observers in the Eastern and Midwestern US who
were cursed with cloudy skies.
However, the
Midcourse Space Experiment (MSX) satellite had
a spectacular view from Earth orbit and
SPIRIT III, an onboard imaging infrared telescope, was used to
repeatedly image the moon during the eclipse.
Above is one of
the images taken during the 70 minute totality,
the Moon completely immersed in
the Earth's shadow.
Infrared light has wavelengths
longer than visible light - human's can not see it but feel it as heat.
The bright spots correspond to the warm areas on the
lunar surface, dark areas are cooler.
The brightest spot below and left of center is the crater Tycho,
the dark region at the upper right is
the Mare Crisium.
The series of SPIRIT III images allow the determination of cooling
curves for geologically different areas, exploring the physical properties
of the Moon's surface.
 APOD: October 10, 1996 - Triton: Neptune's Largest Moon
APOD: October 10, 1996 - Triton: Neptune's Largest Moon
Explanation: Today marks the 150th anniversary of the
discovery of Triton. On October 10 1846, William Lassell
was observing the newly discovered
planet Neptune. He was attempting
to confirm his observation, made just the previous week,
that Neptune had a ring.
But this time he discovered
that Neptune
had a satellite as well. Lassell soon proved the ring
was product of his new telescope's distortion, but the satellite
Triton
remained. The above picture of Triton
was taken in 1989 by the only spacecraft ever to pass Triton:
Voyager 2. Voyager 2 found fascinating terrain,
a thin atmosphere, and even evidence for ice volcanoes on this
world of peculiar orbit and spin. Ironically, Voyager 2 also confirmed the existence of complete thin rings around Neptune
- but these would have been quite invisible to Lassell!
 APOD: September 29, 1996 - The X-Ray Moon
APOD: September 29, 1996 - The X-Ray Moon
Explanation:
This X-Ray image of the Moon was made by
the orbiting Roentgen Observatory Satellite
(ROSAT) in 1990. It shows three distinct regions:
a bright X-ray sky, a bright part of the Moon, and a relatively dark part
of the Moon. The bright X-ray sky is due to the diffuse cosmic
X-ray background.
The bright lunar crescent shines because it reflects X-rays emitted by
the Sun. The dark lunar face is in shadow
and so stands stands out from the relatively bright background -
but, surprisingly it is not completely dark!
Where do those X-rays from?
They are currently thought to result from energetic particles from
the solar wind
bombarding the lunar surface.
 APOD: April 11, 1996 - Unexpected X-rays from Comet Hyakutake
APOD: April 11, 1996 - Unexpected X-rays from Comet Hyakutake
Explanation:
The first X-rays ever detected from a
comet were discovered from
Comet Hyakutake with the
ROSAT
satellite on March 27th.
The
discovery is particularly surprising because there was little previous
indication that comets emit any significant X-radiation. As the
comet passed the Earth in
late March, repeated observations with ROSAT also showed that the X-ray
brightness changed over just a few hours. The crescent shape of the X-ray
emission is also enigmatic. One possible explanation is that X-rays
emitted from the Sun are absorbed by water in the comet's coma causing
fluorescence. Another possible explanation involves interaction with the
solar
wind - fast moving particles streaming away from the
Sun.
 APOD: April 8, 1996 - Uranus's Moon Oberon: Impact World
APOD: April 8, 1996 - Uranus's Moon Oberon: Impact World
Explanation:
Oberon is the most distant and second largest moon of Uranus. Discovered by
William Herschel
in 1787, the properties of the world remained relatively
unknown until the robot spacecraft
Voyager 2
passed it during its flyby of
Uranus in January 1986. Compared to Uranus'
moons
Ariel,
Titania, and
Miranda,
Oberon is heavily cratered, and in this
way resembles
Umbriel.
Like all of Uranus' large moons,
Oberon is composed
of roughly half ice and half rock. Note that Oberon has at least one
large mountain, visible on the limb at the lower left, that rises 6 km off
the surface.
 APOD: April 7, 1996 - Uranus's Moon Umbriel: A Mysterious Dark World
APOD: April 7, 1996 - Uranus's Moon Umbriel: A Mysterious Dark World
Explanation:
Why is Umbriel so dark? This dark moon reflects only half the light of other
Uranus' moons such as
Ariel. And what is that bright ring at the top?
Unfortunately, nobody yet knows. These questions presented themselves when
Voyager 2
passed this satellite of Uranus in January 1986.
Voyager found an old surface with unusually large craters, and determined
Umbriel's composition to be about half ice and half rock.
Umbriel
is the fourth largest and third most distant of Uranus' five
large moons. Umbriel was discovered in 1851 by
William
Lassell.
 APOD: April 3, 1996 - A Lucky Lunar Eclipse
APOD: April 3, 1996 - A Lucky Lunar Eclipse
Explanation:
Tonight's full moon would normally washout the spectacle of
Comet Hyakutake's lovely tail,
even for those far from light
polluted skies. Except that tonight comet observers are in luck - the
dance of the planets calls for a
total lunar eclipse!
Lunar eclipses are
caused when the Moon
passes through the Earth's shadow.
Although dimmed,
the eclipsed Moon may not appear completely dark.
Sunlight scattered into the
Earth's shadow after passing
around the planet's edge and
through its dusty atmosphere
can make the Moon take on dramatic shades of red during totality as
demonstrated in the above photo of the
November 1993 lunar eclipse.
Tonight,
totality begins at 6:26 p.m. EST and lasts
about an hour and a half. Weather permitting, the eclipse will be visible
for all those comet and moon watchers lucky enough to be on the
Earth's nightside.
 APOD: March 31, 1996 - Comet Hyakutake Finder Chart for Early April
APOD: March 31, 1996 - Comet Hyakutake Finder Chart for Early April
Explanation:
During April Comet Hyakutake
heads in toward
the Sun
after passing the
Earth.
At this time
the comet's orbit places it north of the
Earth. Remaining visible in the northern sky
as it nears the Sun, it will set progressively earlier in the evening.
Early in April,
the Moon's glow will diminish viewing
of the comet's tail - except during the
lunar eclipse on April 3rd!
As the comet recedes from the Earth it will appear dimmer even though it is
getting intrinsically brighter as it nears the Sun. In late April the
intrinsic brightening effect will "win" and the comet will again appear to
brighten - possibly getting even brighter than it was last week.
At this point the
comet will appear near sunset low on
the northwestern horizon (see above).
So far
Comet Hyakutake has exceeded most expectations in brightness and length of
tail. If you haven't been impressed by Hyakutake, you probably haven't seen
it from a dark location!
 APOD: March 30, 1996 - An Extreme UltraViolet View of the Comet
APOD: March 30, 1996 - An Extreme UltraViolet View of the Comet
Explanation:
As the Sun floods Comet Hyakutake with
ultraviolet light gases in the coma scatter
the radiation and fluoresce making the
comet a bright source in the ultraviolet sky.
The above image made using data from NASA's
Extreme UltraViolet Explorer (EUVE)
satellite, represents the intensity of the comet in this
invisible high energy band in false color.
The image is about 3/4 of a degree high and 2 degress wide and
offers insights to the composition of this visitor from the
distant solar system that can be obtained from the
highest energy bands of the
ultraviolet spectrum.
The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE)
satellite has also
examined ultraviolet light from the comet and
now reports the
detection of many bands of
molecular emission particularly
those due to molecular carbon (C2), carbon monoxide (CO) and
caron dioxide (C02) ions as well as indications of a rapid increase
in the production of water (H20).
 APOD: March 25, 1996 - Comet Hyakutake Passes the Earth
APOD: March 25, 1996 - Comet Hyakutake Passes the Earth
Explanation:
This picture
of Comet Hyakutake taken the night of March 21/22 in Illinois,
USA shows the enormous tail that has already developed. The silhouette on
the right is a foreground tree, and the superposed green circle on the left
shows the size of the full moon. Today
Comet Hyakutake
makes its closest approach to the
Earth. As the comet moves into the inner
Solar System, it will pass the
Earth at about 40
times the distance of our
Moon.
This
is not the closest a comet has
ever come, though. As recently as 1983
Comet
IRAS-Araki-Alcock
came three times closer than Hyakutake, and in 1770 Comet Lexell got yet
twice closer than that!
Asteroids - usually less massive than
comets -
frequently whiz by inside the
Moon's orbit, with
four
doing so far in this decade. In the distant past,
asteroids have even
struck the Earth.
Comet Hyakutake
is much brighter now than Comet IRAS-Araki-Alcock ever got, and in fact is
the brightest since Comet West in 1976.
Comet Hyakutake will be easily visible all
week.
 APOD: March 24, 1996 - Comet Hyakutake's Closest Approach
APOD: March 24, 1996 - Comet Hyakutake's Closest Approach
Explanation:
The above true color image of Comet Hyakutake was taken the night of
March 21/22.
Tonight, Comet Hyakutake will make its
nearest approach to Earth,
closing to a mere 10 million miles as it
passes over the planet's Northern Hemisphere.
From dark sky areas, it's tail
may be seen to cover about 20 degrees on the sky (40 times the apparent
diameter of the full moon) corresponding to well over 3 million miles.
at the distance of the comet.
The word comet, referring to the tail, derives from
the Greek "aster kometes", meaning
long-haired star - and
the hair of comet Hyakutake continues to grow as it nears the Sun!
The tail grows as the sun heats and sublimates
(changes directly from solid to gas) the material
on the icy surface of the comet nucleus,
sending jets of gas and dust into space. The material is swept
back by the solar wind, so comet tails usually point away
from the sun rather than simply trailing along behind in the
comets' orbit.
Some predict the tail will grow over the next few days
to nearly 50 degrees.
For the rest of
March and most of April Comet Hyakutake will be visible
to Northern viewers (weather permitting).
The tail will be most visible from
dark sky areas. Moonlit skies will tend to
washout the comet as the April 3rd full moon approaches -
however,
on April 3rd, there will be a lunar eclipse!
 APOD: October 2, 1995 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
APOD: October 2, 1995 - Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
Explanation:
Mars, the red planet named for the Roman god of war, has two tiny moons,
Phobos and
Deimos,
whose names are derived from the Greek for Fear and Panic.
These Martian
moons may well be captured
asteroids originating
in the asteroid belt between
Mars and Jupiter
or perhaps from even more
distant reaches of the Solar System.
In this 1977 Viking orbiter image, the largest moon,
Phobos, is seen to be a heavily cratered asteroid-like object.
It is about 17 miles across and zips through the Martian sky completing an
orbit in less than 8 hours. Phobos is doomed. It orbits so close to Mars,
(about 3,600 miles above the surface compared to 250,000 miles for our
Moon)
that gravitational tidal forces are dragging it down. In 100 million
years or so it could crash into the surface or be shattered by stress
caused by the relentless tidal forces, the debris forming a ring around
Mars.
 APOD: August 31, 1995 - X-Raying the Moon
APOD: August 31, 1995 - X-Raying the Moon
Explanation:
Above is a picture of the Moon taken in
X-rays
by the Roentgen Observatory Satellite
ROSAT in 1990. This famous picture shows three distinct regions:
a bright X-ray sky, a bright part of the Moon, and a relatively dark part
of the Moon. The bright X-ray region is exemplary of the mysterious X-ray
background that is seen everywhere on the sky. The bright lunar crescent
shines because it reflects X-rays emitted by the
Sun. The dark lunar face
is surprising because it is not completely dark, and its slight emission is
thought to result from energetic particles from the
solar wind striking the
Moon.
 APOD: June 30, 1995 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
APOD: June 30, 1995 - Ida and Dactyl: Asteroid and Moon
Explanation:
An asteroid with a moon! The robot spacecraft
Galileo
whose primary mission is to explore the Jupiter system, has encountered
and photographed two asteroids during its long journey to Jupiter.
The second asteroid it photographed, called Ida, was discovered to have a moon
which appears as a small dot to the right of Ida in this picture.
The tiny moon, named Dactyl, is about one mile
across, while the potato shaped Ida measures about 36 miles long and
14 miles wide. Dactyl is the first moon of an asteroid ever discovered.
The names Ida and Dactyl are based on characters in Greek mythology.