 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 APOD: 2025 December 20 - A Solstice Sun Tattoo
APOD: 2025 December 20 - A Solstice Sun Tattoo
Explanation:
The word
solstice is from the Latin for Sun and to pause or stand still.
And in the days surrounding a solstice the Sun's annual
north-south drift in planet Earth's sky
does slow down, pause, and then reverse direction.
So near the solstice the daily path of the Sun through the sky
really doesn't change much.
In fact, near the
December solstice,
the Sun's consistent, low arc through northern hemisphere skies,
along with low surface temperatures, has left a noticeable
imprint on this path to the mountain town of Peaio in northern Italy.
The morning frost on the road has melted away only where the sunlight
was able to reach the ground.
But it remains in the areas
persistently shadowed by the fence,
tattooing in frost
an image of the fence on the asphalt surface.
 APOD: 2025 December 7 – The Sun and Its Missing Colors
APOD: 2025 December 7 – The Sun and Its Missing Colors
Explanation:
It is still
not known why the Sun's light is missing some colors.
Here are all the
visible
colors of the
Sun,
produced by passing the Sun's light through a
prism-like device.
The spectrum was created at the
McMath-Pierce Solar Observatory
and shows, first off, that although our
white-appearing
Sun emits light of nearly
every color, it appears brightest in yellow-green light.
The dark patches in the
featured spectrum arise from gas at or above the
Sun's surface
absorbing sunlight emitted below.
Since different types of gas
absorb different colors of light,
it is possible to determine what gasses compose the Sun.
Helium, for example, was
first discovered in
1868 on a solar spectrum and only
later found here on
Earth.
Today, the majority of
spectral absorption lines have been identified - but
not all.
 APOD: 2025 August 11 – Closest Ever Images Near the Sun
APOD: 2025 August 11 – Closest Ever Images Near the Sun
Explanation:
Everybody sees the Sun.
Nobody's been there.
Starting in 2018, though, NASA
launched the robotic
Parker Solar Probe
(PSP) to investigate regions near to the
Sun for the first time.
The featured time-lapse video shows the view looking sideways from
behind PSP's Sun shield in December during the
closest approach of any human-made spacecraft to the Sun,
looping down to only about five solar diameters above the
Sun's hot surface.
The PSP's Wide Field Imager for Solar Probe
(WISPR) cameras took these images over seven hours, but they are digitally compressed here into about 5 seconds.
The solar corona,
including colliding
coronal mass ejections (CMEs), is visible here in
unprecedented detail, with stars
passing far in the background.
The Sun is not only Earth's dominant
energy source, but its variable
solar wind also compresses Earth's atmosphere, triggers auroras, affects power grids, and can even
damage orbiting communication satellites.
 APOD: 2025 July 30 – Coronal Loops on the Sun
APOD: 2025 July 30 – Coronal Loops on the Sun
Explanation:
Our Sun frequently erupts in loops.
Hot solar
plasma jumps off the Sun's surface into
prominences,
with the most common type of prominence being a simple loop.
The loop shape originates from the
Sun's magnetic field,
which is traced by spiraling electrons and protons.
Many loops into the Sun's lower
corona
are large enough to
envelop the Earth
and are stable enough to last days.
They commonly occur near active regions that also include dark
sunspots.
The featured panel shows four loops,
each of which was captured near the
Sun's
edge during 2024 and 2025.
The images were taken by a personal telescope in
Mantova,
Italy and in a
very specific color of light emitted primarily by
hydrogen.
Some solar prominences
suddenly break open and
eject particles into the
Solar System, setting up a
space weather sequence that can affect the
skies and
wires of Earth.
 APOD: 2025 June 15 – Two Worlds One Sun
APOD: 2025 June 15 – Two Worlds One Sun
Explanation:
How different does sunset appear from Mars than from Earth?
For comparison, two images of our common star were taken at
sunset, one from Earth and one from Mars.
These images were scaled to have the same angular width and are
featured here side-by-side.
A quick inspection will reveal that the
Sun appears slightly smaller from
Mars than from
Earth.
This makes sense since
Mars is 50% further from the
Sun than
Earth.
More striking, perhaps, is that the
Martian sunset is noticeably bluer near the Sun than the
typically orange
colors near the setting Sun from Earth.
The reason for the
blue hues from Mars is
not fully understood, but thought to be related to
forward scattering properties of
Martian dust.
The terrestrial sunset was taken in 2012 March from
Marseille,
France, while the Martian sunset was captured in 2015 by
NASA's robotic
Curiosity rover from
Gale crater on
Mars.
 APOD: 2025 May 21 – International Space Station Crosses the Sun
APOD: 2025 May 21 – International Space Station Crosses the Sun
Explanation:
Typically, the International Space Station is visible only at night.
Slowly drifting across the night sky as it orbits the Earth, the
International Space Station (ISS) can be seen as a
bright spot about once a month from many locations.
The ISS
is then visible only just after sunset or just
before sunrise because it shines by reflected sunlight -- once the
ISS enters the
Earth's shadow, it will drop
out of sight.
The only occasion when the
ISS is visible during the day is when it
passes right in front of the Sun.
Then, it passes so quickly that only cameras
taking short exposures can visually freeze the
ISS's silhouette onto the background
Sun.
The
featured picture
did exactly that -- it is actually a series of images taken a month ago from
Sant Feliu de Buixalleu,
Spain
with perfect timing.
This image series
was later combined with a separate image highlighting
the texture of the active Sun which included several
Sun's prominences around the edge.
 APOD: 2025 March 31 – Parker: The Solar System from Near the Sun
APOD: 2025 March 31 – Parker: The Solar System from Near the Sun
Explanation:
If you watch long enough, a comet will appear.
Before then, you will see
our Solar System from inside the orbit of
Mercury as recorded by
NASA's
Parker Solar Probe looping around the
Sun.
The video captures coronal streamers into the
solar wind, a small
Coronal Mass Ejection, and planets including,
in order of appearance,
Mercury,
Venus,
Saturn,
Earth,
Mars, and
Jupiter.
Between the emergence of Earth and Mars,
Comet Tsuchinshan-ATLAS appears with a distinctive tail.
The continuous fleeting streaks are
high energy particles from the Sun impacting Parker's sideways looking
camera.
The featured time-lapse video was taken last year during
Encounter 21,
Parker's 21st close approach to the Sun.
Studying data and images from
Parker are delivering a better understanding of the
dynamic Sun's effects on Earth's
space weather as
well as humanity's power grids,
spacecraft, and space-faring astronauts.
 APOD: 2025 March 16 – Venus and the Triply Ultraviolet Sun
APOD: 2025 March 16 – Venus and the Triply Ultraviolet Sun
Explanation:
This was a very unusual type of solar eclipse.
Typically, it is the
Earth's Moon that
eclipses the Sun.
In 2012, though, the planet
Venus took a turn.
Like a solar eclipse by the Moon, the
phase of Venus became a continually thinner
crescent as Venus became increasingly better
aligned with the Sun.
Eventually the alignment became perfect and the
phase of Venus dropped to zero.
The dark spot of Venus crossed our parent star.
The situation could technically be labeled a Venusian
annular eclipse with an extraordinarily large
ring of fire.
Pictured here during the occultation, the Sun was imaged in three colors of
ultraviolet light by the Earth-orbiting
Solar Dynamics Observatory,
with the dark region toward the right corresponding to a
coronal hole.
Hours later, as Venus continued in its orbit, a
slight crescent phase appeared again.
The next Venusian transit across the Sun will occur in
2117.
 APOD: 2024 September 2 – A Triangular Prominence Hovers Over the Sun
APOD: 2024 September 2 – A Triangular Prominence Hovers Over the Sun
Explanation:
Why is there a triangle hovering over the Sun?
Although the shape is unusual, the type of structure is not:
it is part of an evolving
solar prominence.
Looping magnetic fields on the
Sun channel the flow of
energetic particles, sometimes holding glowing gaseous structures aloft for months.
A prominence
glows brightly because it contains particularly hot, dense, or opaque solar
plasma.
The
surprising triangular structure occurred last week.
Larger than our Earth, the
iconic prominence
was imaged by several solar photographers and
documented by NASA's
Solar Dynamic Observatory
to form and violently dissipate in about a day.
The
featured image was captured in a color of
red light
emitted strongly by
hydrogen.
Below,
solar fibrils carpet the
Sun's chromosphere,
while the background sky is so faint
in comparison that no stars are visible.
Our Sun's surface has been
quite active this year.
 APOD: 2024 July 28 – Sun Dance
APOD: 2024 July 28 – Sun Dance
Explanation:
Sometimes, the surface of our Sun seems to dance.
In the middle of 2012, for example, NASA's Sun-orbiting
Solar Dynamic Observatory spacecraft imaged an
impressive prominence
that seemed to perform a
running dive roll like an acrobatic dancer.
The dramatic explosion was
captured in
ultraviolet light in the
featured time-lapse video covering about three hours.
A looping magnetic field directed the flow of hot
plasma on the
Sun.
The scale of the
dancing prominence is huge -- the entire
Earth would easily fit under the flowing
arch of hot gas.
A quiescent prominence typically lasts about a month and may erupt in a
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME),
expelling hot gas into the
Solar System.
The energy mechanism that creates a
solar prominence is still a topic of
research.
Like in 2012, this year the Sun's surface is again
quite active and features many
filaments and prominences.
 APOD: 2024 June 15 - Prominences and Filaments on the Active Sun
APOD: 2024 June 15 - Prominences and Filaments on the Active Sun
Explanation:
This colorized and digitally sharpened image of the Sun is composed of
frames recording emission from hydrogen atoms in the solar chromosphere
on May 15.
Approaching the maximum of
solar cycle 25,
a multitude of planet-dwarfing active regions
and twisting, snake-like solar filaments are seen
to sprawl across the surface of the active Sun.
Suspended in the active regions' strong magnetic fields,
the filaments of plasma lofted
beyond the Sun's edge
appear as bright solar prominences.
The large prominences seen near 4 o'clock,
and just before 9 o'clock around the solar limb
are post flare loops from two powerful
X-class solar flares
that both
occurred on that day.
In fact, the 4 o'clock prominence is associated with the
monster active region AR 3664
just rotating off the Sun's edge.
 APOD: 2024 May 13 – AR 3664 on a Setting Sun
APOD: 2024 May 13 – AR 3664 on a Setting Sun
Explanation:
It was larger than the Earth.
It was so big you could actually see it on the Sun's surface without magnification.
It contained powerful and
tangled magnetic fields
as well as numerous
dark sunspots.
Labelled
AR 3664, it developed into one of the most energetic areas seen on the
Sun in recent years,
unleashing a series of explosions that led to a
surge of energetic particles striking the Earth, which created
beautiful auroras.
And might continue.
Although
active regions
on the Sun like AR 3664 can be quite dangerous,
this region's
Coronal Mass Ejections
have not done, as yet, much
damage to Earth-orbiting satellites or Earth-surface electrical grids.
Pictured,
the enormous active region was captured on the
setting Sun a few days ago from
Civitavecchia,
Rome,
Italy.
The composite image
includes a very short exposure taken of just the
Sun's surface, but mimics what was actually visible.
Finally,
AR 3664 is
now rotating away from the Earth,
although the region may survive long enough to come around again.
 APOD: 2024 January 13 - Circling the Sun
APOD: 2024 January 13 - Circling the Sun
Explanation:
Earth's orbit around the Sun
is not a circle, it's an ellipse.
The point along its elliptical orbit where our fair planet is
closest to the Sun
is called perihelion.
This year, perihelion was on January 2 at 01:00 UTC, with
the Earth about 3 million miles
closer to the Sun than it was at aphelion (last July 6),
the farthest point in its elliptical orbit.
Of course, distance from the Sun
doesn't determine the seasons,
and it doesn't the determine size of Sun halos.
Easier to see
with the Sun hidden behind a tall tree trunk,
this beautiful ice halo forms a 22 degree-wide
circle around the Sun,
recorded while strolling through the countryside
near Heroldstatt, Germany.
The Sun halo's 22 degree angular diameter is
determined by the six-sided geometry
of water ice crystals
drifting high in planet Earth's atmosphere.
 APOD: 2023 November 19 – Space Station, Solar Prominences, Sun
APOD: 2023 November 19 – Space Station, Solar Prominences, Sun
Explanation:
That's no sunspot.
It's the
International Space Station (ISS)
caught passing in front of the Sun.
Sunspots, individually, have a dark central
umbra, a lighter surrounding
penumbra, and
no Dragon capsules attached.
By contrast, the ISS is a complex and multi-spired mechanism,
one of the largest and most
complicated spacecraft ever created by
humanity.
Also, sunspots circle the
Sun,
whereas the ISS orbits the
Earth.
Transiting the Sun is not very unusual for the
ISS, which orbits the Earth about every 90 minutes,
but getting one's location, timing and equipment just right for a
great image is rare.
The featured picture combined three images all taken in 2021 from the
same location and at nearly the same time.
One image -- overexposed -- captured the faint
prominences seen across the top of the Sun,
a second image -- underexposed -- captured the complex texture of the
Sun's chromosphere,
while the third image -- the hardest to get -- captured the space station as it
shot across
the Sun in a fraction of a second.
Close inspection of the space station's
silhouette even reveals a docked
Dragon Crew capsule.
 APOD: 2023 October 8 – Plane, Clouds, Moon, Spots, Sun
APOD: 2023 October 8 – Plane, Clouds, Moon, Spots, Sun
Explanation:
What's that in front of the Sun?
The closest object is an
airplane, visible just below the Sun's center and caught purely by chance.
Next out are numerous clouds in
Earth's atmosphere, creating a series of darkened horizontal streaks.
Farther out is
Earth's Moon,
seen as the large dark circular bite on the upper right.
Just above the airplane and just below the Sun's surface are sunspots.
The main sunspot group captured here,
AR 2192, was in 2014
one of the largest ever recorded and had been
crackling and bursting with
flares since it came around the edge of the Sun a week before.
This show of solar silhouettes was unfortunately short-lived.
Within a few seconds the plane flew away.
Within a few minutes the clouds drifted off.
Within a few hours the
partial solar eclipse of the Sun by the Moon was over.
Fortunately, when it comes to the Sun, even
unexpected
alignments are
surprisingly frequent.
Perhaps one will be imaged this Saturday when a
new partial solar eclipse will be visible from much of North and South America.
 APOD: 2023 July 11 – Sunspots on an Active Sun
APOD: 2023 July 11 – Sunspots on an Active Sun
Explanation:
Why is our Sun so
active now?
No one is sure.
An increase in surface activity was expected because
our Sun
is approaching
solar maximum in 2025.
However, last month our Sun sprouted more
sunspots than in any month during the entire previous
11-year solar cycle -- and even dating back to 2002.
The
featured picture is a composite of images taken
every day from January to June by
NASA's
Solar Dynamic Observatory.
Showing a high abundance of sunspots, large individual spots can be
tracked across the Sun's disk, left to right, over about two weeks.
As a solar cycle continues, sunspots typically
appear closer to the equator.
Sunspots are just one way that our Sun displays
surface activity -- another is
flares and
coronal mass ejections (CMEs) that expel particles out into the
Solar System.
Since these
particles can affect astronauts and electronics,
tracking surface disturbances is of more than
aesthetic value.
Conversely,
solar activity can have very high aesthetic value -- in the Earth's atmosphere when they trigger aurora.
 APOD: 2023 June 21 – Three Sun Paths
APOD: 2023 June 21 – Three Sun Paths
Explanation:
Does the Sun follow the same path every day?
No.
The Sun's path changes during the year, tracing a longer route during the summer than the winter.
Pictured here, the
Sun's arc was captured from noon to sunset on three days,
from highest in the sky to lowest:
summer solstice,
equinox, and
winter solstice.
The images were taken near
Gatto Corvino Village in
Sicily,
Italy in 2020 and 2021.
The path and time the
Sun spends in the sky
is more important in
determining the season than
how close the Earth is to the
Sun.
In fact, the
Earth is closest to the Sun in January, during northern winter.
Today is a
solstice, so
today
the Sun is taking its longest path of the year across the sky in Earth's
northern hemisphere,
but the shortest path in the
southern hemisphere.
 APOD: 2023 June 11 – The Sun and Its Missing Colors
APOD: 2023 June 11 – The Sun and Its Missing Colors
Explanation:
Here are all the
visible
colors of the
Sun,
produced by passing the Sun's light through a
prism-like device.
The spectrum was created at the
McMath-Pierce Solar Observatory
and shows, first off, that although our
white-appearing
Sun emits light of nearly every color, it appears brightest in yellow-green light.
The dark patches in the
featured spectrum arise from gas at or above the
Sun's surface
absorbing sunlight emitted below.
Since different types of gas
absorb different colors of light,
it is possible to determine what gasses compose the Sun.
Helium, for example, was
first discovered in
1868 on a solar spectrum and only
later found here on
Earth.
Today, the majority of
spectral absorption lines have been identified - but
not all.
 APOD: 2023 February 22 – Our Increasingly Active Sun
APOD: 2023 February 22 – Our Increasingly Active Sun
Explanation:
Our Sun is becoming a busy place.
Only two years ago, the Sun was emerging from a
solar minimum
so quiet that
months would go by
without even a single
sunspot.
In contrast, already this year and well ahead of schedule, our Sun is
unusually active, already nearing solar activity levels seen a decade ago during the last
solar maximum.
Our increasingly active Sun was captured two weeks ago sporting numerous
interesting features.
The image was recorded in a single color of light called
Hydrogen Alpha,
color-inverted, and false colored.
Spicules
carpet much of the Sun's face.
The brightening towards the Sun's edges is caused by
increased absorption of relatively cool solar gas and called
limb darkening.
Just outside the Sun's disk,
several scintillating
prominences protrude,
while prominences on the Sun's face are known as
filaments and show as light streaks.
Magnetically tangled
active regions are both dark and light and contain cool
sunspots.
As our
Sun's magnetic field winds toward solar maximum over the next few years,
whether the
Sun's high activity will continue to increase is unknown.
 APOD: 2023 January 14 - Perihelion Sun 2023
APOD: 2023 January 14 - Perihelion Sun 2023
Explanation:
Perihelion for 2023,
Earth's closest approach to the Sun,
was on January 4 at 16:17 UTC.
That was less than 24 hours after this
sharp image of the Sun's disk
was recorded with telescope and
H-alpha filter from Sydney, Australia, planet Earth.
An H-alpha filter
transmits a characteristic red light from hydrogen atoms.
In views of the Sun it emphasizes the Sun's chromosphere,
a region just above
the solar photosphere or normally visible solar surface.
In this H-alpha image of the
increasingly active Sun
planet-sized sunspot regions are dominated
by bright splotches called plages.
Dark filaments of plasma
snaking across the solar disk transition
to bright prominences when seen
above the solar limb.
 APOD: 2022 December 21 - Sun Halo at Sixty-three Degrees North
APOD: 2022 December 21 - Sun Halo at Sixty-three Degrees North
Explanation:
Happy Solstice!
Today is the December solstice,
marking an astronomical beginning of
summer in the southern hemisphere and winter in the north.
On its yearly trek through planet Earth's skies,
at this solstice the Sun reaches its southern most declination,
23.5 degrees
south, at 21:48
UTC.
About 4 days ago the Sun was near this seasonal southern limit and so only just
above the horizon at local noon
from Ostersund in central Sweden.
This view looking over
the far northern lakeside city finds the midday Sun with a beautiful
solar ice halo.
Naturally occurring
atmospheric ice crystals
can produce the
tantalizing halo displays,
refracting and reflecting the sunlight through their hexagonal geometry.
Still, with the Sun low and near the horizon in the clear sky,
likely sources of the ice crystals producing this
intense halo are snow cannons.
Operating at a local ski area, the snowmaking machines create
a visible plume at the top of the nearby island Froson toward
the right side of the panorama.
 APOD: 2022 November 2 - A Partial Eclipse of an Active Sun
APOD: 2022 November 2 - A Partial Eclipse of an Active Sun
Explanation:
Watch for three things in this unusual eclipse video.
First, watch for a big dark circle to approach from the right to
block out more and more of the Sun.
This dark circle is the
Moon, and the video was made primarily to capture this
partial solar eclipse last week.
Next, watch a
large solar prominence
hover and shimmer over the
Sun's edge.
A close look will show that part of it is actually
falling back to the
Sun.
The prominence is made of hot
plasma that is temporarily held aloft by the
Sun's changing magnetic field.
Finally, watch the Sun's edge
waver.
What is
wavering is a dynamic carpet of
hot gas tubes rising and falling through the
Sun's chromosphere --
tubes known as
spicules.
The entire 4-second
time-lapse video
covers a time of about ten minutes, although the Sun itself is expected to
last another 5 billion years.
 APOD: 2022 September 13 - A Long Snaking Filament on the Sun
APOD: 2022 September 13 - A Long Snaking Filament on the Sun
Explanation:
Earlier this month, the Sun exhibited one of the longer filaments on record.
Visible as the bright curving streak around the image center,
the snaking filament's full extent was estimated to be over
half of the
Sun's radius -- more than 350,000 kilometers long.
A filament is composed of
hot gas held aloft
by the Sun's magnetic field, so that viewed from the side it would appear as a
raised prominence.
A different, smaller prominence is simultaneously visible at the Sun's edge.
The featured image is in false-color and
color-inverted to highlight not only the
filament but the Sun's
carpet
chromosphere.
The bright dot on the upper right is actually a
dark sunspot about the
size of the Earth.
Solar
filaments
typically last from hours to days, eventually collapsing to return hot
plasma back to the Sun.
Sometimes, though, they
explode and
expel particles into the
Solar System, some of which trigger
auroras on Earth.
The pictured filament appeared in early September and continued to
hold steady for about a week.
 APOD: 2022 September 3 - Sun and Moon and ISS
APOD: 2022 September 3 - Sun and Moon and ISS
Explanation:
On August 25 Sun and Moon could both be seen in planet Earth's daytime
skies.
And so could the
International Space Station.
The ISS crossed the disk of the waning crescent Moon as seen
from Shunyi district, Beijing, China at about 11:02 am local time.
Some 40 kilometers to the southwest, in Fengtai district,
the ISS was seen to cross the Sun's disk too.
The solar transit was observed only 29 seconds later.
Both transits are compared in these panels, composed of processed
and stacked video frames from the two locations.
The coordinated captures were made with different equipment,
but adjusted to show the Sun and Moon at the same scale.
The ISS was at a calculated range of 435 kilometers for the
lunar transit
and 491 kilometers when passing in front
of the Sun.
 APOD: 2022 May 31 - Rocket Transits Rippling Sun
APOD: 2022 May 31 - Rocket Transits Rippling Sun
Explanation:
The launch of a rocket at sunrise can result in unusual
but intriguing images that feature both the rocket and the Sun.
Such was the case last month when a
SpaceX
Falcon 9 rocket
blasted off from NASA's
Kennedy Space Center carrying
53 more
Starlink satellites into
low Earth orbit.
In the
featured launch picture,
the rocket's exhaust plume
glows beyond its projection onto the distant
Sun,
the rocket itself appears
oddly jagged,
and the Sun's lower edge shows peculiar
drip-like ripples.
The physical cause of all of these effects is
pockets of relatively hot or rarefied air
deflecting sunlight less strongly than
pockets relatively cool or compressed air:
refraction.
Unaware of the Earthly show, active sunspot
region 3014 -- on the upper left -- slowly
crosses the Sun.
 APOD: 2022 May 22 - A Large Tsunami Shock Wave on the Sun
APOD: 2022 May 22 - A Large Tsunami Shock Wave on the Sun
Explanation:
Tsunamis this large don't happen on Earth.
During 2006, a large solar flare from an Earth-sized
sunspot produced a
tsunami-type
shock wave that was
spectacular even for the Sun.
Pictured here, the
tsunami wave
was captured moving out from active region AR 10930 by the Optical Solar Patrol Network
(OSPAN) telescope in
New Mexico,
USA.
The resulting
shock wave, known technically as a
Moreton wave,
compressed and heated up gasses including
hydrogen in the
photosphere
of the Sun, causing a momentarily brighter glow.
The featured image was taken in a
very specific red color
emitted exclusively by hydrogen gas.
The rampaging tsunami
took out some active filaments on the Sun,
although many re-established themselves later.
The solar tsunami spread at nearly one million kilometers per hour,
and circled the entire
Sun
in a matter of minutes.
 APOD: 2022 April 11 - A Space Station Crosses a Busy Sun
APOD: 2022 April 11 - A Space Station Crosses a Busy Sun
Explanation:
Typically, the International Space Station is visible only at night.
Slowly drifting across the night sky as it orbits the Earth, the
International Space Station (ISS) can be seen as a
bright spot several times a year from many locations.
The ISS
is then visible only just after sunset or just before
sunrise because it shines by reflected sunlight --
once the ISS enters the Earth's shadow, it will drop out of sight.
The only occasion when the
ISS is visible during the day is when it
passes right in front of the Sun.
Then, it passes so quickly that only cameras
taking short exposures can visually freeze the
ISS's silhouette onto the background
Sun.
The featured picture did exactly that --
it is actually a series of images taken earlier this month from
Beijing,
China with perfect timing.
This image series was later combined with separate images
taken at nearly the same time but highlighting the
texture and activity on the busy
Sun.
The solar activity included numerous gaseous
prominences seen around the edge, highlighted in red,
filaments seen against the Sun's face, and a dark
sunspot.
 APOD: 2022 March 6 - Venus and the Triply Ultraviolet Sun
APOD: 2022 March 6 - Venus and the Triply Ultraviolet Sun
Explanation:
This was a very unusual type of solar eclipse.
Typically, it is the
Earth's Moon that
eclipses the Sun.
In 2012, though, the planet
Venus took a turn.
Like a solar eclipse by the Moon, the phase of Venus became a continually thinner
crescent as Venus became increasingly better
aligned with the Sun.
Eventually the alignment became perfect and the
phase of Venus dropped to zero.
The dark spot of Venus crossed our parent star.
The situation could technically be labeled a Venusian
annular eclipse with an extraordinarily large
ring of fire.
Pictured here during the occultation, the Sun was imaged in three colors of
ultraviolet light by the Earth-orbiting
Solar Dynamics Observatory,
with the dark region toward the right corresponding to a
coronal hole.
Hours later, as Venus continued in its orbit, a
slight crescent phase appeared again.
The next Venusian transit across the Sun will occur in
2117.
 APOD: 2022 February 16 - Eiffel Tower Prominence on the Sun
APOD: 2022 February 16 - Eiffel Tower Prominence on the Sun
Explanation:
What's that on the Sun?
Although it may look like a flowing version of the
Eiffel Tower,
it is a
solar prominence that is actually much bigger -- about the
height of Jupiter.
The huge prominence
emerged about ten days ago, hovered over the
Sun's surface for about two days,
and then erupted -- throwing a
coronal mass ejection (CME) into the Solar System.
The featured video,
captured from the astrophotographer's backyard in
Hendersonville,
Tennessee,
USA, shows an hour time-lapse played both forwards and backwards.
That CME did not impact the Earth, but our Sun had
unleashed
other recent CMEs that not only triggered
Earthly auroras, but puffed out the
Earth's atmosphere enough to
cause just-launched
Starlink satellites to
fall back.
Activity on the Sun, including
sunspots,
prominences, CMEs and
flares, continues to increase as the
Sun evolves away from a deep
minimum in its 11-year
magnetic cycle.
 APOD: 2021 December 28 - Sun Halo over Sweden
APOD: 2021 December 28 - Sun Halo over Sweden
Explanation:
What's happened to the Sun?
Sometimes it looks like the Sun is being viewed through a giant
lens.
In the featured video, however, there are actually millions of tiny lenses:
ice crystals.
Water may freeze in the
atmosphere into small, flat, six-sided, ice crystals.
As these crystals flutter to the ground, much time is spent with their
faces flat and parallel to the ground.
An observer may find themselves in the same plane as
many of the falling ice crystals near sunrise or sunset.
During this alignment, each crystal can act like a miniature lens,
refracting sunlight into our
view and creating
phenomena like parhelia, the technical term for
sundogs.
The
featured video was taken in late 2017
on the side of a ski hill at the
Vemdalen Ski Resort in central
Sweden.
Visible in the center is the most direct image of the
Sun, while two bright
sundogs glow prominently from both the left and the right.
Also visible is the bright
22 degree halo -- as well as the rarer and much fainter
46 degree halo --
also created by
sunlight refracting through atmospheric ice
crystals.
 APOD: 2021 December 21 - Solstice Sun and Milky Way
APOD: 2021 December 21 - Solstice Sun and Milky Way
Explanation:
Welcome to December's solstice, first day of winter in the north and
summer for the southern hemisphere.
Astronomical markers of the seasons,
solstice and equinox
dates are based on the Sun's place in its annual journey along the ecliptic, through planet Earth's sky.
At this solstice,
the Sun reaches its maximum southern
declination
of -23.5 degrees today at 15:59
UTC, while its
right ascension
coordinate on the
celestial sphere
is 18 hours.
That puts the Sun in the
constellation Sagittarius in a direction near
the center of our Milky Way galaxy.
In fact, if you could see today's
Solstice Sun
against faint background stars and nebulae (that's
really hard to do, especially in the daytime ...)
your view might look something like this composited panorama.
To make it, images of
our fair galaxy
were taken under dark
Namibian
night skies, then stitched together in a panoramic view.
From a snapshot made on
2015 December 21,
the Sun was digitally overlayed as a brilliant star at today's northern winter
solstice position, close to the center of the Milky Way.
 APOD: 2021 December 9 - A Total Eclipse of the Sun
APOD: 2021 December 9 - A Total Eclipse of the Sun
Explanation:
Few were able to stand in the
Moon's shadow
and watch the
December 4 total eclipse
of the Sun.
Determined by
celestial mechanics and not geographical boundaries, the
narrow path of totality tracked
across planet Earth's relatively inaccessible southernmost continent.
Still, some enthusiastic and well-insulated eclipse chasers were
rewarded with the dazzling
spectacle in Antarctica's cold but clear skies.
Taken just before the brief totality began, this image from a ground-based
telescope inside the edge of the shadow path
at Union Glacier
catches a glimmer of sunlight near the top of the silhouetted lunar disk.
Look closely for the pinkish solar prominences arcing above the Sun's
limb.
During totality, the
magnificent solar corona,
the Sun's outer atmosphere,
made its much anticipated appearance, seen in the composite
view streaming far from the Sun's edge.
 APOD: 2021 November 23 - The Sun in X-rays from NuSTAR
APOD: 2021 November 23 - The Sun in X-rays from NuSTAR
Explanation:
Why are the regions above sunspots so hot?
Sunspots
themselves are a bit cooler than the surrounding
solar surface because the magnetic fields that create them reduce convective heating.
It is therefore unusual that regions overhead --
even much higher up in the
Sun's corona --
can be hundreds of times hotter.
To help find the cause,
NASA directed the Earth-orbiting
Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR)
satellite to point its very sensitive X-ray telescope at the Sun.
Featured here is the Sun in
ultraviolet light,
shown in a red hue as taken by the orbiting
Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO).
Superimposed in false-colored green and blue is emission above
sunspots detected by
NuSTAR
in different bands of high-energy
X-rays,
highlighting regions of extremely
high temperature.
Clues about the Sun's atmospheric
heating
mechanisms come from NuSTAR images like this and shed light
on solar nanoflares and
microflares as brief
bursts of energy that may drive the unusual heating.
 APOD: 2021 November 8 - A Filament Leaps from the Sun
APOD: 2021 November 8 - A Filament Leaps from the Sun
Explanation:
Why, sometimes, does part of the Sun's atmosphere leap into space?
The reason lies in changing
magnetic fields that thread through the
Sun's surface.
Regions of strong surface magnetism, known as
active regions, are usually marked by dark
sunspots.
Active regions can channel charged gas along arching
or sweeping magnetic fields -- gas that sometimes
falls back,
sometimes escapes,
and sometimes not only escapes but
impacts our Earth.
The featured one-hour time-lapse video -- taken with a
small telescope in
France --
captured an eruptive filament that appeared to leap off the Sun late last month.
The filament is huge: for comparison,
the size of the Earth is shown on the upper left.
Just after the
filament lifted off, the
Sun emitted a powerful X-class flare
while the surface rumbled with a tremendous
solar tsunami.
A result was a cloud of charged particles that rushed into
our Solar System but mostly
missed our Earth -- this time.
However, enough solar plasma did impact our
Earth's magnetosphere
to create a few
faint auroras.
 APOD: 2021 September 21 - Sun Spot Hill
APOD: 2021 September 21 - Sun Spot Hill
Explanation:
Is this giant orange ball about to roll down that tree-lined hill?
No, because the giant orange ball is actually
the Sun.
Our Solar System's
central star
was captured rising beyond a hill on Earth
twelve days ago complete with a delightfully detailed foreground.
The Sun's disk showed
five sunspots, quite a lot considering that during the
solar minimum in solar activity of the past few years, most days showed
no spots.
A close look at the hill --
Sierra del
Cid in Perter,
Spain -- reveals not only silhouetted pine trees, but silhouetted people --
by coincidence three brothers of the photographer.
The trees and brothers were about 3.5-kilometers away during the morning of the well-planned image.
A dark filter muted the usually
brilliant Sun
and brought up great detail on the lower
sunspots.
Within a few minutes,
the Sun rose far above the hill, while within a week,
the sunspots rotated
around the Sun, out of view.
The captured scene, however, is now
frozen in time for all to enjoy.
 APOD: 2021 May 4 - Space Station, Solar Prominences, Sun
APOD: 2021 May 4 - Space Station, Solar Prominences, Sun
Explanation:
That's no sunspot.
It's the
International Space Station (ISS)
caught passing in front of the Sun.
Sunspots, individually, have a dark central
umbra,
a lighter surrounding
penumbra, and
no Dragon capsules attached.
By contrast, the ISS is a complex and multi-spired mechanism,
one of the largest and most
complicated spacecraft ever created by
humanity.
Also, sunspots circle the
Sun,
whereas the ISS orbits the
Earth.
Transiting the Sun is not very unusual for the
ISS, which orbits the Earth about every 90 minutes,
but getting one's location, timing and equipment just right for a
great image is rare.
The featured picture combined three images all taken from the
same location and at nearly the same time.
One image -- overexposed -- captured the faint
prominences seen across the top of the Sun,
a second image -- underexposed -- captured the complex texture of the
Sun's chromosphere,
while the third image -- the hardest to get -- captured the space station as it
shot across
the Sun in a fraction of a second.
Close inspection of the space station's
silhouette even reveals a docked
Dragon Crew capsule.
 APOD: 2021 February 17 - Sun Pillar with Upper Tangent Arc
APOD: 2021 February 17 - Sun Pillar with Upper Tangent Arc
Explanation:
This was not a typical sun pillar.
Just after sunrise two weeks ago in
Providence,
Rhode Island,
USA, a photographer, looking out his window, was suddenly awestruck.
The astonishment was caused by a
sun pillar that
fanned out at the top.
Sun pillars, singular columns of light going up from
the Sun, are themselves rare to see, and are known to be caused by sunlight
reflecting from wobbling,
hexagon-shaped ice-disks
falling through
Earth's atmosphere.
Separately, upper
tangent arcs
are known to be caused by sunlight refracting through falling
hexagon-shaped ice-tubes.
Finding a
sun pillar connected to an
upper tangent arc is extraordinary, and, initially,
took some analysis to figure out what was going on.
A leading theory is that this
sun pillar
was also created, in a complex and unusual way, by falling ice tubes.
Few might believe that such a
rare phenomenon was seen again if it
wasn't for the quick thinking of the photographer --
and the camera on his nearby
smartphone.
 APOD: 2020 November 2 - Half Sun with Prominence
APOD: 2020 November 2 - Half Sun with Prominence
Explanation:
What's happening to the Sun?
Clearly, the Sun's lower half is hidden behind a thick cloud.
Averaging over the entire
Earth, clouds block the Sun
about 2/3rds of the time, although much less over many land locations.
On the Sun's upper right is a
prominence of magnetically levitating hot gas.
The prominence might seem small but it could easily
envelop our
Earth
and persist for over a month.
The featured image is a combination of two exposures,
one optimizing the cloud and prominence, and the other optimizing
the Sun's texture.
Both were taken about an hour apart with the same camera and from the same location in
Lynnwood,
Washington,
USA.
The shaggy texture derives from the Sun's
chromosphere,
an atmospheric layer that stands out in the specifically
exposed color.
The uniformity of the texture shows the surface to be
relatively calm, indicative of a Sun just past the solar minimum in its
11-year cycle.
In the years ahead, the Sun will progress toward a
more active epoch where
sunspots, prominences, and ultimately
auroras on Earth will be more common: solar maximum.
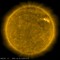 APOD: 2020 October 3 - Driving to the Sun
APOD: 2020 October 3 - Driving to the Sun
Explanation:
How long would it take to drive to the Sun?
Brittany age 7, and D.J. age 12,
ponder this question over dinner one evening.
James also age 7, suggests taking a
really fast racing car while
Christopher age 4, eagerly agrees.
Jerry, a really old guy who is used to estimating driving time
on family trips based on distance divided by speed, offers
to do the numbers.
"Let's see ... the
Sun is 93 million miles away.
If we drove 93 miles per hour the trip would only take us 1 million
hours."
How long is 1 million hours?
One year is 365 days times 24 hours per day, or 8,760 hours.
One hundred years would be 876,000 hours,
but that's still a little short of the 1 million hour drive time.
So the Sun is really quite far away.
Christopher is not impressed, but as he grows older he will be.
You've got to be impressed by something that's 93 million miles
away and still hurts your eyes
when you look at it!
 APOD: 2020 August 19 - The Sun Rotating
APOD: 2020 August 19 - The Sun Rotating
Explanation:
Does the Sun change as it rotates?
Yes, and the changes can vary from subtle to dramatic.
In the
featured time-lapse sequences,
our Sun -- as imaged by
NASA's
Solar Dynamics Observatory --
is shown rotating though an entire month in 2014.
In the large image on the left, the solar
chromosphere is depicted in
ultraviolet light, while the smaller and lighter
image to its upper right simultaneously shows the more familiar solar
photosphere in
visible light.
The rest of the inset six Sun images highlight
X-ray emission
by relatively rare iron atoms located at different heights of the
corona, all
false-colored
to accentuate differences.
The Sun takes just under a month to
rotate
completely -- rotating fastest at the equator.
A large and active
sunspot region rotates into view soon after the video starts.
Subtle effects include changes in
surface texture and the shapes of active regions.
Dramatic effects include numerous flashes in active regions, and fluttering and
erupting prominences visible all around the Sun's edge.
Presently,
our Sun
is passing an unusually low
Solar minimum in activity of its
11-year magnetic cycle.
As the video ends, the same large and
active sunspot region
previously mentioned rotates back into view, this time
looking different.
 APOD: 2020 August 18 - TYC 8998 760 1: Multiple Planets around a Sun Like Star
APOD: 2020 August 18 - TYC 8998 760 1: Multiple Planets around a Sun Like Star
Explanation:
Do other stars have planets like our Sun?
Previous evidence shows that they do, coming mostly from
slight shifts in the star's light created by the orbiting planets.
Recently,
however, and for the first time, a pair of
planets
has been directly imaged around a Sun-like star.
These
exoplanets orbit the star designated
TYC 8998-760-1 and are identified by arrows in the
featured infrared image.
At 17 million years old, the parent star is much younger than the 5-billion-year age of our Sun.
Also, the
exoplanets
are both more massive and orbit further out than their
Solar System analogues:
Jupiter and Saturn.
The exoplanets
were found by the
ESO's
Very Large Telescope in
Chile by their
infrared glow –
after the light from their parent star was
artificially blocked.
As telescope and
technology improve over the next decade, it is
hoped that planets more
closely resembling our
Earth will be directly imaged.
 APOD: 2020 August 5 - Picture Rocks Sun Dagger
APOD: 2020 August 5 - Picture Rocks Sun Dagger
Explanation:
Ancient sun daggers will not hurt you, but they may tell you the time.
A sun dagger is a dagger-shaped gap in a shadow created by sunlight
streaming through a crevice in a nearby rock.
Starting over a thousand year ago, native people of the American southwest carved spiral
petroglyphs
into rocks that became illuminated by
sun daggers
in different ways as the
Sun
shifts in the sky.
A type of sundial, where the end of the
sundagger points in
the spiral at high noon (for example) indicates a time of year, possibly illuminating a
solstice or
equinox.
Sun daggers
are thought to have been used by
Sun Priests
during lone vigils with prayers and offerings.
Of the few known, the
featured video
discusses the historic
Picture Rocks Sun Dagger
near Tucson,
Arizona,
USA,
likely created by a
Hohokam Sun Priest around 1000 AD.
 APOD: 2020 August 2 - Two Worlds One Sun
APOD: 2020 August 2 - Two Worlds One Sun
Explanation:
How different does sunset appear from Mars than from Earth?
For comparison, two images of our common star were taken at
sunset, one from Earth and one from Mars.
These images were scaled to have same angular width and
featured here side-by-side.
A quick inspection will reveal that the
Sun appears slightly smaller from
Mars than from
Earth.
This makes sense since
Mars is 50% further from the
Sun than
Earth.
More striking, perhaps, is that the
Martian sunset is
noticeably bluer
near the Sun than the
typically orange
colors near the setting Sun from Earth.
The reason for the
blue hues from Mars is
not fully understood, but thought to be related to
forward scattering properties of
Martian dust.
The terrestrial sunset was taken in 2012 March from
Marseille,
France, while the Martian sunset was
captured in 2015 by
NASA's robotic
Curiosity rover from
Gale crater on
Mars.
Last week a
new rover and a
helicopter -- onboard
Mars 2020 --
launched for Mars.
 APOD: 2019 October 28 - The Space Station Crosses a Spotless Sun
APOD: 2019 October 28 - The Space Station Crosses a Spotless Sun
Explanation:
Typically, the International Space Station is visible only at night.
Slowly drifting across the night sky as it orbits the Earth, the
International Space Station (ISS) can be seen as a
bright spot about once a month from many locations.
The ISS is then visible only just after sunset or just before sunrise because it shines by reflected sunlight -- once the ISS enters the Earth's shadow, it will drop out of sight.
The only occasion when the
ISS is visible during the day is when it
passes right in front of the Sun.
Then, it passes so quickly that only cameras
taking short exposures can visually freeze the
ISS's silhouette onto the background
Sun.
The
featured picture did exactly that -- it is actually a series of images taken a month ago from
Santa Fe,
Argentina with perfect timing.
This image series was later combined with a separate image
highlighting the texture of the spotless Sun, and an image bringing up the
Sun's prominences around the edge.
At an unusually low
Solar Minimum, the Sun has gone
without sunspots now for most of 2019.
 APOD: 2019 September 23 - Equinox: The Sun from Solstice to Solstice
APOD: 2019 September 23 - Equinox: The Sun from Solstice to Solstice
Explanation:
Today is an equinox, a date when day and night are equal.
Tomorrow, and every day until the next
equinox,
the night will be longer than the day in Earth's northern hemisphere,
and the day will be longer than the night in Earth's southern hemisphere.
An equinox
occurs midway between the two
solstices,
when the days and nights are the least equal.
The featured picture is a composite of hourly images taken of the Sun above
Bursa,
Turkey on key days from solstice to
equinox to solstice.
The bottom Sun band was taken during the north's
winter solstice in 2007 December, when
the Sun
could not rise very high
in the sky nor stay above the horizon very long.
This lack of Sun caused
winter.
The top
Sun band was taken during the northern
summer solstice in 2008 June, when the
Sun rose highest in the sky and
stayed above the horizon for more than 12 hours.
This abundance of Sun caused
summer.
The middle band was taken during an
equinox in 2008 March, but it is the same sun band that
Earthlings see today, the day of the most recent
equinox.
 APOD: 2019 July 15 - The Space Station Crosses a Spotless Sun
APOD: 2019 July 15 - The Space Station Crosses a Spotless Sun
Explanation:
That's no sunspot.
It's the
International Space Station (ISS)
caught passing in front of the Sun.
Sunspots, individually, have a dark central
umbra, a lighter surrounding penumbra, and
no solar panels.
By contrast, the ISS is a complex and multi-spired mechanism,
one of the largest and most sophisticated machines ever created by
humanity.
Also, sunspots occur on the
Sun,
whereas the
ISS orbits the
Earth.
Transiting the Sun is not very unusual for the
ISS, which orbits the Earth about every 90 minutes,
but getting one's timing and equipment just right for a
great image is rare.
Strangely, besides that fake spot, in this recent two-image composite, the Sun
lacked any real sunspots.
The featured picture combines two images -- one capturing the space station transiting the Sun -- and another taken consecutively capturing details of the Sun's surface.
Sunspots have been
rare on the
Sun
since the dawn of the current
Solar Minimum,
a period of low solar activity.
For reasons not yet fully understood, the
number of sunspots occurring during both the previous and current solar minima have been
unusually low.
 APOD: 2019 June 24 - Anticrepuscular Rays Converge Opposite the Sun
APOD: 2019 June 24 - Anticrepuscular Rays Converge Opposite the Sun
Explanation:
Is there ever anything interesting to see in the direction opposite the Sun?
Sometimes there is.
Notable items include
your own shadow,
a shadow of the Moon during a total solar eclipse,
a full moon --
in eclipse if the alignment's good enough,
a full earth,
planets
at
opposition,
glints from
planets,
the gegenschein from interplanetary dust,
the center of a rainbow,
hall-of-mountain fogbows,
an airplane glory,
and something
yet again different if your timing, clouds and Sun position are
just right.
This different effect starts with clouds near the
Sun
that are causing common
crepuscular rays to stream through.
In the featured rare image taken from an airplane in mid-April,
these beams were caught converging
180 degrees around,
on the opposite side of the sky from the Sun, where they are called
anticrepuscular rays.
Therefore, it may look like
something
bright is shining at the
antisolar point
near the image center, but actually it is
reverse-shining because, from your direction, light is streaming in, not out.
 APOD: 2018 October 10 - Sun Dance
APOD: 2018 October 10 - Sun Dance
Explanation:
Sometimes, the surface of our Sun seems to dance.
In the middle of 2012, for example, NASA's Sun-orbiting
Solar Dynamic Observatory spacecraft imaged an
impressive prominence
that seemed to perform a
running dive roll like an acrobatic dancer.
The dramatic explosion was
captured in
ultraviolet light in the
featured time-lapse video covering about three hours.
A looping magnetic field directed the flow of hot
plasma on the
Sun.
The scale of the
dancing prominence is huge -- the entire
Earth would easily fit under the flowing
arch of hot gas.
A quiescent prominence typically lasts about a month, and may erupt in a
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME)
expelling hot gas into the
Solar System.
The energy mechanism that creates a
solar prominence is still a topic of
research.
Unlike 2012, this year the Sun's surface is significantly
more serene, featuring fewer spinning prominences,
as it is near the minimum in its
11-year magnetic cycle.
 APOD: 2018 September 26 - The Sun's Spectrum with its Missing Colors
APOD: 2018 September 26 - The Sun's Spectrum with its Missing Colors
Explanation:
It is still not known why the Sun's light is missing some colors.
Here are all the
visible
colors of the
Sun,
produced by passing the Sun's light through a
prism-like device.
The spectrum was created at the
McMath-Pierce Solar Observatory
and shows, first off, that although our
white-appearing
Sun emits light of nearly every color, it does indeed appear brightest in yellow-green light.
The dark patches in the
above spectrum arise from gas at or above the
Sun's surface
absorbing sunlight emitted below.
Since different types of gas
absorb different colors of light,
it is possible to determine what gasses compose the Sun.
Helium, for example, was
first discovered
in 1870 on a solar spectrum and only
later found here on
Earth.
Today, the majority of
spectral absorption lines have been identified - but
not all.
 APOD: 2018 August 20 - Active Prominences on a Quiet Sun
APOD: 2018 August 20 - Active Prominences on a Quiet Sun
Explanation:
Why is the Sun so quiet?
As the Sun enters into a period of time known as a
Solar Minimum, it is, as expected, showing fewer
sunspots and
active regions than usual.
The quietness is somewhat unsettling, though, as so far this year, most days show no sunspots at all.
In contrast, from 2011 - 2015, during
Solar Maximum,
the Sun displayed spots just about every day.
Maxima and minima occur on an
11-year cycle, with the
last Solar Minimum
being the most quiet in a century.
Will this current Solar Minimum
go even deeper?
Even though the
Sun's activity affects the Earth and its surroundings,
no one knows for sure
what the Sun will do next,
and the physics behind the processes remain an
active topic of research.
The
featured image was taken
three weeks ago and shows that our Sun is busy even on a quiet day.
Prominences of hot
plasma,
some larger than the Earth,
dance continually and are most easily visible over the edge.
 APOD: 2018 June 18 - An Active Prominence on the Sun
APOD: 2018 June 18 - An Active Prominence on the Sun
Explanation:
Sometimes the Sun's surface becomes a whirlwind of activity.
Pictured is a time-lapse video of the
Sun's surface taken over a two hour period in early May, run both forwards and backwards.
The Sun's surface was blocked out so that
details
over the edge could be imaged in greater detail.
Hot plasma is seen swirling over the
solar
limb in an ongoing battle between changing
magnetic fields and constant gravity.
The featured
prominence rises about one
Earth-diameter over the Sun's surface.
Energetic events like
this are becoming less common as the Sun nears a minimum in its
11-year activity cycle.
 APOD: 2018 June 6 - A Sun Pillar over Norway
APOD: 2018 June 6 - A Sun Pillar over Norway
Explanation:
Have you ever seen a sun pillar?
When the air is cold and the Sun is rising or
setting, falling ice
crystals
can reflect sunlight and create an
unusual column of light.
Ice sometimes forms flat, six-sided
shaped crystals as it falls from high-level
clouds.
Air resistance causes these crystals to
lie nearly flat much of the time as they flutter to the ground.
Sunlight reflects off crystals that are
properly aligned,
creating the sun-sun-pillar
effect.
In the featured picture taken last week,
a sun-pillar reflects light from a
Sun setting over
Fensfjorden,
Norway.
 APOD: 2018 May 27 - Coronal Rain on the Sun
APOD: 2018 May 27 - Coronal Rain on the Sun
Explanation:
Does it rain on the
Sun?
Yes, although what falls is not water but extremely hot
plasma.
An example occurred
in mid-July 2012 after an eruption on the Sun that produced both a
Coronal Mass Ejection
and a moderate solar flare.
What was more unusual, however, was what happened next.
Plasma in the nearby
solar corona
was imaged cooling and falling back, a phenomenon known as
coronal rain.
Because they are electrically charged,
electrons,
protons, and
ions in the rain were
gracefully channeled along existing
magnetic loops near the Sun's surface,
making the scene appear as a surreal three-dimensional sourceless waterfall.
The resulting
surprisingly-serene spectacle is shown in
ultraviolet light
and highlights matter glowing at a temperature of about 50,000
Kelvin.
Each second in the
featured time lapse video
takes about 6 minutes in real time, so that the entire
coronal rain sequence lasted about 10 hours.
Recent observations have confirmed that that coronal rain can also occur in smaller loops for as long as 30 hours.
 APOD: 2018 April 9 - The Sun Unleashed: Monster Filament in Ultraviolet
APOD: 2018 April 9 - The Sun Unleashed: Monster Filament in Ultraviolet
Explanation:
One of the most spectacular solar sights is an explosive flare.
In 2011 June, the Sun unleashed somewhat impressive,
medium-sized solar flare as rotation carried
active regions
of sunpots toward the solar limb.
That flare,
though, was followed by an
astounding gush of magnetized
plasma -- a monster filament seen erupting at the Sun's edge
in this extreme ultraviolet image from NASA's
Solar Dynamics Observatory.
Featured here is a time-lapse video of
that hours-long event showing darker, cooler
plasma raining down across a broad area of the Sun's surface,
arcing along otherwise invisible
magnetic field lines.
An associated coronal mass ejection,
a massive cloud of high energy
particles, was blasted in the general direction of the
Earth,and made a glancing blow to
Earth's magnetosphere.
 APOD: 2018 February 4 - Venus and the Triply Ultraviolet Sun
APOD: 2018 February 4 - Venus and the Triply Ultraviolet Sun
Explanation:
An unusual type of solar eclipse occurred in 2012.
Usually it is the
Earth's Moon that
eclipses the Sun.
That year, most unusually, the planet
Venus took a turn.
Like a solar eclipse by the Moon, the phase of Venus became a continually thinner
crescent as Venus became increasingly
better aligned with the Sun.
Eventually the alignment became perfect and the
phase of Venus dropped to zero.
The dark spot of Venus crossed our parent star.
The situation could technically be labeled a Venusian
annular eclipse with an extraordinarily large
ring of fire.
Pictured here during the occultation, the Sun was imaged in three colors of ultraviolet light by the Earth-orbiting
Solar Dynamics Observatory,
with the dark region toward the right corresponding to a
coronal hole.
Hours later, as Venus continued in its orbit, a
slight crescent phase appeared again.
The next Venusian transit across the Sun will occur in
2117.
 APOD: 2018 January 1 - Sun Halo over Sweden
APOD: 2018 January 1 - Sun Halo over Sweden
Explanation:
What's happened to the Sun?
Sometimes it looks like the Sun is being viewed through a giant
lens.
In the featured video, however, there are actually millions of tiny lenses:
ice crystals.
Water may freeze in the
atmosphere into small, flat, six-sided, ice crystals.
As these crystals flutter to the ground, much time is spent
with their
faces flat and parallel to the ground.
An observer may find themselves in the same plane as
many of the falling ice crystals near sunrise or sunset.
During this alignment, each crystal can act like a miniature lens,
refracting sunlight into our
view and creating
phenomena like parhelia, the technical term for
sundogs.
The
featured video was taken a month ago
on the side of a ski hill at the
Vemdalen Ski Resort in central
Sweden.
Visible in the center is the most direct image of the
Sun, while two bright
sundogs glow prominently from both the left and the right.
Also visible is the bright
22 degree halo -- as well as the rarer and much fainter
46 degree halo --
also created by
sunlight refracting through atmospheric ice
crystals.
 APOD: 2017 December 21 - Solstice Sun and Milky Way
APOD: 2017 December 21 - Solstice Sun and Milky Way
Explanation:
Welcome to
December's solstice, first day of winter in the north and
summer for the southern hemisphere.
Astronomical markers of the seasons,
solstice
and equinox dates are based
on the Sun's place in its annual journey along the ecliptic,
through planet Earth's sky.
At this solstice, the Sun reaches its maximum southern
declination of -23.5 degrees today at 16:28 UTC, while
its right ascension coordinate on the
celestial sphere
is 18 hours.
That puts the Sun in the constellation Sagittarius in a direction near
the center of our Milky Way galaxy.
In fact, if you could see today's Solstice Sun against faint background
stars and nebulae (that's really hard to do, especially in the daytime ...)
your view might look something like this composited panorama.
To make it, images of
our fair galaxy
were taken under dark Namibian night skies, then stitched together
in a panoramic view.
From a snapshot made on December 21, 2015, the Sun was digitally
overlayed as a brilliant star at today's northern winter
solstice position, close to the center of
the Milky Way.
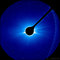 APOD: 2017 November 13 - Comet Machholz Approaches the Sun
APOD: 2017 November 13 - Comet Machholz Approaches the Sun
Explanation:
Why is Comet Maccholz so depleted of carbon-containing chemicals?
Comet 96P/Machholz's
original fame derives from its getting closer to the Sun than any other short period comet -- half as close as
Mercury --
and doing so every five years.
To better understand this unusual comet, NASA's Sun-monitoring
SOHO spacecraft tracked the comet during its latest
approach to the Sun in October.
The featured image composite shows the tail-enhanced comet swooping past the Sun.
The Sun's bright surface is hidden from view behind a dark occulter,
although parts of the Sun's extended
corona are visible.
Neighboring stars dot the background.
One hypothesis holds that these close solar approaches somehow cause
Comet Machholz to shed its
carbon,
while another hypothesis posits that the comet formed with
this composition
far away -- possibly even in
another star system.
 APOD: 2017 September 7 - The Flash Spectrum of the Sun
APOD: 2017 September 7 - The Flash Spectrum of the Sun
Explanation:
In clear Madras, Oregon skies, this colorful eclipse
composite captured the
elusive
chromospheric or flash spectrum of the Sun.
Only three exposures, made on August 21 with telephoto lens and
diffraction grating, are aligned in the frame.
Directly imaged at the far left, the Sun's
diamond ring-like appearance
at the beginning and end of totality brackets a
silhouette of the lunar disk at maximum eclipse.
Spread by the
diffraction grating into
the spectrum of colors toward the right, the Sun's
photospheric spectrum
traces the two continuous streaks.
They correspond to the diamond ring glimpses of the
Sun's normally overwhelming disk.
But individual eclipse images also appear at each wavelength of light
emitted by atoms along the thin, fleeting arcs of
the solar chromosphere.
The brightest images, or strongest
chromospheric emission,
are due to Hydrogen atoms.
Red hydrogen alpha emission is at the far right with blue
and purple hydrogen series emission to the left.
In between, the brightest yellow emission is caused by atoms of
Helium,
an element only first discovered in the
flash spectrum of the Sun.
 APOD: 2017 August 28 - A Fleeting Double Eclipse of the Sun
APOD: 2017 August 28 - A Fleeting Double Eclipse of the Sun
Explanation:
Last week, for a fraction of a second, the Sun was eclipsed twice.
One week ago today, many people in
North America
were treated to a standard, single,
partial solar eclipse.
Fewer people, all congregated along a narrow path, experienced the
eerie daytime darkness of a total solar eclipse.
A dedicated few with fast enough camera equipment, however, were able to capture a
double eclipse -- a simultaneous partial eclipse of the
Sun by both the
Moon and the
International Space Station (ISS).
The Earth-orbiting
ISS crossed the Sun in less than a second, but to keep the
ISS from appearing
blurry, exposure times must be less than 1/1000th of a second.
The featured image composite captured the
ISS
multiple times in succession as it zipped across the
face of the Sun.
The picture was taken from Huron, California in a
specific color
emitted by
hydrogen which highlights the
Sun's chromosphere,
a layer hotter and higher up than the usually photographed
photosphere.
 APOD: 2017 July 17 - Moon Shadow versus Sun Reflection
APOD: 2017 July 17 - Moon Shadow versus Sun Reflection
Explanation:
What are those lights and shadows crossing the Earth?
As the featured five-second
time-lapse video
progresses, a full day on planet Earth is depicted as seen from
Japan's
Himawari-8 satellite in
geostationary orbit high above the
Pacific Ocean.
The Sun rises to the right and sets to the left,
illuminating the
half of Earth that is most directly below.
A reflected image of the Sun -- a
Sun glint --
is visible as a bright spot that moves from right to left.
More unusual, though, is the
dark spot that moves from the lower left to upper right
That is the
shadow of the Moon,
and it can only appear when the Moon goes
directly between the Earth and the Sun.
Last year, on the day these images were taken, the most deeply shadowed
region experienced a
total eclipse of the Sun.
Next month
a similarly dark shadow will sweep
right across the USA.
 APOD: 2017 April 11 - Man, Dog, Sun
APOD: 2017 April 11 - Man, Dog, Sun
Explanation:
This was supposed to be a shot of trees in front of a setting Sun.
Sometimes, though, the unexpected can be photogenic.
During some planning shots, a
man walking his dog unexpected crossed the ridge.
The result was so striking that, after cropping, it became the main shot.
The reason the Sun
appears so large
is that the image was taken from about a kilometer away through a telephoto lens.
Scattering of blue light by the
Earth's atmosphere makes the bottom of the Sun appear slightly
more red that the top.
Also, if you look closely at
the Sun, just above the man's head, a large
group of sunspots
is visible.
The image was taken just last week in
Bad
Mergentheim,
Germany.
 APOD: 2017 February 19 - Black Sun and Inverted Starfield
APOD: 2017 February 19 - Black Sun and Inverted Starfield
Explanation:
Does this strange dark ball look somehow familiar?
If so, that might be because it is our Sun.
In the featured image from 2012, a
detailed solar view was captured originally in a
very specific color
of red light, then rendered in black and white, and then color inverted.
Once complete, the resulting image was added to a
starfield,
then also color inverted.
Visible in the image of the Sun are
long light filaments, dark active regions,
prominences peeking around the edge, and a
moving carpet
of hot gas.
The surface of our Sun can be a busy place, in particular during
Solar Maximum, the time when its surface
magnetic field
is wound up the most.
Besides an active Sun being so picturesque, the
plasma
expelled can also become picturesque when it impacts the
Earth's magnetosphere and creates
auroras.
 APOD: 2016 December 21 - Traces of the Sun
APOD: 2016 December 21 - Traces of the Sun
Explanation:
This
year the December Solstice
is today, December 21, at 10:44 UT, the first day of
winter in the north and summer in the south.
To celebrate, watch
this amazing timelapse video tracing the
Sun's apparent movement over an entire year from Hungary.
During the year, a fixed video camera captured an image every minute.
In total, 116,000 exposures follow the Sun's position across the field of
view, starting from the 2015 June 21 solstice through
the 2016 June 20 solstice.
The intervening 2015 December 22
solstice is at the bottom of the frame.
The timelapse sequences constructed show the Sun's movement over
one day to begin with, followed by traces of the
Sun's position during the days of one year, solstice to solstice.
Gaps in the daily curves are due to cloud cover.
The video ends with stunning animation sequences of analemmas,
those figure-8 curves you get by photographing the Sun
at the same time each day throughout a year, stepping across
planet Earth's sky.
 APOD: 2016 September 19 - 50000 Kilometers over the Sun
APOD: 2016 September 19 - 50000 Kilometers over the Sun
Explanation:
What's happening at the edge of the Sun?
Although it may look like a
monster is rampaging,
what is pictured is actually only a monster prominence -- a sheath of thin gas held above the surface by the
Sun's magnetic field.
The solar event was captured just this past weekend with a small telescope, with the resulting image then
inverted and
false-colored.
As indicated with illustrative lines, the
prominence
rises over 50,000 kilometers above the
Sun's surface,
making even our 12,700-diameter
Earth seem
small by comparison.
Below the
monster prominence is
active region 12585,
while light colored filaments can be seen hovering over a flowing
solar carpet of fibrils.
Filaments are actually prominences seen against the disk of the Sun, while similarly, fibrils are actually spicules
seen against the disk.
Energetic events like this are becoming less common as the Sun evolves toward a minimum in its
11-year activity cycle.
 APOD: 2016 May 8 - Mercurys Transit: An Unusual Spot on the Sun
APOD: 2016 May 8 - Mercurys Transit: An Unusual Spot on the Sun
Explanation:
What's that dot on the Sun?
If you look closely, it is almost perfectly round.
The dot is the result of an unusual type of
solar eclipse that occurred in 2006.
Usually it is the
Earth's Moon that eclipses the Sun.
This time, the planet
Mercury
took a turn.
Like the approach to New Moon before a
solar eclipse,
the phase of Mercury became a continually thinner
crescent as the planet
progressed toward an alignment with the Sun.
Eventually the phase of
Mercury dropped to zero and
the dark spot of
Mercury crossed our parent star.
The situation could technically be labeled a Mercurian
annular
eclipse with an extraordinarily large
ring of fire.
From above the
cratered planes
of the night side of
Mercury, the Earth appeared in its fullest phase.
Hours later, as Mercury continued in its orbit, a slight
crescent phase appeared again.
This was ten years ago -- the next Mercurian solar eclipse will
occur tomorrow.
 APOD: 2016 May 1 - Contemplating the Sun
APOD: 2016 May 1 - Contemplating the Sun
Explanation:
Have you contemplated your home star recently?
Featured here, a Sun partially eclipsed on the top left by the Moon is also seen eclipsed by
earthlings contemplating the eclipse below.
The spectacular menagerie of silhouettes was taken in 2012 from the
Glen Canyon National Recreation Area
near Page,
Arizona,
USA, where park rangers and astronomers expounded on the
unusual event to interested gatherers.
Also faintly visible on the Sun's disk,
just to the lower right of the dark Moon's disk, is a group of
sunspots.
Although a partial solar eclipse by the Moon is indeed a good chance to contemplate the Sun, a great chance -- and one that is significantly
more rare -- will occur
next week when the Sun undergoes a partial eclipse by the
planet Mercury.
 APOD: 2016 March 12 - The Flash Spectrum of the Sun
APOD: 2016 March 12 - The Flash Spectrum of the Sun
Explanation:
In a flash, the
visible spectrum of the Sun changed from
absorption to emission on March 9
during the total solar eclipse.
That fleeting moment, at the beginning the total
eclipse phase, is captured by telephoto lens and
diffraction grating in this image from clearing skies over
Ternate, Indonesia.
At left, the overwhelming light from the Sun is just blocked
by the lunar disk.
The normally dominant absorption spectrum of the
solar photosphere is hidden.
What remains, spread by the
diffraction grating into
the spectrum of colors to the right of the eclipsed Sun,
are individual eclipse images.
The images appear at each wavelength of light
emitted by atoms along the thin visible arc of
the solar chromosphere and in an
enormous prominence extending beyond the Sun's upper limb.
The brightest images, or strongest
chromospheric emission lines,
are due to Hydrogen atoms that produce the red hydrogen
alpha emission at the far right and blue hydrogen beta
emission to the left.
In between, the bright yellow emission image is caused by atoms of
Helium,
an element only first discovered in the
flash spectrum of the Sun.
 APOD: 2016 January 10 - Sun Storm: A Coronal Mass Ejection
APOD: 2016 January 10 - Sun Storm: A Coronal Mass Ejection
Explanation:
What's happening to our Sun?
Another
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME)!
The Sun-orbiting
SOHO spacecraft has imaged many
erupting filaments lifting off
the active solar surface and blasting enormous bubbles of
magnetic plasma into space.
Direct light from the sun is blocked in the inner part of the
featured image, taken in 2002, and replaced by a simultaneous image of the Sun in
ultraviolet light.
The field of view extends over two million kilometers from the
solar surface.
While hints of
these explosive events, called
coronal mass ejections or CMEs,
were discovered by spacecraft in the early 70s,
this dramatic image is part of a detailed record
of this CME's development from the presently operating
SOHO spacecraft.
Near the maximum of the
solar activity cycle,
CMEs now typically occur several times a week.
Strong CMEs may profoundly influence
space weather.
Those directed toward our planet can have
serious effects.
 APOD: 2015 June 29 - Sunspot Group AR 2339 Crosses the Sun
APOD: 2015 June 29 - Sunspot Group AR 2339 Crosses the Sun
Explanation:
How do sunspots evolve?
Large dark
sunspots -- and the active regions that contain them -- may last for weeks, but all during that time they are constantly changing.
Such variations were particularly apparent a few weeks ago as the active region
AR 2339
came around the limb of the Sun and was tracked for the next 12 days by NASA's
Solar Dynamic Observatory.
In the
featured time lapse video,
some sunspots drift apart, while others merge.
All the while, the dark central
umbral regions
shift internally and their surrounding lighter penumbras shimmer and wave.
The surrounding
Sun
appears to flicker as the carpet of yellow
granules come and go on the time scale of hours.
In general, sunspots
are relatively cool regions where the local
magnetic field
pokes through the Sun's surface and inhibits heating.
Over the past week, an even more active region --
AR 2371 -- has been crossing the Sun and releasing powerful flares that have resulted in
impressive auroras here on Earth.
 APOD: 2015 June 28 - All the Colors of the Sun
APOD: 2015 June 28 - All the Colors of the Sun
Explanation:
It is still not known why the Sun's light is missing some colors.
Here are all the
visible
colors of the
Sun,
produced by passing the Sun's light through a
prism-like device.
The spectrum was created at the
McMath-Pierce Solar Observatory
and shows, first off, that although our
white-appearing
Sun emits light of nearly
every color, it does indeed appear brightest in yellow-green light.
The dark patches in the
above spectrum arise from gas at or above the
Sun's surface
absorbing sunlight emitted below.
Since different types of gas
absorb different colors of light,
it is possible to determine what gasses compose the Sun.
Helium, for example, was
first discovered
in 1870 on a solar spectrum and only
later found here on
Earth.
Today, the majority of
spectral absorption lines have been identified - but
not all.
 APOD: 2015 April 30 - Across the Sun
APOD: 2015 April 30 - Across the Sun
Explanation:
A long solar filament stretches across the relatively calm
surface of the Sun in this telescopic snap shot from April 27.
The negative or inverted
narrowband image was made in the light of
ionized hydrogen atoms.
Seen at the upper left, the magnificent curtain of magnetized plasma
towers above surface and actually reaches beyond the Sun's edge.
How long is the solar filament?
About as long as the distance from Earth to Moon, illustrated
by the scale insert at the left.
Tracking toward the right across
the solar disk a day later
the long filament erupted, lifting away from the Sun's surface.
Monitored by
Sun
staring satellites, a coronal mass ejection was
also blasted from the site but is expected to swing wide of
our fair planet.
 APOD: 2015 April 3 - Sun and Moon Halo
APOD: 2015 April 3 - Sun and Moon Halo
Explanation:
Two pictures captured on April 1
are combined in this
creative
day
and
night
composite.
Separated in time by about 10 hours the images otherwise match, looking
along the coast at Östersund Sweden.
The relative times were chosen to show the Sun and a nearly full Moon
at the same place in the
cold, early springtime sky.
In the night scene Jupiter also shines above the waterfront lights,
while Sun and Moon are both surrounded by a beautiful circular ice halo.
The Sun and Moon halos really do align, each with an
angular radius of 22 degrees.
That radius is a constant, not determined by the brightness
of Sun or Moon but
only
by the hexagonal geometry of
atmospheric
ice crystals
and the reflection and refraction of light.
Of course tomorrow, April 4, will find the Sun and Moon
on opposite sides of planet Earth for a
total lunar eclipse.
 APOD: 2015 March 22 - A Double Eclipse of the Sun
APOD: 2015 March 22 - A Double Eclipse of the Sun
Explanation:
Can the Sun be eclipsed twice at the same time?
Last Friday was noteworthy because part of the Earth was treated to a rare
total eclipse of the Sun.
But also on Friday, from a
part of the Earth
that only saw part of the Sun eclipsed, a second object
appeared simultaneously in front of the Sun: the Earth-orbiting
International Space Station.
Although
space station
eclipses are very quick -- in this case only 0.6 seconds, they are
not so rare.
Capturing this composite image took a lot of planning and a little luck,
as the photographer had to dodge a series of third objects that kept,
annoyingly, also lining up in front of the Sun:
clouds.
The above superposed time-lapse sequence was taken from
Fregenal de la Sierra in southern
Spain.
The dark disk of the Moon dominates the lower right, while the
Sun's textured surface shows several
filaments and, over an edge, a
prominence.
 APOD: 2015 February 21 - 45 Days in the Sun
APOD: 2015 February 21 - 45 Days in the Sun
Explanation:
From January 11 to February 25 2013, a pinhole
camera sat in a field near Budapest,
Hungary, planet Earth to create this intriguing
solargraph.
And for 45 days, an old Antonov An-2 biplane stood still
while the Sun rose and set.
The camera's continuous exposure began about 20 days after the
northern hemispere's
winter
solstice, so each day
the Sun's trail arcs steadily higher through the sky.
These days in the Sun were recorded on a piece of black and white
photosensitive paper tucked in to the simple plastic film container.
The long exposure produced a visible
color image on the paper that was then digitally scanned.
Of course, cloudy days left gaps in the
solargraph's
Sun trails.
 APOD: 2015 February 17 - Fibrils Flower on the Sun
APOD: 2015 February 17 - Fibrils Flower on the Sun
Explanation:
When does the Sun look like a flower?
In a specific color of red light emitted by hydrogen, as
featured here, some regions of the
solar chromosphere may resemble a
rose.
The color-inverted image was taken in 2014 October and shows
active solar region 2177.
The petals dominating the frame are actually magnetically confined tubes of hot
plasma called
fibrils,
some of which extend longer than the diameter of the Earth.
In the central
region many of these fibrils are seen end-on, while the surrounding regions are typically populated with curved fibrils.
When seen over the Sun's edge, these huge plasma tubes are called
spicules,
and when they occur in passive regions they are termed
mottles.
Sunspot
region 2177 survived for several more days before the complex and tumultuous
magnetic field
poking through the
Sun's surface evolved yet again.
 APOD: 2015 February 10 - An Extremely Long Filament on the Sun
APOD: 2015 February 10 - An Extremely Long Filament on the Sun
Explanation:
Yesterday, the Sun exhibited one of the longest filaments ever recorded.
It may still be there today.
Visible as the dark streak just below the center in the featured image,
the enormous filament extended across the face of the Sun a distance
even longer than the Sun's radius -- over 700,000 kilometers.
A filament is actually
hot gas held aloft
by the Sun's magnetic field, so that viewed from the side it would appear as a
raised prominence.
The featured image shows the filament in
light emitted by hydrogen and therefore highlights the
Sun's chromosphere.
Sun-following telescopes including NASA's
Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) are tracking
this unusual feature, with SDO yesterday recording a
spiraling magnetic field engulfing it.
Since
filaments
typically last only from hours to days, parts of this one may
collapse or
erupt at any time, either returning hot plasma back to the Sun or
expelling it into the Solar System.
Is the filament still there?
You can check by clicking on
SDO's current solar image.
 APOD: 2014 December 29 - The Sun in X rays from NuSTAR
APOD: 2014 December 29 - The Sun in X rays from NuSTAR
Explanation:
Why are the regions above sunspots so hot?
Sunspots themselves are a bit cooler than the surrounding solar surface because the magnetic fields that create them reduce convective heating.
It is therefore unusual that regions overhead -- even much higher up in the Sun's corona -- can be hundreds of times hotter.
To help find the cause,
NASA directed the Earth-orbiting
Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR)
satellite to point its very sensitive X-ray telescope at the Sun.
Featured above is the Sun in ultraviolet light,
shown
in a red hue as taken by the orbiting
Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO).
Superimposed in false-colored green and blue is emission above sunspots detected by
NuSTAR in different bands of
high-energy
X-rays,
highlighting regions of extremely
high temperature.
Clues about the Sun's atmospheric
heating
mechanisms may not only come from this initial image,
but future NuSTAR images aimed at finding hypothesized
nanoflares,
brief bursts of energy that may drive the unusual heating.
 APOD: 2014 October 27 - Plane, Clouds, Moon, Spots, Sun
APOD: 2014 October 27 - Plane, Clouds, Moon, Spots, Sun
Explanation:
What's that in front of the Sun?
The closest object is an
airplane, visible just below the Sun's center and caught purely by chance.
Next out are numerous clouds in
Earth's atmosphere, creating a series of darkened horizontal streaks.
Farther out is Earth's Moon, seen as the large dark circular bite on the upper right.
Just above the airplane and just below the Sun's surface are sunspots.
The main sunspot group captured here,
AR 2192, is one of the largest ever recorded and has been
crackling and bursting with
flares since it came around the edge of the Sun early last week.
Taken last Thursday, this show of solar silhouettes was unfortunately short-lived.
Within a few seconds the plane flew away.
Within a few minutes the clouds drifted off.
Within a few hours the
partial solar eclipse of the Sun by the Moon was over.
Only the sunspot group remains, but within a few more days even AR 2192 will disappear around the edge of the Sun.
Fortunately, when it comes to the Sun, even
unexpected alignments are
surprisingly frequent.
 APOD: 2014 October 7 - From the Temple of the Sun to the Temple of the Moon
APOD: 2014 October 7 - From the Temple of the Sun to the Temple of the Moon
Explanation:
What connects the Sun to the Moon?
Many answers have been given throughout
history, but in the case of today's featured image, it appears to be the plane of our
Milky Way Galaxy.
The 16-image panorama was taken in
Capitol Reef National Park,
Utah, USA where two
sandstone monoliths -- the Temple of the Moon on the right and the
Temple of the Sun
on the left -- rise dramatically from the desert.
Each
natural monument
stands about 100 meters tall and survives from the
Jurassic period 160 million years ago.
Even older are many of the stars and nebulas that dot the celestial background, including the
Andromeda Galaxy.
Tomorrow the Earth will connect the Sun to the Moon by way of its shadow: a
total lunar eclipse will be visible from many locations around the globe.
 APOD: 2014 August 24 - Mercury's Transit: An Unusual Spot on the Sun
APOD: 2014 August 24 - Mercury's Transit: An Unusual Spot on the Sun
Explanation:
What's that dot on the Sun?
If you look closely, it is almost perfectly round.
The dot is the result of an unusual type of
solar eclipse that occurred in 2006.
Usually it is the
Earth's Moon that eclipses the Sun.
This time, the planet
Mercury
took a turn.
Like the approach to New Moon before a
solar eclipse,
the phase of Mercury became a continually thinner
crescent as the planet
progressed toward an alignment with the Sun.
Eventually the phase of
Mercury dropped to zero and
the dark spot of Mercury crossed our parent star.
The situation could technically be labeled a Mercurian
annular
eclipse with an extraordinarily large
ring of fire.
From above the
cratered planes
of the night side of Mercury, the Earth appeared in its fullest phase.
Hours later, as Mercury continued in its orbit, a slight
crescent phase appeared again.
The next Mercurian solar eclipse
will occur in 2016.
 APOD: 2014 June 4 - A Green Flash from the Sun
APOD: 2014 June 4 - A Green Flash from the Sun
Explanation:
Many think it is just a myth.
Others think it is true but its cause isn't known.
Adventurers pride themselves on having seen it.
It's a green flash from the
Sun.
The truth is the
green flash
does exist and its cause is well understood.
Just as the setting
Sun disappears completely from view,
a last glimmer appears startlingly
green.
The effect is typically visible only from locations with a low,
distant horizon, and lasts just a few seconds.
A green flash is also visible for a rising
Sun, but takes better timing to spot.
A dramatic
green flash, as well as an even more rare
red flash, was caught in the
above photograph recently
observed
during a sunset visible from the
Observatorio del Roque de Los Muchachos in the
Canary Islands,
Spain.
The Sun itself does not turn
partly
green or red --
the effect is caused by layers of the
Earth's atmosphere acting like a prism.
 APOD: 2014 May 6 - Orange Sun Sparking
APOD: 2014 May 6 - Orange Sun Sparking
Explanation:
Our Sun has become quite a busy place.
Taken only two weeks ago, the
Sun was captured sporting numerous tumultuous regions including active sunspot regions
AR 2036 near the image top and AR 2038 near the center.
Only four years ago the Sun was emerging from an
unusually quiet
Solar Minimum that had lasted for years.
The above image was recorded in a
single color of light called
Hydrogen Alpha, inverted, and false colored.
Spicules cover much of the Sun's face like a carpet.
The gradual brightening towards the Sun's edges is caused by
increased absorption of relatively cool solar gas and called
limb darkening.
Just over the Sun's edges, several filamentary prominences protrude,
while prominences on the Sun's face are seen as light streaks.
Possibly the most visually interesting of all are the magnetically tangled active regions containing relatively cool sunspots, seen as white dots.
Currently at Solar Maximum -- the most active phase in its 11-year magnetic cycle, the Sun's twisted magnetic field is creating numerous solar
"sparks" which include eruptive solar prominences,
coronal mass ejections,
and flares which emit clouds of particles
that may impact the Earth and cause auroras.
One flare two years ago
released such a torrent of charged particles
into the Solar System that it might have disrupted satellites and compromised power grids had it
struck planet Earth.
 APOD: 2014 April 30 - A Partially Eclipsed Setting Sun
APOD: 2014 April 30 - A Partially Eclipsed Setting Sun
Explanation:
If you look closely, you will see something quite unusual about this setting Sun.
There are birds flying to the Sun's left, but that's
not
so
unusual.
A dark sea covers the Sun's bottom, and dark clouds cover parts of the middle, but they are also
not
very
unusual.
More unusual is the occulted piece at the top right.
And that's no occulting cloud --
that's
the
Moon.
Yesterday the Moon moved in front of part of the Sun as visible from
Australia, and although many locations reported annoying clouds, a
partially eclipsed Sun would occasionally peek through as it set.
The above image was captured yesterday on the western horizon of
Adelaide,
South Australia.
The maximum eclipse was visible only from a small part of
Antarctica
where the entire Moon could be seen covering the
entire center of the Sun in what is known as an
annular eclipse, leaving only a
ring of fire from the Sun
peeking out around the edges.
The
next solar eclipse will be another
partial eclipse,
will occur on 2014 October 23, and will be visible from most of
North America
near sunset.
 APOD: 2014 March 12 - The Sun Rotating
APOD: 2014 March 12 - The Sun Rotating
Explanation:
Does the Sun change as it rotates?
Yes, and the changes can vary from subtle to dramatic.
In the
above time-lapse sequences,
our Sun -- as imaged by
NASA's
Solar Dynamics Observatory --
is shown rotating though the entire month of January.
In the large image on the left, the solar
chromosphere is depicted in
ultraviolet light, while the smaller and lighter
image to its upper right simultaneously shows the more familiar solar
photosphere in visible light.
The rest of the inset six Sun images highlight
X-ray emission
by relatively rare iron atoms located at different heights of the
corona, all
false-colored
to accentuate differences.
The Sun takes just under a month to
rotate
completely -- rotating fastest at the equator.
A large and active
sunspot region rotates into view soon after the video starts.
Subtle effects include changes in
surface texture and the shapes of active regions.
Dramatic effects include numerous flashes in active regions, and fluttering and
erupting prominences visible all around the Sun's edge.
This year our Sun is near its
Solar maximum
activity of its 11-year magnetic cycle.
As the video ends, the same large and active sunspot region previously mentioned rotates back into view, this time
looking different.
 APOD: 2014 March 4 - Sun and Prominence
APOD: 2014 March 4 - Sun and Prominence
Explanation:
Dramatic prominences can sometimes be seen looming just beyond the edge of the sun.
Such was the case last week as a large prominence,
visible above, highlighted a highly active recent Sun.
A waving sea of hot gas
is visible in the foreground chromosphere in great detail as it was imaged in one
specific color
of light emitted by hydrogen.
A solar prominence is a cloud of solar gas held just above the surface by the
Sun's magnetic field.
The Earth, illustrated in the inset,
is smaller than the prominence.
Although very hot, prominences typically
appear dark when viewed against the
Sun,
since they are slightly cooler than the
photosphere below them.
A quiescent prominence
typically lasts about a month, and may
erupt in a
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) expelling hot gas into the
Solar System, some of which may strike the Earth and trigger
auroras.
 APOD: 2013 December 21 - SDO's Multiwavelength Sun
APOD: 2013 December 21 - SDO's Multiwavelength Sun
Explanation:
Today, the solstice
is at 17:11 Universal Time, the Sun reaching the
southernmost declination in its yearly journey through planet Earth's
sky.
The December
solstice marks the astronomical beginning of winter in the
northern hemisphere and summer in the south.
To celebrate, explore this creative visualization of the Sun from
visible to extreme ultraviolet wavelengths, using image data from the
orbiting Solar Dynamics Observatory
(SDO).
Against a base image made at a
visible wavelengths,
the wedge-shaped segments show the solar disk at
increasingly shorter ultraviolet and extreme ultraviolet wavelengths.
Shown in false-color and rotating in a clockwise direction,
the filters decrease in wavelength from
170 nanometers
(in pink) through 9.4 nanometers (green).
At shorter wavelengths, the altitude and temperature of
the regions revealed in the solar atmosphere tend to increase.
Bright at visible wavelengths, the solar photosphere looks darker in
the ultraviolet, but sunspots glow
and bright plasma
traces looping magnetic fields.
Watch the filters sweep around the solar disk in
this
animation of SDO's multiwavelength view of the Sun.
 APOD: 2013 November 15 - The Flash Spectrum of the Sun
APOD: 2013 November 15 - The Flash Spectrum of the Sun
Explanation:
In a flash, the
visible spectrum of the Sun changed from
absorption to emission on November 3rd,
during the brief total phase of a solar eclipse.
That
fleeting moment is captured by telephoto lens and
diffraction grating in this well-timed image
from clearing skies over Gabon in equatorial Africa.
With overwhelming light from the Sun's disk
blocked by the Moon, the normally dominant
absorption spectrum of the solar photosphere is hidden.
What remains, spread by the
diffraction grating into
the spectrum of colors to the right of the eclipsed Sun,
are individual eclipse images at each wavelength of light
emitted by atoms along the thin arc of
the solar chromosphere.
The brightest images, or strongest
chromospheric emission lines,
are due to Hydrogen atoms that produce the red hydrogen
alpha emission at the far right and blue hydrogen beta
emission to the left.
In between, the bright yellow emission image is caused by atoms of Helium,
an element only first discovered in the
flash spectrum of the Sun.
 APOD: 2013 November 11 - An Active Sun During a Total Eclipse
APOD: 2013 November 11 - An Active Sun During a Total Eclipse
Explanation:
Sometimes, a total eclipse of the Sun is an opportunity.
Taking advantage of such, the above image shows the
solar eclipse earlier this month
as covered and uncovered by several different solar observatories.
The innermost image shows the Sun in
ultraviolet light as recorded over a few hours by the
SWAP instrument aboard the
PROBA2 mission in a
sun-synchronous low Earth orbit.
This image is surrounded by a ground-based eclipse image, reproduced
in blue, taken from
Gabon.
Further out is a circularly blocked region used to artificially dim the central sun by the
LASCO instrument aboard the Sun-orbiting
SOHO spacecraft.
The outermost image -- showing the outflowing
solar corona -- was taken by LASCO ten minutes after the eclipse and shows an outflowing solar corona.
Over the past few weeks, our Sun has been showing an
unusually high
amount of
sunspots,
CMEs, and
flares -- activity that was generally expected as the Sun is currently going through
Solar Maximum -- the busiest part of its 11 year
solar cycle.
The above resultant image is a picturesque montage of many solar layers at once that allows
solar astronomers to better match up active areas on or near the Sun's surface with
outflowing jets in the Sun's corona.
 APOD: 2013 October 2 - All the Colors of the Sun
APOD: 2013 October 2 - All the Colors of the Sun
Explanation:
It is still not known why the Sun's light is missing some colors.
Here are all the
visible colors of the
Sun,
produced by passing the Sun's light through a
prism-like device.
The spectrum was created at the
McMath-Pierce Solar Observatory
and shows, first off, that although our
white-appearing
Sun emits light of nearly
every color, it does indeed appear brightest in yellow-green light.
The dark patches in the
above spectrum arise from gas at or above the
Sun's surface
absorbing sunlight emitted below.
Since different types of gas
absorb different colors of light,
it is possible to determine what gasses compose the Sun.
Helium, for example, was
first discovered
in 1870 on a solar spectrum and only
later found here on
Earth.
Today, the majority of
spectral absorption lines have been identified - but
not all.
 APOD: 2013 August 20 - Venus and the Triply Ultraviolet Sun
APOD: 2013 August 20 - Venus and the Triply Ultraviolet Sun
Explanation:
An unusual type of solar eclipse occurred last year.
Usually it is the
Earth's Moon that
eclipses
the Sun.
Last June, most unusually, the planet
Venus took a turn.
Like a solar eclipse by the Moon, the phase of Venus became a continually thinner
crescent as Venus became increasingly
better aligned with the Sun.
Eventually the alignment became perfect and the
phase of Venus dropped to zero.
The dark spot of Venus crossed our parent star.
The situation could technically be labeled a Venusian
annular eclipse with an extraordinarily large
ring of fire.
Pictured above
during the occultation, the Sun was imaged in three colors of ultraviolet light by the Earth-orbiting
Solar Dynamics Observatory,
with the dark region toward the right corresponding to a
coronal hole.
Hours later, as Venus continued in its orbit, a
slight crescent phase appeared again.
The next Venusian solar eclipse will occur in
2117.
 APOD: 2013 May 20 - Blue Sun Bursting
APOD: 2013 May 20 - Blue Sun Bursting
Explanation:
Our Sun is not a giant blueberry.
Our Sun can be made to
appear similar to the
diminutive fruit, however,
by imaging it in a
specific color
of extreme violet light called
CaK
that is emitted by the very slight abundance of ionized Calcium in the
Sun's atmosphere,
and then false color-inverting the image.
This solar depiction
is actually scientifically illuminating as a level of the Sun's
chromosphere
appears quite prominent, showing a crackly textured surface, cool
sunspots appearing distinctly bright,
and surrounding hot active regions
appearing distinctly dark.
The Sun is currently near the
maximum
activity level in its 11 year cycle, and has emitted
powerful flares over the past week.
During times of high activity, streams of energetic particles
from Sun may impact the
Earth's magnetosphere and
set off
spectacular auroras.
 APOD: 2012 December 18 - A Sun Pillar Over Sweden
APOD: 2012 December 18 - A Sun Pillar Over Sweden
Explanation:
Have you ever seen a
sun pillar?
When the air is cold and the Sun is rising or
setting, falling ice
crystals
can reflect sunlight and create an
unusual column of light.
Ice sometimes forms flat, six-sided
shaped crystals as it falls from high-level
clouds.
Air resistance causes these crystals to lie nearly
flat much of the time as they flutter to the ground.
Sunlight reflects off crystals that are
properly aligned, creating the
sun-pillar
effect.
In the
above picture
taken last week, a
sun-pillar reflects light from a Sun setting over
�stersund,
Sweden.
 APOD: 2012 October 15 - Black Sun and Inverted Starfield
APOD: 2012 October 15 - Black Sun and Inverted Starfield
Explanation:
Does this strange dark ball look somehow familiar?
If so, that might be because it is our Sun.
In the above image, a
detailed solar view
was captured originally in a
very specific color
of red light, then rendered in black and white, and then color inverted.
Once complete, the resulting image was added to a starfield, then also color inverted.
Visible in the above image of the Sun are
long light filaments, dark active regions,
prominences peeking around the edge, and a
moving carpet
of hot gas.
The surface of our Sun has become a particularly busy place over the
past two years because it is now nearing
Solar Maximum, the time when its surface
magnetic field
is wound up the most.
Besides an active Sun being so picturesque, the
plasma
expelled can also become picturesque when it impacts the
Earth's magnetosphere and creates
auroras.
 APOD: 2012 September 23 - Equinox: The Sun from Solstice to Solstice
APOD: 2012 September 23 - Equinox: The Sun from Solstice to Solstice
Explanation:
Yesterday was an equinox, a date when day and night are equal.
Today, and every day until the next
equinox,
the night will be longer than the day in Earth's northern hemisphere,
and the day will be longer than the night in Earth's southern hemisphere.
An equinox
occurs midway between the two
solstices,
when the days and nights are the least equal.
The picture is a composite of hourly images taken of the Sun above
Bursa,
Turkey on key days from solstice to
equinox to solstice.
The bottom Sun band was taken during the
winter solstice in 2007 December, when
the Sun could not rise very high in the sky nor stay above the
horizon very long.
This lack of Sun caused
winter.
The top Sun band was taken during the
summer solstice in 2008 June, when the
Sun rose highest in the
sky and
stayed above the horizon for more than 12 hours.
This abundance of Sun caused
summer.
The middle band was taken during the
Vernal Equinox in 2008 March, but it is the same sun band that
Earthlings saw yesterday, the day of the
Autumnal Equinox.
 APOD: 2012 August 20 - A Filament Across the Sun
APOD: 2012 August 20 - A Filament Across the Sun
Explanation:
Is that a cloud hovering over the Sun?
Yes, but it is quite different than a cloud hovering over the Earth.
The long light feature on the left of the
above color-inverted image
is actually a solar filament and is composed of mostly charged
hydrogen gas held aloft by the Sun's
looping magnetic field.
By contrast, clouds over the Earth are usually much
cooler,
composed mostly of tiny water droplets, and are
held aloft
by upward air motions because they are weigh so little.
The above filament was captured on the Sun about two weeks ago near the
active solar region
AR 1535 visible on the
right with dark sunspots.
Filaments typically last for a few days to a week, but a long
filament
like this might hover over the Sun's surface for a month or more.
Some filaments trigger large
Hyder flares
if they suddenly collapse back
onto the Sun.
 APOD: 2012 June 20 - Venus Transits the Midnight Sun
APOD: 2012 June 20 - Venus Transits the Midnight Sun
Explanation:
Today's solstice,
the astronomical beginning of summer in the north,
is at 23:09 UT when the Sun reaches the northernmost declination in
its yearly trek through planet Earth's sky.
While most in the northern hemisphere will experience the longest
day of the year,
for some the Sun won't set at all,
still standing just above the horizon at midnight as
far south as about 66.6 degrees northern latitude.
Of course, as summer comes to the north the midnight Sun comes earlier
to higher latitudes.
Recorded near midnight,
this
time series from June 6 follows the Sun
gliding above a mountainous horizon
from a latitude of 69 degrees north.
The remarkable scene looks north over the Norwegian Sea from
Sortland, Norway.
The 2012 transit of Venus
is already in progress, with Earth's
sister planet in silhouette at the upper left against the bright
disk of the midnight Sun.
 APOD: 2012 June 8 - When Venus Rises with the Sun
APOD: 2012 June 8 - When Venus Rises with the Sun
Explanation:
This dramatic telephoto view
across the Black Sea on June 6
finds Venus rising with the Sun,
the planet in silhouette against a ruddy and ragged solar disk.
Of course, the reddened light is due to scattering in planet
Earth's atmosphere and the rare
transit of Venus didn't
influence the strangely shaped and distorted Sun.
In fact, seeing the Sun in the shape of an
Etruscan Vase
is relatively common, especially compared to
Venus transits.
At sunset and sunrise, the effects of atmospheric refraction
enhanced by long, low, sight lines and strong
atmospheric temperature gradients produce the
visual distortions and mirages.
That situation is often favored by a
sea horizon.
 APOD: 2012 June 5 - Live: Watching for Venus to Cross the Sun
APOD: 2012 June 5 - Live: Watching for Venus to Cross the Sun
Explanation:
Today Venus moves in front of the Sun.
One way to
follow this rare event
is to actively reload the above live image of the Sun during the
right time interval
and look for an unusual circular dark dot.
The smaller sprawling dark areas are
sunspots.
The circular dot is the planet
Venus.
The dark dot will only appear during a few very specific hours,
from about 22:10 on 2012 June 5 through 4:50 2012 June 6,
Universal
Time.
This transit is the rarest type of solar eclipse known --
much more rare than an eclipse of the Sun by
the Moon or even by the
planet Mercury.
In fact, the next transit of Venus across the Sun will be in 2117.
Anyone with a
clear view of the Sun can go outside and
carefully view
the transit for themselves by projecting sunlight through a
hole in a card
onto a wall.
Because this
Venus transit is so unusual and
visible from so much of the Earth, it is expected to be one of the
more photographed celestial events in history.
The above live image on the Sun is being taken by the Earth-orbiting
Solar
Dynamics Observatory and can be updated about every 15 minutes.
Editor's note: Since the transit has ended, the live image was replaced by one taken just before Venus crossed out of Sun.
 APOD: 2012 May 28 - Contemplating the Sun
APOD: 2012 May 28 - Contemplating the Sun
Explanation:
Have you contemplated your home star recently?
Pictured above, a Sun partially eclipsed on the top left by the Moon is also seen eclipsed by
earthlings contemplating the eclipse below.
The above menagerie of silhouettes was taken from the
Glen Canyon National Recreation Area
near Page,
Arizona,
USA, where park rangers and astronomers expounded on the
unusual event to interested gatherers.
Also faintly visible on the Sun's disk, just to the lower right of the dark Moon's
disk, is a group of
sunspots.
Although exciting, some consider this event a warm-up act for next week's
chance to comtemplate the Sun -- a much more rare partial eclipse by the
planet Venus.
 APOD: 2012 May 11 - Sun vs Super Moon
APOD: 2012 May 11 - Sun vs Super Moon
Explanation:
The Super Moon wins, by just a little, when
its apparent size is
compared to the Sun in this ingenious composite picture.
To make it, the Full Moon on May 6 was photographed
with the same camera and telescope used to image the Sun
(with a dense solar filter!) on the following day.
Of course, on May 6 the
Moon was at perigee,
the closest point to Earth in its eliptical orbit,
making it the largest Full Moon of 2012.
Two weeks later, on May 20, the
Moon will be near
apogee, the most distant point in its orbit, so by then it will
be nearly at its smallest apparent size.
It will also be a dark
New Moon on that date.
And for some the New Moon will be surprisingly easy
to compare to the Sun, because on
May 20 the
first solar eclipse of 2012
will be visible from much of Asia, the Pacific, and North America.
Along a path 240 to 300 kilometers wide, the
eclipse will
be annular.
Near apogee the smaller silhouetted Moon will fit just
inside the bright solar disk.
 APOD: 2012 March 19 - Sunspot Group 1429 and the Distant Sun
APOD: 2012 March 19 - Sunspot Group 1429 and the Distant Sun
Explanation:
What's that on the
Sun?
Over the past two weeks, one of the most energetic sunspot regions of recent years crossed the face of the Sun.
Active Region 1429, visible above as the group of dark spots on the Sun's upper right, blasted out several
solar flares and
coronal mass ejections
since coming around the
edge of the Sun almost a month ago.
Fast moving particles from these
solar explosions have impacted
the Earth and been responsible for many colorful auroras seen over the past two weeks.
The picturesque foreground features trees and birds near
Merida,
Spain, where the above image was taken about a week ago.
Although AR 1429 has continued to rotate
to the right and gone around the limb of the Sun -- as seen from the Earth -- monitoring of the region will be continued by one of the
STEREO satellites, however, which is orbiting the
Sun well ahead of the Earth.
 APOD: 2011 December 22 - Through a Sun Tunnel
APOD: 2011 December 22 - Through a Sun Tunnel
Explanation:
Today the Sun stands still at 05:30 UT.
Halting its steady march toward southern declinations and
begining its annual journey north, the event is known as
a solstice.
In the northern hemisphere
December's solstice marks
the astronomical start of winter.
And if you're in
the Great Basin Desert outside of
Lucin, Utah, USA, near solstice dates you can watch the Sun rise
and set through
Sun Tunnels.
A monumental earthwork by artist Nancy Holt, the Sun Tunnels are
constructed of four 9 foot diameter cast concrete pipes each 18 feet long.
The tunnels are arranged in a wide X
to achieve the solstitial sunset and sunrise alignments.
In this dramatic snapshot through a Sun Tunnel
the Sun is just on the horizon.
The cold, cloudy sunset was near the
2010 winter solstice.
During daylight hours, holes in the sides of the pipes
project spots of sunlight on their interior walls,
forming a map of the principal stars in the
constellations
Draco, Perseus, Columba, and Capricorn.
Fans of planet
earthworks and
celestial landart
should note that the Sun Tunnels are about 150 miles by car from
Robert Smithson's (Holt's late husband)
Spiral Jetty.
 APOD: 2011 November 15 - Orange Sun Scintillating
APOD: 2011 November 15 - Orange Sun Scintillating
Explanation:
Our Sun is becoming a busy place.
Taken just last week, the Sun was captured sporting numerous interesting features including one of the larger sunspot groups yet recorded: AR 1339 visible on the image right.
Only last year, the Sun was emerging from an
unusually quiet
Solar Minimum that lasted for years.
The above image was recorded in a
single color of light called
Hydrogen Alpha, inverted, and false colored.
Spicules cover much of the Sun's face.
The gradual brightening towards the Sun's edges is caused by increased absorption of relatively cool solar gas and called
limb darkening.
Just over the Sun's edges, several scintillating prominences protrude,
while prominences on the Sun's face are seen as light streaks.
Possibly the most visually interesting of all are the magnetically tangled active regions containing cool sunspots.
As our Sun's magnetic field winds toward
Solar Maximum over the next few years,
increased
activity will likely create times when the Sun's face is even more complex.
 APOD: 2011 November 6 - Orange Sun Oozing
APOD: 2011 November 6 - Orange Sun Oozing
Explanation:
The Sun's surface keeps changing.
The above movie shows how the
Sun's surface oozes during a single hour.
The
Sun's photosphere
has thousands of bumps called
granules and usually a few dark depressions called
sunspots.
The
above time-lapse movie centered on
Sunspot 875 was taken in 2006 by the
Vacuum Tower Telescope in the
Canary Islands of
Spain using
adaptive optics to resolve details below 500 kilometers across.
Each of the numerous granules is the size of an Earth continent, but much shorter lived.
A granule
slowly changes its shape over an hour, and can even completely disappear.
Hot hydrogen
gas rises in the bright center of a granule, and
falls back into the Sun along a dark granule edge.
The above movie and similar movies
allows students and solar scientists to study how granules and
sunspots evolve as well as how
magnetic sunspot regions produce powerful
solar flares.
A few days ago, the
largest sunspot group in recent years rotated into view.
 APOD: 2011 October 5 - Comet and CME on the Sun
APOD: 2011 October 5 - Comet and CME on the Sun
Explanation:
Did a sun-diving comet just cause a solar explosion?
Probably not.
This past weekend a comet dove toward the Sun and was followed very quickly by a
Coronal Mass Ejection (CMEs) from the other side of the Sun.
The first two sequences in the
above video shows the spectacular unfolding of events as seen by the Sun-orbiting
SOHO satellite, while the same events were
also
captured by both Sun-orbiting
STEREO satellites.
Now sungrazer comets that break up as they pass near the Sun are not all that rare --
hundreds have been cataloged over the past few years.
CMEs are even more common, with perhaps three lesser events occurring even during the eight hours of the above time-lapse movie.
Therefore, the
best bet of solar scientists is that the two events were
unrelated.
Another basis for this judgment is that CMEs are caused by rapid changes in the Sun's magnetic field, changes that a
small comet seem unlikely to make.
Such coincidences are even more likely during periods of high activity on the Sun's surface -- like
now.
 APOD: 2011 September 25 - A Large Tsunami Shock Wave on the Sun
APOD: 2011 September 25 - A Large Tsunami Shock Wave on the Sun
Explanation:
Tsunamis this large don't happen on Earth.
During 2006, a large solar flare from an Earth-sized
sunspot produced a
tsunami-type
shock wave that was spectacular even for the Sun.
Pictured above,
the
tsunami wave was captured moving out from active region AR 10930 by the
Optical Solar Patrol Network
(OSPAN) telescope in
New Mexico,
USA.
The resulting
shock wave, known technically as a
Moreton wave, compressed and heated up gasses including
hydrogen in the
photosphere
of the Sun, causing a momentarily brighter glow.
The
above image
was taken in a
very specific red color
emitted exclusively by hydrogen gas.
The rampaging tsunami took out some active
filaments on the Sun,
although many re-established themselves later.
The solar tsunami spread at nearly one million kilometers per hour,
and circled the entire
Sun in a matter of minutes.
 APOD: 2011 August 18 - A Sun Pillar Over Ontario
APOD: 2011 August 18 - A Sun Pillar Over Ontario
Explanation:
What is that on the horizon?
No, it's not an
alien starship
battling distant Earthlings, but rather a sun pillar.
When driving across
Ontario,
Canada in early June,
the photographer was surprised to encounter such an "eerie and beautiful"
vista, and immediately took pictures.
When the atmosphere is cold, ice sometimes forms flat six-sided
crystals as it falls from
high-level clouds.
Air resistance
then causes these crystals to
lie nearly flat much of the time as they flutter to the ground.
If viewed toward a
rising or setting Sun, these
flat crystals will reflect sunlight and create an unusual column of light -- a
sun pillar
as seen above.
Such columns of light are not uncommon to see, and a retrospective of
past APODs
that have featured picturesque sun pillars
can be
found here.
 APOD: 2011 February 7 - Sun 360: STEREO Captures Views of the Entire Sun
APOD: 2011 February 7 - Sun 360: STEREO Captures Views of the Entire Sun
Explanation:
For the first time, the entire Sun is being imaged all at once.
This has become possible because the two
STEREO satellites orbiting and monitoring the Sun are now on opposite sides of the Sun.
The two satellites have been
drifting apart,
as expected, since their
launch in 2006, since one satellite orbits slightly closer to the Sun than the other.
The above image shows nearly the entire Sun as it appeared one day last week, a few days before maximum exposure.
Yesterday, the dark gap in the center closed completely, and
STEREO was able to beam back to Earth full 360 degree images of the
closest star.
Full solar images are useful scientifically for a number of reasons, including catching rapidly evolving
flares,
coronal mass ejections,
tsunamis, and
filaments, no matter where they occur on the Sun,
as well as monitoring days-long
sunspots and
active regions without losing them as they rotate out of view.
Even though the
STEREO satellites will continue to drift apart at about 44 degrees per year,
Sun-staring instruments on or near the Earth will augment them to provide a full
view of the Sun for the next several years.
 APOD: 2011 January 10 - A Sun Halo Beyond Stockholm
APOD: 2011 January 10 - A Sun Halo Beyond Stockholm
Explanation:
What's happened to the Sun?
Sometimes it looks like the Sun is being viewed through a large
lens.
In the above case, however, there are actually millions of lenses:
ice crystals.
As water freezes in the upper
atmosphere, small, flat, six-sided, ice crystals might be formed.
As these crystals flutter to the ground, much time is spent
with their faces flat, parallel to the ground.
An observer may pass through the same plane as
many of the falling ice crystals near sunrise or sunset.
During this alignment, each crystal can act like a miniature lens,
refracting sunlight into our
view and creating
phenomena like parhelia, the technical term for
sundogs.
The above image was taken
last year in
Stockholm,
Sweden.
Visible in the image center is the Sun, while two bright
sundogs glow prominently from both the left and the right.
Also visible is the bright
22 degree halo -- as well as the rarer and much fainter
46 degree halo --
also created by
sunlight reflecting off of atmospheric ice
crystals.
 APOD: 2011 January 4 - A Green Flash from the Sun
APOD: 2011 January 4 - A Green Flash from the Sun
Explanation:
Many think it is just a myth.
Others think it is true but its cause isn't known.
Adventurers pride themselves on having seen it.
It's a green flash from the
Sun.
The truth is the
green flash
does exist and its cause is well understood.
Just as the setting
Sun disappears completely from view,
a last glimmer appears startlingly
green.
The effect is typically visible only from locations with a low,
distant horizon, and lasts just a few seconds.
A green flash is also visible for a rising
Sun, but takes better timing to spot.
A dramatic
green flash, as well as an even more rare
blue flash, was caught in the
above photograph recently
observed
during a sunset visible from
Teide Observatory at
Tenerife,
Cannary Islands,
Spain.
The Sun itself does not turn
partly
green or blue --
the effect is caused by layers of the
Earth's atmosphere acting like a prism.
 APOD: 2010 October 18 - It Came from the Sun
APOD: 2010 October 18 - It Came from the Sun
Explanation:
What's that
coming over the edge of the Sun?
What might appear at first glance to be some sort of
Sun monster
is actually a
solar prominence.
The above prominence, captured by the Sun-orbiting SOHO satellite
earlier this year during an early stage of
its eruption, rapidly became one of the
largest ever on record.
Even as pictured, the prominence is huge -- the
Earth would easily fit inside.
A solar prominence is a thin cloud of solar gas held
just above the surface by the
Sun's
magnetic field.
A quiescent prominence
typically lasts about a month, while an
eruptive prominence like the one developing above may erupt within hours into a
Coronal Mass Ejection
(CME), expelling hot gas into the
Solar System.
Although very hot, prominences typically
appear dark when viewed against the
Sun,
since they are slightly cooler than the surface.
As our Sun evolves toward
Solar maximum
over the next three years, more
large eruptive prominences are expected.
 APOD: 2010 September 23 - Equinox and the Iron Sun
APOD: 2010 September 23 - Equinox and the Iron Sun
Explanation:
Today, the Sun
crosses the celestial equator heading south at 03:09
Universal Time.
Known as an equinox, this
astronomical event
marks the first day of autumn in the northern hemisphere and
spring in the south.
Equinox means
equal
night.
With the Sun on the celestial equator,
Earth dwellers will experience
nearly 12 hours
of daylight and 12 hours of darkness.
Of course, in the north the days continue to grow shorter, the
Sun marching lower
in the sky as winter approaches.
To celebrate
the equinox, consider this view of the Sun in
extreme ultraviolet light from the Sun staring
Solar Dynamics Observatory.
Recorded yesterday, the false-color image shows emission from highly
ionized iron atoms.
Loops and arcs
trace the glowing plasma
suspended in magnetic fields above
solar active regions.
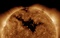 APOD: 2010 August 28 - Hole in the Sun
APOD: 2010 August 28 - Hole in the Sun
Explanation:
This ominous, dark shape sprawling across the face of the Sun
is a coronal hole --
a low density region extending above
the surface where the solar magnetic field opens freely into
interplanetary space.
Studied extensively
from
space since the 1960s in
ultraviolet and
x-ray light, coronal holes are known to be the source of
the high-speed
solar wind, atoms and electrons
which flow outward along the open
magnetic field lines.
During periods of low activity,
coronal holes typically cover
regions just above the Sun's poles.
But this extensive coronal hole
dominated the Sun's northern hemisphere earlier this week, captured
here in extreme ultraviolet light by cameras onboard
the Solar Dynamics Observatory.
The solar wind streaming from this coronal hole
triggered auroral displays
on planet Earth.
 APOD: 2010 July 21 - The Crown of the Sun
APOD: 2010 July 21 - The Crown of the Sun
Explanation:
During a total solar eclipse,
the Sun's
extensive outer atmosphere, or corona, is an inspirational sight.
Subtle shades and shimmering features
that engage
the eye span a brightness range of over
10,000 to 1, making them notoriously difficult
to capture in a single photograph.
But this composite of 7 consecutive digital images
over a range of exposure times comes close to revealing
the crown of the
Sun in all its glory.
The telescopic views were recorded from the Isla de Pascua
(Easter Island) during July 11's
total solar eclipse
and also show solar prominences extending
just beyond the edge of the
eclipsed
sun.
Remarkably, features on the dim, near side of the New Moon can also be
made out, illuminated by sunlight reflected from a
Full Earth.
 APOD: 2010 July 4 - Companion of a Young, Sun-like Star Confirmed
APOD: 2010 July 4 - Companion of a Young, Sun-like Star Confirmed
Explanation:
The first direct image of an extrasolar planet orbiting a star similar to our Sun has been confirmed.
Located just 500 light-years away toward the constellation
Scorpius,
the parent star, cataloged as 1RXS J160929.1-210524,
is only slightly less massive and a little cooler than
the Sun.
The star is, however, much younger, a few
million years old
compared to the middle-aged Sun's 5
billion years.
This sharp infrared
image shows the young star's planetary companion
positioned above and left of center.
The planet is estimated to have a mass about 8 times
the mass of Jupiter, and orbit a whopping 330 times the Earth-Sun
distance from its parent star.
The young planetary companion is still hot and relatively
bright in
infrared light, likely due to
the heat generated during its
formation by gravitational contraction.
In fact, such newborn planets
are easier to detect before they age and cool and become much more faint.
The discovery image, shown above, was taken in 2008 but
confirmed only recently
by noting that the planet stayed with its parent star as background stars slightly shifted over time.
 APOD: 2010 June 27 - All the Colors of the Sun
APOD: 2010 June 27 - All the Colors of the Sun
Explanation:
It is still not known why the Sun's light is missing some colors.
Shown above are all the
visible colors of the
Sun,
produced by passing the Sun's light through a
prism-like device.
The above spectrum was created at the
McMath-Pierce Solar Observatory
and shows, first off, that although our
white-appearing
Sun emits light of nearly
every color, it does indeed appear brightest in yellow-green light.
The dark patches in the
above spectrum arise from gas at or above the
Sun's surface
absorbing sunlight emitted below.
Since different types of gas
absorb different colors of light,
it is possible to determine what gasses compose the Sun.
Helium, for example, was
first discovered
in 1870 on a solar spectrum and only
later found here on
Earth.
Today, the majority of
spectral absorption lines have been identified - but
not all.
 APOD: 2010 June 9 - Orange Sun Simmering
APOD: 2010 June 9 - Orange Sun Simmering
Explanation:
Even a quiet Sun can be a busy place.
And over the deep
Solar Minimum
of the past few years, our Sun has been
unusually quiet.
The above image, taken last week in a
single color of light called
Hydrogen Alpha and then false colored, records a great amount of detail of the simmering surface of
our parent star.
The gradual brightening towards the Sun's edge in this color-inverted image, called
limb darkening, is caused by increased absorption of
relatively cool solar gas.
Just over the Sun's edges, several
prominences are visible,
while two prominences on the Sun's face are
seen as light streaks just above and right of the image center.
Two particularly active areas
of the Sun are marked by dark
plages.
In contrast to recent quiet times,
our Sun is moving toward Solar Maximum, and
for years will likely
appear
much
more
active.
 APOD: 2010 March 23 - Reinvigorated Sun and Prominence
APOD: 2010 March 23 - Reinvigorated Sun and Prominence
Explanation:
Dramatic prominences can sometimes be seen looming just beyond the edge of the sun.
Such was the case last week as a giant prominence,
visible above on the right, highlighted a Sun showing increased
activity as it comes off an unusually quiet Solar
Minimum.
A changing carpet of hot gas is visible in the
chromosphere
of the Sun in the
above image taken in a very
specific color
of light emitted by hydrogen.
A solar prominence is a cloud of solar gas held
just above the surface by the
Sun's magnetic field.
The Earth would easily fit below the
prominence on the right.
Although very hot, prominences typically
appear dark when viewed against the
Sun,
since they are slightly cooler than the surface.
A quiescent prominence
typically lasts about a month, and may
erupt in a
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) expelling hot gas into the
Solar System.
The next day, the
same prominence looked slightly different.
 APOD: 2010 February 23 - Exceptional Rocket Waves Destroy Sun Dog
APOD: 2010 February 23 - Exceptional Rocket Waves Destroy Sun Dog
Explanation:
What created those rocket waves, and why did they destroy that sun dog?
Close inspection of the
above image shows not only a rocket rising near the center, but unusual air ripples around it and a colorful sundog to the far right.
The rocket, carrying the
Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), lifted off two weeks ago from
Cape
Canaveral,
Florida,
USA into a cold blue sky.
The SDO is designed to observe the Sun continuously over the next several years,
exploring the
Sun's atmosphere
at high resolution and fast time scales.
The air ripples -- seen about one minute after launch -- were unexpected,
as was the sudden disappearance of the
sundog after the ripples passed.
Noticed and recorded by
several
onlookers, there has been much speculation about the origin of
the ripples.
An ongoing discussion about them can be joined
here in APOD's discussion board
the Asterisk.
A leading hypothesis holds that the ripples resulted from a
sonic boom created as the rocket broke the
sound barrier,
which then jumbled a thin layer of
ice crystals
that were aligned to create the
sundog.
Lingering questions include why
other rocket launches
don't produce air ripples as noticeable,
and why the ripples appeared more prominent above the rocket.
If you know of images of any other
aircraft or
spacecraft that have produced similar air ripples, please post them to
the discussion thread -- they may be
help create a better understanding of the effect.
 APOD: 2010 February 8 - A Sun Halo Over Cambodia
APOD: 2010 February 8 - A Sun Halo Over Cambodia
Explanation:
Have you ever seen a halo around the Sun?
This fairly common sight occurs when high thin clouds containing millions of tiny
ice crystals cover much of the sky.
Each
ice crystal acts like a
miniature lens.
Because
most
of the crystals have a similar elongated
hexagonal
shape, light entering one crystal face and exiting
through the opposing face refracts 22
degrees,
which corresponds to the radius of the Sun halo.
A similar Moon halo
may be visible during the night.
Pictured above, a nearly complete
sun halo was photographed high above the ancient
Bayon temple in
Angkor,
Cambodia.
Exactly how
ice-crystals form in clouds remains under
investigation.
 APOD: 2010 January 16 - New Year Sun Grazer
APOD: 2010 January 16 - New Year Sun Grazer
Explanation:
Intense and overwhelming, the direct glare of the Sun is blocked by the
smooth occulting disk in this image from the
sun-staring SOHO
spacecraft.
Taken on January 3rd, an extreme
ultraviolet image of the Sun to scale,
is superimposed at the center of the disk.
Beyond the disk's outer boundary is a
sungrazer
comet, one of the
brightest yet seen by SOHO.
The comet was discovered
(movie link)
by Australian amateur astronomer Alan Watson,
while examining earlier images from
another sun-watching spacecraft,
STEREO-A.
Based on their orbits, sungrazers are believed to belong
to the Kreutz
family of comets, created by successive
break ups from a single large parent comet
that passed very near the Sun in the twelfth century.
Subjected to strong
tidal forces
and intense solar heat, this sungrazer comet did not survive its
close encounter.
 APOD: 2009 November 4 - Blue Sun Bristling
APOD: 2009 November 4 - Blue Sun Bristling
Explanation:
Our Sun may look like all soft and fluffy, but it's not.
Our Sun is an
extremely large ball of
bubbling hot gas, mostly
hydrogen gas.
The above picture of our Sun was taken last month in a
specific red color of light emitted by hydrogen gas called
Hydrogen-alpha
and then color inverted to appear blue.
In this light, details of the Sun's
chromosphere are particularly visible, highlighting numerous thin tubes of
magnetically-confined hot gas known as
spicules rising from the Sun like
bristles from a shag carpet.
Our Sun glows because it is hot, but it is
not on fire.
Fire is the rapid acquisition of oxygen,
and there is very little
oxygen on the Sun.
The energy source of our Sun is the nuclear
fusion of hydrogen into
helium deep within its core.
No sunspots or
large active regions were visible on the Sun this day, although some solar prominences
are visible around the edges.
 APOD: 2009 April 5 � Orange Sun Oozing
APOD: 2009 April 5 � Orange Sun Oozing
Explanation:
The Sun's surface keeps changing.
Click the central arrow and watch how the
Sun's surface oozes during a single hour.
The
Sun's photosphere
has thousands of bumps called
granules and usually a few dark depressions called
sunspots.
The
above time-lapse movie centered on
Sunspot 875 was taken in 2006 by the
Vacuum Tower Telescope in the
Canary Islands of
Spain using
adaptive optics to resolve details below 500 kilometers across.
Each of the numerous granules is the size of an Earth continent, but much shorter lived.
A granule
slowly changes its shape over an hour, and can even completely disappear.
Hot hydrogen
gas rises in the bright center of a granule, and falls back into the Sun along a dark granule edge.
The above movie and
similar movies
allows students and solar scientists to study how granules and
sunspots evolve as well as how
magnetic sunspot regions produce powerful
solar flares.
 APOD: 2008 December 15 - A Sun Pillar Over North Carolina
APOD: 2008 December 15 - A Sun Pillar Over North Carolina
Explanation:
Have you ever seen a sun pillar?
When the air is cold and the Sun is rising or
setting, falling ice
crystals
can reflect sunlight and create an
unusual column of light.
Ice sometimes forms flat, six-sided
shaped crystals as it falls from high-level
clouds.
Air resistance causes these crystals to lie nearly
flat much of the time as they flutter to the ground.
Sunlight reflects off crystals that are
properly aligned,
creating the
sun-pillar
effect.
In the
above picture
taken in 2007 January, a
sun-pillar reflects light from a Sun setting over
Lake Norman,
North Carolina,
USA.
 APOD: 2008 November 2 - Spicules: Jets on the Sun
APOD: 2008 November 2 - Spicules: Jets on the Sun
Explanation:
Imagine a pipe as wide as a state and as long as half the Earth.
Now imagine that this pipe is filled with
hot gas moving 50,000 kilometers per hour.
Further imagine that this pipe is not made of metal but a transparent
magnetic field.
You are envisioning just one of thousands of young
spicules on the
active Sun.
Pictured
above
is perhaps the highest
resolution image yet of these enigmatic solar flux tubes.
Spicules dot the
above frame of
solar active region 10380 that crossed the Sun in 2004 June,
but are particularly evident as a
carpet of dark tubes on the right.
Time-sequenced images have recently shown that
spicules last about five minutes,
starting out as
tall tubes
of rapidly rising gas but eventually
fading as the gas peaks and falls back down to the
Sun.
These images also indicate that the ultimate cause of
spicules
is sound-like waves that flow over the
Sun's
surface but leak into the
Sun's atmosphere.
 APOD: 2008 September 24 - Active Region 1002 on an Unusually Quiet Sun
APOD: 2008 September 24 - Active Region 1002 on an Unusually Quiet Sun
Explanation:
Why has the Sun been so quiet recently?
No one is sure.
Our Sun
has shown few active regions -- that house even fewer associated
sunspots --
for over a year now, and such a
period of relative calm is quite unusual.
What is well known is that our Sun is in
a transitional period between
solar cycles called a
Solar Minimum,
where solar activity has historically been reduced.
The stark lack of surface tumult is unusual even during a
Solar Minimum, however, and activity
this low has not been seen for many
decades.
A few days ago, however, a
bona-fide
active region -- complete with sunspots
--appeared and continues to
rotate across
the Sun's face.
Visible above, this region, dubbed
Active Region 1002 (AR 1002), was imaged in
ultraviolet light yesterday by the
SOHO spacecraft, which co-orbits the Sun
near the Earth.
Besides the
tranquility on the Sun's surface, recent data from the
Ulysses spacecraft, across the Solar System,
indicate that the intensity of the
solar wind blowing out from the Sun is at a fifty
year low.
Predictions hold, however, that our Sun
will show more and more
active regions
containing more and more sunspots and flares until
Solar Maximum occurs in about four years.
 APOD: 2008 September 22 - Equinox: The Sun from Solstice to Solstice
APOD: 2008 September 22 - Equinox: The Sun from Solstice to Solstice
Explanation:
Today is an equinox, a date when day and night are equal.
Tomorrow, and every day until the next
equinox,
the night will be longer than the day in Earth's northern hemisphere,
and the day will be longer than the night in Earth's southern hemisphere.
An equinox
occurs midway between the two
solstices,
when the days and nights are the least equal.
The picture is a composite of hourly images taken of the Sun above
Bursa, Turkey on key days from solstice to
equinox to solstice.
The bottom Sun band was taken during the
winter solstice in 2007 December, when
the Sun could not rise very high in the sky nor stay above the
horizon very long.
This lack of Sun caused
winter.
The top Sun band was taken during the
summer solstice in 2008 June, when the
Sun rose highest in the sky and stayed above the horizon
for more than 12 hours.
This abundance of Sun caused
summer.
The middle band was taken during the
Vernal Equinox in 2008 March, but it is the same sun band that
Earthlings will see today, the day of the
Autumnal Equinox.
 APOD: 2008 September 19 - Companion of a Young, Sun-like Star
APOD: 2008 September 19 - Companion of a Young, Sun-like Star
Explanation:
Located just 500 light-years away toward the constellation
Scorpius,
this star is only slightly less massive and a little cooler than
the Sun.
But it is much younger, a few
million years old
compared to the middle-aged Sun's 5
billion years.
This sharp infrared
image shows the young star has a likely companion
positioned above and left - a hot planet with about 8 times
the mass of Jupiter, orbiting a whopping 330 times the Earth-Sun
distance from its parent star.
The young planetary companion is still hot and relatively
bright in
infrared light due to
the heat generated during its formation by
gravitational contraction.
In fact, such newborn planets are easier to detect
before they age and cool, becoming much fainter.
Though over 300
extrasolar
planets have been found using other
techniques, this picture likely represents the
first direct image
of a planet belonging to a star
similar to the Sun.
 APOD: 2008 August 8 - The Crown of the Sun
APOD: 2008 August 8 - The Crown of the Sun
Explanation:
During a total solar eclipse,
the Sun's
extensive outer atmosphere, or corona, is an inspirational sight.
The subtle shades and
shimmering features of the corona
that
engage the eye span a brightness range of over
10,000 to 1, making them notoriously difficult
to capture in a single picture.
But this composite of 28 digital images
ranging in exposure time from 1/1000 to 2 seconds
comes close to revealing
the crown of the
Sun in all its glory.
The
telescopic views were recorded near Kochenevo, Russia during
the August 1 total solar eclipse
and also show solar prominences extending
just beyond the edge of the
eclipsed
sun.
Remarkably, features on the dark near side of the New Moon can also be
made out, illuminated by sunlight reflected from
a Full Earth.
 APOD: 2008 July 30 - The International Space Station Transits the Sun
APOD: 2008 July 30 - The International Space Station Transits the Sun
Explanation:
That's no sunspot.
It's the
International Space Station (ISS)
caught by chance passing in front of the Sun.
Sunspots, individually, have a dark central
umbra, a lighter surrounding penumbra,
and no solar panels.
By contrast, the ISS is a complex and multi-spired mechanism,
one of the largest and most sophisticated machines ever created by
humanity.
Also, sunspots occur on the
Sun, whereas the ISS orbits the
Earth.
Transiting the Sun is not very unusual for the
ISS, which orbits the Earth about every 90 minutes,
but getting one's timing and equipment just right for a
great image is rare.
Strangely, besides that fake spot, the Sun, last week,
lacked any real sunspots.
Sunspots have been
rare
on the Sun since the dawn of the current
Solar Minimum,
a period of low solar activity.
Although fewer sunspots have been
recorded during this
Solar Minimum
than for
many previous decades, the low solar activity is
not, as yet, very unusual.
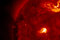 APOD: 2007 December 10 - A Jet from the Sun
APOD: 2007 December 10 - A Jet from the Sun
Explanation:
What powers the solar wind?
Our Sun is known to emit a powerful
wind of particles with gusts that can even
affect astronauts and satellites
orbiting Earth.
The cause of the
solar wind
has been debated for decades but is thought to be rooted in
Alfv�n waves
generated by the ever changing
magnetic field of the Sun.
Newly released images
from the Japanese
Hinode satellite appear to bolster this hypothesis, imaging an average of 240 daily
plasma jets
that are excellent candidates to fuel the outwardly moving
Alfv�n waves.
The jets and waves are themselves ultimately created by
magnetic reconnection
events, rapid events where lines of constant
magnetic field
suddenly move extremely rapidly, dragging
electrons and
protons along with them.
On the image left, one such jet is visible in
X-ray light.
Bright spots show relatively energetic regions
elsewhere on the Sun.
 APOD: 2007 November 6 - An X Class Flare Region on the Sun
APOD: 2007 November 6 - An X Class Flare Region on the Sun
Explanation:
Why does the Sun flare?
Unpredictably, our
Sun unleashes tremendous
flares
expelling hot gas into the
Solar
System
that can affect satellites, astronauts, and power grids on Earth.
This close up of an active region on the Sun that produced a powerful
X-class flare
was captured by the orbiting
TRACE satellite.
Clicking on the image should bring up a movie that shows the evolution of
Active Region 9906 over about four hours.
The glowing gas flowing around the relatively stable
magnetic
field loops above the
Sun's photosphere
has a temperature of over ten million degrees
Celsius.
These flows occurred after violently unstable
magnetic
reconnection events above the Sun produced the flare.
Many things about
solar active regions are not well
understood including the presence of
dark regions that appear to move inward during the movie.
 APOD: 2007 July 9 - The Most Distant Sun
APOD: 2007 July 9 - The Most Distant Sun
Explanation:
When is the Sun most distant from Earth?
It happened again
just this past weekend.
A common misconception is that the Sun is most distant during
the winter, when it's the coldest.
In truth, however, the
seasonal temperatures
are more
greatly
influenced
by the number of daylight hours and how high the Sun rises.
For example, during northern winter, the tilt of the Earth causes the
Sun to be above the horizon for a
shorter time and remain lower in the sky than in northern summer.
The picture
compares the
relative size of the Sun during Earth's closest approach in
January (northern winter) on the left,
and in July (northern summer) on the right.
The angular size of the Sun is
noticeably smaller during July, when it is farther away.
If the Earth's orbit
was perfectly circular,
the Sun would always appear to be the same size.
These two solar images
were taken from
Spain during 2006,
but the same effect can be seen in any year from any
Earth-bound location.
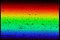 APOD: 2007 June 24 - All the Colors of the Sun
APOD: 2007 June 24 - All the Colors of the Sun
Explanation:
It is still not known why the Sun's light is missing some colors.
Shown above are all the
visible colors of the
Sun, produced by passing the Sun's light through a
prism-like device.
The above spectrum was created at the
McMath-Pierce Solar Observatory
and shows, first off, that although our yellow-appearing
Sun emits light of nearly
every color, it does indeed appear brightest in yellow-green light.
The dark patches in the
above spectrum arise from gas at or above the
Sun's surface
absorbing sunlight emitted below.
Since different types of gas
absorb different colors of light,
it is possible to determine what gasses compose the Sun.
Helium, for example, was
first discovered
in 1870 on a solar spectrum and only
later found here on
Earth.
Today, the majority of
spectral absorption lines have been identified - but
not all.
 APOD: 2007 June 21 - Stars and the Solstice Sun
APOD: 2007 June 21 - Stars and the Solstice Sun
Explanation:
If you could
turn off the atmosphere's ability to scatter
overwhelming sunlight, today's daytime sky might look something
like this ... with the Sun surrounded by the stars of the
constellations Taurus and Gemini.
Of course, today is
the Solstice.
Traveling along the
ecliptic plane,
the Sun is at its northernmost
position in planet Earth's sky, marking the
astronomical beginning
of summer in the north.
Accurate for the exact time of today's Solstice,
this
composite image also shows the Sun at the proper scale
(about the angular
size of the Full Moon).
Open star cluster M35 is to the Sun's left,
and the other two bright stars in view are
Mu and Eta Geminorum.
Digitally superimposed on a nighttime image of the stars, the Sun
itself is a composite of a picture taken through a solar filter and a series
of images of the solar corona recorded during the
solar eclipse of
February 26, 1998 by Andreas Gada.
 APOD: 2007 May 22 - Orange Sun Oozing
APOD: 2007 May 22 - Orange Sun Oozing
Explanation:
The Sun's surface keeps changing.
Click the central arrow and watch how the
Sun's surface oozes during a single hour.
The
Sun's photosphere
has thousands of bumps called
granules and usually a few dark depressions called
sunspots.
The
above time-lapse movie centered on
Sunspot 875 was taken last year by the
Vacuum Tower Telescope in the
Canary Islands of
Spain using
adaptive optics to resolve details below 500 kilometers across.
Each of the numerous granules is the size of an Earth continent, but much shorter lived.
A granule
slowly changes its shape over an hour, and can even completely disappear.
Hot hydrogen
gas rises in the bright center of a granule, and falls back into the Sun along a dark granule edge.
The above movie and similar movies allow solar scientists to study how granules and
sunspots evolve as well as how
magnetic sunspot regions produce powerful
solar flares.
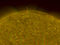 APOD: 2007 April 24 - The Sun in Three Dimensions
APOD: 2007 April 24 - The Sun in Three Dimensions
Explanation:
What does the Sun look like in all three spatial dimensions?
To find out,
NASA launched two
STEREO satellites
to perceive three dimensions on the Sun much like two eyes allow
humans to
perceive three dimensions
on the Earth.
Such a perspective is designed to allow new insight into the surface of the
rapidly changing Sun,
allowing humans to better understand and predict things like
Coronal Mass Ejections
and solar flares
that affect the Earth as well as satellites and astronauts orbiting the Earth.
Pictured above are two simultaneous images of the Sun taken by STEREO A and
STEREO B, now digitally combined to give one of the
first 3-D pictures of the Sun ever taken.
To fully appreciate the image, one should view it with
3-D red-blue glasses.
The teeming and
bubbling solar surface can be seen sporting a
prominent solar prominence
near the top of the image.
 APOD: 2007 February 6 - Sun Storm: A Coronal Mass Ejection
APOD: 2007 February 6 - Sun Storm: A Coronal Mass Ejection
Explanation:
What's happening to our Sun?
Another
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME)!
The Sun-orbiting
SOHO spacecraft has imaged many
erupting filaments lifting off
the active solar surface and blasting enormous bubbles of
magnetic plasma into space.
Direct light from the sun is blocked in the inner part of the
above image, taken in 2002, and replaced by a simultaneous image of the Sun in
ultraviolet light.
The field of view extends over two million kilometers from the solar surface.
While hints of
these explosive events, called
coronal mass ejections or CMEs,
were discovered by spacecraft in the early 70s,
this dramatic image is part of a detailed record
of this CME's development from the presently operating
SOHO spacecraft.
Near the minimum of the
solar activity cycle
CMEs occur about once a week, but near solar maximum rates
of two or more per day are typical.
Strong CMEs may profoundly influence
space weather.
Those directed toward our planet can have
serious effects.
 APOD: 2006 December 13 - A Large Tsunami Shock Wave on the Sun
APOD: 2006 December 13 - A Large Tsunami Shock Wave on the Sun
Explanation:
Tsunamis this large don't happen on Earth.
One week ago, a large solar flare from an Earth-sized
sunspot produced a
tsunami-type
shock wave that was spectacular even for the Sun.
Pictured above, the
tsunami wave was captured moving out from active region AR 10930 by the
Optical Solar Patrol Network
(OSPAN) telescope in
New Mexico,
USA.
The resulting
shock wave, known technically as a
Moreton wave, compressed and heated up gasses including
hydrogen in the
photosphere
of the Sun, causing a momentarily brighter glow.
The
above image
was taken in a
very specific red color
emitted exclusively by hydrogen gas.
The rampaging tsunami took out some active
filaments on the Sun,
although many re-established themselves later.
The solar tsunami spread at nearly one million kilometers per hour,
and circled the entire
Sun in a matter of minutes.
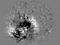 APOD: 2006 October 29 - The Sun Puffs
APOD: 2006 October 29 - The Sun Puffs
Explanation:
Our Earth endures bursts of particles from the Sun.
On 1997 April 7, at 10 am (EDT), ground monitors of the
SOHO spacecraft,
which continually monitors the Sun,
noticed a weak spot in the solar corona was buckling again,
this time letting loose a large, explosive
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME).
Almost simultaneously, NASA's
WIND spacecraft
began detecting bursts of
radio waves
from electrons involved in this magnetic storm.
Supersonic waves rippled though the
solar corona as a puff of high energy gas shot out into the
Solar System.
The above image shows two photographs of the
Sun taken about 15 minutes apart and subtracted,
highlighting the explosion.
CME's are not unusual.
The CME gas had little lasting effect on the Earth, but likely created fleeting, if not
picturesque, Earth
auroras.
 APOD: 2006 July 10 - Dark Sun Sizzling
APOD: 2006 July 10 - Dark Sun Sizzling
Explanation:
Is this our Sun? Yes.
Even on a normal day, our Sun is
sizzling
ball of
seething hot
gas.
Unpredictably, regions of strong and tangled
magnetic fields arise, causing
sunspots and bright
active regions.
The Sun's surface bubbles as hot
hydrogen gas streams along
looping magnetic fields.
These active regions channel gas along
magnetic loops, usually falling back but sometimes
escaping into the
solar corona or out into space as the
solar wind.
Pictured above is our Sun in three colors of
ultraviolet light.
Since only active regions emit significant amounts of energetic
ultraviolet light, most of the Sun appears dark.
The colorful portions glow spectacularly, pinpointing the Sun's hottest and
most violent regions.
Although the Sun is constantly changing, the rate of
visible light it emits has been
relatively stable
over the past five billion years, allowing
life to emerge on Earth.
 APOD: 2006 January 2- A Sun Pillar Over Maine
APOD: 2006 January 2- A Sun Pillar Over Maine
Explanation:
Have you ever seen a sun pillar?
When the air is cold and the Sun is rising or
setting, falling ice
crystals
can reflect sunlight and create an
unusual column of light.
Ice sometimes forms flat, six-sided
shaped crystals as it falls from high-level
clouds.
Air resistance causes these crystals to lie nearly
flat much of the time as they flutter to the ground.
Sunlight reflects off crystals that are
properly aligned,
creating the sun-pillar effect.
In the above picture taken late last month, a
sun-pillar reflects light from a Sun setting over
Bangor, Maine,
USA.
 APOD: 2005 April 11 - Clouds, Plane, Sun, Eclipse
APOD: 2005 April 11 - Clouds, Plane, Sun, Eclipse
Explanation:
How can part of the Sun just disappear?
When that part is really
hiding behind the Moon.
Last Friday, the first
partial solar eclipse of 2005 and the
last total eclipse of the Sun until March 2006 was visible.
During a solar eclipse, the
Sun,
Moon and
Earth are aligned.
The total solar eclipse
was primarily visible from the Southern
Pacific Ocean, while a partial
solar eclipse was discoverable across
South America and lower
North America.
The above image composite was taken with a handheld
digital camera last Friday.
After a day of rain in Mt. Holly,
North Carolina,
USA, a partially eclipsed Sun momentarily peeked through a
cloudy sky.
After taking a sequence of images, the
best eclipse shot was digitally combined with a less
good eclipse shot that featured a
passing airplane.
 APOD: 2004 December 6 - Filaments Across the Sun
APOD: 2004 December 6 - Filaments Across the Sun
Explanation:
Two unusually long filaments crossed part of the Sun last week.
The filaments are actually relatively cool and dark
prominences of solar
plasma held up by the Sun's
magnetic field but seen against the
face of the Sun.
Filaments typically last a few weeks before falling back.
Pictured above, the
two filaments are visible on the
Sun's right side.
It would take twenty Earths, set end-to-end, to match the
length of one of the filaments.
Also visible are bright hot regions called
plages and a carpet of hundreds of
granules that provide the Sun's texture.
The above image
was taken early last week through a small telescope in a
very specific color of light emitted primarily by
hydrogen.
 APOD: 2004 August 2 - Spicules: Jets on the Sun
APOD: 2004 August 2 - Spicules: Jets on the Sun
Explanation:
Imagine a pipe as wide as a state and as long as half the Earth.
Now imagine that this pipe is filled with
hot gas moving 50,000 kilometers per hour.
Further imagine that this pipe is not made of metal but a transparent
magnetic field.
You are envisioning just one of thousands of young
spicules on the
active Sun.
Pictured above is perhaps the highest
resolution image yet of these enigmatic solar flux tubes.
Spicules dot the
above frame of
solar active region 10380 that crossed the Sun in June,
but are particularly evident as a
carpet of dark tubes on the right.
Time-sequenced images have recently shown that
spicules last about five minutes,
starting out as tall tubes of rapidly rising gas but eventually
fading as the gas peaks and falls back down to the Sun.
These images also indicate, for the first time, that the ultimate cause of
spicules is sound-like waves that flow over the
Sun's
surface but leak into the
Sun's atmosphere.
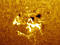 APOD: 2004 July 26 - A Large Active Region Crosses the Sun
APOD: 2004 July 26 - A Large Active Region Crosses the Sun
Explanation:
An unexpectedly large sunspot region is now crossing the Sun.
The active region is home to rivers of hot
plasma, explosive
flares,
strong magnetic fields, a powerful
Coronal Mass Ejection
(CME), and a
sunspot group
so large it can be seen by the protected eye without magnification.
In fact,
this region appears larger than
Venus did when it crossed the Sun last month.
Pictured above is a close-up of this
sunspot group, officially tagged
AR 10652, taken just four days ago.
The region is now nearing the
Sun's eastern limb and will
disappear from view in a few days.
Energetic ions from sunspot group 652 continue to impact the
Earth and create rare
purple auroras.
 APOD: 2004 July 20 - Space Station, Venus, Sun
APOD: 2004 July 20 - Space Station, Venus, Sun
Explanation:
On June 8,
Venus was not the only celestial object to pass in front of the Sun.
A few well-situated photographers caught the
International Space Station
also crossing the Sun simultaneously.
Pictured above is a unique time-lapse image of the unprecedented double transit, a rare event that was visible for less than a
second from a narrow band on
Earth.
The above image is a combination of
12 frames taken 0.033 seconds apart and each
themselves lasting only 1/10,000 th of a second.
The image was taken from the small village of
Stupava in
Slovakia.
The next time Venus will
appear to
cross the Sun from
Earth will be in 2012.
 APOD: 2004 June 8 - A Planet Transits the Sun
APOD: 2004 June 8 - A Planet Transits the Sun
Explanation:
Today an astronomical event will occur that no living person has ever seen:
Venus will cross directly in front of the Sun.
A Venus crossing, called a transit, last occurred in 1882 and was
front-page
news
around the world.
Today's transit will be visible in its entirety throughout
Europe and most of Asia and Africa.
The northeastern half of
North America will see the Sun rise with the
dark dot of Venus already superposed.
Never look directly at the Sun, even when
Venus is in front.
Mercury's closer proximity to the Sun cause it to transit every few years.
In fact, the above image mosaic of Mercury
crossing the Sun is from
two
transits
ago, in November 1999.
Will anyone living see the next Venus transit? Surely yes since it occurs in 2012.
 APOD: 2004 April 19 - Comet Bradfield Passes the Sun
APOD: 2004 April 19 - Comet Bradfield Passes the Sun
Explanation:
Today,
Comet Bradfield is passing the Sun.
The above image, taken yesterday in the direction of the
Sun by the
SOHO
LASCO
instrument, shows the comet and its
dust tail
as the elongated white streak.
The Sun
would normally be seen in the very center but has been
blocked from view.
Comet C/2004 F4 (Bradfield) was discovered
just one month ago and has brightened dramatically
as it neared the Sun.
Careful sky gazers can see
Comet Bradfield
with the unaided eye near the Sun, although
NASA's
sun-orbiting SOHO satellite has the best view.
During the day,
Comet Bradfield will continually shift inside the
LASCO frame as it rounds the Sun.
There is even the possibility that the comet will
break up.
If not, the bright comet's trajectory will carry it
outside the field of LASCO sometime tomorrow.
Along with T7 and
Q4,
Comet Bradfield is now the
third comet that is currently visible
on the sky with the unaided eye, the most ever of which we are aware
and quite possibly the most in
recorded
history.
 APOD: 2004 March 21 - A Green Flash from the Sun
APOD: 2004 March 21 - A Green Flash from the Sun
Explanation:
Many think it is just a myth.
Others think it is true but its cause isn't known.
Adventurers pride themselves on having seen it.
It's a green flash from the
Sun.
The truth is the
green flash
does exist and its cause is well understood.
Just as the setting
Sun disappears completely from view,
a last glimmer appears startlingly
green.
The effect is typically visible only from locations with a low,
distant horizon, and lasts just a few seconds.
A green flash is also visible for a rising
Sun, but takes better timing to spot.
A dramatic green flash was caught in the
above photograph in 1992 from
Finland.
The Sun itself does not turn
partly green, the effect is caused by layers of the
Earth's atmosphere acting like a prism.
 APOD: 2003 November 22 - Moon AND Sun
APOD: 2003 November 22 - Moon AND Sun
Explanation:
This composite image was made from 22 separate pictures
of the Moon and Sun all taken from
Chisamba, Zambia during the
total phase of the 2001 June 21 solar eclipse.
The multiple exposures
were digitally processed and combined to
simultaneously show a wealth of detail which no single camera
exposure or naked-eye observation could easily reveal.
Most striking are the incredible flowing streamers
of the Sun's outer atmosphere or
solar corona, notoriously difficult to see except when
the
new Moon blocks the bright solar disk.
Features on the darkened near side
of the Moon can
also be made out,
illuminated
by sunlight reflected from
a
full Earth.
A giant solar prominence seems to hang
just beyond the Moon's eastern (left) edge while about one
diameter farther east of the eclipsed Sun is the
relatively faint (4th magnitude)
star 1 Geminorum.
The still active
Sun
will be totally eclipsed by the Moon tomorrow,
but the path of the total eclipse will mostly cross the relatively
inaccessible continent
of Antarctica.
 APOD: 2003 July 29 -Orange Sun Simmering
APOD: 2003 July 29 -Orange Sun Simmering
Explanation:
Even a quiet Sun is a busy place.
The above image,
taken in a
single color of light called
Hydrogen Alpha, records a great amount of detail
of the simmering surface of
our parent star.
The gradual darkening towards the Sun's edge, called
limb darkening, is caused by increased absorption of
relatively cool solar gas.
Further over the edge, a
giant prominence is visible,
while a different prominence can be seen in
silhouette as the
dark streak near the image center.
Two active areas of the Sun are marked by bright
plages.
The above amateur photograph of the Sun was
taken just last month through a small telescope
and a standard digital camera.
In contrast, there are times when our Sun
appears
much
more
active.
 APOD: 2003 July 7 - At the Edge of the Sun
APOD: 2003 July 7 - At the Edge of the Sun
Explanation:
Dramatic prominences can sometimes be seen looming
just beyond the edge of the sun.
A solar prominence is a cloud of solar gas held
just above the surface by the
Sun's magnetic field.
The Earth would easily fit below the
prominence on the left.
A quiescent prominence
typically lasts about a month, and may erupt in a
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) expelling hot gas into the
Solar System.
Although very hot, prominences typically
appear dark when viewed against the
Sun,
since they are slightly cooler than the surface.
The above image in false color was taken on June 1 from Stuttgart,
Germany with an amateur telescope and camera.
 APOD: 2003 June 24 - The Sun's Surface in 3D
APOD: 2003 June 24 - The Sun's Surface in 3D
Explanation:
How smooth is the Sun?
The new
Swedish 1-m Solar Telescope,
deployed in the Canary Islands
only last year, allows imaging of objects less than 100-km across on the
Sun's surface.
When pointed toward the
Sun's edge, surface
objects now begin to block each other, indicating true
three-dimensional information.
Close inspection of the image reveals much vertical
information, including
spectacular light-bridges
rising nearly 500-km above the floor of
sunspots near the top of the image.
Also visible in the
above false-color image are hundreds of bubbling
granules, each about
1000-km across, and small bright regions known as
faculas.
 APOD: 2003 June 18 - Clouds and the Moon Move to Block the Sun
APOD: 2003 June 18 - Clouds and the Moon Move to Block the Sun
Explanation:
High above a small church near Vienna,
Austria, clouds and the Moon vied for
position in front of the Sun.
Such was the case on the ground late
last month during a
partial eclipse of the Sun
visible throughout
Europe and
Asia.
Nearing the farthest part of its
orbit around the Earth, the
Moon's angular size was too small to
block the entire Sun, a situation that would have resulted in a
total solar eclipse.
The next solar eclipse visible from Earth will occur on
November 23.
Although a total eclipse will be visible only from parts of
Antarctica,
parts of the Sun will momentarily disappear for observers across
Australia,
New Zealand, and the southernmost tip of
South America.
 APOD: 2003 May 13 - Mercury Transits the Sun
APOD: 2003 May 13 - Mercury Transits the Sun
Explanation:
How big is the Sun?
The Sun
is not only larger than any planet,
it is larger than all of the
planets put together.
The Sun accounts for about 99.9 percent of all the mass in its
Solar System.
Merely stating the Sun's diameter is about 1,400,000
kilometers does not do it justice.
Last week a chance to gain visual size perspective
occurred when planet
Mercury made a rare crossing in front to Sun.
Mercury, a planet over a third of the diameter of our Earth, is the dark dot on the upper right.
In comparison to the Sun, Mercury is so small it is initially
hard to spot.
Also visible on the Sun are dark circular sunspots, bright plages, and dark elongated
prominences -- many of which are larger than Mercury.
The above contrast-enhanced picture was
captured last week from
France.
 APOD: 2003 March 18 - Coronal Holes on the Sun
APOD: 2003 March 18 - Coronal Holes on the Sun
Explanation:
The ominous, dark shapes haunting the left side of the Sun are
coronal
holes -- low density regions extending above
the surface
where the solar magnetic field opens freely into
interplanetary space.
Studied extensively
from
space since the 1960s in ultraviolet
and x-ray light,
coronal holes are known to be the source of
the high-speed solar wind, atoms and electrons
which flow outward along the open
magnetic field lines.
During periods of low activity,
coronal holes typically cover
regions just above the Sun's poles.
These coronal holes, however, have just
moved into view near the Sun's equator,
and particles escaping them have already caused
notable aurora here on Earth.
Coronal holes
like this one may last for a few solar rotations
before the magnetic fields shift and change configurations.
Shown in false-color, this picture of the Sun on March 9
was made in extreme ultraviolet light by the
EIT
instrument on board the space-based SOHO observatory.
 APOD: 2003 February 24 - Comet NEAT Passes an Erupting Sun
APOD: 2003 February 24 - Comet NEAT Passes an Erupting Sun
Explanation:
As Comet NEAT flared last week, the
Sun roared.
Just as the comet swooped inside the orbit of
Mercury
and developed a long and flowing tail of gas and
dust,
the Sun emitted a huge
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME).
Neither the fortuitous
hot ball of solar gas
nor the intense glare of sunlight appeared to disrupt the
comet's nucleus.
The action was too close to the
Sun to be easily visible by
humans,
but the orbiting Sun-pointing
SOHO satellite had a clear view of the celestial daredevil show.
The above image was taken on February 18 when the
comet
was so bright it created an
artificial horizontal streak on the camera image.
During the encounter,
Comet NEAT, official designation (C/2002 V1),
brightened to second
magnitude.
An opaque disk blocked the Sun's image.
The now-outbound comet remains
bright but will surely fade as it moves away from the Sun.
Nevertheless, Comet NEAT will likely be visible with binoculars
to southern hemisphere observers for the next month.
 APOD: 2003 February 10 - Comet NEAT Approaches the Sun
APOD: 2003 February 10 - Comet NEAT Approaches the Sun
Explanation:
A comet
may likely become visible to the unaided eye over the
next few days above the
horizon where the Sun has just set.
Comet NEAT (C/ 2002 V1), discovered last November, has
brightened dramatically as it approached the Sun.
Over the next few days, the
quickly setting comet could
appear as bright as second
magnitude.
On February 18 it will round the Sun well within the orbit of
Mercury.
During surrounding days, the Sun's glare will effectively
hide the comet to human observers.
It is quite probable, though, that
Comet NEAT will standout prominently in
images taken by the Sun-looking
SOHO satellite.
Pictured above,
Comet NEAT's complex and developing
tail was photographed on
January 29 (top) and February 2.
Sky enthusiasts
should remember to never look directly at the Sun.
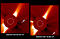 APOD: 2003 January 30 - Comet Kudo-Fujikawa: Days in the Sun
APOD: 2003 January 30 - Comet Kudo-Fujikawa: Days in the Sun
Explanation:
Cruising through
the inner Solar System, new
Comet
Kudo-Fujikawa reached perihelion, its closest
approach to the Sun, yesterday, January 29.
Passing within
28.4 million kilometers of the Sun, this
comet came much closer than innermost planet Mercury basking
only 57.9 million kilometers from our parent star.
So close to the Sun, comet Kudo-Fujikawa was extremely bright but
impossible for earthbound observers to see against the solar glare.
Still, the space-based
SOHO
observatory captured these
views
of the comet as it neared perihelion by
using a coronograph's occulting disk to
block the overwhelming sunlight.
In the series of images, the size and location of the blocked-out
Sun is indicated by white circles, while arrows point to the
traveling
comet's bright coma and developing
tail.
Though fading on its outbound journey,
Kudo-Fujikawa should
soon be visible to southern hemisphere
comet-watchers
in February's evening skies.
 APOD: 2003 January 23 - Launch of the Sun Pillar
APOD: 2003 January 23 - Launch of the Sun Pillar
Explanation:
On January 16, NASA's space shuttle
Columbia roared into blue morning
skies above Kennedy Space Center on
STS-107,
the first shuttle mission of 2003.
But this is not a picture of
that launch!
It was taken on the morning of January 16 though, at sunrise, looking
eastward toward Lake Ontario from just outside of Caledon, Ontario,
Canada.
In the picture a sun pillar, sunlight reflecting
from ice crystals
gently falling through the cold air, seems to shoot above the fiery
Sun still low on the horizon.
By chance, fog
and clouds forming over the relatively warm lake look
like billowing smoke from a rocket's
exhaust plume and complete the
launch illusion.
Amateur photographer Lauri Kangas stopped on his way to work to record
the eye-catching
sun pillar launch.
 APOD: 2002 December 30 - A Sun Pillar
APOD: 2002 December 30 - A Sun Pillar
Explanation:
Have you ever seen a sun pillar?
When the air is cold and the Sun is rising or
setting, falling
ice crystals can reflect sunlight and create an
unusual column of light.
Ice sometimes forms flat, stop-sign
shaped crystals as it falls from high-level
clouds.
Air resistance causes these crystals to lie nearly
flat much of the time as they flutter to the ground.
Sunlight reflects off crystals that are
properly aligned,
creating the sun-pillar effect.
In the above picture, a
sun-pillar reflects light from a setting Sun.
 APOD: 2002 December 13 - The Crown of the Sun
APOD: 2002 December 13 - The Crown of the Sun
Explanation:
During
a total solar eclipse,
the
Sun's extensive outer atmosphere
or corona
is an awesome and inspirational sight.
Yet the subtle shades and shimmering features of the corona that
engage the eye span a brightness range of over
10,000 to 1, making them notoriously difficult to
capture in a photograph.
Still, this single five second exposure
comes very close to
revealing the crown of the Sun in all its glory.
The color picture was taken with a
specially
built coronal camera
and telescope during the December 4th total eclipse
from Messina, South Africa.
The camera's design incorporates a
precisely made
filter whose density,
or ability to block light, decreases markedly with
distance from the filter center, compensating for the
difference between the brighter inner portion of the corona at
the Sun's edge
and the much fainter outer regions.
The central spot in the image corresponds to a calibration
window centered on the eclipsed Sun.
 APOD: 2002 November 10 - A Green Flash from the Sun
APOD: 2002 November 10 - A Green Flash from the Sun
Explanation:
Many think it is just a myth.
Others think it is true but its cause isn't known.
Adventurers pride themselves on having seen it.
It's a green flash from the Sun.
The truth is the
green flash
does exist and its cause is well understood.
Just as the setting
Sun disappears completely from view,
a last glimmer appears startlingly
green.
The effect is typically visible only from locations with a low,
distant horizon, and lasts just a few seconds. A green flash is also visible for a rising
Sun, but takes better timing to spot.
A dramatic green flash was caught in the
above photograph in 1992 from
Finland.
The
Sun itself does not turn
partly green, the effect is caused by layers of the
Earth's atmosphere acting like a prism.
 APOD: 2002 July 29 - A Setting Sun Trail
APOD: 2002 July 29 - A Setting Sun Trail
Explanation:
The Sun appears to move on the sky because the
Earth rotates.
The extreme brightness of the
Sun,
however, makes it difficult to capture a sun-trail --
the path the Sun traces on the sky.
To capture the above picture, a very
dark filter covered the camera lens for most of the time,
allowing only a trifle of light from the bright
Sun to peek through.
Just after the Sun had dipped below the
horizon
but before it was completely dark,
the thick filter was removed and the
pretty foreground scene
was captured.
Slight flares
appeared when the Sun went behind thin clouds.
Star-trails and
planet-trails
are much easier to image, and a similar
Moon trail has also recently been imaged.
 APOD: 2002 June 24 - The Sun's Heliosphere and Heliopause
APOD: 2002 June 24 - The Sun's Heliosphere and Heliopause
Explanation:
Where does the Sun's influence end? Nobody is sure.
Out past the orbits of
Neptune and
Pluto
extends a region named the
heliosphere where the
Sun's magnetic field and particles from the
Solar Wind continue to dominate.
The surface where the
Solar Wind drops below
sound speed is called the termination shock and is depicted as the inner oval in the
above computer-generated illustration.
It is thought that this surface occurs as close as 75-90
AU -- so close that a
Pioneer or
Voyager spacecraft may soon glide through it as they exit the
Solar System at about 3 AU/year.
The actual contact sheet between the Sun's
ions and the Galaxy's ions is called the
heliopause and is thought to occur at about 110 AU.
It is depicted above as the middle surface.
The Sun's heliopause moves through the
local interstellar medium
much as a boat moves on water, pushing a
bow shock out in front,
thought to occur near 230 AU.
 APOD: 2002 March 21 - S is for Sun
APOD: 2002 March 21 - S is for Sun
Explanation:
Taken yesterday from the SOHO spacecraft, this
false-color image shows the active
Sun
near the March
Equinox,
the beginning of
Autumn in the south and Spring in the northern hemisphere.
Recorded in a band of extreme
ultraviolet light emitted
by highly ionized iron
atoms, the Sun's upper atmosphere or
solar corona shines
with an array of active regions and plasma loops suspended
in magnetic fields.
The bright coronal structures and loops seen here
have temperatures of about 1.5 million
kelvins.
By chance, the Sun's earth-facing
side also seems to be
marked with a twisting complex of dark
filament channels
shaped like a giant "S".
Filaments represent relatively (!) cool material in the corona
which show up as prominences when seen at the Sun's edge.
For planet Earth, recent
solar activity has made auroral displays
likely around this year's March Equinox.
 APOD: 2001 June 20 - Total Eclipse of the Active Sun
APOD: 2001 June 20 - Total Eclipse of the Active Sun
Explanation:
A
total
eclipse of the Sun is that special
geocentric
celestial event where the Moon passes exactly
in front of the solar disk.
During a fleeting
few minutes of totality, fortunate earthdwellers located
within the path of the Moon's dark shadow
can witness
the wondrous shimmering solar corona sharing
the sky with stars and bright planets.
The next total solar eclipse will occur
tomorrow, June 21.
Since the Sun is still
near the maximum
of its 11 year activity cycle,
careful
eclipse-watchers will also likely see the spectacle of bright solar
prominences lofted above active regions around the Sun's edge.
In fact, a telescopic view could be similar to this stunningly
detailed image -- a picture of the solar eclipse of August 1999
taken at the beginning of totality from Kecel, Hungary.
The upcoming
2001 June 21 event
will be visible as a partial eclipse
from some of South America and much of Africa,
but will only be total along a
125 mile wide path that tracks across land
through Southern Africa and Madagascar.
Of course, if you can't travel to
Africa
tomorrow (and you're not already there),
web sites plan
to offer live views from the Moon's shadow!
 APOD: 2001 May 3 - Far Side of the Sun
APOD: 2001 May 3 - Far Side of the Sun
Explanation:
You may think it's impossible to see
through the Sun, but maps of
the Sun's far side
are now made routinely by instruments on board the
sun-staring SOHO spacecraft.
This is one such map from April 12.
At right, is a map projection of calculated magnetic field strengths on
the Earth-facing solar hemisphere with yellow and red indicating high
magnetic fields characteristic of solar active regions.
At left is a similar map of the solar hemisphere opposite planet Earth,
which shows the large active region AR9393 as the 27-day
solar rotation carried it across
the
far side.
The largest sunspot group in a decade,
AR9393 was easily seen
as it tracked across the Sun's Earth-facing hemisphere in late March.
When AR9393 swung around
to
the Sun's far side, SOHO's
Michelson
Doppler Interferometer
(MDI) instrument continued to map its position
by measuring changes
in
motions caused by
solar
sound waves - transmitted through the Sun and
influenced by the active region's strong magnetic fields.
Known as
helioseismology, analyzing
solar sound waves is like
using seismological records of earthquakes to probe the
interior of the Earth.
On the Sun, sound waves are produced by turbulent convection
cells seen on the surface as
dynamic solar granules.
 APOD: 2001 March 13 - A Sun Pillar
APOD: 2001 March 13 - A Sun Pillar
Explanation:
Have you ever seen a sun pillar?
When the air is cold and the Sun is rising or
setting, falling
ice crystals can reflect sunlight and create an
unusual column of light.
Ice sometimes forms flat, stop-sign
shaped crystals as it falls from high-level
clouds.
Air resistance causes these crystals to lie nearly
flat much of the time as they flutter to the ground.
Sunlight reflects off crystals that are properly aligned,
creating the sun-pillar effect.
In the above picture, a
sun-pillar reflects light from a setting Sun.
 APOD: 2001 March 1 - Maximum Sun
APOD: 2001 March 1 - Maximum Sun
Explanation:
Astronomers recently witnessed an astounding, large scale solar event
as the Sun's north and south magnetic poles changed places!
But, this complete
solar magnetic field flip
was actually anticipated.
It occurs every 11 years during the
maximum
of the solar activity cycle.
Plagues of sun spots, flaring
active regions, and huge
prominences
are also hard-to-miss signs that the solar maximum is here.
On February 12, the sungazing
SOHO spacecraft captured this
dramatic
image of a magnificent prominence above the Sun's limb.
Seen at the lower right, streams of relatively cool dense
plasma
were lofted along looping magnetic field lines extending outward
about 30 times the diameter of planet Earth.
Far above the limb at the upper right, a disconnected
ghostly arc surrounds a dark cavity with bright central emission.
These features are telltale signs of a
coronal mass ejection --
yet another violent expulsion
of material from the active Sun.
Enormous, intensely bright active regions also mottle the
solar surface
in this image, recorded in the light of energetic
Helium atoms by SOHO's
Extreme
ultraviolet Imaging Telescope.
 APOD: 2001 January 29 - An Airplane in Front of the Sun
APOD: 2001 January 29 - An Airplane in Front of the Sun
Explanation:
Sometimes, good planes come to those who wait.
Experienced solar photographer
Thierry Lagault had noticed planes crossing
in front of the
Sun from his home in suburban
Paris.
He then got the idea for the above photograph,
but had to wait through many near misses.
About two weeks ago, he got his wish: a jet
crossed directly in front of the Sun when his
solar imaging equipment was set up.
The
resulting image, shown above, was taken in a
specific color of red light called
Hydrogen-Alpha, and the
picture's contrast has been digitally enhanced.
Dark
prominences can be
seen lacing the
Sun's busy surface.
The airplane is an
MD-11.
 APOD: 2000 May 7 - A Green Flash from the Sun
APOD: 2000 May 7 - A Green Flash from the Sun
Explanation:
Many think it is just a myth.
Others think it is true but its cause isn't known.
Adventurers pride themselves on having seen it.
It's a green flash from the Sun.
The truth is the
green flash
does exist and its cause is well understood.
Just as the setting
Sun disappears completely from view,
a last glimmer appears startlingly green.
The effect is typically visible only from locations with a low,
distant horizon, and lasts just a few seconds. A green flash is also visible for a rising
Sun, but takes better timing to spot.
A slight variant of this was caught in the
above photograph, where much of the
Sun was still visible,
but the very top appeared momentarily green. The
Sun itself does not turn
partly green, the effect is caused by layers of the
Earth's atmosphere acting like a prism.
 APOD: 2000 May 5 - Planets In The Sun
APOD: 2000 May 5 - Planets In The Sun
Explanation:
Today,
all five naked-eye
planets
(Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn)
plus the Moon and the Sun will at least approximately line-up.
As viewed
from planet Earth, they will be clustered
within about 26 degrees, the closest alignment for all
these celestial bodies since
February 1962, when there was a
solar eclipse!
Such
planetary
alignments are not dangerous,
except of course that the Sun might hurt your eyes when
you look at it.
So it might
be easier to
appreciate today's
solar system spectacle
if you use a space-based coronagraph ... like
the LASCO
instrument onboard the SOHO observatory.
In this recent
LASCO image, an occulting disk supported by a structure
seen projecting from the lower left blocks out the overwhelming
sunlight.
It shows three of the planets along with the Sun's location and
bright solar wind regions against a background of stars,
but Mars and Venus are unfortunately outside LASCO's roughly
15 degree field of view.
The horizontal bars through the planets are digital image artifacts.
And what about the Moon?
The SOHO spacecraft is
positioned
well beyond lunar orbit where its view of the Sun is
never interrupted by the Moon.
 APOD: 2000 January 10 - Brown Sun Bubbling
APOD: 2000 January 10 - Brown Sun Bubbling
Explanation:
Our Sun may look like all soft and fluffy, but its not.
Our Sun is an extremely large ball of
bubbling hot gas, mostly
hydrogen gas.
The
above picture was taken in a
specific color of light emitted by hydrogen gas called
Hydrogen-alpha.
Granules cover the solar
photosphere surface like shag
carpet,
interrupted by bright regions containing dark
sunspots.
Visible at the left edge is a
solar prominence.
Our Sun glows because it is hot, but it is not on fire.
Fire is the rapid acquisition of oxygen,
and there is very little
oxygen on the Sun.
The energy source of our Sun is the nuclear
fusion of hydrogen into
helium deep within its core.
Astronomers are still working to understand,
however, why so few
neutrinos are
measured from the
Sun's core.
 APOD: November 19, 1999 - Mercury And The Sun
APOD: November 19, 1999 - Mercury And The Sun
Explanation:
Just days before the peak of the
Leonid meteor shower,
skywatchers were offered another astronomical treat as
planet Mercury crossed the face of the Sun on November 15.
Viewed from planet Earth, a
transit of Mercury is not all that rare.
The last
occurred in 1993 and the next will happen in 2003.
Enjoying a mercurial transit does require an
appropriately filtered telescope,
still the event can be dramatic
as the diminutive well-done world
drifts past the dominating solar disk.
This slow loading gif
animation is based on images
recorded by the earth-orbiting
TRACE satellite.
The false-color TRACE images were made in ultraviolet light
and tend to show the hot gas just above the Sun's visible surface.
Mercury's disk is silhouetted against the
seething plasma as it follows a trajectory near the edge of the Sun.
 APOD: August 18, 1999 - Sun Block
APOD: August 18, 1999 - Sun Block
Explanation:
During a total solar eclipse,
Earth's moon blocks the sun -
almost exactly.
While the sun is about 400 times wider than the moon, it is also
about 400 times farther away and each appears to be
half a degree or so in diameter.
On August 11, this remarkable coincidence in the apparent size of two
vastly different celestial bodies produced tantalizing solar
spectacles for denizens of Europe and Asia.
For example, prominences along the sun's limb peer around the
moon's dark edge in
this dramatic picture of totality recorded
as the lunar shadow swept across Hungary.
Subtle structures in the sun's inner corona are also visible
streaming beyond the silhouetted moon.
This total eclipse of the sun was the last to grace planet Earth's
skies for this
millennium.
Although four partial
eclipses will occur in the year 2000, the
next total eclipse will not be until 2001 June 21.
 APOD: July 6, 1999 - A Sun Pillar
APOD: July 6, 1999 - A Sun Pillar
Explanation:
Have you ever seen a sun pillar? When the air is cold and the Sun is rising or
setting, falling
ice crystals can reflect sunlight and create an
unusual column of light.
Ice sometimes forms flat, stop-sign
shaped crystals as it falls from high-level
clouds.
Air resistance causes these crystals to lie nearly
flat much of the time as they flutter to the ground.
Sunlight reflects off crystals that are properly aligned,
creating the sun-pillar effect.
In the above picture, the sun-pillar can be traced
up to the cloud that is raining the reflecting ice-crystals.
 APOD: June 15, 1999 - The Sun Oscillates
APOD: June 15, 1999 - The Sun Oscillates
Explanation:
Our Sun is in a continual state of oscillation.
Large patches of the
Sun vibrate in and out, back and forth, even as the
Sun rotates.
One mode of Solar oscillation is depicted graphically
above, with blue indicating outward motion,
and red indicating inward motion.
Although sensitive optical solar observatories can only directly detect surface motions,
they give information about vibrations occurring much deeper in the
Sun.
In helioseismology, these oscillations are
being analyzed and are revealing unprecedented
information about the density, temperature,
motion, and chemical composition of the
entire Sun.
 APOD: January 11, 1999 - Perihelion Sun
APOD: January 11, 1999 - Perihelion Sun
Explanation:
The Earth's orbit is not a perfect, sun-centered circle.
At aphelion, the most distant
point in Earth's orbit, the Sun is
150 million kilometers away and
at perihelion, the closest point, Earth
approaches the Sun to within about 147 million kilometers.
While aphelion occurs in July, perihelion
for planet Earth comes in January.
In fact, inhabitants of the Northern Hemisphere, particularly
those wearily weathering winter storms, may be surprised to learn that
Earth reached its closest point to the Sun on January 3rd
this year.
This
false-color picture recorded near perihelion is from
the earth-orbiting Yohkoh Solar Observatory.
It shows
an increasingly active Sun in
the light of X-rays.
A negative color scheme is used, darker colors representing
more intense X-ray light.
 APOD: December 21, 1998 - Solstice Sun In Soft X-rays
APOD: December 21, 1998 - Solstice Sun In Soft X-rays
Explanation:
The solstice occurs today at 8:56 PM Eastern Standard Time.
At the solstice
the sun reaches its most southerly
position in the sky
and winter begins for the Northern Hemisphere while summer starts
South of the Equator.
This false-color
image of the sun was made about 48 hours before the
solstice in the
light of soft (lower energy) X-rays by a telescope on board the
space-based
Yohkho solar observatory.
The normally bright, visible solar surface or photosphere appears
dark in X-ray light while
active regions in the solar corona
which lie above the photosphere are particularly X-ray bright.
Solar photospheric temperatures are about 6,000 degrees C. but
the X-ray bright coronal regions have temperatures of millions of degrees.
Why is the sun's corona so hot?
 APOD: December 12, 1998 - Driving To The Sun
APOD: December 12, 1998 - Driving To The Sun
Explanation:
How long would it take to drive to the Sun?
Brittany, age 7, and D.J., age 12,
ponder this question over dinner one evening.
James, also age 7, suggests taking a really fast racing car while
Christopher, age 4, eagerly agrees.
Jerry, a really old guy who is used to estimating driving time
on family trips based on distance divided by speed, offers
to do the numbers.
"Let's see ... the Sun is 93 million miles away.
So, if we drove 93 miles per hour the trip would only take us 1 million
hours."
How long is 1 million hours?
One year is 365 days times 24 hours per day, or 8,760 hours.
One hundred years would be 876,000
hours, still a little short of the 1 million hour drive time --
so the Sun is really quite far away.
Christopher is not impressed, but as he grows older he will be.
You've got to be impressed by something that's 93 million miles
away and still hurts your eyes when
you look at it!
 APOD: September 23, 1998 - Autumn and the Active Sun
APOD: September 23, 1998 - Autumn and the Active Sun
Explanation:
As the Sun heads South, crossing the celestial equator today
at 1:37 a.m. Eastern Time,
Autumn begins for Earth's Northern Hemisphere.
This Autumnal Equinox
finds an increasingly active Sun steadily
approaching a solar cycle maximum expected
around the year 2003.
The solar activity cycle is driven by a periodic winding up of
the Sun's internal magnetic field.
This colorized picture is a mosaic of
recent ultraviolet images from the orbiting
TRACE satellite
sensitive to light emitted by
highly charged iron atoms.
Growing in
number,
the intricate structures visible are
the Sun's hot active regions
with temperatures over
a million
degrees Fahrenheit
and their associated magnetic loops.
 APOD: August 30, 1998 - The Sun Erupts
APOD: August 30, 1998 - The Sun Erupts
Explanation:
The
Sun is a seething ball of extremely hot gas. Above, the
Sun was
captured by
Skylab in 1973 throwing off one the largest eruptive prominences in recorded history.
The Sun has survived for about 5 billion
years, and will likely survive for another 5 billion. The Sun is
not on fire, will
never explode, and a
solar flare will never destroy the Earth.
The
Sun continues to present many unanswered questions. For example:
Why is the Sun's corona so hot?
What causes the Sun's unusual magnetic field?
Why does the
Sun's center emit so few neutrinos?
 APOD: August 24, 1998 - An Annular Eclipse of the Sun
APOD: August 24, 1998 - An Annular Eclipse of the Sun
Explanation:
An annular eclipse of the Sun was visible in parts of the Eastern Hemisphere on Saturday.
The
above picture was taken
at that time by a video camera in
Mersing on the East Coast of
Malaysia and emailed to
APOD
yesterday from an internet cafe in Kuala Lumpur.
An
annular solar eclipse will occur when the Moon's angular size is slightly less than the Sun's angular size.
Therefore, when the Moon is directly in front of the Sun,
the edges of the Sun are still visible. This solar ring is so bright that the Moon's surface normally
appears dark by comparison. The
angular sizes of the Sun and Moon change slightly because of the elliptical nature of the Moon's and Earth's orbit. A
total solar eclipse
would have occurred were the Moon much closer to the Earth.
 APOD: June 16, 1998 - An Active Region of the Sun
APOD: June 16, 1998 - An Active Region of the Sun
Explanation:
The Sun is a busy place.
This false-color image depicts an active region
near an edge of the
Sun.
Hot plasma is seen exploding off the Sun's photosphere and traveling along loops
defined by the Sun's magnetic field.
The red regions are particularly hot,
indicating that some magnetic field loops
carry hotter gas than others.
These active loops were so large that the Earth could easily fit under one. The TRACE satellite was launched in
April with plans to continue high-resolution imaging as the
Sun passes
Solar Maximum in the next few years.
 APOD: June 1, 1998 - Solar Flares Cause Sun Quakes
APOD: June 1, 1998 - Solar Flares Cause Sun Quakes
Explanation:
An 11th magnitude
quake has been recorded on the Sun, immediately following a moderate
solar flare.
The quake was the first ever recorded on the
Sun, but only because astronomers have only
recently figured out when and how to find
them using the orbiting SOHO spacecraft. Dark waves from the quake can
be seen in the above picture spreading out from an
explosive bright flare. The solar ripples are similar in
appearance to waves caused by a rock thrown into a pond.
The magnitude and evolution of these quakes gives
information about the physical nature of solar flares, the surface of the
Sun,
and even the Sun's interior.
 APOD: May 26, 1998 - A Seemingly Square Sun
APOD: May 26, 1998 - A Seemingly Square Sun
Explanation:
Isn't the Sun round? Yes, but in the above picture, the
Earth's atmosphere makes it appear almost square.
Here a layer of air near the Earth was so warm it acted like a giant lens, creating increasingly distorted
paths for sunlight to reach the camera.
Similarly, on a long flat highway, it may appear that
the road in the distance is covered with water. In this case,
light from the blue sky is being unusually refracted by warm air just above the dry road.
No matter how the
Earth's atmosphere makes the Sun appear, the
Sun will always be spherical. This setting Sun was
photographed over Lake Michigan in
Muskegon, MI.
 APOD: May 15, 1998 - TRACE and the Active Sun
APOD: May 15, 1998 - TRACE and the Active Sun
Explanation:
This
dramatic high resolution picture
looking across the edge of the Sun
was taken April 24th by a telescope on board
the newly launched
Transition Region and Coronal Explorer (TRACE) satellite.
It shows graceful arcs of intensely hot gas
suspended in
powerful looping magnetic fields which
soar above a solar active region.
The colorized image was made in the extreme ultraviolet light
radiated by highly
ionized Iron atoms.
With a temperature of a mere 6,000
degrees Celsius,
the sun's surface is relatively cool and dark at these wavelengths,
but the million degree hot plasma loops glow strongly!
Such TRACE images follow the plasma and magnetic structures arising
from the surface of the sun as they merge with the tenuous, hot
solar Corona or outer atmosphere.
By operating the
TRACE instruments during the Sun's increasingly
active phase,
scientists hope to explore the connections between
complex
solar magnetic fields and
potentially hazardous solar eruptions.
 APOD: April 13, 1998 - The Sun Changes
APOD: April 13, 1998 - The Sun Changes
Explanation:
Our Sun changes every day.
This recent picture was taken in a very specific red color called
Hydrogen-Alpha.
Dark spots that might appear on the image are usually
sunspots,
dark magnetic depressions that are
slightly cooler than the rest of the Sun's surface.
Bright spots that might appear are usually
plages, active regions that are slightly hotter
than the rest of the Sun's surface.
Over the next few years the average number of
sunspots and plages will increase until "Solar Maximum"
occurs in 2001.
The Sun usually goes through a maximum and
minimum every 11 years. From
1645 to 1715, however,
almost no sunspots at all were recorded, for reasons unknown.
(An updated picture
can be found here.)
 APOD: September 9, 1997 - A Green Flash from the Sun
APOD: September 9, 1997 - A Green Flash from the Sun
Explanation:
Many think it is just a myth.
Others think it is true but its cause isn't known.
Adventurers pride themselves on having seen it. It's a green flash from the
Sun.
The truth is the
green flash does exist and its cause is well understood.
Just as the setting
Sun disappears completely from view,
a last glimmer appears startlingly green.
The effect is typically visible only from locations with a low,
distant horizon, and lasts just a few seconds. A
green flash is also visible for a rising
Sun, but takes better timing to spot.
A slight variant of this was caught in the above photograph,
where much of the
Sun was still visible,
but the very top appeared momentarily green. The
Sun itself does not turn
partly green, the effect is caused by layers of the
Earth's atmosphere acting like a prism.
 APOD: September 4, 1997 - Rivers in the Sun
APOD: September 4, 1997 - Rivers in the Sun
Explanation:
The surface of the Sun is shifting. By watching
sunspots, it has long been known that our
Sun
rotates. It was also known that the center of the
Sun
rotates faster than the poles. Now, recent measurements by the
Solar Oscillations
Investigations group of the
SOHO Observatory have found that the
surface of the sun moves in other ways, too.
Hot, electrically charged gas flows along and beneath the
Sun's surface as depicted in the
above computer generated diagram. The speed of these
solar rivers
is false-color coded with red
hydrogen moving faster than blue. Over the course of a year plasma moves from the equator to the poles,
while internal eddies circulate gas from deep inside the
Sun.
One surprise is the similarity to the motion of air in the
Earth's atmosphere - indicating that scientists might learn
more about
Earth's global weather by studying the
Sun.
 APOD: January 7, 1997 - Red Sun Streaming
APOD: January 7, 1997 - Red Sun Streaming
Explanation: The Sun is leaking. In fact, it is gushing:
particles stream away from the Sun
at hundreds of kilometers per second. Some of these particles
strike the Earth and cause aurora.
Most particles, however, either surround the Sun
as a huge solar corona
or glide into interstellar space
as the solar wind.
Don't worry about the Sun
totally evaporating - it loses too little mass to have any lasting
effect. The above false-color picture
was taken with the Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronograph
on board the SOlar and Heliospheric Observatory
(SOHO). This instruments blocks out the central solar disk so
it can image the regions surrounding the Sun.
The large streamers visible are typical. Where these charged ions get their enormous streaming energy is still a mystery!
 APOD: January 6, 1997 - Blue Sun Glaring
APOD: January 6, 1997 - Blue Sun Glaring
Explanation: The Sun is a bubbling ball of extremely hot
gas. In this false-color picture,
light blue regions are extremely hot - over 1 million degrees,
while dark blue regions are slightly cooler. The camera filter used
was highly sensitive to the emission of highly charged iron ions,
which trace the magnetic field
of the Sun. The rich structure of
the image shows the great complexity of the Sun's
inner corona. A small active region
can be seen just to the right and above center. This picture
was taken in ultraviolet (extremely
blue) light by the Extreme-ultraviolet Imaging Telescope
(EIT) on board the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory
(SOHO) spacecraft, which is orbiting the Sun
just ahead of the Earth, at the L1 point.
SOHO was launched in 1995 and will continually monitor the Sun
for several years.
 APOD: September 16, 1996 - The Sun Erupts
APOD: September 16, 1996 - The Sun Erupts
Explanation: The Sun is
a seething ball of extremely hot gas. Above, the Sun was captured by Skylab in
1973 throwing off one the largest eruptive prominences in recorded history.
The Sun has
survived for about 5 billion years, and will likely survive for
another 5 billion. The Sun is not on fire,
will never explode,
and a solar flare will never destroy the Earth. The Sun
continues to present many unanswered questions.
For example: Why is the Sun's corona so hot?
What causes the Sun's unusual magnetic field?
Why does the Sun's center emit so few neutrinos?
 APOD: May 18, 1996 - The Sun Today
APOD: May 18, 1996 - The Sun Today
Explanation:
Our Sun shows a different face every day. The above picture was taken on
May 15, but a similar picture of the
Sun actually taken today can be found
here.
The above picture was taken in red light and so is shown in red. The
bright spots to the right of center are active regions known as
plages.
Currently, the
Sun is showing very few active regions or sunspots, and is considered to be in a solar minimum. Solar
activity will pick up over
the next six years until a "solar maximum" is reached. The Sun goes
through this cycle of maxima and minima every 11 years.
Sol,
our Sun, is
hundreds of times more massive than all the
planets in the Solar System
combined. However, the
Sun itself contains only a small amount of the total
angular
momentum of the Solar System.
 APOD: May 16, 1996 - Comet Hyakutake Passes the Sun
APOD: May 16, 1996 - Comet Hyakutake Passes the Sun
Explanation:
On May 1,
Comet Hyakutake
made its closest approach to the
Sun. During this
time it was not possible to view the comet with most astronomical
instruments because of the brightness of the nearby Sun. But the orbiting
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) spacecraft contains telescopes
meant to look directly at the Sun and so were able to track the comet
during this crucial time.
This picture,
taken May 2, shows the
tails of Comet Hyakutake
pointing away from the Sun, as expected. During its closest approach,
Comet Hyakutake
passed inside the orbit of
Mercury.
Comet Hyakutake
will not return to the inner
Solar System for another 14,000
years.
 APOD: October 4, 1995 - The Sun Spews X-rays
APOD: October 4, 1995 - The Sun Spews X-rays
Explanation:
Our
Sun is really very hot. The Sun's outer
atmosphere is so hot that it emits much light in the
X-ray band, which was unexpected.
X-rays are usually emitted from objects having a temperature in the
millions of degrees, not the mere thousands of degrees of the Sun's
surface. The above X-ray picture shows the
Sun one particularly active day
in August of 1992. Evident are hot spots on the solar surface, showing that
areas above the
Sun's
surface really do reach millions of degrees. But
possibly more puzzling is the broader X-ray glow visible surrounding the
Sun.
This glow is now attributed to the Sun's X-ray
corona,
the origin of which is currently a subject of much discussion and debate. The
Sun
is one of the most photographed objects, with frequently updated pictures
available
over the WWW. In fact, an X-ray picture from Yohkoh taken earlier today
is usually
available
over the WWW. Compare it to the above picture!
 APOD: August 13, 1995 - The Sun Erupts
APOD: August 13, 1995 - The Sun Erupts
Explanation:
The sun
was captured in 1973 throwing one of the largest eruptive prominences
ever recorded.
Sol, our sun, is a normal star. It formed about 5 billion years
ago, and will last about another 5 billion years.
The sun
will never explode, and a solar flare will never destroy the earth.
Eventually the sun will become a
white dwarf star.
The sun is made of mostly
hydrogen and
helium.
The sun's center is so hot that when hydrogen nuclei collide, they stick
together and release energy - a process called nuclear
fusion
No one knows why the center of the sun emits so few
neutrinos.