 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
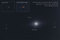 APOD: 2024 April 17 – Total Eclipse and Comets
APOD: 2024 April 17 – Total Eclipse and Comets
Explanation:
Not one, but two comets appeared near the Sun during
last week's total solar eclipse.
The expected comet was
Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks,
but it was disappointingly dimmer than many had hoped.
However, relatively unknown Comet SOHO-5008 also appeared in long duration camera exposures.
This comet was the 5008th comet identified on images taken by
ESA &
NASA's Sun-orbiting
SOHO spacecraft.
Likely much smaller, Comet SOHO-5008 was a sungrazer which
disintegrated within hours as it passed too
near the Sun.
The featured image is not only unusual for capturing
two comets during an eclipse,
but one of the rare times that a
sungrazing comet has been photographed from the Earth's surface.
Also visible in the image is the
sprawling corona of
our Sun and the planets
Mercury (left) and
Venus (right).
Of these planets and comets, only
Venus was easily visible to
millions of people in the
dark shadow of the Moon that
crossed North America on April 8.
 APOD: 2024 February 19 – Looking Sideways from the Parker Solar Probe
APOD: 2024 February 19 – Looking Sideways from the Parker Solar Probe
Explanation:
What's happening near the Sun?
To help find out, NASA
launched the robotic
Parker Solar Probe (PSP) to
investigate
regions closer to the Sun than ever before.
The PSP's looping
orbit
brings it nearer to the Sun
each time around -- every few months.
The featured time-lapse video
shows the view looking sideways from
behind PSP's Sun shield during its 16th approach to the Sun last year --
from well within the orbit of
Mercury.
The PSP's Wide Field Imager for Solar Probe
(WISPR)
cameras took the images over eleven days,
but they are digitally compressed here into about one minute video.
The waving of the
solar corona is visible, as is a
coronal mass ejection,
with stars, planets, and even the central band of our
Milky Way Galaxy streaming by in the background as the
PSP orbits the Sun.
PSP has found the solar neighborhood to be
surprisingly complex and to include
switchbacks --
times when the
Sun's magnetic field briefly reverses itself.
 APOD: 2024 January 12 - Good Morning Moon
APOD: 2024 January 12 - Good Morning Moon
Explanation:
Yesterday, the
Moon was New.
But on January 9, early morning risers around planet Earth were treated
to the sight of an old Moon, low in the east as the sky grew
bright before
dawn.
Above the city of Saarburg in
Rhineland-Palatinate, western Germany,
this simple snapshot found the waning Moon's
sunlit crescent
just before sunrise.
But also never wandering far from the Sun
in Earth's sky,
inner planets Venus
and Mercury shared the
cold morning skyview.
In the foreground are the historic city's tower and castle
with ruins from the 10th century.
 APOD: 2023 November 28 – Ganymede from Juno
APOD: 2023 November 28 – Ganymede from Juno
Explanation:
What does the largest moon in the Solar System look like?
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede, larger than even
Mercury and
Pluto,
has an icy surface speckled with bright young craters overlying a mixture of
older, darker, more cratered terrain laced with
grooves and ridges.
The cause of the grooved terrain remains a
topic of research,
with a leading hypothesis relating it to shifting ice plates.
Ganymede is thought to have an
ocean layer that contains more water than Earth -- and
might contain life.
Like Earth's Moon, Ganymede keeps the
same face towards
its central planet, in this case Jupiter.
The
featured image was captured in 2021 by NASA's robotic Juno spacecraft when it passed by the immense moon.
The close pass reduced Juno's orbital period around Jupiter from 53 days to 43 days.
Juno continues to study the
giant planet's high gravity,
unusual magnetic field, and
complex cloud structures.
 APOD: 2023 October 27 - Encke and the Tadpoles
APOD: 2023 October 27 - Encke and the Tadpoles
Explanation:
History's second known periodic comet is
Comet Encke (2P/Encke).
As it swings through the inner
Solar System, Encke's
orbit takes it from an aphelion, its greatest distance from the Sun,
inside the orbit of Jupiter to a
perihelion just inside the orbit of Mercury.
Returning to its perihelion every 3.3 years, Encke has the shortest
period of the Solar System's
major comets.
Comet Encke is also associated with
(at least)
two annual meteor showers on
planet Earth, the
North and South Taurids.
Both showers are active in late October and early November.
Their two separate radiants lie near bright star Aldebaran in the head-strong
constellation Taurus.
A faint comet, Encke was captured in
this telescopic field of view
imaged on the morning of August 24.
Then, Encke's pretty greenish coma was close on the sky to
the young, embedded star cluster and light-years long,
tadpole-shaped
star-forming clouds in emission nebula IC 410.
Now near bright star Spica
in Virgo Comet Encke passed its 2023 perihelion only five days ago,
on October 22.
 APOD: 2023 August 21 – Introducing Comet Nishimura
APOD: 2023 August 21 – Introducing Comet Nishimura
Explanation:
Will Comet Nishimura become visible to the unaided eye?
Given the unpredictability of comets, no one can say for sure,
but it currently seems like a good bet.
The comet was
discovered only ten days ago by Hideo Nishimura
during 30-second exposures with a standard digital camera.
Since then,
C/2023 P1 Nishimura has increased in brightness and
its path across the inner
Solar System determined.
As the comet dives toward the Sun, it will surely continue to
intensify and possibly become a naked-eye object in early September.
A problem is that
the comet will also be angularly near the Sun,
so it will only be possible to see it
near sunset or sunrise.
The comet will get so
close to the Sun -- inside the orbit of
planet Mercury --
that its nucleus may
break up.
Pictured,
Comet Nishimura was imaged three days ago from
June Lake,
California,
USA
while sporting a green coma and a thin tail.
 APOD: 2023 August 3 - The Falcon and the Redstone
APOD: 2023 August 3 - The Falcon and the Redstone
Explanation:
In a photo from the early hours of July 29 (UTC),
a Redstone rocket and Mercury capsule
are on display at Cape Canaveral
Launch Complex 5.
Beyond the Redstone, the 8 minute long exposure has
captured the arcing launch streak of a SpaceX
Falcon Heavy rocket.
The Falcon's heavy
communications satellite payload, at a record setting 9 metric tons,
is bound for
geosynchronous orbit
some 22,000 miles above planet Earth.
The historic launch of a Redstone rocket
carried astronaut
Alan Shepard
on a suborbital spaceflight in May 1961
to an altitude of about 116 miles.
Near the top of the frame, this Falcon rocket's two
reusable side boosters separate and execute brief entry burns.
They
returned
to land side by side at Canaveral's Landing Zone 1 and 2
in the distance.
 APOD: 2023 January 2 – After Sunset Planet Parade
APOD: 2023 January 2 – After Sunset Planet Parade
Explanation:
Look up tonight and see a whole bunch of planets.
Just after sunset, looking west, planets
Venus,
Saturn,
Jupiter and
Mars will all be
simultaneously visible.
Listed west to east, this planetary lineup will have Venus nearest the horizon, but setting shortly after the Sun.
It doesn't matter where on
Earth you live because this early evening
planet parade will be visible
through clear skies all around the globe.
Taken late last month, the featured image captured
all of these planets and more: the
Moon and planet
Mercury were also simultaneously visible.
Below visibility were the planets
Neptune and
Uranus,
making this a nearly
all-planet panorama.
In the foreground are hills around the small village of Gökçeören,
Kaş,
Turkey, near the
Mediterranean coast.
Bright stars
Altair,
Fomalhaut, and
Aldebaran
are also prominent, as well as the
Pleiades star cluster.
Venus will
rise higher in the sky at sunset as January continues,
but Saturn will descend.
 APOD: 2022 August 9 - Leaving Earth
APOD: 2022 August 9 - Leaving Earth
Explanation:
What it would look like to leave planet Earth?
Such an event was recorded visually
in great detail
by the MESSENGER spacecraft as it swung
back past the Earth in 2005 on its way in toward the
planet Mercury.
Earth can be seen rotating in
this time-lapse video, as it recedes into the distance.
The sunlit half of Earth is
so bright that background
stars are not visible.
The robotic MESSENGER spacecraft orbit around
Mercury from 2011 to 2015 has conducted the first
complete map of the surface.
On occasion, MESSENGER has continued to
peer back at its home world.
MESSENGER is one of the few things created on the
Earth that will
never return.
At the end of its mission MESSENGER crashed into
Mercury's surface.
 APOD: 2022 June 29 - Solar System Family Portrait
APOD: 2022 June 29 - Solar System Family Portrait
Explanation:
Yes, but have you ever seen all of the planets at once?
A rare roll-call of planets has
been occurring in the morning sky for
much of June.
The featured fisheye all-sky image, taken a few mornings ago near the town of
San Pedro de Atacama in
Chile,
caught not only the entire planet parade, but the Moon between Mars and Venus.
In order, left to right along the
ecliptic plane,
members of this
Solar System family portrait are
Earth,
Saturn,
Neptune,
Jupiter,
Mars,
Uranus,
Venus,
Mercury, and
Earth.
To emphasize their locations, Neptune and Uranus have been artificially enhanced.
The volcano just below Mercury is
Licancabur.
In July, Mercury will move into the Sun's glare but
reappear a few days later on the evening side.
Then, in August,
Saturn will drift past the direction
opposite the Sun
and so become visible at dusk instead of dawn.
The next time that all eight planets will be
simultaneously visible in the evening sky will be in 2122.
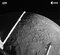 APOD: 2022 June 28 - Mercury from Passing BepiColombo
APOD: 2022 June 28 - Mercury from Passing BepiColombo
Explanation:
Which part of the Moon is this?
No part -- because this is the
planet Mercury.
Mercury's
old surface is heavily
cratered like that of
Earth's Moon.
Mercury, while only slightly larger than
Luna, is much denser and more massive than any
Solar System
moon because it is made mostly of
iron.
In fact, our Earth is the only planet more dense.
Because Mercury rotates exactly three times for every two orbits around the Sun,
and because Mercury's orbit is so
elliptical,
visitors on Mercury
could see the Sun rise,
stop in the sky, go back toward the rising horizon,
stop again, and then set quickly over the other horizon.
From Earth, Mercury's proximity to the Sun causes it to be
visible only for a short time just after sunset or just before sunrise.
The featured image was captured last week by
ESA and
JAXA's passing
BepiColombo spacecraft as it
sheds energy and
prepares to orbit the innermost planet starting in 2025.
 APOD: 2022 June 17 - Good Morning Planets from Chile
APOD: 2022 June 17 - Good Morning Planets from Chile
Explanation:
On June 15, innermost planet Mercury had wandered
about as far from the Sun as it ever gets
in planet Earth's sky.
Near the eastern horizon just before sunrise
it stands over distant Andes mountain peaks in
this predawn snapshot
from the valley of Rio Hurtado in Chile.
June's other morning planets are arrayed above it,
as all the naked-eye planets of the Solar System stretch in a line
along the ecliptic
in the single wide-field view.
Tilted toward the north, the Solar System's ecliptic plane arcs steeply
through southern hemisphere skies.
Northern hemisphere early morning risers will see the
lineup of planets
along the ecliptic at a shallower angle
tilting toward the south.
From both hemispheres
June's beautiful morning
planetary display finds
the visible planets in order of their increasing
distance from the Sun.
 APOD: 2022 May 3 - Mercury's Sodium Tail
APOD: 2022 May 3 - Mercury's Sodium Tail
Explanation:
That's no comet.
Below the Pleiades star cluster
is actually a planet: Mercury.
Long exposures of our
Solar System's innermost planet may reveal something unexpected: a tail.
Mercury's thin
atmosphere
contains small amounts of
sodium
that glow when excited by light from the Sun.
Sunlight also liberates these atoms from
Mercury's surface and pushes them away.
The yellow glow from
sodium, in particular, is relatively bright.
Pictured, Mercury and its
sodium tail
are visible in a deep image taken last week from
La Palma,
Spain
through a filter that primarily transmits
yellow light
emitted by sodium.
First
predicted
in the 1980s, Mercury's tail was first
discovered in 2001.
Many tail details were revealed in
multiple observations by
NASA's robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft
that orbited Mercury between 2011 and 2015.
Tails, of course, are usually associated with
comets.
 APOD: 2021 December 5 - Total Solar Eclipse Below the Bottom of the World
APOD: 2021 December 5 - Total Solar Eclipse Below the Bottom of the World
Explanation:
Yesterday there was a total solar eclipse visible only at the end of the Earth.
To capture the
unusual phenomenon,
airplanes took flight below the clouded seascape of
Southern Ocean.
The featured image
shows one relatively spectacular capture where the
bright spot is the outer
corona of the Sun and the
eclipsing Moon
is seen as the dark spot in the center.
A wing and engine of the
airplane are visible across
the left and bottom of the image, while
another airplane observing the eclipse
is visible on the far left.
The dark area of the sky surrounding the
eclipsed Sun is called a
shadow cone.
It is dark because you are looking down a
long corridor of air shadowed by the Moon.
A careful inspection of the eclipsed Sun will reveal the
planet Mercury just to the right.
The next total solar eclipse
shadow
will cross parts of
Australia and
Indonesia in April of 2023, while
the one after that will cross
North America in
April of 2024.
 APOD: 2021 October 9 - 50 Light years to 51 Pegasi
APOD: 2021 October 9 - 50 Light years to 51 Pegasi
Explanation:
It's only 50 light-years
to 51 Pegasi.
That star's position is indicated in this snapshot from
August, taken on a hazy night with mostly brighter stars visible above
the dome at Observatoire de Haute-Provence in France.
Twenty-six years ago,
in October of 1995, astronomers
Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz
announced a profound discovery made at the observatory.
Using a precise spectrograph they had detected a planet orbiting 51 Peg,
the first known exoplanet orbiting a sun-like star.
Mayor and Queloz had used the spectrograph to measure changes in the
star's radial velocity,
a regular wobble caused by the gravitational
tug of the orbiting planet.
Designated 51 Pegasi b,
the planet was determined to
have a mass at least half of Jupiter's mass
and an orbital period of 4.2 days,
making it much closer to its parent star than Mercury is to the Sun.
Their discovery was quickly confirmed and Mayor and Queloz
were ultimately awarded the
Nobel Prize in physics
in 2019.
Now recognized as the prototype for the class of exoplanets
fondly known as
hot Jupiters,
51 Pegasi b was formally
named Dimidium,
latin for half, in 2015.
Since its discovery, over 4,000
exoplanets have been found.
 APOD: 2021 July 10 - Mercury and the Da Vinci Glow
APOD: 2021 July 10 - Mercury and the Da Vinci Glow
Explanation:
On July 8th early morning risers saw Mercury near an old Moon
low on the eastern horizon.
On that date
bright planet, faint glow of lunar night side, and sunlit crescent
were captured in this predawn skyscape from Tenerife's
Teide National Park in the Canary Islands.
Never far from the Sun in planet Earth's sky, the
fleeting inner planet
shines near its brightest in the morning twilight scene.
Mercury lies just below the zeta star of the constellation Taurus,
Zeta Tauri,
near the
tip
of the celestial bull's horn.
Of course the Moon's ashen glow is
earthshine, earthlight reflected
from the Moon's night side.
A description of earthshine, in terms of sunlight
reflected by Earth's oceans illuminating
the Moon's dark surface, was written over 500 years ago by
Leonardo da Vinci.
Waiting for the coming dawn in the foreground are the
Teide Observatory's
sentinels of the Sun, also known as (large domes left to right) the
THEMIS,
VTT, and GREGOR solar telescopes.
 APOD: 2021 July 6 - Saturn and Six Moons
APOD: 2021 July 6 - Saturn and Six Moons
Explanation:
How many moons does Saturn have?
So far 82 have been confirmed, the smallest being only a fraction
of a kilometer across.
Six of its largest satellites can be seen here
in a
composite image
with 13 short exposure of the bright planet, and
13 long exposures of the brightest of its faint moons,
taken over
two weeks last month.
Larger than Earth's Moon and even slightly larger than
Mercury,Saturn's largest moon
Titan has a diameter of 5,150 kilometers and was captured making
nearly a complete orbit around its
ringed parent planet.
Saturn's first known natural satellite, Titan was
discovered in 1655 by
Dutch astronomer
Christiaan Huygens, in contrast with several
newly discovered moons announced in 2019.
The trail on the far right belongs to
Iapetus, Saturn's third largest moon.
The radius of
painted Iapetus' orbit is so large
that only a portion of it was captured here.
Saturn leads Jupiter across the night sky
this month, rising soon after sunset toward the southeast,
and remaining visible until
dawn.
 APOD: 2021 May 7 - Mercury-Redstone 3 Launch
APOD: 2021 May 7 - Mercury-Redstone 3 Launch
Explanation:
Sixty years ago, near the
dawn of the space age,
NASA controllers "lit the candle" and sent
Mercury astronaut Alan Shepard
arcing into space atop a Redstone rocket.
His cramped space capsule was dubbed Freedom 7.
Broadcast live to a global television audience, the historic
Mercury-Redstone 3
(MR-3) spacecraft was launched from
Cape Canaveral Florida at 9:34 a.m. Eastern Time on May 5, 1961.
The flight of Freedom 7,
the first space flight by an American, followed less
than a month after the first human venture into space
by Soviet Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin.
The 15 minute sub-orbital flight achieved an altitude of 116 miles
and a maximum speed of 5,134 miles per hour.
As Shepard looked back
near the peak of Freedom 7's
trajectory, he could see the outlines of
the west coast of Florida, Lake Okeechobe in central Florida,
the Gulf of Mexico, and the Bahamas.
Shepard would later
view planet Earth from a more distant perspective
and walk on the Moon as commander of the
Apollo 14 mission.
 APOD: 2020 November 14 - Venus, Mercury, and the Waning Moon
APOD: 2020 November 14 - Venus, Mercury, and the Waning Moon
Explanation:
Yesterday, early morning risers around planet Earth were treated
to a waning Moon low in the east as the sky grew
bright before dawn.
From the Island of Ortigia, Syracuse, Sicily, Italy this
simple snapshot found the slender sunlit crescent
just before sunrise.
Never wandering far from the Sun in Earth's sky, inner planets Venus
and Mercury shared the calm seaside view.
Also in the frame,
right of the line-up of Luna and planets, is bright
star Spica, alpha star of the constellation Virgo and one of the 20
brightest stars
in Earth's night.
Tomorrow the Moon will be
New.
The dark lunar disk means mostly dark nights for planet Earth in
the coming week and a good chance to watch the annual
Leonid Meteor Shower.
 APOD: 2020 July 8 - Mercury's Sodium Tail
APOD: 2020 July 8 - Mercury's Sodium Tail
Explanation:
What is that fuzzy streak extending from Mercury?
Long exposures of our
Solar System's innermost planet may reveal something unexpected: a tail.
Mercury's thin
atmosphere
contains small amounts of
sodium
that glow when excited by light from the Sun.
Sunlight also liberates these molecules from
Mercury's surface and pushes them away.
The yellow glow from sodium, in particular, is relatively bright.
Pictured, Mercury and its
sodium tail
are visible in a deep image taken in late May from
Italy
through a filter that primarily transmits
yellow light emitted by sodium.
First
predicted
in the 1980s, Mercury's tail was first
discovered in 2001.
Many tail details were revealed in
multiple observations by
NASA's robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft
that orbited Mercury between 2011 and 2015.
Tails are usually associated with
comets.
The tails of
Comet NEOWISE are currently
visible with the unaided eye in the
morning sky.
 APOD: 2020 June 20 - Northern Summer on Titan
APOD: 2020 June 20 - Northern Summer on Titan
Explanation:
Today's solstice
brings summer to planet Earth's northern hemisphere.
But the northern summer
solstice arrived
for ringed planet Saturn over three years ago on May 24, 2017.
Orbiting the gas giant,
Saturn's moon Titan experiences the
Saturnian
seasons that are about 7 Earth-years long.
Larger than inner planet Mercury, Titan was captured in this
Cassini spacecraft image
about two weeks after its northern summer began.
The near-infrared view finds bright methane clouds drifting through
Titan's dense, hazy atmosphere
as seen from a distance of about 507,000 kilometers.
Below the clouds, dark
hydrocarbon lakes sprawl near
its fully illuminated north pole.
 APOD: 2020 May 30 - Green Flashes: Sun, Moon, Venus, Mercury
APOD: 2020 May 30 - Green Flashes: Sun, Moon, Venus, Mercury
Explanation:
Follow
a sunset on a clear day against a distant horizon and you might
glimpse green just as the Sun disappears from view.
The green flash
is caused by refraction of light rays traveling to the eye
over a long path through the atmosphere.
Shorter wavelengths refract more strongly than longer redder wavelengths
and the separation of colors lends a green hue to the last
visible vestige of the solar disk.
It's harder to see a
green flash from the Moon,
not to mention the diminutive disks
of Venus
and Mercury.
But a telescope or telephoto lens and camera can help
catch this tantalizing result of atmospheric refraction
when the celestial bodies are near the horizon.
From Sicily, the top panels were recorded
on March 18, 2019 for the Sun and May 8, 2020 for the Moon.
Also from the Mediterranean island,
the bottom panels were shot during the twilight apparition
of Venus and Mercury
near the western horizon on May 24.
 APOD: 2020 May 29 - Mercury Meets Crescent Venus
APOD: 2020 May 29 - Mercury Meets Crescent Venus
Explanation:
That's not a bright star
and crescent Moon
caught between branches of a eucalyptus tree.
It's Venus in a crescent phase and Mercury.
Near the western horizon after sunset, the two inner planets
closely shared this telescopic field of view on May 22, seen from
a balcony in Civitavecchia, Italy.
Venus, the very bright
celestial beacon,
is wandering lower into the evening twilight.
It grows larger in apparent size and shows a
thinner crescent
as it heads toward its inferior conjunction, positioned between
Earth and Sun on June 3.
Mercury, in
a fuller phase, is climbing in the western sky though,
reaching its maximum angular distance from the Sun on June 4
Still, this
remarkably close pairing
with brilliant Venus made
Mercury, usually lost in bright twilight skies, easier to spot
from planet Earth.
 APOD: 2020 May 19 - Posters of the Solar System
APOD: 2020 May 19 - Posters of the Solar System
Explanation:
Would you like a NASA astronomy-exploration poster?
You are just one page-print away.
Any of the panels you see on
the featured image can appear on your
wall.
Moreover,
this NASA page has, typically,
several more posters of each of the
Solar System objects depicted.
These posters highlight many of the places humanity, through
NASA, has explored in the past 50 years,
including our
Sun, and planets
Mercury,
Venus,
Earth,
Mars,
Jupiter,
Saturn,
Uranus, and
Neptune.
Moons of Jupiter that have been posterized include
Europa,
Ganymede,
Callisto, and
Io,
while moons of Saturn that can be framed include
Enceladus and
Titan.
Images of
Pluto,
Ceres,
comets and asteroids are also presented, while six deep space scenes --
well beyond
our Solar System -- can also be prominently displayed.
If you
lack wall space or blank poster sheets don't despair --
you can still print many of these out as
trading cards.
 APOD: 2020 May 4 - Earth Flyby of BepiColombo
APOD: 2020 May 4 - Earth Flyby of BepiColombo
Explanation:
What it would look like to approach planet Earth?
Such an event was recorded visually in great detail by
ESA's and
JAXA's robotic
BepiColombo
spacecraft last month as it swung back past Earth on its journey in to the planet
Mercury.
Earth
can be seen rotating on approach as it comes out
from behind the spacecraft's high-gain antenna in this nearly 10-hour time-lapse video.
The Earth is so bright that
no background stars are visible.
Launched in 2018,
the robotic
BepiColombo used the
gravity
of Earth to adjust its course, the first of
nine planetary flybys over the next seven years -- but the only one
involving Earth.
Scheduled to enter orbit in 2025, BepiColombo will take images and data of the
surface and magnetic field of
Mercury in an effort to
better understand the
early evolution of our Solar System and its innermost planet.
 APOD: 2020 February 11 - Launch of the Solar Orbiter
APOD: 2020 February 11 - Launch of the Solar Orbiter
Explanation:
How does weather on the Sun affect humanity?
To help find out, the
European Space Agency (ESA) and
NASA have just launched the
Solar Orbiter.
This Sun-circling robotic spaceship will monitor the Sun's changing light,
solar wind, and
magnetic field not only from the
usual perspective of Earth but also from above and below the Sun.
Pictured,
a long duration exposure of the
launch of the
Solar Orbiter
shows the graceful arc of the bright engines of
United Launch Alliance's
Atlas V rocket
as they
lifted the satellite off the
Earth.
Over the next few years, the
Solar Orbiter will use the
gravity
of Earth and Venus to
veer out of the
plane of the planets and closer to the
Sun than Mercury.
Violent weather on the Sun, including
solar flares and
coronal mass ejections, has shown the ability to
interfere with power grids on the Earth and
communications satellites in Earth orbit.
The Solar Orbiter is expected to coordinate observations with the also Sun-orbiting
Parker Solar
Probe
launched in 2018.
 APOD: 2020 January 21 - Parker: Sounds of the Solar Wind
APOD: 2020 January 21 - Parker: Sounds of the Solar Wind
Explanation:
What does the solar wind sound like?
A wind
of fast moving particles blows out from
our Sun, and although
space transmits sound poorly,
particle impact and variable-field data from
NASA's near-Sun
Parker Solar Probe
is being translated into
sound.
The disarming audio track of the featured video recounts several of
these reverberations,
including spooky-sounding Langmuir Waves (heard first), hurricane-sounding
Whistler
Mode Waves (heard next), and hard-to-describe Dispersive Chirping Waves (heard last).
Also impressive is the video's time-lapse visual track which shows
Parker's view to the side of its sun shield,
and where the planets
Earth,
Jupiter,
Mercury and
Venus
appear in succession, interspersed with bursts of
powerful cosmic rays
impacting the imager.
The nature of the solar wind near Mercury is
surprisingly different
from near the Earth, and
much study is underway to better understand the differences.
 APOD: 2019 December 2 - Mercury Crosses a Quiet Sun
APOD: 2019 December 2 - Mercury Crosses a Quiet Sun
Explanation:
What's that black dot crossing the Sun?
The planet Mercury.
Mercury
usually passes over or under the
Sun,
as seen from
Earth,
but last month the Solar System's innermost planet appeared to go just about
straight across the middle.
Although witnessed by planet admirers across
the globe,
a particularly clear view was captured by the
Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) in
Earth orbit.
The featured video
was captured by the
SDO's HMI instrument in
a broad range of visible light, and
compresses
the 5 1/2 hour transit into about 13 seconds.
The background Sun was unusually
quiet -- even for being near
Solar Minimum
-- and showed no sunspots.
The next
solar transit by Mercury will
occur in 2032.
 APOD: 2019 November 28 - Moon and Planets at Twilight
APOD: 2019 November 28 - Moon and Planets at Twilight
Explanation:
This week's ongoing conjunction
of Venus and Jupiter
may have whetted your appetite for skygazing.
Tonight is the main course though.
On November 28, a young
crescent Moon will join them posing
next to the two bright planets above the western horizon at twilight.
Much like tonight's
visual
feast, this night skyscape shows
a young lunar crescent and brilliant Venus in the western evening
twilight on October 29.
The celestial beacons are setting over distant mountains and the
Minya monastery,
Ganzi Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan,
China, planet Earth.
Then Mercury, not Jupiter, was a celestial companion to Venus and the Moon.
The fleeting innermost planet is just visible here in the bright
twilight,
below and left of Venus and near the center of the frame.
Tomorrow, November 29, the crescent Moon will also help you
spot planet
Saturn
for dessert.
 APOD: 2019 November 14 - Mercury and the Quiet Sun
APOD: 2019 November 14 - Mercury and the Quiet Sun
Explanation:
On
November 11, 2019 the Sun was mostly quiet,
experiencing a minimum in its
11 year cycle of activity.
In fact, the only spot visible was actually planet
Mercury, making a leisurely 5 1/2 hour transit
in front of the calm solar disk.
About 1/200th the apparent diameter of the Sun, the silhouette of
the solar system's inner most planet is near center in this sharp,
full Sun snapshot.
Taken with a hydrogen alpha filter and safe solar telescope, the
image also captures
prominences around the solar limb,
the glowing plasma trapped in arcing magnetic fields.
Of course, only inner planets Mercury
and Venus
can transit the Sun to appear in silhouette when viewed
from planet Earth.
Following its transit
in 2016, this was Mercury's 4th of 14
transits across the solar disk
in
the 21st century.
The next transit of Mercury will be on November 13, 2032.
 APOD: 2019 November 13 - Mercury in Silhouette
APOD: 2019 November 13 - Mercury in Silhouette
Explanation:
The small, dark,
round spot in this solar close up is planet Mercury.
In the high resolution telescopic image, a colorized
stack of 61 sharp video frames,
a turbulent array of photospheric convection cells tile
the bright solar surface.
Mercury's more regular silhouette still stands out though.
Of course, only inner planets Mercury
and Venus
can transit the Sun to appear in silhouette when viewed
from planet Earth.
For this
November 11, 2019
transit of Mercury, the
innermost planet's silhouette
was a mere 1/200th the solar diameter.
So even under clear daytime skies it was difficult to see
without the aid of a safe solar telescope.
Following its transit
in 2016, this was Mercury's 4th of 14
transits across the solar disk
in
the 21st century.
The next transit of Mercury will be on November 13, 2032.
 APOD: 2019 November 10 - A Mercury Transit Sequence
APOD: 2019 November 10 - A Mercury Transit Sequence
Explanation:
Tomorrow -- Monday --
Mercury
will cross the
face of the
Sun, as
seen from Earth.
Called a
transit,
the last time this happened was in
2016.
Because the plane of Mercury's orbit is not exactly coincident with the
plane of Earth's orbit,
Mercury usually appears to pass over or under the Sun.
The featured time-lapse sequence, superimposed on a single frame,
was taken from a balcony in
Belgium shows the entire
transit of 2003 May 7.
That solar crossing
lasted over five hours, so that the above
23 images were taken roughly 15 minutes apart.
The north pole of the
Sun,
the Earth's orbit, and
Mercury's
orbit, although all different, all occur in directions
slightly above the left of the image.
Near the center and on the far right,
sunspots
are visible.
After Monday, the next
transit of Mercury will occur in 2032.
 APOD: 2019 November 9 - Saturn the Giant
APOD: 2019 November 9 - Saturn the Giant
Explanation:
On May 25, 1961 U.S. president
John
Kennedy announced the goal of landing astronauts on the Moon
by the end of the decade.
By November 9, 1967
this Saturn V rocket
was ready for launch and the first full test of its capabilities on the
Apollo 4 mission.
Its development directed by rocket pioneer Wernher Von Braun,
the three stage
Saturn
V stood over 36 stories tall.
It had a cluster of five first stage engines
fueled by liquid oxygen and kerosene which together were capable of producing
7.9 million
pounds of thrust.
Giant Saturn V rockets
ultimately hurled nine
Apollo missions to the
Moon and back again with six landing on
the
lunar surface.
The first landing mission,
Apollo 11,
achieved Kennedy's goal on July 20, 1969.
 APOD: 2019 October 21 - A Mercury Transit Music Video from SDO
APOD: 2019 October 21 - A Mercury Transit Music Video from SDO
Explanation:
What's that small black dot moving across the Sun?
Mercury.
Possibly the clearest view of
Mercury crossing
in front of the Sun in 2016 May was from Earth orbit.
The Solar Dynamics Observatory obtained an uninterrupted vista
recording it not only in optical light but also in bands of
ultraviolet light.
Featured here is a composite movie of the crossing set to music.
Although the event might prove
successful scientifically for better
determining components of Mercury' ultra-thin atmosphere,
the event surely proved
successful culturally by involving
people throughout the world
in observing a rare astronomical phenomenon.
Many spectacular images of this
Mercury transit from around (and above) the globe were
proudly
displayed.
The next
transit of Mercury
will take place in three weeks: on 2019 November 11.
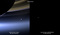 APOD: 2019 October 12 - Interplanetary Earth
APOD: 2019 October 12 - Interplanetary Earth
Explanation:
In an interplanetary first, on July 19, 2013
Earth was photographed on the same day from two other worlds
of the Solar System,
innermost planet Mercury and ringed gas giant Saturn.
Pictured on the left, Earth is the
pale blue dot
just below the rings of Saturn, as captured by the
robotic
Cassini spacecraft then orbiting the
outermost gas giant.
On that same day people across
planet Earth snapped many
of their own pictures of Saturn.
On the right, the
Earth-Moon system is seen against the dark
background of space as captured by the
robotic MESSENGER
spacecraft, then in Mercury orbit.
MESSENGER took its image as part of a search for
small natural satellites of Mercury, moons that would be
expected to be quite dim.
In the
MESSENGER image, the Earth (left) and Moon (right) are overexposed
and
shine brightly with reflected sunlight.
Destined not to return to their home world, both
Cassini
and
MESSENGER
have since retired from their missions of Solar System exploration.
 APOD: 2019 August 25 - Leaving Earth
APOD: 2019 August 25 - Leaving Earth
Explanation:
What it would look like to leave planet Earth?
Such an event was recorded visually
in great detail
by the MESSENGER spacecraft as it swung back past the Earth in 2005
on its way in toward the
planet Mercury.
Earth can be seen rotating in
this time-lapse video, as it recedes into the distance.
The sunlit half of Earth is
so bright that background
stars are not visible.
The robotic MESSENGER spacecraft is now in orbit around
Mercury and has recently concluded the first
complete map of the surface.
On occasion, MESSENGER has continued to
peer back at its home world.
MESSENGER is one of the few things created on the
Earth that has left and will
never return -- at the end of its mission MESSENGER crashed into
Mercury's surface.
 APOD: 2019 April 28 - All of Mercury
APOD: 2019 April 28 - All of Mercury
Explanation:
Only six years ago, the
entire surface
of planet Mercury was finally mapped.
Detailed observations of the
innermost planet's surprising crust began when the robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft
first passed Mercury in 2008 and continued until its
controlled crash landing in 2015.
Previously, much of the
Mercury's surface was unknown as it is too far
for Earth-bound telescopes to see clearly, while the
Mariner 10
flybys in the 1970s observed only about half.
The featured video
is a compilation of thousands of images of
Mercury
rendered in exaggerated colors
to better contrast different surface features.
Visible on the rotating world are
rays emanating from a
northern impact that stretch across much of the planet,
while about half-way through the video the light colored
Caloris Basin rotates into view,
a northern ancient impact feature that filled with
lava.
Recent analysis of MESSENGER data indicates that Mercury has a
solid inner core.
 APOD: 2018 August 16 - Parker vs Perseid
APOD: 2018 August 16 - Parker vs Perseid
Explanation:
The brief flash of a bright Perseid meteor streaks across the
upper right in this composited series of exposures
made early Sunday morning near the peak of the annual
Perseid meteor shower.
Set
up about two miles from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape
Canaveral Air Force Station, the photographer also captured the
four minute long trail of a Delta IV Heavy rocket carrying the
Parker
Solar Probe into the dark morning sky.
Perseid meteors aren't slow.
The grains of dust
from periodic comet Swift-Tuttle vaporize as they
plow through Earth's upper atmosphere at about
60 kilometers per second (133,000 mph).
On its way
to seven gravity-assist flybys of Venus
over its seven year mission, the Parker Solar Probe's closest
approach to the Sun will steadily decrease,
finally reaching a distance of 6.1 million kilometers
(3.8 million miles).
That's about 1/8 the distance between Mercury and the Sun,
and within the solar corona,
the Sun's tenuous outer atmosphere.
By then it will be traveling roughly 190 kilometers per second
(430,000 mph) with respect to the Sun, a record for fastest spacecraft
from planet Earth.
 APOD: 2018 March 31 - Twilight in a Western Sky
APOD: 2018 March 31 - Twilight in a Western Sky
Explanation:
A slender crescent Moon and inner
planets
Venus and Mercury never
wander far from the Sun
in planet Earth's skies.
In the fading evening twilight of March 18, they line up near the western
horizon in this atmospheric skyscape.
While the celestial scene was enjoyed around the world,
this photo captures the trio, with fainter Mercury at the far right,
above the crags of Big Bend National Park in southwest Texas.
Tonight the Moon will be
full though, and rise opposite the Sun.
Look for it
high in the sky at midnight, near bright star Spica.
 APOD: 2018 March 4 - Clouds, Birds, Moon, Venus
APOD: 2018 March 4 - Clouds, Birds, Moon, Venus
Explanation:
Sometimes the sky above can become quite a show.
In early September of 2010, for example, the
Moon and Venus converged, creating quite a
sight by itself for
sky enthusiasts around the
globe.
From some locations, though, the sky was even more picturesque.
In the featured image taken in
Spain, a crescent Moon and the planet Venus, on the far right,
were captured during sunset posing against a deep blue sky.
In the foreground, dark
storm clouds loom across the image bottom,
while a white anvil cloud shape appears above.
Black specks dot the frame, caused by a
flock of birds taking flight.
Very soon after this picture was taken, however, the
birds passed by, the storm ended, and Venus and the Moon set.
Bright Venus is again visible just after sunset this month
(2018 March) and will appear
quite near Mercury tonight and the rest of this week.
 APOD: 2017 December 23 - Phaethon's Brood
APOD: 2017 December 23 - Phaethon's Brood
Explanation:
Based on its well-measured orbit,
3200 Phaethon
(sounds like FAY-eh-thon)
is recognized as the source of the meteroid stream responsible for the annual
Geminid meteor shower.
Even though most meteor showers' parents are comets, 3200 Phaethon
is a known and
closely tracked
near-Earth asteroid with a 1.4 year orbital period.
Rocky and sun-baked, its
perihelion or closest
approach to the Sun is well within the orbit of innermost planet Mercury.
In this telescopic field of view, the asteroid's rapid motion against
faint background stars of the heroic constellation Perseus
left a short trail during the two minute total exposure time.
The parallel streaks of its meteoric children flashed much more
quickly across the scene.
The family portrait was recorded near the Geminid meteor shower's
very active peak on December 13.
That was just before 3200 Phaethon's historic December 16 closest
approach
to planet Earth.
 APOD: 2017 December 11 - Mercury Visualized from MESSENGER
APOD: 2017 December 11 - Mercury Visualized from MESSENGER
Explanation:
What would it be like to fly over the planet Mercury?
Images and data taken from NASA's robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft that
orbited Mercury from 2011 to 2015 have been digitally combined to envision a virtual flight that highlights much of the hot planet's surface.
In general,
the Solar System's innermost world appears similar to
Earth's Moon as it is covered by a heavily cratered gray terrain.
MESSENGER discovered much
about Mercury including that shadows near its poles likely host water ice.
The featured video opens as
Mercury is viewed from the Sun-facing side and concludes with the virtual spacecraft
retreating into Mercury's night.
Mercury actually rotates so slowly that it only completes three rotations for every two trips around the Sun.
In 2018, Europe and Japan plan to launch
BepiColombo
to better map Mercury's surface and
probe its
magnetic field.
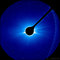 APOD: 2017 November 13 - Comet Machholz Approaches the Sun
APOD: 2017 November 13 - Comet Machholz Approaches the Sun
Explanation:
Why is Comet Maccholz so depleted of carbon-containing chemicals?
Comet 96P/Machholz's
original fame derives from its getting closer to the Sun than any other short period comet -- half as close as
Mercury --
and doing so every five years.
To better understand this unusual comet, NASA's Sun-monitoring
SOHO spacecraft tracked the comet during its latest
approach to the Sun in October.
The featured image composite shows the tail-enhanced comet swooping past the Sun.
The Sun's bright surface is hidden from view behind a dark occulter,
although parts of the Sun's extended
corona are visible.
Neighboring stars dot the background.
One hypothesis holds that these close solar approaches somehow cause
Comet Machholz to shed its
carbon,
while another hypothesis posits that the comet formed with
this composition
far away -- possibly even in
another star system.
 APOD: 2017 September 21 - A September Morning Sky
APOD: 2017 September 21 - A September Morning Sky
Explanation:
The Moon, three planets, and a bright star gathered near the
ecliptic plane
in the September 18 morning
sky over Veszprem Castle, Hungary.
In this twilight skyscape,
Mercury
and Mars still shine close to the
eastern horizon, soon to disappear in the glare of the Sun.
Regulus, alpha star of the constellation Leo, is the bright point
next to a waning crescent Moon, with brilliant Venus near the top
of the frame.
The beautiful morning conjunction of Moon, planets, and bright star
could generally be followed by early morning risers all around
planet Earth.
But remarkably, the
Moon
also occulted, or passed directly in front of, Regulus and each of the
three planets within 24 hours, all on September 18 UT.
Visible from different
locations, timing and watching the
lunar occultations was much more difficult though, and mostly required
viewing in daytime skies.
 APOD: 2017 July 23 - Mercury as Revealed by MESSENGER
APOD: 2017 July 23 - Mercury as Revealed by MESSENGER
Explanation:
Mercury had never been seen like this before.
In 2008, the robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft buzzed past
Mercury
for the second time and imaged terrain mapped previously only by
comparatively crude radar.
The featured image was recorded as
MESSENGER looked back 90 minutes after passing,
from an altitude of about 27,000 kilometers.
Visible in the image, among many other newly imaged features,
are unusually long
rays that appear to run like
meridians of
longitude
out from a young crater near the northern limb.
MESSENGER entered orbit around Mercury in 2011 and finished its primary mission in 2012, but took
detailed measurements until 2015, at which time it ran out of fuel and so was instructed to
impact Mercury's surface.
 APOD: 2016 October 8 - Moon, Mercury, and Twilight Radio
APOD: 2016 October 8 - Moon, Mercury, and Twilight Radio
Explanation:
Sharing
dawn's twilight with the Moon on September 29,
Mercury was about as far from the Sun as it can wander,
the innermost planet close to its maximum elongation in
planet Earth's skies.
In this colorful scene fleeting Mercury is
joined by a waning sunlit lunar crescent and earthlit
lunar nightside,
the New Moon in the Old Moon's arms.
Below is the Italian
Medicina Radio
Astronomical Station near Bologna with a low row of antennae that is
part of Italy's first radio telescope array dubbed the "Northern Cross",
and a 32-meter-diameter parabolic dish.
Of course, moonwatchers won't have to rise in early morning hours
on October 8.
After sunset the Moon will be high and bright in evening skies,
at its first quarter phase for
International Observe
the Moon Night.
 APOD: 2016 September 1 - Light at the End of the Road
APOD: 2016 September 1 - Light at the End of the Road
Explanation:
The bright light at the end of this country road is actually a remarkably
close conjunction
of two planets.
After sunset on August 27 brilliant Venus and
Jupiter
almost appear as a single celestial beacon in the
night skyscape taken near Lake Wivenhoe, Queensland,
Australia.
A spectacular vertical panorama from the
southern hemisphere,
it shows the central Milky Way near zenith, posed on
top of a pillar of Zodiacal light along the ecliptic plane.
Of course Mars and Saturn are near the ecliptic
too, just below the galaxy's central bulge.
Above and left of a tree on the horizon, fleeting planet
Mercury also adds to the light at the
end of the road.
 APOD: 2016 August 6 - Las Campanas Moon and Mercury
APOD: 2016 August 6 - Las Campanas Moon and Mercury
Explanation:
Last Thursday the view toward sunset from the 2.5 kilometer summit of
Cerro Las Campanas in the remote Chilean Andes was amazing.
Bright but fading Mercury stood
very close to a two day old Moon.
Both a sunlit lunar crescent and
earthlit lunar nightside
are captured with the fleeting
innermost planet
in this breathtaking mountainscape.
Even below the conjunction of Moon and Mercury, a close pairing of
brilliant Venus and bright star Regulus hangs in the sky,
still above the colorful western horizon.
Of course amazing skies
above Las Campanas are not unexpected.
The region is currently home to the twin Magellan telescopes of the
Las Campanas Observatory and
the summit location is the site of the future
Giant Magellan Telescope.
 APOD: 2016 July 17 - Mercury on the Horizon
APOD: 2016 July 17 - Mercury on the Horizon
Explanation:
Have you ever seen the planet Mercury?
Because
Mercury
orbits so close to the Sun, it never wanders far from the Sun in
Earth's sky.
If trailing the Sun,
Mercury will be visible
low on the horizon for only a short while
after sunset.
If leading the Sun,
Mercury will be visible only shortly before sunrise.
So at certain times of the year,
informed skygazers with a little determination can usually pick
Mercury out from a site with an unobscured horizon.
Above, a lot of determination has been combined
with a little
digital manipulation to
show Mercury's successive positions during March of 2000.
Each picture was taken from the same location in Spain
when the Sun itself was 10 degrees below the
horizon and superposed on the single most
photogenic sunset.
Currently,
Mercury
is rising higher above the horizon with each passing sunset, and
just now is angularly
very close to the brighter planet Venus.
 APOD: 2016 May 20 - 3D Mercury Transit
APOD: 2016 May 20 - 3D Mercury Transit
Explanation:
On May 9, innermost planet
Mercury crossed
IN FRONT of the Sun.
Though pictures project the event in only two dimensions, a
remarkable three dimensional perspective on the transit is possible
by free viewing
this stereo pair.
The images
were made 23 minutes apart and rotated so that
Mercury's position shifts horizontally between the two.
As a result, Mercury's orbital motion produced
an exaggerated parallax simulating binocular vision.
Between the two exposures, the appropriately named planet's
speedy
47.4 kilometer per second
orbital
velocity actually carried it over 65,000 kilometers.
Taken first, the left image is intended for the right eye, so a
cross-eyed view is needed to see
Mercury's tiny silhouette
suspended in the foreground.
Try it. Merging the text below the images helps.
 APOD: 2016 May 13 - ISS and Mercury Too
APOD: 2016 May 13 - ISS and Mercury Too
Explanation:
Transits of Mercury are relatively rare.
Monday's leisurely 7.5 hour long event was only the 3rd of 14 Mercury
transits in the 21st century.
If you're willing to travel,
transits of the International
Space Station can be more frequent though, and much quicker.
This sharp
video frame composite was taken from a well-chosen location
in Philadelphia, USA.
It follows the space station, moving from upper right to lower
left, as it crossed the Sun's disk in 0.6 seconds.
Mercury
too is included as the small, round, almost stationary
silhouette just below center.
In apparent size, the International Space Station looms larger
from low Earth orbit,
about 450 kilometers from Philadelphia.
Mercury was about 84 million kilometers away.
(Editor's note:
The stunning
video includes another
double transit, Mercury and a Pilatus PC12 aircraft. Even quicker
than the ISS to cross the Sun, the aircraft was about 1 kilometer
away.)
 APOD: 2016 May 12 - A Transit of Mercury
APOD: 2016 May 12 - A Transit of Mercury
Explanation:
On May 9,
the diminutive disk of Mercury spent about seven and
a half hours crossing in front of the Sun
as viewed from the general
vicinity of Earth.
It was the third of 14 transits of the Solar System's innermost
planet in the
21st century.
Captured from Fulham, London, England, planet Earth the tiny
silhouette shares
the enormous solar disk with
prominences, filaments, and active regions in this sharp image.
But Mercury's round disk (left of center)
appears to be the only dark spot,
despite the
planet-sized sunspots
scattered across the Sun.
Made with an H-alpha filter that narrowly transmits the red
light from hydrogen atoms, the image emphasizes
the
chromosphere,
stretching above the photosphere or normally visible solar surface.
In H-alpha pictures of the chromosphere, normally dark sunspot regions
are dominated by bright splotches
called
plages.
 APOD: 2016 May 11 - A Mercury Transit Music Video from SDO
APOD: 2016 May 11 - A Mercury Transit Music Video from SDO
Explanation:
What's that small black dot moving across the Sun?
Mercury.
Possibly the clearest view of
Mercury crossing
in front of the Sun earlier this week was from Earth orbit.
The Solar Dynamics Observatory obtained an uninterrupted vista
recording it not only in optical light but also in bands of
ultraviolet light.
Featured here is a composite movie of the crossing set to music.
Although the event might prove
successful scientifically for better
determining components of Mercury' ultra-thin atmosphere,
the event surely proved
successful culturally by involving
people throughout the world
in observing a rare astronomical phenomenon.
Many spectacular images of this
Mercury transit from around (and above) the globe are being
proudly
displayed.
 APOD: 2016 May 9 - Webb Telescope Mirror Rises after Assembly
APOD: 2016 May 9 - Webb Telescope Mirror Rises after Assembly
Explanation:
Move over Hubble -- here comes the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
JWST
promises to be the new most powerful telescope in space.
In the last month, the 18-segment gold-plated primary mirror for JWST was
unveiled.
In the
featured time-lapse video taken last week, the 6.5-meter diameter mirror was raised to a vertical position.
The dramatic 30-second sequence shows NASA engineers monitoring the test as room lights glint brightly off the mirror's highly reflective surface.
The beryllium
mirrors have been coated with a thin film of
gold
to make them more reflective to
infrared light.
The science goals of JWST
include studying the workings of the
early universe and the properties of planets orbiting nearby stars.
Because of the mirror's great size, it will be folded for launch and then,
assuming all goes as planned, dramatically
unfolded again in space.
The JWST, a joint mission of the space agencies of the
USA,
Europe, and
Canada,
is currently scheduled to be launched in late 2018.
 APOD: 2016 May 8 - Mercurys Transit: An Unusual Spot on the Sun
APOD: 2016 May 8 - Mercurys Transit: An Unusual Spot on the Sun
Explanation:
What's that dot on the Sun?
If you look closely, it is almost perfectly round.
The dot is the result of an unusual type of
solar eclipse that occurred in 2006.
Usually it is the
Earth's Moon that eclipses the Sun.
This time, the planet
Mercury
took a turn.
Like the approach to New Moon before a
solar eclipse,
the phase of Mercury became a continually thinner
crescent as the planet
progressed toward an alignment with the Sun.
Eventually the phase of
Mercury dropped to zero and
the dark spot of
Mercury crossed our parent star.
The situation could technically be labeled a Mercurian
annular
eclipse with an extraordinarily large
ring of fire.
From above the
cratered planes
of the night side of
Mercury, the Earth appeared in its fullest phase.
Hours later, as Mercury continued in its orbit, a slight
crescent phase appeared again.
This was ten years ago -- the next Mercurian solar eclipse will
occur tomorrow.
 APOD: 2016 May 4 - A Mercury Transit Sequence
APOD: 2016 May 4 - A Mercury Transit Sequence
Explanation:
This coming Monday,
Mercury will cross the
face of the
Sun, as
seen from Earth.
Called a
transit,
the last time this happened was in
2006.
Because the plane of Mercury's orbit is not exactly coincident with the
plane of Earth's orbit,
Mercury usually appears to pass over or under the Sun.
The above time-lapse sequence, superimposed on a single frame,
was taken from a balcony in
Belgium shows the entire
transit of 2003 May 7.
The solar crossing
lasted over five hours, so that the above
23 images were taken roughly 15 minutes apart.
The north pole of the
Sun, the
Earth's orbit, and
Mercury's orbit,
although all different, all occur in directions
slightly above the left of the image.
Near the center and on the far right,
sunspots
are visible.
After Monday, the next
transit of Mercury will occur in 2019.
 APOD: 2016 April 15 - Mercury and Crescent Moon Set
APOD: 2016 April 15 - Mercury and Crescent Moon Set
Explanation:
Innermost planet Mercury
and a thin crescent Moon are never found far from the Sun
in planet Earth's skies.
Taken
near dusk on April 8, this colorful evening skyscape
shows them both setting toward the western horizon just after the Sun.
The broad Tagus River and city lights of Lisbon, Portugal run through the
foreground under the serene twilight sky.
Near perigee or closest approach to Earth, the Moon's bright,
slender crescent represents about 3 percent of the
lunar disk in sunlight.
Of course as seen from the Moon, a nearly full Earth would light up the
lunar night, and that strong perigee
earthshine makes
the rest of the lunar disk visible in this scene.
Bright Mercury stays well above the western horizon at sunset
for northern skywatchers
in the
coming days.
The fleeting planet reaches maximum elongation, or angular distance
from the Sun, on April 18.
But Mercury will swing back toward the Sun and actually
cross the solar disk on May 9, the first
transit of Mercury
since November 8, 2006.
 APOD: 2016 February 6 - Five Planets at Castell de Burriac
APOD: 2016 February 6 - Five Planets at Castell de Burriac
Explanation:
February's five planet line-up stretches
across
a clear sky in this predawn scene.
A hilltop
Castell
de Burriac looms in the foreground,
overlooking the town of Cabrera de Mar near Barcelona, Spain,
planet Earth.
The
mosaicked, panoramic image looks south.
It merges three different exposure times
to record a bright Last Quarter Moon, planets, seaside city lights,
and dark castle ruins.
Seen on February 1st the Moon was near Mars on the sky.
But this week early morning risers have watched it move on,
passing near Saturn and finally Venus and Mercury, sliding along
near the ecliptic toward the dawn,
approaching the February 7 New Moon.
 APOD: 2016 January 30 - A Five Planet Dawn
APOD: 2016 January 30 - A Five Planet Dawn
Explanation:
As January closes and in the coming days of February,
early morning risers
can spot the five naked-eye planets before dawn.
Though some might claim to see six planets,
in this seaside panoramic view
all five celestial wanderers were
found above the horizon along with a bright waning gibbous Moon
on January 27.
Nearly aligned along the
plane of the ecliptic,
but not along a line with the Sun, the
five
planets are spread well over 100 degrees across the sky.
Just arriving on the predawn scene, fleeting Mercury stands
above the southeastern horizon in the golden light
of the approaching sunrise.
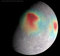 APOD: 2015 May 5 - Gravitational Anomalies of Mercury
APOD: 2015 May 5 - Gravitational Anomalies of Mercury
Explanation:
What's that under the surface of Mercury?
The robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft that had been orbiting planet
Mercury for the past four years had been transmitting its data back to Earth with
radio waves of very precise energy.
The planet's gravity, however,
slightly changed this energy when measured on Earth, which enabled the reconstruction of a
gravity map of unprecedented precision.
Here gravitational anomalies are shown in
false-color, superposed on an image of the
planet's cratered surface.
Red hues
indicate areas of slightly higher gravity,
which in turn indicates areas that must have unusually dense matter under the surface.
The central area is
Caloris Basin,
a huge impact feature measuring about 1,500 kilometers across.
Last week, after completing
its mission and running low on fuel,
MESSENGER was purposely crashed onto Mercury's surface.
 APOD: 2015 May 1 - MESSENGER's Last Day on Mercury
APOD: 2015 May 1 - MESSENGER's Last Day on Mercury
Explanation:
The first
to orbit Mercury, the MESSENGER spacecraft
came to rest
on this region of
Mercury's surface yesterday.
Constructed from MESSENGER image and laser altimeter data,
the scene looks north over the northeastern rim of the
broad, lava filled
Shakespeare basin.
The large, 48 kilometer (30 mile) wide crater Janacek
is near the upper left edge.
Terrain height is color coded with red regions
about 3 kilometers above blue ones.
MESSENGER'S final orbit was predicted to end
near the center, with the spacecraft impacting the surface
at nearly 4 kilometers per second (over 8,700 miles per hour)
and creating a new crater about 16 meters (52 feet) in diameter.
The
impact on the far side of Mercury was
not observed by telescopes, but
confirmed when no signal was detected from the spacecraft
given time to emerge from behind the planet.
Launched in 2004, the MErcury Surface,
Space ENvironment, GEochemisty and
Ranging spacecraft completed over 4,000 orbits after reaching the
Solar System's innermost planet in 2011.
 APOD: 2015 April 18 - The Great Crater Hokusai
APOD: 2015 April 18 - The Great Crater Hokusai
Explanation:
One of the largest young craters on Mercury,
114 kilometer (71 mile) diameter Hokusai crater's bright
rays are known to extend across
much of the planet.
But this mosaic of oblique views focuses on Hokusai close up,
its sunlit
central peaks, terraced
crater walls, and
frozen sea of impact melt on the
crater's floor.
The images were captured by the MESSENGER spacecraft.
The first to orbit Mercury,
since 2011 MESSENGER has conducted
scientific explorations, including
extensive imaging of the
Solar System's innermost planet.
Now running out of propellant and unable to counter orbital
perturbations caused by the Sun's gravity,
MESSENGER is predicted to
impact
the surface of Mercury on April 30.
 APOD: 2015 March 5 - Enhanced Color Caloris
APOD: 2015 March 5 - Enhanced Color Caloris
Explanation:
The sprawling Caloris basin
on Mercury
is one of the solar system's largest
impact basins,
created during the early history of the solar system by the impact of
a large asteroid-sized body.
The multi-featured,
fractured basin spans about 1,500 kilometers in this
enhanced
color mosaic based on image data from the Mercury-orbiting
MESSENGER spacecraft.
Mercury's youngest large impact basin,
Caloris was subsequently filled
in by lavas that appear orange in the mosaic.
Craters made after the flooding
have excavated material from beneath the surface lavas.
Seen as contrasting blue hues, they likely offer a glimpse of
the original basin floor material.
Analysis of these craters suggests the thickness
of the covering volcanic lava to be 2.5-3.5 kilometers.
Orange splotches around the basin's perimeter are thought to be
volcanic vents.
 APOD: 2015 January 15 - Venus and Mercury at Sunset
APOD: 2015 January 15 - Venus and Mercury at Sunset
Explanation:
Inner planets
Venus and
Mercury can never
wander far from the Sun in Earth's sky.
This week you've probably seen them both gathered near the
western horizon just
after sunset, a close conjunction of bright
celestial beacons in the fading twilight.
The pair are framed in this early evening skyview captured on
January 13 from the ruins of
Szarvasko Castle in northwestern Hungary.
Above the silhouette of the landscape's prominent volcanic hill
Venus is much the brighter, separated from Mercury by little more
than the width of two Full Moons.
On Friday, planet Earth's
early morning risers will also be
treated to a close conjunction,
when Saturn meets an old crescent Moon
near the southeastern horizon at dawn.
 APOD: 2014 August 24 - Mercury's Transit: An Unusual Spot on the Sun
APOD: 2014 August 24 - Mercury's Transit: An Unusual Spot on the Sun
Explanation:
What's that dot on the Sun?
If you look closely, it is almost perfectly round.
The dot is the result of an unusual type of
solar eclipse that occurred in 2006.
Usually it is the
Earth's Moon that eclipses the Sun.
This time, the planet
Mercury
took a turn.
Like the approach to New Moon before a
solar eclipse,
the phase of Mercury became a continually thinner
crescent as the planet
progressed toward an alignment with the Sun.
Eventually the phase of
Mercury dropped to zero and
the dark spot of Mercury crossed our parent star.
The situation could technically be labeled a Mercurian
annular
eclipse with an extraordinarily large
ring of fire.
From above the
cratered planes
of the night side of Mercury, the Earth appeared in its fullest phase.
Hours later, as Mercury continued in its orbit, a slight
crescent phase appeared again.
The next Mercurian solar eclipse
will occur in 2016.
 APOD: 2013 November 23 - Comet ISON from STEREO
APOD: 2013 November 23 - Comet ISON from STEREO
Explanation:
Still intact, on November 21
Comet
ISON (C/2012 S1) swept into
this animated field of view (left) from the HI-1 camera on the
STEREO-A spacecraft.
The camera has also captured
periodic Comet Encke, Mercury, and Earth,
with the Sun cropped out of the frame at the right, the source of
the billowing solar wind.
From
STEREO's perspective in interplanetary space,
planet Earth is actually
the most distant of the group, seen in its orbit beyond the Sun.
Mercury is closest, but both planets are still so bright they
create sharp vertical lines in the camera's detector.
Both comets clearly sport substantial tails,
but ISON is closer to
the camera and will continue to move more rapidly through the field.
Cameras on STEREO and SOHO spacecraft will be able to
follow
Comet ISON as it falls towards its close encounter with
the Sun on November 28, even as ISON gets more
difficult to see
in the bright
dawn skies of planet Earth.
 APOD: 2013 August 5 - Leaving Earth
APOD: 2013 August 5 - Leaving Earth
Explanation:
What it would look like to leave planet Earth?
Such an event was recorded visually in great detail
by the MESSENGER spacecraft as it swung back past the Earth,
eight years ago, on its way in toward the
planet Mercury.
Earth can be seen rotating in
this time-lapse video, as it recedes into the distance.
The sunlit half of Earth is
so bright that background
stars are not visible.
The robotic MESSENGER spacecraft is now in orbit around
Mercury and has recently concluded the first
complete map of the surface.
On occasion, MESSENGER has continued to
peer back at its home world.
MESSENGER is one of the few things created on the
Earth that has left and will never return -- at the end of its mission MESSENGER will be crashed into
Mercury's surface.
 APOD: 2013 July 23 - Two Views of Earth
APOD: 2013 July 23 - Two Views of Earth
Explanation:
In a cross-Solar System interplanetary first,
our Earth was photographed during the same day from both Mercury and Saturn.
Pictured on the left, Earth is the
pale blue dot
just below the rings of Saturn, as captured by the
robotic Cassini spacecraft
now orbiting the gas giant.
Pictured on the right, the
Earth-Moon system is seen against a dark background,
as captured by the
robotic MESSENGER spacecraft
now orbiting Mercury.
In the
MESSENGER image, the Earth (left) and Moon (right)
shine brightly with reflected sunlight.
MESSENGER took the overexposed image last Friday as part of a search for small natural satellites of the innermost planet, moons that would be expected to be quite dim.
During this same day,
humans across
planet Earth snapped many of their own
pictures of Saturn.
 APOD: 2013 June 13 - Four Planet Sunset
APOD: 2013 June 13 - Four Planet Sunset
Explanation:
You can see four planets in
this serene sunset image,
created from a series of stacked digital exposures captured
near dusk on May 25.
The composite picture follows the trail of three of them,
Jupiter, Venus, and Mercury (left to right) dropping toward the
western horizon, gathered close in last month's remarkable
triple planetary conjunction.
Similar in brightness to planet Mercury, the star
Elnath (Beta Tauri)
is also tracked across the scene, leaving its dotted trail
still farther to the right.
Of course, in the foreground are the
still, shallow waters of Alikes salt lake, reflecting the striking colors of
sunset over Kos Island, Greece,
planet Earth.
For now, Jupiter has wandered into the glare of the setting Sun,
but Mercury and Venus remain low in
the west at
twilight.
 APOD: 2013 June 12 - All of Mercury
APOD: 2013 June 12 - All of Mercury
Explanation:
For the first time, the
entire surface
of planet Mercury has been mapped.
Detailed observations of the
innermost planet's
surprising crust have been ongoing since the robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft
first passed Mercury in 2008 and began orbiting in 2011.
Previously, much of the
Mercury's surface was unknown as it is too far
for Earth-bound telescopes to see clearly, while the
Mariner 10
flybys in the 1970s observed only about half.
The above video
is a compilation of thousands of images of Mercury rendered in
exaggerated colors to better contrast different surface features.
Visible on the rotating world are
rays emanating from a
northern impact that stretch across much of the planet,
while about half-way through the video the light colored
Caloris Basin rotates into view,
a northern ancient impact feature that filled with lava.
MESSENGER has now
successfully completed
its primary and first extended missions.
 APOD: 2013 March 1 - Colors of Mercury
APOD: 2013 March 1 - Colors of Mercury
Explanation:
The colors of the solar system's
innermost planet
are enhanced in
this
tantalizing view,
based on global image data from the
Mercury-orbiting MESSENGER
spacecraft.
Human eyes would not discern the
clear color differences but they are real none the less, indicating distinct
chemical, mineralogical, and physical regions across the
cratered surface.
Notable at
the upper right, Mercury's large, circular, tan colored feature
known as the Caloris basin was created by an impacting comet
or asteroid during the solar system's
early years.
The ancient basin was subsequently flooded with lava from
volcanic activity, analogous to the formation of the
lunar maria.
Color contrasts also make the
light blue and white young crater rays,
material blasted out by recent impacts, easy to follow
as they extend across a darker blue,
low reflectance terrain.
 APOD: 2013 February 19 - Mercury on the Horizon
APOD: 2013 February 19 - Mercury on the Horizon
Explanation:
Have you ever seen the planet Mercury?
Because
Mercury
orbits so close to the Sun, it never wanders far from the Sun in
Earth's sky.
If trailing the Sun,
Mercury will be visible
low on the horizon for only a short while
after sunset.
If leading the Sun,
Mercury will be visible only shortly before sunrise.
So at certain times of the year an
informed skygazer with a little determination can usually pick
Mercury
out from a site with an unobscured horizon.
Above, a lot of determination has been combined
with a little
digital manipulation to
show Mercury's successive positions during March of 2000.
Each picture was taken from the same location in Spain
when the Sun itself was 10 degrees below the
horizon and superposed on the single most
photogenic sunset.
Currently, Mercury is
visible in the western sky after sunset, but will disappear in the Sun's glare after a few days.
 APOD: 2012 December 1 - Northern Mercury
APOD: 2012 December 1 - Northern Mercury
Explanation:
Innermost planet Mercury
would probably not be a good location for an
interplanetary winter olympics.
But new results based on data from the
Mercury orbiting
MESSENGER spacecraft indicate that
it does have substantial water ice
in permanently shadowed regions within
craters near its north pole.
The possibility of ice on Mercury has been entertained for
years, inspired by the discovery of radar bright, hence
highly reflective, regions near the north pole.
Highlighted in
yellow in this map based on projected
MESSENGER images,
radar bright regions are seen to correspond
with floors and walls of north polar impact craters.
Farther from the pole the regions are concentrated
on the north facing crater walls.
MESSENGER's
neutron
spectroscopy and
thermal models for the
craters indicate material in these regions has a hydrogen content
consistent with nearly pure water ice and is
trapped in an area with temperatures that remain below
100 kelvins
(-280 deg.F, -173 deg.C).
In circumstances similar to permanent shadows in craters
of the Moon,
debris from comet impacts is thought to be the source of
ice on Mercury.
 APOD: 2012 May 27 - Mercury Spotting
APOD: 2012 May 27 - Mercury Spotting
Explanation:
Can you spot the planet?
The diminutive disk of Mercury, the solar system's
innermost planet,
spent about five hours crossing in front of the enormous solar disk in 2003,
as
viewed from the general vicinity of planet Earth.
The Sun was above the horizon during
the entire transit for observers
in Europe, Africa, Asia, or Australia, and the horizon was
certainly
no problem for the sun-staring SOHO spacecraft.
Seen as a dark spot,
Mercury progresses
from left to right (top panel to bottom) in these four images from SOHO's extreme
ultraviolet camera.
The panels' false-colors correspond to different wavelengths in
the extreme ultraviolet which highlight regions above the Sun's
visible surface.
This
was the first of 14 transits of Mercury which will occur during the 21st
century.
Next week, however, an event much more rare but
easier to spot will occur -- a
transit of Venus
across the Sun.
Need help spotting Mercury?
Just
click
on the picture.
 APOD: 2012 April 26 - Morning, Moon, and Mercury
APOD: 2012 April 26 - Morning, Moon, and Mercury
Explanation:
Last week
Mercury
wandered far to the west of the Sun.
As the solar system's
innermost planet
neared its greatest elongation
or greatest angle from the Sun (for this apparition about 27 degrees)
it was joined by an old crescent Moon.
The conjunction was an engaging
sight
for early morning risers
in the southern hemisphere.
There the pair rose together in predawn skies, climbing
high above the horizon along a steeply inclined
ecliptic plane.
This well composed sequence captures the rising Moon and Mercury
above the city lights of
Brisbane in Queensland, Australia.
A stack of digital images, it consists of an exposure made
every 3 minutes beginning at 4:15 am local time on
April 19.
Mercury's track is at the far right, separated from
the Moon's path by about 8 degrees.
 APOD: 2012 March 27 - Unusual Hollows Discovered on Planet Mercury
APOD: 2012 March 27 - Unusual Hollows Discovered on Planet Mercury
Explanation:
What are those unusual features on planet Mercury?
The slightly bluish tinge of features dubbed hollows has been exaggerated on the above image by the robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft currently
orbiting Mercury.
The rounded depressions appear different than impact craters and nothing like them has been noted on
Earth's Moon or anywhere else in the
Solar System.
The above image is a section of the floor of
Raditladi
impact basin about 40 kilometers wide that includes the mountains of the central peak.
One progenitor hypothesis is that the hollows formed from the
sublimation of
material exposed
and heated during the violent impact that created the
Raditladi basin.
NASA's MESSENGER
is the first spacecraft ever to orbit Mercury, and is
currently scheduled
to explore the Solar System's innermost planet into 2013.
 APOD: 2011 October 8 - MESSENGER's First Day
APOD: 2011 October 8 - MESSENGER's First Day
Explanation:
One solar day on a planet is the length of time
from noon to noon.
A solar day lasts 24 hours on planet Earth.
On Mercury a solar day is about 176 Earth days long.
And during its
first Mercury solar day
in orbit
the MESSENGER spacecraft has
imaged nearly the entire surface of the
innermost planet
to generate a global monochrome map at 250 meters per
pixel resolution and a 1 kilometer per pixel resolution color map.
Examples of the maps, mosaics constructed from thousands of
images made under uniform lighting conditions,
are shown (monochrome at left), both centered along the
planet's 75 degrees East longitude
meridian.
The MESSENGER spacecraft's second Mercury solar day will
likely include more high resolution
targeted observations
of the planet's surface features.
(Editor's note: Due to Mercury's 3:2 spin-orbit
resonance, a Mercury solar day is 2
Mercury years long.)
 APOD: 2011 July 2 - Moon and Venus at Dawn
APOD: 2011 July 2 - Moon and Venus at Dawn
Explanation:
Brilliant Venus and a thin crescent Moon stood together
above the eastern horizon just before sunrise on June 30.
The lovely celestial pairing is captured in
this
colorful twilight skyview
overlooking a reservoir near Izmir, Turkey.
For some, the close conjunction could be viewed as a
daylight occultation.
While Venus is nearing the end of its latest
performance as planet Earth's
morning star,
the old lunar cresent, about 24 hours from its New Moon phase,
was also
bidding
farewell for now to the dawn.
In fact, for the next two nights a young Moon
can be spotted just after sunset.
Look for
a thin sunlit sliver
close to the western horizon, not far from bright planet Mercury.
 APOD: 2011 June 22 - MESSENGER's Degas View
APOD: 2011 June 22 - MESSENGER's Degas View
Explanation:
Now imaging inner planet Mercury
from orbit, the MESSENGER spacecraft
wide angle camera has returned
this impressive color
view of Degas Crater,
with a full resolution
of 90 meters per pixel.
Named for
the impressionist
painter,
the 52 kilometer diameter crater
is also shown in an inset context image from the
Mariner 10
flyby mission in the mid 1970s.
In MESSENGER's view,
the crater floor is seen to be filled with
an intricate series of cracks, formed as the molten surface resulting
from the impact cooled and contracted.
Starkly bright, patchy deposits,
suggesting compositional differences and freshly exposed material,
standout around the crater's central peaks and walls.
Details of similar
bright deposits are seen in even higher resolution images from
MESSENGER.
 APOD: 2011 June 16 - Mercury's Surface in Exaggerated Color
APOD: 2011 June 16 - Mercury's Surface in Exaggerated Color
Explanation:
The robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft
recently completed over
100 orbits of
Mercury.
MESSENGER's cameras have recorded
detailed pictures utilizing eight different colors across
visible and near
infrared light, exploring the surface
composition and looking for clues to the history and evolution
of the solar system's innermost planet.
This sharp
image combines three of the MESSENGER wide angle camera's colors,
but in exaggerated fashion.
Otherwise, to the unaided human eye, Mercury's surface colors would appear
comparatively muted.
The image is about 1,000 kilometers across and
features as small as a single kilometer are discernible at the original
resolution.
Today, the MESSENGER project
will release new images and science findings from the
first spacecraft to orbit Mercury.
 APOD: 2011 June 4 - Dawn's Grande Finale
APOD: 2011 June 4 - Dawn's Grande Finale
Explanation:
After more than a month, the lovely lineup
of four naked-eye
planets in dawn skies is coming to a close.
Still, on May 31st a slender Moon joined the grouping along the
eastern horizon for a final
celestial performance,
presented in this early morning scene from a beach
near Buenos Aires, Argentina.
A favorable view
of the configuration in the southern hemisphere autumn,
the photo was taken about 30 minutes before sunrise.
In order from bottom to top,
wandering Mercury, Venus, Mars, and Jupiter
are stretched along the ecliptic plane.
The Moon's sunlit crescent is sinking into the colorful twilight glow just
left of Mercury.
In
dawns to come,
Mars and Jupiter will continue to rise while
Venus and Mercury sink toward the horizon, drawing closer
to the rising Sun.
 APOD: 2011 May 21 - Planets, Endeavour at Dawn
APOD: 2011 May 21 - Planets, Endeavour at Dawn
Explanation:
When dawn broke over Kennedy Space Center on Monday, May 16,
the space shuttle orbiter
Endeavour still stood on pad 39A.
Its final launch, on
mission STS-134 to the International Space
Station, was only hours away.
Shining through the early morning
twilight four planets
were also poised above the eastern horizon,
a moving scene captured here from across the Banana River
at the center's Saturn V VIP viewing site.
Scattered by planet Earth's dense atmosphere, floodlight beams play
over the launch pad,
glancing skyward toward the celestial beacons.
Jupiter is highest, near the top of the frame, but even the solar
sytem's ruling gas giant is outshone by brilliant Venus near picture
center.
Innermost planet Mercury is below Venus, to the right.
Below and left, Mars almost fades into the twilight glow.
The four planets
continue to hug the eastern horizon at dawn throughout the month,
while Endeavour
is now scheduled to make
its final approach to planet Earth on June 1.
 APOD: 2011 May 7 - Dawn of the Planets
APOD: 2011 May 7 - Dawn of the Planets
Explanation:
This month, four of the five
naked-eye
planets gather
along the eastern horizon near dawn.
The celestial grouping is seen here just before sunrise on May 5,
from a beach near Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Starting near the top of the frame, the brightest beacon is Venus.
Mercury is below and right of Venus and brilliant Jupiter is
lower still, near image center.
Below Jupiter, Mars is relatively faint and struggles
the most to shine through a thin cloud bank
and the warming twilight glow.
Watch, and as the month progresses
the tantalizing configuration will change,
with Mars and Jupiter moving higher while
Venus and Mercury wander through the sky
closer to the rising sun.
 APOD: 2011 May 5 - 50 Years Ago: Freedom 7 Flies
APOD: 2011 May 5 - 50 Years Ago: Freedom 7 Flies
Explanation:
Fifty years ago, near the
dawn
of the space age, NASA controllers "lit the candle" and sent
Mercury
astronaut Alan Shepard arcing into space
atop a Redstone rocket.
His cramped space capsule was dubbed
Freedom 7.
Broadcast live to a global television audience, the historic
Mercury-Redstone 3 (MR-3) spacecraft was launched from
Cape Canaveral Florida at 9:34 a.m. Eastern Time on May 5, 1961.
The
flight of Freedom 7 - the first space flight by an American -
followed less than a month after the first human venture into space
by Soviet Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin.
The 15 minute sub-orbital flight achieved an altitude of 116 miles
and a maximum speed of 5,134 miles per hour.
As
Shepard looked back toward planet Earth near the peak of Freedom 7's
trajectory, he could see the outlines of
the west coast of Florida, Lake Okeechobe in central Florida,
the Gulf of Mexico, and the Bahamas.
 APOD: 2011 March 31 - MESSENGER at Mercury
APOD: 2011 March 31 - MESSENGER at Mercury
Explanation:
On March 17, the
MESSENGER spacecraft became the first
to orbit Mercury, the solar system's
innermost planet.
This is its
first processed color image
since entering Mercury orbit.
Larger, denser, and with almost twice the surface gravity of
Earth's moon,
Mercury still looks moon-like at first glance.
But in this view its terrain shows light blue and brown areas near
craters and long bright rays of material streaking the surface.
The prominent bright ray crater Debussy at the upper right
is 80 kilometers (50 miles) in diameter.
Terrain toward the bottom of
the historic image
extends to Mercury's south pole and
includes a region
not previously imaged from space.
 APOD: 2011 March 18 - Mercury and Jupiter at Sunset
APOD: 2011 March 18 - Mercury and Jupiter at Sunset
Explanation:
When warm
sunset
hues begin to fade, two celestial beacons
now shine in the evening twilight, Mercury and Jupiter.
Wandering away
from the Sun in planet Earth's sky, Mercury will offer
good views
this month as spring approaches in the northern hemisphere
where the ecliptic
plane makes a steep angle with the western horizon.
But Jupiter will continue sinking lower in the sky after sunset.
In fact, the normally elusive Mercury shines
well above Jupiter and the orange sunset glow in
this serene sky.
Captured earlier this week from the island of
of
Frösön in northern Sweden,
the scene looks across
Lake Storsjön toward the village of Hallen and distant mountains.
Of course, even better views of Mercury can be had by the
MESSENGER spacecraft, now orbiting
the Solar System's
innermost planet!
 APOD: 2011 February 23 - The Solar System from MESSENGER
APOD: 2011 February 23 - The Solar System from MESSENGER
Explanation:
If you looked out from the center of the Solar System, what would you see?
Nearly
such a view was taken recently from the
MESSENGER spacecraft currently orbiting the Sun from the distance of
Mercury.
The Sun's planets all appear as points of light, with the closest and largest planets appearing the brightest.
The planets
all appear to orbit in the same direction and are (nearly) confined to the same
great circle around the sky -- the
ecliptic plane.
Mercury,
Venus,
Earth, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn are all visible in the above horizontally
compressed image, while the positions of Uranus and Neptune are labeled even though they are too faint to make out.
Pluto, which has had its
planetary status recently called into question, is much too faint to see.
Earth's Moon is visible, however, as are the
Galilean moons of Jupiter.
The above image is the reverse of
one taken from the outside of the Solar System in 1990 by
Voyager 1.
MESSENGER, which has
flown by Mercury three times now, is on schedule to
enter orbit
around the Solar System's innermost planet next month.
 APOD: 2010 September 1 - Earth and Moon from MESSENGER
APOD: 2010 September 1 - Earth and Moon from MESSENGER
Explanation:
What does Earth look like from the planet Mercury?
The robotic spacecraft
MESSENGER
found out as it looked toward the
Earth during its closest approach to the
Sun about three months ago.
The Earth and Moon
are visible as the double spot on the lower left of the
above image.
Now MESSENGER was not at Mercury when it took the above image, but at a
location
from which the view would be similar.
From Mercury, both the
Earth and its
comparatively large moon will always appear as small circles of reflected sunlight and will never show a
crescent phase.
MESSENGER has zipped right by
Mercury three
times since being
launched in 2004, and is scheduled to enter orbit around the innermost planet in March of 2011.
 APOD: 2010 July 31 - Four Planet Sunset
APOD: 2010 July 31 - Four Planet Sunset
Explanation:
This mesmerizing sunset photo was taken from the summit of volcanic
Mount Lawu,
3,265 meters above sea level, on July 21.
The view looks west, toward the city lights of
Surakarta
(aka Solo), Central Java, Indonesia.
Two other volcanic peaks, sharp Merapi (left) and Merbabu
lie along the colorful horizon.
Four planets shine in the twilight sky above them.
Spread out near the
plane of the ecliptic are
Mercury,
Venus,
Mars, and
Saturn, along with bright
Regulus, alpha star of the constellation Leo.
For help finding them, just put your cursor over the picture.
In fact, these four planets still shine in western skies at sunset,
with Venus, Mars, and Saturn
grouped much more tightly
this weekend and in
early August.
By August 12, a young crescent Moon will join
the four planet sunset.
 APOD: 2010 April 22 - Venus, Mercury, and Moon
APOD: 2010 April 22 - Venus, Mercury, and Moon
Explanation:
Earlier this month, Venus and Mercury
climbed into the western twilight,
entertaining skygazers around
planet Earth
in a lovely conjunction of evening stars.
Combining 8 images spanning April 4 through April 15, this composite
tracks their progress through skies
above Portsmouth, UK.
Each individual image was captured at 19:50 UT.
The sequential path for both bright planets begins low and to the left.
But while Venus
continues
to swing away from the setting Sun, moving
higher above the western horizon,
Mercury first rises then falls.
Its highest point is from the image taken on April 11.
Of course on April 15, Venus and Mercury were joined by a young
crescent Moon.
 APOD: 2010 April 12 - Mercury and Venus Over Paris
APOD: 2010 April 12 - Mercury and Venus Over Paris
Explanation:
Go outside tonight and see one of the more interesting
planetary conjunctions of recent years.
Just after
sunset, the planets
Mercury and
Venus
are visible quite near each other.
Now Venus, being commonly
discernible as one of the brightest objects in the sky,
is frequently mistaken for an airplane. (Venus will set quite slowly, though.)
Mercury, however, is dimmer and usually harder to find.
Recently, though, Mercury can be
found just to the right of Venus,
appearing increasingly below the
brighter planet over the next week.
Pictured above,
Venus and Mercury were imaged next to the famous
Notre Dame Cathedral in
Paris, France.
A careful inspection of the image will further reveal
that the bright object nearly below Venus is iconic
Eiffel Tower.
 APOD: 2010 April 9 - Discovery's Dawn
APOD: 2010 April 9 - Discovery's Dawn
Explanation:
On April 5, visitors to Kennedy Space Center saw
these colorful clouds, twisting and drifting through
dawn skies.
Of course, the clouds were
rocket engine plumes from the
predawn
launch of the space shuttle Discovery
on the STS-131 mission to the
International Space Station.
Their layered colors are created as they reflect the reddened light
from the still rising Sun.
Fittingly, denizens of the space center's
rocket garden are lit in
the foreground.
At the far left is a 1960s vintage multistage
Atlas-Agena
rocket.
Together on the right, are
Mercury-Redstone and
Mercury-Atlas rockets.
 APOD: 2010 April 7 - Venus and Mercury in the West
APOD: 2010 April 7 - Venus and Mercury in the West
Explanation:
In this twilight skyview, a
windmill
stands in silent witness to a lovely
pairing of planets in the west.
The picture was recorded on April 5 from
Gallegos del Campo, Zamora, Spain.
Venus (left) and Mercury (right) are near their much
anticipated conjunction
in the early evening sky.
But even in the coming days, these two
evening stars will remain
close in the western
sky at sunset.
In fact, with brighter Venus as a marker,
sky watchers will have an excellent guide for
spotting Mercury
nearby, a planet often hidden in the Sun's glare.
 APOD: 2009 October 22 - Moon and Planets in the Morning
APOD: 2009 October 22 - Moon and Planets in the Morning
Explanation:
Last Friday, a gathering of three bright planets and the Moon
graced the morning sky.
With Mercury, Venus, Saturn, and a narrow lunar crescent
close to the eastern horizon in the dawn twilight, this picture of
the beautiful conjunction
was recorded near Noerdlingen, Germany.
These planets are wandering apart now and
Mercury is sinking
closer toward the rising Sun.
But if you also scan the rest of the sky this week
you should be able to add Jupiter and Mars to your planet spotting list,
as Mars rises around midnight and Jupiter shines brightly
after sunset.
In fact, if you want a better view of Jupiter
than Galileo had,
you might check out the
2009 International Year of Astronomy
activities
and events during these next few
Galilean Nights
(October 22-24).
 APOD: 2009 October 7 - A Double Ringed Basin on Mercury
APOD: 2009 October 7 - A Double Ringed Basin on Mercury
Explanation:
What caused the smooth floor inside the double ringed basin on Mercury?
No one is sure.
The unusual feature spans 160 kilometers and was imaged during the robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft's swing past our
Solar System's innermost planet last week.
Double and multiple ringed basins, although rare, have also been imaged in years past on Mars,
Venus,
Earth, and Earth's Moon.
Mercury itself has several doubles, including huge
Caloris basin,
Rembrandt basin, and enigmatic
Raditladi
basin.
Most large multiple ringed basins on planets and moons are caused initially by a
forceful impact by a single asteroid or comet fragment.
One interesting feature of the above-imaged double ring is that the basin center appears much smoother than the region between the rings.
Possibly, the internal floor was smoothed by later volcanic activity.
Also possible, however, is that the floor was smoothed by melting and
flowing of material upon
impact.
MESSENGER has now completed its last flyby of Mercury but will return and attempt to enter orbit in 2011 March.
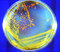 APOD: 2009 August 30 - D. rad Bacteria: Candidate Astronauts
APOD: 2009 August 30 - D. rad Bacteria: Candidate Astronauts
Explanation:
These bacteria could survive on another planet.
In an Earth lab, Deinococcus radiodurans (D. rad) survive extreme levels of
radiation,
extreme temperatures,
dehydration, and exposure to
genotoxic chemicals.
Amazingly, they even have the ability to repair their own
DNA,
usually within 48 hours.
Known as an extremophile,
bacteria such as
D. rad are of interest to
NASA
partly because they might be adaptable to help human
astronauts
survive on other worlds.
A recent
map of D. rad's
DNA
might allow biologists to augment their
survival skills with the ability to produce medicine, clean water, and oxygen.
Already they have been
genetically engineered to
help clean up spills of toxic
mercury.
Likely one of the oldest surviving life forms,
D. rad was discovered by accident in the 1950s when scientists investigating
food preservation
techniques could not easily kill it.
Pictured above,
Deinococcus radiodurans grow quietly
in a dish.
 APOD: 2009 July 30 - 6 Minutes 42 Seconds
APOD: 2009 July 30 - 6 Minutes 42 Seconds
Explanation:
The July 22nd total solar eclipse was
the longest of the
21st century.
From the point of maximum eclipse
along the Moon's shadow track
across the Pacific Ocean, the Moon completely blocked the Sun
for a total of 6 minutes and 39 seconds.
But from the deck of this cruise ship
the duration of the total
eclipse phase
was extended to a
whopping 6 minutes and 42 seconds
by the ship's motion along the shadow track.
This panoramic view of the scene shows the
shimmering solar corona
in a darkened daytime sky, with clouds silhouetted by a bright
sky on the distant horizon,
beyond the Moon's shadow.
Mercury can be seen near the eclipsed Sun.
Venus lies near the upper right edge of the frame.
 APOD: 2009 July 6 - Unknown Dark Material on Mercury
APOD: 2009 July 6 - Unknown Dark Material on Mercury
Explanation:
What is that strange material on Mercury?
When
flying by Mercury last October, the robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft imaged much of the solar system's
innermost planet
in unprecedented detail.
As common in science, new data bring new mysteries.
Pictured above on the lower right, a large crater -- about 100 kilometers across --
has unusual dark material of unknown composition near its center.
The material's darkness does not appear to be caused by
shadows, as the Sun was near
zenith
when the image was taken.
One origin hypothesis is that the
dark material was uncovered from
beneath Mercury's surface during the impact that created the surrounding crater.
If so, the composition of the dark mound might be similar to the composition of some
mysterious
dark rings
also recently discovered on Mercury.
Alternatively, the dark material could be related to an unusual composition of the impacting rock.
MESSENGER will
buzz past Mercury again later this year before entering orbit in 2011.
 APOD: 2009 May 27 - Volcanic Terrain on Mercury
APOD: 2009 May 27 - Volcanic Terrain on Mercury
Explanation:
Why are many large craters on Mercury relatively smooth inside?
Recent images from the robotic
MESSENGER
spacecraft that flew by Mercury last October show previously uncharted regions of
Mercury that have large craters with an internal smoothness similar to the
maria on Earth's own Moon.
Therefore, like
our Moon's maria, these
craters on Mercury are thought to have been flooded by lava floes that are old but not as old as the surrounding more highly cratered surface.
The above image mosaic of the western limb of Mercury was created by MESSENGER as it approached the Solar System's innermost planet last October.
Old and heavily textured terrain runs across much of the image bottom, while across the middle left lies comparatively smooth
impact basins
where small craters may appear similar at first to protruding hills.
MESSENGER will buzz
past Mercury
again later this year before entering orbit in 2011.
 APOD: 2009 May 4 - Rembrandt Impact Basin on Mercury
APOD: 2009 May 4 - Rembrandt Impact Basin on Mercury
Explanation:
Why do portions of this huge crater on Mercury have so much iron?
The unusual
Rembrandt impact basin was discovered recently
in images taken during the robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft's
2008 October flyby of the
Solar System's
innermost planet.
The unusual Rembrandt
spans over 700 kilometers and at 4 billion years old is
possibly the youngest
large impact basin on the planet.
Multicolored images of the crater floor, however, indicate reflections from areas containing unusually high amounts of
iron and
titanium.
These elements
indicate that some exposed materials have not been covered by more recent
lava floes,
and so might originate from an epoch of Mercury's formation.
Data from Rembrandt and across
Mercury
are now being interpreted as indicating a relatively active and volcanic past for Mercury that includes surface tectonics.
Close inspection of the
above image will reveal rings of
Mercury's Rembrandt
impact basin circling around the image center.
Mercury's limb is visible on the upper left, high cliffs and small craters are
visible inside Rembrandt,
and the terminator between night and day runs diagonally through the image.
MESSENGER is on track to fly past
Mercury again this September and enter orbit around
Mercury in 2011.
 APOD: 2009 April 30 - Framed by Clouds
APOD: 2009 April 30 - Framed by Clouds
Explanation:
Last Sunday's fading evening twilight featured a young crescent Moon
along the western horizon.
The young Moon also shared the sky with the lovely
Pleiades star cluster and
wandering planet Mercury.
Framed by clouds in this
serene
skyscape from Selsey, UK,
a similar twilight scene was visible around the globe.
Emerging from the cloud bank below the Pleiades, the
narrow sunlit lunar crescent
is overexposed.
Still, the Moon's dim night side is impressively clear, illuminated by
earthshine.
Bright, innermost
planet Mercury lies near the
bottom of the field.
Mercury will remain near the Pleiades,
low in the west
after sunset over the coming days, an
ongoing conjunction of planet and star cluster that will offer
skygazers some excellent binocular views.
 APOD: 2009 February 26 - Moon, Mercury, Jupiter, Mars
APOD: 2009 February 26 - Moon, Mercury, Jupiter, Mars
Explanation:
When the Moon rose in predawn skies on February 23rd,
it sported a sunlit crescent.
It also offered
early morning
risers a tantalizing view
of earthshine, the dark portion of the
lunar disk illuminated by
sunlight reflected from the Earth.
Of course, on that morning a remarkable
conjunction with three
wandering planets added an impressive touch to the
celestial scene.
Recorded just before sunrise,
this
serene skyview looks east toward
a glowing horizon across Tuggerah Lake on the Central Coast of New South
Wales, Australia.
Along with the waning
crescent Moon,
the picture captures (top to bottom) bright
Mercury,
Jupiter, and
Mars.
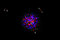 APOD: 2008 November 17 - HR 8799: Discovery of a Multi planet Star System
APOD: 2008 November 17 - HR 8799: Discovery of a Multi planet Star System
Explanation:
How common are planetary systems like our own Solar System?
In the twelve years previous to 2008,
over 300 candidate planetary systems have been found orbiting nearby stars.
None, however, were directly imaged, few showed evidence for multiple planets, and many had a Jupiter-sized planet orbiting inside the orbit of Mercury.
Last week, however, together with
recent images of
Fomalhaut b, the
above picture was released showing one of first confirmed images of planets orbiting a distant Sun-like star.
HR 8799 has a mass about 1.5 times that of our own Sun, and lies about 130 light years from the Sun -- a distance similar to many stars easily visible in the night sky.
Pictured above, a 10-meter
Keck telescope in
Hawaii
captured in infrared light three planets orbiting an artificially obscured central star.
The 8-meter
Gemini North
telescope captured a
similar image.
Each planet likely contains several times the mass of
Jupiter, but even the innermost planet,
labelled d, has an orbital radius near the equivalent of the Sun-
Neptune distance.
Although the
HR 8799 planetary system has significant differences with our Solar System, it is a
clear demonstration that complex planetary systems exist, systems that could conceivable contain an
Earth-like planet.
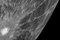 APOD: 2008 November 3 - A Spectacular Rayed Crater on Mercury
APOD: 2008 November 3 - A Spectacular Rayed Crater on Mercury
Explanation:
Why does Mercury have so many rayed craters?
No one is sure.
The robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft that is taking unprecedented images as it swoops past the innermost planet has provided dramatic confirmation that
Mercury has more
rayed craters than
Earth's Moon.
Pictured
above,
a particularly spectacular rayed crater spanning approximately 80 kilometers was imaged by
MESSENGER
during last month's flyby from about 20,000 kilometers up.
The rays prevalence is a mystery because
space weathering
effects such as dust accumulation and
solar wind attenuation should be greater on Mercury than on the Moon.
Hypothesized solutions currently include the
optical properties of Mercurian dust,
and that Mercury's high mass and proximity to the Sun cause more
violent impacts, thus typically raising more light material.
MESSENGER will buzz past Mercury again next year before entering orbit in 2011.
 APOD: 2008 October 8 - Mercury as Revealed by MESSENGER
APOD: 2008 October 8 - Mercury as Revealed by MESSENGER
Explanation:
The planet Mercury has been known since history has been recorded, but parts of the Solar System's innermost planet have never been seen like this before.
Two days ago the robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft buzzed past
Mercury
for the second time and imaged terrain mapped previously only by
comparatively crude radar.
The above image was recorded as
MESSENGER looked back 90 minutes after passing,
from an altitude of about 27,000 kilometers.
Visible in the
above image, among many other newly imaged features,
are unusually long
rays that appear to run like
meridians of
longitude
out from a young crater near the northern limb.
MESSENGER is scheduled to fly past
Mercury
once more before firing its thrusters to enter orbit in 2011.
 APOD: 2008 September 30 - Planets Ahoy
APOD: 2008 September 30 - Planets Ahoy
Explanation:
Can you spot the Solar System's four
rocky planets?
In the above
image taken on September 20,
all of them were visible in a single glance,
but some of them may be different than you think.
Pictured above, the brightest and highest object in the sky is the
planet Venus.
The object lowest in the sky is the
planet Mars,
while the object furthest to the left is the
planet Mercury.
The last remaining
point of light is . . . the bright
star Spica, which leaves the question --
where is the fourth rocky planet?
That would be
Earth, specifically part of
Australia,
visible across the entire bottom of the image.
 APOD: 2008 September 12 - Planets over Perth
APOD: 2008 September 12 - Planets over Perth
Explanation:
A bright trio of
terrestrial planets
was joined by a young Moon on September 1st,
in planet Earth's early evening skies.
In this view of the celestial gathering
from Perth,
Western Australia, the Moon's sunlit crescent is
nearly horizontal at Perth's southern latitude of about
32 degrees.
Venus, then
Mercury, and finally
Mars shine above
colorful city lights on the far shore of the Swan River.
The six unlit towers on the left surround a large
cricket stadium.
For now,
the planetary trio still lingers low in the west
just after sunset.
But in the coming days Venus will move farther from the Sun,
climbing higher after sunset,
while Mercury and Mars will steadily sink into the
glare along the western
horizon.
 APOD: 2008 July 10 - Enhanced Color Caloris
APOD: 2008 July 10 - Enhanced Color Caloris
Explanation:
The sprawling Caloris basin
on Mercury
is one of the solar system's largest impact basins.
Created during the early history of the solar system by the impact of
a large asteroid-sized body, the basin spans about 1,500 kilometers
and is seen in yellowish hues in
this enhanced
color mosaic.
The image data is from the January 14th
flyby of the
MESSENGER spacecraft,
captured with the
MDIS
instrument.
Orange splotches around the basin's perimeter are now thought to be
volcanic vents,
new evidence
that Mercury's smooth plains are indeed lava flows.
Other discoveries at Mercury
by NASA's MESSENGER mission include
evidence that Mercury, like planet Earth, has a global
magnetic field
generated by a
dynamo
process in its large core,
and that Mercury's surface has
contracted significantly as its core cooled.
 APOD: 2008 May 21 - A Dangerous Sunrise on Gliese 876d
APOD: 2008 May 21 - A Dangerous Sunrise on Gliese 876d
Explanation:
On planet Gliese 876d, sunrises might be dangerous.
Although nobody really knows what conditions are like on this close-in planet orbiting variable
red dwarf star
Gliese 876, the
above artistic illustration gives one impression.
With an orbit well inside
Mercury
and a mass several times that of Earth,
Gliese 876d might
rotate so slowly that dramatic differences exist between night and day.
Gliese 876d
is imagined above showing significant
volcanism, possibly caused by
gravitational tides flexing and
internally heating the planet,
and possibly more volatile during the day.
The rising
red dwarf
star shows expected stellar
magnetic activity which includes
dramatic and
violent prominences.
In the sky above, a hypothetical moon has its
thin atmosphere blown away by the red dwarf's
stellar wind.
Gliese 876d excites the
imagination partly because it is one of the few
extrasolar planets
known to be close to the
habitable zone of its parent star.
 APOD: 2008 May 9 - Moon Meets Mercury
APOD: 2008 May 9 - Moon Meets Mercury
Explanation:
On Tuesday, May 6, while standing on
planet Earth
and sweeping your binoculars along the western horizon just
after sunset,
you might have encountered this arresting skyscape.
The view features a slender crescent Moon and
bright planet Mercury separated on the sky by only
about 2 degrees.
Cradled in the
sunlit lunar crescent, the night
side of the Moon is faintly illuminated by earthshine --
sunlight reflected from planet Earth.
Of course, the clouds in silhouette and fading twilight colors
are common elements in pictures of the sky after sunset,
but much less often seen is inner planet Mercury,
usually hiding
close to the Sun in Earth's sky.
Still, the coming week will be a
good
time to
spot Mercury near the western horizon
about 30 minutes after sunset.
As for the Moon,
tonight and
tomorrow
night the crescent Moon will wander close to Mars
in the early evening sky.
 APOD: 2008 March 19 - Mercury in Accentuated Color
APOD: 2008 March 19 - Mercury in Accentuated Color
Explanation:
The colors of Mercury are subtle but beautiful.
At first glance, our
Solar System's
innermost planet appears simply
black and white,
but images that include
infrared
colors normally beyond human vision accentuate a world of detail.
One such image, shown above, was acquired by the robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft
that swung by Mercury in mid-January.
Here, most generally, the hot world itself acquires a slightly more brown hue.
Many craters that appear on top of other craters -- and so surely have formed more recently -- appear here as bright with bright rays that include a slightly blue tint, indicating that soil upended during the impact was light in color.
A few craters, such as some in the huge
Caloris Basin impact feature visible on the upper right, appear unexpectedly to be ringed with a dark material, the nature of which is being researched.
MESSENGER continues to glide through the inner Solar System and will pass
Mercury
again this October and next September, before entering orbit around the desolate world in 2011.
 APOD: 2008 March 10 - Planets Align Over Australian Radio Telescope Array
APOD: 2008 March 10 - Planets Align Over Australian Radio Telescope Array
Explanation:
Last week,
Mercury,
Venus, and the
Moon all appeared close together in Earth's sky.
This picturesque conjunction was caught on camera behind elements of
the Australia Telescope
Compact Array (ATCA) near the town of Narrabri in rural
New South Wales.
The ATCA
consists of six
radio telescopes
in total, each one larger than a house.
Together they form one of the highest resolution
measurement devices in the world.
Impressive
planetary
conjunctions occur every few years.
Involving the brightest objects in the night sky,
this alignment was easy to spot just before sunrise.
In the picture, taken on the morning of March 6,
Mercury is the highest
of the three bright celestial beacons.
 APOD: 2008 February 4 - A Spider Shaped Crater on Mercury
APOD: 2008 February 4 - A Spider Shaped Crater on Mercury
Explanation:
Why does this crater on Mercury look like a spider?
When the robotic
MESSENGER spacecraft
glided by the planet Mercury
last month, it was able to image portions of the Sun's closest planet that had never been seen before.
When imaging the center of Mercury's extremely large
Caloris Basin,
MESSENGER found a crater, pictured above, with a set of unusual
rays emanating out from its center.
A crater with such troughs has never been seen before anywhere in
our Solar System.
What isn't clear is the relation of the crater to the radial troughs.
Perhaps the crater created the
radial rays, or perhaps the two features appear only by a chance superposition --
the topic is sure to be one of future research.
MESSENGER is scheduled to fly past Mercury twice more before
firing its thrusters to
enter orbit in 2011.
 APOD: 2008 January 27 - Mercury on the Horizon
APOD: 2008 January 27 - Mercury on the Horizon
Explanation:
Have you ever seen the planet Mercury?
Because
Mercury orbits so close to the Sun,
it never wanders far from the Sun in
Earth's sky.
If trailing the Sun,
Mercury will be visible
low on the horizon for only a short while
after sunset.
If leading the Sun, Mercury
will be visible only shortly before
sunrise.
So at certain times of the year an
informed skygazer with a little determination
can usually pick Mercury
out from a site with an unobscured horizon.
Above, a lot of determination has been combined
with a little
digital trickery to
show Mercury's successive positions during March of 2000.
Each picture was taken from the same location in Spain
when the Sun itself was 10 degrees below the
horizon and superposed
on the single most
photogenic sunset.
Mercury is
currently visible in the western sky
after sunset, but will disappear in the Sun's glare after a few days.
 APOD: 2008 January 26 - Crescent Mercury in Color
APOD: 2008 January 26 - Crescent Mercury in Color
Explanation:
Hard to spot against the
twilight glow near planet Earth's horizon,
a crescent Mercury was imaged close up by the
MESSENGER
spacecraft early last week.
Colors in this
remarkable picture were
created using data
recorded through infrared, red, and violet filters.
The combination enhances color differences otherwise not visible to
the eye across the innermost planet's
cratered surface.
In this view,
light
bluish material seems to surround
relatively new craters,
contrasting with the mostly
drab, brown terrain.
Mercury itself is 4,880 kilometers in diameter.
The full resolution image shows features as small as 10 kilometers
across.
 APOD: 2008 January 21 - Mercury's Horizon from MESSENGER
APOD: 2008 January 21 - Mercury's Horizon from MESSENGER
Explanation:
What would it look like to fly past Mercury?
Just such an adventure was experienced last week by the MESSENGER spacecraft during its
first flyby of the strange
moon-like world nearest the Sun.
Pictured above is the limb of
Mercury
seen by MESSENGER
upon approach, from about 1 1/2
Earth diameters away.
Visible on the hot and barren planet are many
craters, many appeared to be more shallow than similarly sized craters on the Moon.
The comparatively high
gravity of
Mercury helps
flatten
tall structures like high crater walls.
MESSENGER
was able to take over 1,000 images of Mercury which will be beamed back to
Earth for
planetary geologists
to study.
The robotic MESSENGER spacecraft is
scheduled to fly past Mercury twice more before firing its thrusters
to enter orbit in 2011.
 APOD: 2008 January 16 - MESSENGER Passes Mercury
APOD: 2008 January 16 - MESSENGER Passes Mercury
Explanation:
Two days ago, the MESSENGER spacecraft became only the
second spacecraft in human history to swoop past Mercury.
The last spacecraft to visit the Sun's closest planet was
Mariner 10 over
35 years ago.
Mariner 10 was not able to
photograph Mercury's entire
surface, and the
images it did send back raised many questions.
Therefore, much about
planet Mercury
remains unknown.
This week's flyby of
MESSENGER
was only the first of three flybys.
Over the next few years MESSENGER will swing past twice more and finally enter Mercury's orbit in 2011.
MESSENGER is currently moving too fast to enter orbit around Mercury now.
The above image was taken two days ago during MESSENGER's flyby and shows part of Mercury's surface that has
never been imaged
in detail before.
Many more detailed images of Mercury
are expected to be sent back over the next few days.
The data acquired by
MESSENGER
will hopefully help scientists
better understand how Mercury's surface was formed, and why it is so dense.
 APOD: 2008 January 12 - Mercury Chases the Sunset
APOD: 2008 January 12 - Mercury Chases the Sunset
Explanation:
This colorful view of the western sky at sunset features
last Wednesday's slender crescent Moon.
Of course, when the Moon is in its
crescent phase it can
never be far from the Sun in the sky.
Also always close to the Sun in Earth's sky
is innermost
planet
Mercury, seen here below and right of center
against the bright orange glow along the horizon.
Mercury is usually
difficult
to glimpse because
of overwhelming sunlight, but increasingly better views of
the small planet after sunset will be possible as
it wanders farther
east of the Sun in the coming days.
On January 14th, NASA's MESSENGER
spacecraft will have a
good view
too, as it makes
its first Mercury flyby.
 APOD: 2007 October 3 - Comet Encke s Tail Ripped off
APOD: 2007 October 3 - Comet Encke s Tail Ripped off
Explanation:
Swinging inside the orbit of Mercury, on April 20th periodic
comet Encke
encountered a blast from the Sun in the form of a
Coronal
Mass Ejection (CME).
When CMEs, enormous clouds of energetic particles ejected from
the Sun, slam into
Earth's magnetosphere, they often trigger
auroral displays.
But in this case, the collison carried the tail of the comet away.
The tail was likely ripped off by interacting
magnetic fields rather than the mechanical pressure of the
collision.
Clicking on the two panel image will play a movie gif of the
remarkable event as recorded by the
Heliospheric Imager onboard the
STEREO A spacecraft.
In the movie, the time between frames is about 45 minutes,
while the frames span about 14x20 million kilometers at the
distance of the comet.
Of course, similar collisions have happened
before as the ancient comet loops through
its 3.3 year solar orbit.
So don't worry, Encke's
tail grows back!
 APOD: 2007 January 20 - SOHO: Comet McNaught Movie
APOD: 2007 January 20 - SOHO: Comet McNaught Movie
Explanation:
This frame from a spectacular time lapse movie shows
Comet
McNaught - the Great
Comet of 2007 -
sweeping through
the inner solar system.
The movie frames were recorded from
January 12 through Jan 16 by a
coronograph onboard the
sun-staring SOHO spacecraft.
Bright planet Mercury also glides dramatically through
the field of view but the Sun itself remains fixed,
hidden behind the coronograph's central occulting disk.
The broad-tailed
comet is
so bright it almost overwhelms SOHO's
sensitive camera designed to explore the
fainter structures in
the Sun's outer atmosphere.
Comet McNaught's
closest approach to the Sun (perihelion on
January 12) was only 0.17
astronomical
units, or about half the distance between the Sun and Mercury.
(Note: To download the movie file, click on the picture.)
 APOD: 2007 January 15 - Comet McNaught Over Catalonia
APOD: 2007 January 15 - Comet McNaught Over Catalonia
Explanation:
This past weekend Comet McNaught peaked at a brightness that surpassed even Venus.
Fascinated sky enthusiasts in the Earth's northern hemisphere were treated to an
instantly visible comet head and a faint elongated tail
near sunrise and sunset.
Recent brightness estimates had
Comet McNaught
brighter than
magnitude -5 (minus five) over this past weekend, making it the
brightest comet since
Comet Ikeya-Seki in 1965,
which was recorded at -7 (minus seven).
The Great Comet of 2007
reached its brightest as it rounded the Sun well inside the orbit of Mercury.
Over the next week
Comet McNaught
will begin to fade as it moves south and away from the Sun.
The unexpectedly bright comet
should remain visible to
observers in the southern hemisphere with unaided
eyes for the rest of January.
The above image, vertically compressed, was taken at sunset last Friday from
mountains above
Catalonia,
Spain.
 APOD: 2007 January 5 - Comet McNaught Heads for the Sun
APOD: 2007 January 5 - Comet McNaught Heads for the Sun
Explanation:
Early morning risers with a clear and unobstructed eastern horizon
can enjoy the
sight
of Comet McNaught (C/2006 P1)
in dawn skies over the next few days.
Discovered in August by R. H. McNaught
(Siding Spring Survey)
the comet has grown bright enough to see with the unaided
eye but will soon be lost in the glare of the Sun.
Still, by January 11 sun-staring spacecraft SOHO should be able to
offer web-based views as the
comet
heads toward a perihelion
passage inside the orbit of Mercury.
This
image captures the new naked-eye
comet
at about 2nd
magnitude
in twilight skies near sunset on January 3rd.
After rounding the Sun
and emerging from the solar glare later this month,
Comet
McNaught could be even brighter.
 APOD: 2006 December 9 - Three Planets in Dawn Skies
APOD: 2006 December 9 - Three Planets in Dawn Skies
Explanation:
Three children of the Sun rise in
the east in this peaceful dawn skyview recorded
December 7th near Bolu, Turkey.
Inner planet Mercury,
fresh from its second transit of the 21st
century, stands highest in the bright sky at the top right.
Gas giant Jupiter lies below the cloud bank near picture center.
A newsworthy Mars is also visible,
right of Jupiter and just above the dark cloud bank.
On Sunday, these planets will form a much
tighter grouping
before
sunrise, while in the coming days the
western sky after sunset will be ruled by brilliant
planet Venus, also
known as the evening star.
 APOD: 2006 November 25 - 3D Mercury Transit
APOD: 2006 November 25 - 3D Mercury Transit
Explanation:
Mercury is now visible shortly before dawn, the
brightest "star" just above the eastern horizon.
But almost
two weeks ago Mercury actually crossed
the face of the Sun for the second time in the 21st century.
Viewed with
red/blue
glasses, this stereo anaglyph combines
space-based images of the Sun and innermost planet in a
just-for-fun 3D
presentation of the
Mercury transit.
The solar disk image is from
Hinode.
(sounds like "hee-no-day", means sunrise).
A sun-staring observatory, Hinode was launched from Uchinoura Space Center
and viewed
the transit from Earth orbit.
Superimposed on Mercury's dark silhouette is
a detailed image
of the planet's rugged surface based on data from the
Mariner 10
probe that flew by Mercury in 1974 and 1975.
 APOD: 2006 November 17 - Hand Drawn Transit
APOD: 2006 November 17 - Hand Drawn Transit
Explanation:
The sight of
Mercury's tiny round disk drifting slowly
across the face of the Sun
inspired
and
entertained
many
denizens of planet Earth last week.
In fact, artist and astronomer Mark Seibold viewed both the
1999 and
2006 transits
of the solar system's innermost planet
through solar filtered
telescopes and composed
this
rendering
of Mercury "hovering in the
photosphere" near the edge of an enormous solar disk.
The original work is a 23 by 17 inch pastel sketch.
While the
artist's hand
is creatively superimposed, Seibold
concentrated on offering an impression of Mercury's silhouette,
surrounded by shadings reflecting his visual experience that
are not easily captured in photographic exposures.
Of course, before the age of cameras
drawings were more
widely used to record telescopic observations
of sunspots
and planetary transits.
 APOD: 2006 November 16 - Children of the Sun
APOD: 2006 November 16 - Children of the Sun
Explanation:
For a
moment, planets
Jupiter,
Venus,
Mars, and
Mercury
all posed near their parent star in this Sun-centered view,
recorded on November 11.
The picture, from a coronograph onboard the space-based
SOlar Heliospheric
Observatory, spans 15 degrees with
the Sun's size and position indicated by the white circle.
Background stars are also visible as the otherwise
overwhelming sunlight is blocked by
the coronograph's occulting disk.
But the planets themselves, in particular Jupiter and Venus, are
still bright enough to cause significant horizontal streaks in
the image.
Mercury is actually
moving most rapidly (left to right) through
the field and
days
earlier was seen to
cross
in front of the solar disk.
So what's that bright double star to the left of Mars?
Zubenelgenubi, of course.
 APOD: 2006 November 14 - Mercurys Transit: An Unusual Spot on the Sun
APOD: 2006 November 14 - Mercurys Transit: An Unusual Spot on the Sun
Explanation:
What's that dot
on the Sun?
If you look closely, it is almost perfectly round.
The dot is the result of an unusual type of
solar eclipse that occurred last week.
Usually it is the
Earth's Moon that eclipses the Sun.
Last week, for the first time in over three years, the planet
Mercury
took a turn.
Like the approach to New Moon before a
solar eclipse,
the phase of Mercury became a continually thinner
crescent as the planet
progressed toward an alignment with the Sun.
Eventually the phase of
Mercury dropped to zero and
the dark spot of Mercury crossed our parent star.
The situation could technically be labeled a Mercurian
annular
eclipse with an extraordinarily large
ring of fire.
From above the
cratered planes
of the night side of Mercury, the Earth appeared in its fullest phase.
Hours later, as Mercury continued in its orbit, a slight
crescent phase appeared again.
The next Mercurian solar eclipse
will occur in 2016.
 APOD: 2006 November 10 - Mercury and the Chromosphere
APOD: 2006 November 10 - Mercury and the Chromosphere
Explanation:
Enjoying Wednesday's
transit
of Mercury from Dallas, Texas, astronomer Phil Jones recorded
this detailed image of the Sun.
Along with a silhouette of the innermost planet,
a network of cells and dark
filaments can be seen against
a bright solar disk with spicules and
prominences along
the Sun's edge.
The composited image
was taken through a telescope equiped with an H-alpha filter
that narrowly transmits only the red light from
hydrogen atoms.
Such images emphasize the
solar chromosphere,
the region of the Sun's atmosphere immediately above
its photosphere or normally visible surface.
Left of center, the tiny disk of Mercury seems to be
imitating a small sunspot that looks a little too round.
But in H-alpha pictures,
sunspot regions are usually dominated by bright splotches (called
plages) on the
solar chromosphere.
 APOD: 2006 November 8 - Simulated Transit of Mercury
APOD: 2006 November 8 - Simulated Transit of Mercury
Explanation:
Mercury, the solar system's innermost planet,
will spend about five hours crossing
in front of the Sun
today - beginning at 1912
UT
(2:12pm EST), November 8.
Specially equipped telescopes are highly recommended to safely
spot the planet's diminutive
silhouette however, as Mercury should
appear about 200 times smaller than the enormous solar disk.
This simulated
view is based on a filtered solar image recorded on November 3rd.
It shows active regions and
the
Mercury transit across the Sun
at six positions
from lower
left to middle right.
Depending on your location, the Sun may not be above
the horizon during the entire transit, but webcasts of
the event are
planned - including one using images from the
sun-staring SOHO spacecraft.
This is the second of 14 transits of Mercury during the
21st century.
The next similar event will be a transit of Venus in
June of 2012.
 APOD: 2006 August 28 - Eight Planets and New Solar System Designations
APOD: 2006 August 28 - Eight Planets and New Solar System Designations
Explanation:
How many planets are in the Solar System?
This popular question now has a new formal answer according the
International Astronomical Union (IAU): eight.
Last week, the IAU voted on a
new definition for planet and
Pluto did not make the cut.
Rather, Pluto was re-classified as a
dwarf planet and is considered as a prototype for a new category of
trans-Neptunian objects.
The eight planets now recognized by the IAU are:
Mercury,
Venus,
Earth,
Mars,
Jupiter,
Saturn,
Uranus, and
Neptune.
Solar System objects now classified as dwarf planets are:
Ceres,
Pluto, and the currently unnamed
2003 UB313.
Planets, by the new IAU definition, must be in orbit around the sun, be nearly spherical,
and must have cleared the neighborhood around their orbits.
The demotion of
Pluto to dwarf planet
status is a source of continuing
dissent and controversy in the astronomical community.
 APOD: 2006 June 29 - Old Moon and Sister Stars
APOD: 2006 June 29 - Old Moon and Sister Stars
Explanation:
An old crescent Moon shares the
eastern sky over
Menton, France
with the sister stars
of the Pleiades cluster in this early
morning skyscape
recorded just last Friday, June 23rd.
(Bright Venus was also near the eastern horizon, but
is not pictured here.)
Astronomical images of the
well-known Pleiades often show the
cluster's alluring blue reflection nebulae, but they are washed out here
by the bright moonlight.
Still, while the
crescent Moon is overexposed,
surface features can be seen on the dim lunar night
side illuminated by earthshine - light from sunlit planet
Earth.
Of course, you can spot a young
crescent Moon in the early evening
sky tonight.
Having left the Pleiades behind, a lovely lunar crescent now
appears in the west,
lining up with planets Mars, Saturn,
and Mercury along the solar system's
ecliptic plane.
 APOD: 2006 June 17 - Saturn, Mars, and the Beehive Cluster
APOD: 2006 June 17 - Saturn, Mars, and the Beehive Cluster
Explanation:
Grab a pair of binoculars and check out
Saturn and Mars
in the early evening sky tonight!
Looking west
shortly after sunset, your view could
be similar to this one - recorded on June 14.
But while this picture shows the two bright planets
(Saturn at left) separated by around 1.5 degrees and
neatly flanking M44, the Beehive Star
Cluster, tonight should find those planets even closer together.
In fact, Saturn and Mars are scheduled to achieve their closest
alignment near sunset,
approaching to within about half a degree.
The Beehive will still stand out in the distant starry
background.
Still got those binoculars in hand?
You might
as well
look for
Mercury and Jupiter too.
 APOD: 2005 August 17 - Planets over Paranal
APOD: 2005 August 17 - Planets over Paranal
Explanation:
Very bright planets and very
large telescopes
are part of this sunset view of
Paranal Observatory.
The observatory's four, massive 8.2 meter telescope units
are situated on top of the 2,600 meter high mountain,
Cerro Paranal,
in the dry Atacama Desert in northern Chile.
The individual unit telescopes can be used separately or in
combination and
are named Antu, Kueyen, Melipal, and
Yepun.
Together they are fittingly known as the European Southern
Observatory's Very Large Telescope.
Of course, the very bright planets are Venus (near center), joined by
Mercury (below) and Saturn (left) in late June's western
evening skies.
 APOD: 2005 July 15 - Reflections on the Inner Solar System
APOD: 2005 July 15 - Reflections on the Inner Solar System
Explanation:
Only Mars
is missing from this reflective view of the major
rocky bodies of the inner
solar system.
Captured on July 8th, the serene, twilight picture looks out over the
Flat Tops Wilderness area from near Toponas, Colorado, USA and
includes planets Mercury, Venus, Earth,
and Earth's large
natural satellite, the Moon.
The Moon is in a young
crescent
phase about three degrees above
bright planet Venus.
Forest fires contribute to a layer of
smoke in Earth's sky that almost hides
planet Mercury,
still visible very near the horizon.
Just a week earlier
Venus and Mercury were joined by
Saturn, forming a notable grouping in the west also
enjoyed by skygazers
across planet Earth.
 APOD: 2005 July 2 - Three Planets by the Sea
APOD: 2005 July 2 - Three Planets by the Sea
Explanation:
On Tuesday, June 28th, the setting Sun flooded the horizon with
a beautiful warm light in
this view from
the beach beside the pier at Brighton in Adelaide,
South Australia.
The Sun also illuminated three planets gathered in the
western sky,
Mercury, Venus, and Saturn.
From this perspective
Mercury is at the
highest point in the celestial triangle, brilliant
Venus
is just below, and Saturn
stands farther to the left and below the
close pair.
Of course, the planets only appear close together on the sky
but are actually quite far apart in space.
The orbits
of Mercury and Venus are both interior to
Earth's orbit, while gas giant
Saturn lies in the outer
solar system, over nine
astronomical units
from the Sun.
Late next week,
Venus and Mercury will share western
skies with the young
crescent Moon.
 APOD: 2005 June 30 - Three Planets from Mt Hamilton
APOD: 2005 June 30 - Three Planets from Mt Hamilton
Explanation:
Venus, Mercury, and Saturn
wandered close together
in western evening skies last week.
On Saturnday,
June 25, astronomer R. Jay GaBany recorded
this snapshot of their eye-catching planetary conjunction,
from historic Lick Observatory
on Mt. Hamilton,
California, USA.
The view looks toward the Pacific shortly after sunset
with the lights of San Jose and the southern San Francisco
Bay area in the foreground.
Of course, Venus is
the brightest of the trio.
Mercury is nearby on the right
and Saturn is below and left,
closest to the horizon.
Farther to the right of the planetary triangle are
Pollux and Castor,
twin
stars of Gemini, with
Regulus,
bright star
of the constellation Leo, at the very upper left corner of the
picture.
In the
coming days, Venus and Mercury remain close,
while Saturn continues to drop below them, toward the horizon.
 APOD: 2005 June 24 - Planets in the West
APOD: 2005 June 24 - Planets in the West
Explanation:
This weekend
three planets will grace
the western sky,
forming a lovely trio easily visible shortly after sunset.
Saturday evening in particular will find
Saturn,
Venus, and
Mercury all within a 2 degree circle
(about the size of your thumb held at arm's length)
above the western horizon.
Recorded last Sunday, June 19, this image shows the same
three planets arrayed along the
ecliptic plane above a Colorado
Rocky Mountain skyline.
Venus is easiest to pick out of the twilight, the brightest
celestial beacon below picture center, with Saturn
above and to the left of Venus, and Mercury closest to the
horizon, right of prominent Pinnacle Peak.
By Saturday, the
wandering planets
will draw even closer together.
For help spotting the planets here, put your cursor over the
picture.
 APOD: 2005 March 18 - Moon, Mercury, Monaco
APOD: 2005 March 18 - Moon, Mercury, Monaco
Explanation:
Low on the western horizon after sunset, a
slender crescent Moon and
wandering planet Mercury join
the lights of Menton and Monaco
along the French Riviera.
Astronomer
Vincent Jacques took advantage of this
gorgeous photo opportunity
a week ago on March 11, when the Moon and Mercury
were separated in the sky by just three degrees.
Of course, the Moon in a slender crescent
phase
is always
seen near the horizon, as is Mercury - a bright planet which
can be otherwise difficult to glimpse as it never strays far
from the Sun in Earth's sky.
In the coming days
good views of Mercury will indeed be
fleeting as the solar system's
innermost
planet is rapidly
dropping closer to the glare of the setting Sun.
But tonight a waxing Moon will join another bright planet
wandering overhead
through the evening sky,
Saturn.
 APOD: 2005 March 7 - Mercury Over Leeds
APOD: 2005 March 7 - Mercury Over Leeds
Explanation:
Have you ever seen the planet Mercury?
This week might be a good time.
Because Mercury
orbits so close to the Sun, it never wanders far from the Sun in Earth's sky.
If trailing the Sun, Mercury will be
visible
low on the horizon for only a short while after
sunset.
If leading the Sun, Mercury will be
visible only shortly before sunrise.
So at certain times of the year an informed
skygazer with a little determination can usually
pick Mercury out
from a site with an clear horizon.
Above, a lot of determination has been combined with a
little digital trickery to show
Mercury's successive positions
during March of 2004.
Each picture was taken from the same location in Leeds,
England exactly 33 minutes after sunset.
Over the next two weeks, Mercury
will again be well placed for
viewing above the western horizon at sunset,
but by the third week in March it will have faded
and dropped into the twilight.
 APOD: 2004 September 12 - Mercury: A Cratered Inferno
APOD: 2004 September 12 - Mercury: A Cratered Inferno
Explanation:
Mercury's surface looks similar to our Moon's.
Each is heavily
cratered and made of rock.
Mercury's diameter is about 4800 km, while the
Moon's is slightly less at about 3500 km
(compared with about 12,700 km for the
Earth).
But
Mercury is unique in many ways.
Mercury is the closest planet to the
Sun,
orbiting at about 1/3 the radius of the
Earth's orbit.
As Mercury slowly rotates, its surface temperature
varies from an unbearably cold -180 degrees
Celsius to an unbearably hot 400 degrees
Celsius.
The place nearest the
Sun in
Mercury's
orbit changes slightly each orbit - a fact used by
Albert Einstein
to help verify the correctness of his then
newly discovered theory of gravity:
General Relativity.
The above picture was taken by the only spacecraft ever to pass
Mercury:
Mariner 10 in 1974.
A new mission, Messenger,
launched for Mercury last month
and is scheduled to enter orbit around the Solar System's
innermost planet in in 2011.
 APOD: 2004 September 1 - An Inner Neptune for 55 Cancri
APOD: 2004 September 1 - An Inner Neptune for 55 Cancri
Explanation:
Is our Solar System unique?
The discovery
of a Neptune-mass planet in an sub-Mercury orbit around nearby
Sun-like star
55 Cancri,
announced yesterday along with the discovery of other similar systems, gives a new indication that planetary systems as complex as our own
Solar System
likely exist elsewhere.
The planet,
discovered in data from the
Hobby-Eberly telescope in Texas, the
Lick Observatory
in California, and the orbiting
Hubble Space Telescope,
is one of four planets now known to orbit
55 Cancri
-- the others being similar in mass to Jupiter.
The finding involved noting
subtle changes in the speed of the star caused by its orbiting planets.
The above drawing depicts what this planet might look like,
assuming a mass similar to
Neptune, but a
composition similar to Earth.
The star
55 Cancri, only 40 light-years distant, is
visible with
binoculars towards the constellation of Cancer.
 APOD: 2004 August 14 - Messenger Launch
APOD: 2004 August 14 - Messenger Launch
Explanation:
Streaking
into the early morning sky on August 3rd, a
Delta II rocket launches NASA's
Messenger
spacecraft on an interplanetary voyage to
Mercury.
Scheduled to become the first probe to orbit Mercury, Messenger
will begin by
looping through the inner Solar System in a
series of close flybys of planet Earth and Venus.
The flybys are designed as trajectory changing
gravity
assist encounters to ultimately achieve the goal of orbiting
Mercury in 2011.
Prior to entering orbit, Messenger will also flyby Mercury
in 2008 and 2009 as the first spacecraft to visit
the Solar System's innermost planet since
Mariner 10 in the
mid 1970s.
This dramatic view
of the Messenger launch was recorded from
a pier in Jetty Park at the north end of Cocoa Beach
about 2.5 miles from the
Cape
Canaveral launch site.
So what's that erratic blue streak on the right?
It's the reflection from a camera
blurred in the time exposure.
 APOD: 2004 June 8 - A Planet Transits the Sun
APOD: 2004 June 8 - A Planet Transits the Sun
Explanation:
Today an astronomical event will occur that no living person has ever seen:
Venus will cross directly in front of the Sun.
A Venus crossing, called a transit, last occurred in 1882 and was
front-page
news
around the world.
Today's transit will be visible in its entirety throughout
Europe and most of Asia and Africa.
The northeastern half of
North America will see the Sun rise with the
dark dot of Venus already superposed.
Never look directly at the Sun, even when
Venus is in front.
Mercury's closer proximity to the Sun cause it to transit every few years.
In fact, the above image mosaic of Mercury
crossing the Sun is from
two
transits
ago, in November 1999.
Will anyone living see the next Venus transit? Surely yes since it occurs in 2012.
 APOD: 2004 June 6 - Mercury Spotting
APOD: 2004 June 6 - Mercury Spotting
Explanation:
Can you spot the planet?
The diminutive disk of Mercury, the solar system's
innermost planet,
spent about five hours crossing in front of the enormous solar disk
on 2003 May 7,
as
viewed from the general vicinity of planet Earth.
The Sun was above the horizon during
the entire transit for observers
in Europe, Africa, Asia, or Australia, and the horizon was
certainly
no problem for the sun-staring SOHO spacecraft.
Seen as a dark spot,
Mercury progresses from left to right
(top panel to bottom) in these four images from SOHO's extreme
ultraviolet camera.
The panels' false-colors correspond to different wavelengths in
the extreme ultraviolet which highlight regions above the Sun's
visible surface.
This
was the first of 14 transits of Mercury which will occur during the 21st
century,
but the next similar event will be a much more rare
transit of Venus this coming Tuesday.
Need help spotting Mercury?
Just click on the picture.
 APOD: 2004 May 16 - Venus: Earth's Cloudy Twin
APOD: 2004 May 16 - Venus: Earth's Cloudy Twin
Explanation:
This picture by the
Galileo spacecraft shows just how cloudy
Venus is.
Venus is very similar to Earth in size
and mass - and so is sometimes referred to as Earth's sister planet - but
Venus
has a quite different climate.
Venus' thick clouds and closeness to the
Sun
(only Mercury is closer) make it
the hottest planet - much hotter than the
Earth.
Humans could not survive there, and no life of any sort has ever been found.
When Venus is visible it is usually the brightest object in the sky
after the Sun and the Moon.
More than 20 spacecraft have visited
Venus
including Venera 9, which landed on the surface, and
Magellan,
which used radar to peer through the clouds and make a map of the
surface.
This visible light picture of Venus
was taken by the Galileo spacecraft
that orbited Jupiter from 1995 to 2003.
Many things about Venus remain unknown, including the cause of
mysterious bursts of radio waves.
 APOD: 2004 April 25 - D rad Bacteria: Candidate Astronauts
APOD: 2004 April 25 - D rad Bacteria: Candidate Astronauts
Explanation:
These bacteria could survive on another planet.
In an Earth lab, Deinococcus radiodurans (D. rad) survive extreme levels of
radiation, extreme temperatures,
dehydration, and exposure to
genotoxic chemicals.
Amazingly, they even have the ability to repair their own
DNA,
usually with 48 hours.
Known as an extremophile,
bacteria such as
D. rad are of interest to
NASA
partly because they might be adaptable to help human
astronauts
survive on other worlds.
A recent
map of D. rad's
DNA might allow biologists to augment their
survival skills with the ability to produce medicine, clean water, and oxygen.
Already they have been
genetically engineered to
help clean up spills of toxic
mercury.
Likely one of the oldest surviving life forms,
D. rad was discovered by accident in the 1950s when scientists investigating
food preservation
techniques could not easily kill it.
Pictured above,
Deinococcus radiodurans grow quietly
in a dish.
 APOD: 2004 April 2 - Mercury and Venus in the West
APOD: 2004 April 2 - Mercury and Venus in the West
Explanation:
Doing their part in the
ongoing dance of the planets,
Mercury and Venus both reached their greatest
elongation or maximum apparent distance from the Sun
only a few days ago, on March 29th.
Eager to record their celestial accomplishment, astronomer
Jimmy Westlake snapped this view of the two
inner most planets
shining in western twilight skies above Yampa,
Colorado, USA.
The picture was taken using a digital camera mounted on a tripod.
Mercury is easily the brightest
celestial object near the horizon, appearing to the right of the
foreground structure and
just above a thin cloud silhouetted by fading sunlight.
Still, near the top of the picture
brilliant Venus dominates the scene as the
magnificent evening star.
After climbing in western skies throughout the month of March,
Venus lies just
below the Pleiades star cluster.
Tonight and tomorrow night,
skygazers can spot Venus
at the southern edge of the Pleiades.
 APOD: 2004 March 26 - Moon and Planets Sky
APOD: 2004 March 26 - Moon and Planets Sky
Explanation:
Look up into the sky tonight and without a telescope
or binoculars you might have
a
view like this one of Moon, planets and stars.
The lovely
photo was taken on March 23rd,
and captures the crescent Moon on the horizon with Venus above it.
Both brilliant celestial bodies are over-exposed.
Farther above Venus is the tinted glow of Mars with
the Pleiades star cluster just to the red planet's right.
The V-shaped arrangement of
stars to the left of Mars is the Hydaes star cluster.
Bright red giant
Aldebaran, not itself a member of the Hyades
cluster, marks the top left of the V.
During
the next week, all five naked-eye planets,
Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn, along with
the Moon
will grace the evening sky together - a
lunar and planetary spectacle that can be
enjoyed by skygazers
around the world.
But look just after sunset, low on the western horizon,
to see Mercury before it sets.
The next similar gathering
of the planets will be in 2008.
 APOD: 2003 May 27 - A Mercury Transit Sequence
APOD: 2003 May 27 - A Mercury Transit Sequence
Explanation:
Earlier this month, the planet
Mercury crossed the face of the Sun, as seen from
Earth.
Because the plane of Mercury's orbit is not exactly coincident with the
plane of Earth's orbit,
Mercury usually appears to pass over or under the Sun.
The above time-lapse sequence, superimposed on a single frame,
was taken from a balcony in
Belgium on May 7 and shows the entire
transit.
The solar crossing
lasted over five hours, so that the above
23 images were taken roughly 15 minutes apart.
The north pole of the Sun, the
Earth, Mercury's orbit,
although all different, all occur in directions
slightly above the left of the image.
Near the center and on the far right,
sunspots
are visible.
 APOD: 2003 May 13 - Mercury Transits the Sun
APOD: 2003 May 13 - Mercury Transits the Sun
Explanation:
How big is the Sun?
The Sun
is not only larger than any planet,
it is larger than all of the
planets put together.
The Sun accounts for about 99.9 percent of all the mass in its
Solar System.
Merely stating the Sun's diameter is about 1,400,000
kilometers does not do it justice.
Last week a chance to gain visual size perspective
occurred when planet
Mercury made a rare crossing in front to Sun.
Mercury, a planet over a third of the diameter of our Earth, is the dark dot on the upper right.
In comparison to the Sun, Mercury is so small it is initially
hard to spot.
Also visible on the Sun are dark circular sunspots, bright plages, and dark elongated
prominences -- many of which are larger than Mercury.
The above contrast-enhanced picture was
captured last week from
France.
 APOD: 2003 May 8 - Mercury Spotting
APOD: 2003 May 8 - Mercury Spotting
Explanation:
Can you spot the planet?
The diminutive disk of Mercury, the solar system's
innermost planet,
spent about five hours crossing in front of the enormous solar disk
yesterday (Wednesday, May 7th),
as
viewed from the general vicinity of planet Earth.
The Sun was above the horizon during
the entire transit for observers
in Europe, Africa, Asia, or Australia, and the horizon was
certainly
no problem for the sun-staring SOHO spacecraft.
Seen as a dark spot,
Mercury progresses from left to right
(top panel to bottom) in these four images from SOHO's extreme
ultraviolet camera.
The panels' false-colors correspond to different wavelengths in
the extreme ultraviolet which highlight regions above the Sun's
visible surface.
This
is the first
of 14 transits of Mercury which
will occur during the 21st
century,
but the next similar event will be a
transit
of Venus in June of 2004.
Need help spotting Mercury?
Just click on the picture.
 APOD: 2003 April 12 - Mercury on the Horizon
APOD: 2003 April 12 - Mercury on the Horizon
Explanation:
Have you ever seen the planet Mercury?
Because
Mercury orbits so close to the Sun,
it never wanders far from the Sun in
Earth's sky.
If trailing the Sun,
Mercury will be visible
low on the horizon for only a short while
after sunset.
If leading the Sun, Mercury
will be visible only shortly before
sunrise.
So at certain times of the year an
informed skygazer with a little determination
can usually pick Mercury
out from a site with an unobscured horizon.
Above, a lot of determination has been combined
with a little
digital trickery to
show Mercury's successive positions during March of 2000.
Each picture was taken from the same location in Spain
when the Sun itself was 10 degrees below the
horizon and superposed
on the single most
photogenic sunset.
By the middle of this month, Mercury will again be well
placed for viewing above the western horizon at sunset,
but by the end of April it will have faded and dropped into the
twilight.
On May 7th,
Mercury
will cross the Sun's disk.
 APOD: 2003 February 24 - Comet NEAT Passes an Erupting Sun
APOD: 2003 February 24 - Comet NEAT Passes an Erupting Sun
Explanation:
As Comet NEAT flared last week, the
Sun roared.
Just as the comet swooped inside the orbit of
Mercury
and developed a long and flowing tail of gas and
dust,
the Sun emitted a huge
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME).
Neither the fortuitous
hot ball of solar gas
nor the intense glare of sunlight appeared to disrupt the
comet's nucleus.
The action was too close to the
Sun to be easily visible by
humans,
but the orbiting Sun-pointing
SOHO satellite had a clear view of the celestial daredevil show.
The above image was taken on February 18 when the
comet
was so bright it created an
artificial horizontal streak on the camera image.
During the encounter,
Comet NEAT, official designation (C/2002 V1),
brightened to second
magnitude.
An opaque disk blocked the Sun's image.
The now-outbound comet remains
bright but will surely fade as it moves away from the Sun.
Nevertheless, Comet NEAT will likely be visible with binoculars
to southern hemisphere observers for the next month.
 APOD: 2003 February 16 - Southwest Mercury
APOD: 2003 February 16 - Southwest Mercury
Explanation:
The planet Mercury resembles a moon. Mercury's old surface is heavily cratered like many moons.
Mercury is larger than most moons but smaller than
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede and
Saturn's moon
Titan.
Mercury is much denser and more massive than any moon,
though, because it is made mostly of iron. In fact, the
Earth is the only planet more dense.
A visitor to Mercury's surface
would see some strange sights.
Because
Mercury rotates exactly three times every two orbits around the
Sun, and because
Mercury's orbit is so elliptical, a visitor to
Mercury might see the
Sun rise, stop in the sky, go back toward the rising
horizon,
stop again, and then set quickly over the
other horizon.
From Earth, Mercury's proximity to the
Sun causes it to be
visible only for a short time just after
sunset or just before sunrise.
 APOD: 2003 February 10 - Comet NEAT Approaches the Sun
APOD: 2003 February 10 - Comet NEAT Approaches the Sun
Explanation:
A comet
may likely become visible to the unaided eye over the
next few days above the
horizon where the Sun has just set.
Comet NEAT (C/ 2002 V1), discovered last November, has
brightened dramatically as it approached the Sun.
Over the next few days, the
quickly setting comet could
appear as bright as second
magnitude.
On February 18 it will round the Sun well within the orbit of
Mercury.
During surrounding days, the Sun's glare will effectively
hide the comet to human observers.
It is quite probable, though, that
Comet NEAT will standout prominently in
images taken by the Sun-looking
SOHO satellite.
Pictured above,
Comet NEAT's complex and developing
tail was photographed on
January 29 (top) and February 2.
Sky enthusiasts
should remember to never look directly at the Sun.
 APOD: 2002 July 16 - Outbound from Mercury
APOD: 2002 July 16 - Outbound from Mercury
Explanation:
After just passing Mercury, the robot spacecraft Mariner 10 looked back.
The
above picture is what it saw.
Mercury,
the closest planet to the
Sun, is heavily cratered much like
Earth's Moon.
As Mercury slowly rotates, its surface
temperature varies from an unbearably cold -180 degrees
Celsius in the half facing away from the Sun,
to an unbearably hot 400 degrees
Celsius
in the half facing toward the Sun.
Mercury is slightly larger than
Earth's Moon and much
denser.
The Mariner 10 spacecraft swooped by
Mercury three times in its journey around the inner
Solar System in the mid-1970s.
This outbound view has similarities to the
inbound view.
Nearly half of
Mercury's surface
has yet to be photographed in detail.
 APOD: 2002 May 10 - Trailing Planets
APOD: 2002 May 10 - Trailing Planets
Explanation:
Positioning his camera and tripod on
planet Earth,
near Maricopa, Arizona, USA,
astrophotographer
Joe Orman created this trailing display of the ongoing
sky-full-of-planets
on May 3rd.
He initially captured the grouping in a 20 second
long time exposure
recording the positions of the bright planets and stars.
Covering the camera lens for five minutes, he then exposed the same
frame for 45 minutes,
tracing the gentle arcs of the celestial
wanderers
as the Earth's rotation carried them toward the western
horizon.
Of course these planets,
Mercury,
Venus,
Mars,
Jupiter, and
Saturn all
still dazzle
in western skies near sunset,
but sky gazers who want to see Mercury should look soon.
Mercury starts the evening closest to the horizon -
visible here
above the wide bright trail left by Venus - and in the coming days
Mercury will be the first to leave the evening sky entirely as it moves
closer to the setting Sun.
Tonight Venus and Mars
will appear very close
together, separated by only one third of a degree.
 APOD: 2002 April 29 - Dusk of the Planets
APOD: 2002 April 29 - Dusk of the Planets
Explanation:
A great grouping of
planets is
now visible to the west just after sunset.
Over the next two weeks,
Mercury,
Venus,
Earth,
Mars,
Jupiter, and
Saturn -- the innermost six planets of our
Solar System -- can be seen in a single knowing glance.
The image on the left captured them all in one frame.
Connecting the planetary dots delineates the edge-on
ecliptic,
the plane in which the planets orbit the
Sun.
The shot was taken on April 23 near Chatsworth,
New Jersey,
USA, and even includes scattered
light from the Sun and the
Moon.
Besides the planets, the
Pleiades and
Hyades
open clusters
of stars are visible.
 APOD: 2002 April 18 - Planets in the West
APOD: 2002 April 18 - Planets in the West
Explanation:
Have you seen any bright planets lately?
Chances are if you've been outside
under clear skies
just after sunset, then you have.
Now shining in the west as bright
"stars"
in the night sky, are all five planets of the solar
system known to ancient astronomers -
Mercury, Venus, Mars, Saturn, and
Jupiter.
Recorded from Holt, Michigan, USA about 40 minutes after sunset
on April 14th,
this
digital image captures three of them, Venus,
Mars, and Saturn, along with a young
crescent Moon.
Also indicated are the Pleiades
star cluster and
bright red giant star Aldebaran in Taurus.
Mercury,
setting, is lost in the trees and glow along the horizon,
while Jupiter is off the top of this view.
The coming weeks
will see photo opportunities galore
as all five planets gradually move closer together, posing
after sunset with the Moon and stars in the western
sky.
Venus, Mars,
and Saturn will form the closest trio,
drawing within a 5 degree circle (about the apparent
size of your fist with arm extended) above Aldebaran by May 3rd.
 APOD: 2002 February 14 - Solar System Portrait
APOD: 2002 February 14 - Solar System Portrait
Explanation:
On another
Valentine's Day
(February 14, 1990), cruising four billion
miles from the Sun, the
Voyager 1
spacecraft looked back to make this
first ever family portrait
of our Solar System.
The complete portrait is a
60 frame mosaic
made from a vantage point 32 degrees above the
ecliptic plane.
Voyager's wide angle camera frames sweep through the
inner Solar System (far left) linking up with
gas giant Neptune, at the time
the
Solar System's outermost planet (scroll right).
Positions
for Venus,
Earth, Jupiter,
Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
are indicated by the corresponding letters while the Sun is the
bright spot near the center of the circle of frames.
The inset frames
for each of the planets are
from Voyager's narrow field camera.
Unseen in the portrait are
Mercury, too close to the Sun
to be detected, and Mars, unfortunately hidden by sunlight
scattered in the camera's optical system.
Small, faint Pluto's
position was not covered.
 APOD: 2001 November 24 - Mariner's Mercury
APOD: 2001 November 24 - Mariner's Mercury
Explanation:
Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, remains
the most mysterious of the
Solar System's inner planets.
Hiding in the Sun's glare it is
a
difficult target for Earth bound observers.
The only spacecraft to
explore Mercury
close-up was Mariner 10 which
executed three
flybys of Mercury
in 1974 and 1975, surveying approximately 45
percent of its surface.
Mariner
10 deftly manuevered to
photograph part of the sunlit
hemisphere during each approach, passed behind the planet,
and continued to image the sun-facing side as the spacecraft receded.
Its highest resolution
photographs recorded features
approximately a mile across.
A reprocessing
of the
Mariner 10 data has resulted in this dramatic mosaic.
Like the Earth's Moon, Mercury's surface
shows the scars of impact cratering -
the smooth vertical band and patches visible above represent regions
where no image information is available.
 APOD: 2001 August 19 - Mercury: A Cratered Inferno
APOD: 2001 August 19 - Mercury: A Cratered Inferno
Explanation:
Mercury's surface looks similar to our Moon's.
Each is heavily
cratered and made of rock.
Mercury's diameter is about 4800 km, while the
Moon's is slightly less at about 3500 km
(compared with about 12,700 km for the
Earth).
But
Mercury is unique in many ways.
Mercury is the closest planet to the
Sun,
orbiting at about 1/3 the radius of the
Earth's orbit.
As Mercury slowly rotates, its surface temperature
varies from an unbearably cold -180 degrees
Celsius to an unbearably hot 400 degrees
Celsius.
The place nearest the
Sun in
Mercury's
orbit changes slightly each orbit - a fact used by
Albert Einstein
to help verify the correctness of his then
newly discovered theory of gravity:
General Relativity.
The above picture was taken by the only spacecraft ever to pass
Mercury:
Mariner 10 in 1974.
 APOD: 2001 May 5 - Shepard Flies Freedom 7
APOD: 2001 May 5 - Shepard Flies Freedom 7
Explanation:
Forty years ago today
(May 5, 1961), at the
dawn of the space age,
NASA controllers "lit the candle" and sent
Alan Shepard arcing into space atop
a Redstone rocket.
The picture shows the pressure-suited Shepard before launch in his
cramped space capsule dubbed
"Freedom 7".
Broadcast live to a global television audience,
the
flight of Freedom 7 - the first space flight by an American - followed
less than a month after the first human venture into space
by Soviet Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin.
Freedom 7's
historic flight was suborbital,
lasting only about 15 minutes, but
during it Shepard demonstrated manual control of his capsule.
Naval aviator Shepard was chosen as one
of the original seven
Mercury Program astronauts.
He considered
this first flight the greatest
challenge and actively sought the assignment.
Shepard's career as an astronaut spanned a remarkable
period in human achievement and in 1971
he walked on the moon as commander of the
Apollo 14 mission.
A true pioneer and intrepid explorer,
Alan Shepard died in 1998
at age 74.
 APOD: 2001 March 8 - Bright Venus
APOD: 2001 March 8 - Bright Venus
Explanation:
Have you seen a bright evening star
in the western sky lately?
That's no star, that's planet Venus the second "rock"
from the Sun.
Blazing at -4.6
magnitude, Venus, after the Sun and Moon,
is the third brightest celestial body in
planet Earth's sky.
Venus is closer to the Sun than Earth and
as Venus orbits
the Sun it is seen to go through
phases similar to the Moon.
But unlike the Moon, as
Venus waxes and wanes
its distance from Earth and hence its apparent size changes drastically.
This causes
Venus to look brighter
as it looms large in its
crescent phases than when it is smaller and nearly full.
Taken on January 28th, this dramatic picture finds a crescent
Venus near its brightest to the right of a crescent Moon.
The brilliant rivals seem poised above a satellite dish of the
Scripps Satellite Oceanography Facility.
Closer to the horizon,
just below and to the right of the satellite dish,
Mercury pierces the twilight glow.
 APOD: 2001 February 9 - Nashville Four Planet Skyline
APOD: 2001 February 9 - Nashville Four Planet Skyline
Explanation:
So far this February,
evening skies have been blessed with
a glorious Moon and three bright planets;
Venus, Jupiter, and Saturn.
But just last week, on January 30th,
an extreme wide-angle lens allowed
astrophotographer Larry Koehn to capture this twilight view
of Moon and four
planets above Nashville, Tennessee, USA.
These major
solar system
bodies lie along the ecliptic plane and
so follow a diagonal line through the picture.
Starting near the upper left corner is bright
Jupiter, which takes
on a slightly triangular shape due to the lens distortion.
Just below and right of Jupiter
is Saturn.
Continuing along the diagonal toward the lower right
is an overexposed, six day
old Moon
and brilliant Venus seemingly
embedded in clouds.
The fourth planet pictured is Mercury.
Notoriously hard to see from planet Earth because it never
wanders far from the Sun,
Mercury is visible just above
the lower right corner.
The line from Jupiter to Mercury spans about 92 degrees
across the Nashville sky.
 APOD: 2000 December 16 - Degas Ray Crater on Mercury
APOD: 2000 December 16 - Degas Ray Crater on Mercury
Explanation:
Like the Earth's Moon,
Mercury is scarred with craters
testifying to an intense bombardment during the
early history of
the Solar System.
In 1974,
the
Mariner 10 spacecraft
surveyed this innermost planet up close,
producing the only detailed images of its tortured surface.
In the above mosaic the bright rays
emanating from the 45 kilometer wide
Degas crater almost appear to be painted on.
The rays consist of light colored material blasted out during the
crater's formation.
Craters older than Degas are covered by the
ray material while younger craters are seen
superimposed on the rays.
Mercury's gravity and density
are about twice
that of Earth's Moon
so such bright
ray
craters on the lunar surface tend to be much larger.
NASA plans to launch MESSENGER
to the least explored terrestrial planet
in 2004.
 APOD: 2000 March 20 - Mercury on the Horizon
APOD: 2000 March 20 - Mercury on the Horizon
Explanation:
Have you ever seen the planet Mercury?
Because
Mercury orbits so close to the Sun,
it is never seen far from the Sun,
and so is only visible near
sunrise or
sunset.
If trailing the Sun,
Mercury will be visible
for several minutes before it follows the
Sun behind the
Earth.
If leading the Sun,
Mercury will be
visible for only several minutes before the
Sun rises and hides it with increasing glare.
An
informed skygazer can usually pick Mercury out of a dark
horizon glow
with little more than determination.
Above, a lot of determination has been combined
with a little
digital trickery to
show Mercury's successive positions
during the middle of last month.
Each picture was taken from the same location in Spain
when the Sun was 10 degrees below the
horizon and superposed
on the single most
photogenic sunset.
 APOD: 2000 March 10 - Sky and Planets
APOD: 2000 March 10 - Sky and Planets
Explanation:
On February 10th, an
evocative
evening sky above Rocklin, California, USA
inspired astrophotographer Steve Sumner
to record this remarkable sight - five planets and the Moon.
Near its first quarter phase, the bright
Moon was intentionally overexposed
but Saturn,
Jupiter,
Mars, and
Mercury
(and, of course,
planet Earth's horizon)
are all clearly visible in the deepening twilight.
Notably absent in this grouping of naked-eye planets is
Venus which
is still putting in an early appearance as the
morning star.
This month, Mercury has joined Venus in the dawn twilight while
Saturn, Jupiter, and Mars still shine brightly in the western sky at
nightfall
making another gorgeous close grouping with the crescent
Moon.
 APOD: 2000 February 13 - Southwest Mercury
APOD: 2000 February 13 - Southwest Mercury
Explanation:
The planet Mercury resembles a moon. Mercury's old surface is heavily cratered like many moons.
Mercury is larger than most moons but smaller than
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede and
Saturn's moon
Titan.
Mercury is much denser and more massive than any moon,
though, because it is made mostly of iron. In fact, the
Earth is the only planet more dense.
A visitor to Mercury's surface
would see some strange sights.
Because
Mercury rotates exactly three times every two orbits around the
Sun, and because
Mercury's orbit is so elliptical, a visitor to
Mercury might see the
Sun rise, stop in the sky, go back toward the rising
horizon,
stop again, and then set quickly over the other horizon.
From
Earth, Mercury's proximity to the
Sun cause it to be
visible only for a short time just after sunset or just before sunrise.
 APOD: 2000 January 28 - Astronomy From An F-18
APOD: 2000 January 28 - Astronomy From An F-18
Explanation:
In an era of blossoming
ground and space-based observatories,
astronomers are also pushing the envelope with airborne
instrumentation - successfully
capturing an asteroid occultation
from a high performance jet aircraft.
This blinking animation represents two digitized frames from inflight
data of
asteroid number 308, Polyxo, passing in front
of or occulting a faint
star near the center of the field.
The camera used, known as the
SouthWest Ultraviolet Imaging System (SWUIS) -A,
was mounted in
the cockpit of a
NASA F/A-18 jet
(inset lower left).
A former US Navy fighter aircraft,
the F/A-18 was able to
maneuver to the precise position to record the occultation
while cruising above clouds and much of Earth's obscuring atmosphere.
Using the SWUIS-A data to time the
occultation will reveal
the size of the asteroid which is otherwise too small to be imaged
by even the orbiting
Hubble Space Telescope.
Future
SWUIS-A airborne missions may include a hunt for Vulcanoids,
a suspected population of small
asteroids
circling the Sun inside
the orbit of Mercury.
 APOD: December 10, 1999 - Spot The Planet
APOD: December 10, 1999 - Spot The Planet
Explanation:
OK, it's a picture of the Sun (duh!),
but can you
spot the planet?
Of course, most of the spots you've spotted are sunspots,
as large or larger than planet Earth itself.
The sunspots are
regions of strong surface magnetic fields which
are dark in this picture only because they are relatively cool
compared to their surroundings.
Over the past few years,
the number of sunspots
has been steadily increasing
as the Sun approaches the maximum in its 11 year activity cycle.
But
also
visible in
this photograph from November 15,
is planet Mercury.
At just over 1/3 Earth's size, Mercury
is passing in front of the Sun, its silhouette briefly creating
a diminutive dark spot
drifting across an enormous solar disk.
While "transits" of Mercury
do occur 13 times a century, this one
was additionally a very rare grazing transit of our
Solar System's innermost planet.
Spotted Mercury yet? Click on the picture for a hint.
 APOD: November 19, 1999 - Mercury And The Sun
APOD: November 19, 1999 - Mercury And The Sun
Explanation:
Just days before the peak of the
Leonid meteor shower,
skywatchers were offered another astronomical treat as
planet Mercury crossed the face of the Sun on November 15.
Viewed from planet Earth, a
transit of Mercury is not all that rare.
The last
occurred in 1993 and the next will happen in 2003.
Enjoying a mercurial transit does require an
appropriately filtered telescope,
still the event can be dramatic
as the diminutive well-done world
drifts past the dominating solar disk.
This slow loading gif
animation is based on images
recorded by the earth-orbiting
TRACE satellite.
The false-color TRACE images were made in ultraviolet light
and tend to show the hot gas just above the Sun's visible surface.
Mercury's disk is silhouetted against the
seething plasma as it follows a trajectory near the edge of the Sun.
 APOD: November 11, 1999 - Mercury And The Moon
APOD: November 11, 1999 - Mercury And The Moon
Explanation:
Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun and
never moves far from our parent
star in Earth's sky.
Racing around its tight orbit, this well-done world
is a little over 1/3 the diameter of Earth and
is often lost to
our view in the solar glare.
But, just one day before the August 11 total
solar eclipse, astronomer
Tunc Tezel captured this fleeting view of a close conjunction of Mercury
and the soon to be
silhouetted Moon as seen from Turkey.
Mercury at the lower right shines brightly in reflected sunlight
while only a thin crescent of the almost new
Moon is directly illuminated.
The rest of the lunar nearside is faintly visible though,
illuminated by light from an
almost full Earth.
On Monday,
November 15th, Mercury will actually be seen to
transit or pass across the disk of the Sun for well placed
observers in the
pacific hemisphere.
 APOD: November 6, 1999 - X ray Transit of Mercury
APOD: November 6, 1999 - X ray Transit of Mercury
Explanation:
This sequence of
false color X-ray images captures a rare event -
the passage or
transit of planet Mercury in front of the Sun.
Mercury's small disk is
silhouetted against the bright background of X-rays from the hot
Solar Corona.
It appears just to the right of center in the
top frame and moves farther right as the sequence progresses toward
the bottom.
The dark notch is
a coronal hole near
the Solar South Pole, while
a flaring coronal bright point can be seen to the left of the notch
in the top frames.
The frames were recorded on November 6, 1993 by the
Soft X-ray Telescope
on board
the orbiting Yohkoh satellite.
Transits of Mercury (and Venus) were historically used to discover
the geometry of the solar system and to
map planet Earth itself.
The next transit of Mercury will occur on November 15.
 APOD: September 18, 1999 - Mercury Astronauts and a Redstone
APOD: September 18, 1999 - Mercury Astronauts and a Redstone
Explanation:
Space suited
project Mercury astronauts
John H. Glenn,
Virgil I. Grissom, and
Alan B. Shepard Jr.
(left to right) are posing in front of a
Redstone rocket
in this vintage 1961 NASA publicity photo.
Project Mercury was the
first U.S. program designed to put humans in space.
It resulted in 6 flights
using one-man capsules and
Redstone and
Atlas rockets.
Shortly after the
first U.S. manned flight on May 5, 1961, a suborbital flight piloted
by Alan Shepard, President Kennedy announced
the goal of a manned lunar landing by 1970.
This goal was achieved by NASA's
Apollo program and Shepard himself
walked on the moon
as commander of the Apollo 14 mission.
Alan Shepard
passed away in 1998.
Virgil Grissom died in a tragic fire
during an Apollo launch pad test in 1967.
Senator
John Glenn flew again on the
25th voyage of the Space Shuttle Discovery.
 APOD: September 8, 1999 - A Superior Conjunction Of Mercury
APOD: September 8, 1999 - A Superior Conjunction Of Mercury
Explanation:
In astronomical parlance, an interior planet is at
superior conjunction
when it is located on the opposite side of the Sun from Earth.
Mercury, the solar system's innermost planet,
zips past this point in its orbit today.
In fact, this
recent picture from a solar coronagraph on board the
the space-based SOHO observatory shows
Mercury positioned
very close to the Sun as seen from a near Earth vantage point.
The coronagraph uses an internal occulting disk to block the intense
solar glare which otherwise hides this sight from ground-based observers.
The shadow of the occulting disk is at the center
with the Sun's size and position indicated by the white circle.
Mercury is the bright dot with a horizontal line (a digital artifact),
while faint dots scattered throughout the field
are stars.
Bright regions of the
sun's outer atmosphere are also visible.
As
Mercury continues in its orbit, on
November 15 it will actually appear to
cross the disk
of the Sun as viewed
from Earth.
 APOD: May 6, 1999 - Liberty Bell 7
APOD: May 6, 1999 - Liberty Bell 7
Explanation:
Today, the space capsule Liberty Bell 7 rests about 3 miles
below the surface of the Atlantic Ocean.
But on July 21, 1961, astronaut
Virgil I. "Gus" Grissom rode this
tiny craft 118 miles above the
Earth to become the second
American in space.
Grissom's flight was suborbital -
like fellow
Mercury astronaut Alan Shepard's
first flight -
however his capsule was different, with a window,
a new manual spacecraft control system, and an explosive hatch.
Unfortunately, after Grissom brought
Liberty Bell 7 to a successful
splash down in the planned area, the hatch blew prematurely
and rough seas began to flood the capsule.
While Grissom was able to get out,
the military recovery helicopter
could not lift the waterlogged spacecraft.
This dramatic picture was taken from the helicopter shortly
before Liberty Bell 7 was released and sank.
 APOD: March 25, 1999 - March of the Planets
APOD: March 25, 1999 - March of the Planets
Explanation:
This March stargazers have been treated to
eye-catching formations of
bright planets in western evening skies.
On March 3rd, looking toward a beautiful sunset from a beach on
the Hawaiian isle of Maui, photographer Rick Scott recorded
this fleeting, four-planet "hockey stick"
array.
Mercury, closest to the horizon and immersed in fading sunlight,
is easily visible between silhouetted clouds.
To the left and up in the deepening blue is Jupiter
with a brilliant Venus above
and Saturn shining in the darkened sky near the top of the image.
The planets are seen to lie close to
the ecliptic - the
apparent path of the sun - which is nearly perpendicular to the
horizon for
Hawaiian latitudes at this time of year.
 APOD: January 2, 1999 - Mercury: A Cratered Inferno
APOD: January 2, 1999 - Mercury: A Cratered Inferno
Explanation:
Mercury's surface looks similar to our Moon's. Each is heavily
cratered and made of rock.
Mercury's diameter is about 4800 km, while the
Moon's is slightly less at about 3500 km (compared with about 12,700 km for the
Earth). But
Mercury is unique in many ways.
Mercury is the closest planet to the
Sun, orbiting at about 1/3 the radius of the
Earth's orbit. As
Mercury slowly rotates, its surface temperature varies from an unbearably cold -180 degrees
Celsius to an unbearably hot 400 degrees
Celsius. The place nearest the
Sun in
Mercury's orbit changes slightly each orbit - a fact used by
Albert Einstein to help verify the correctness of his then newly discovered theory of gravity:
General Relativity.
The above picture was taken by the only spacecraft ever to pass
Mercury:
Mariner 10 in 1974.
 APOD: October 29, 1998 - John Glenn: Friendship 7 To Discovery
APOD: October 29, 1998 - John Glenn: Friendship 7 To Discovery
Explanation:
Rehearsing for his
historic flight on February 20, 1962,
Mercury program astronaut
John H. Glenn Jr. works
in a cramped training capsule preparing
for a few hours'
voyage through space.
Dubbed
Friendship 7, his own snug spacecraft was launched by an Atlas
rocket and carried Glenn
three times around planet Earth
at an altitude of about 120 miles,
returning him safely to a "splashdown" in the Atlantic Ocean.
The first American in orbit,
Senator Glenn's remarkable return to space will be 36 years later
as a payload specialist on the Space Shuttle
Discovery mission STS-95.
Discovery is a roomier craft which will carry a crew of 7
and an array of scientific payloads, such as the
International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker.
Scheduled for
launch today at 2:00 PM Eastern Time,
Discovery will orbit at an altitude of 320 miles and land
after 8 days at Kennedy Space Center's shuttle landing facility.
Godspeed the
crew of STS-95 !
 APOD: October 1, 1998 - Happy 40th Birthday NASA
APOD: October 1, 1998 - Happy 40th Birthday NASA
Explanation:
Happy Birthday, NASA!
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration
officially began operations on October 1, 1958,
absorbing its forerunner organization the
National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, NACA.
Its landmark achievements in
human spaceflight include the
Mercury and Gemini Projects culminating in the Apollo Project
moon landings in the 1960s and early 1970s,
Apollo-Soyuz and Skylab in the 1970s,
and the Space Shuttle program of the 1980s and 1990s.
(Pictured is
the June 1998
launch of the Space Shuttle Discovery.)
NASA's science programs have produced the robotic exploration of
our Solar System,
views of the Universe across the electromagnetic
spectrum, and
valuable meteorological
and remote-sensing Earth observations.
At birth, NASA's priorities were largely driven by
the pressures and competitions of the Cold War.
But looking back over 40 years, the sum of its accomplishments have
produced needed new technologies and a vital new perspective on
Planet Earth and the Cosmos.
 APOD: September 6, 1998 - Mariner's Mercury
APOD: September 6, 1998 - Mariner's Mercury
Explanation:
Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun,
remains the most mysterious of the Solar System's inner planets.
Hiding in the
Sun's glare it is
a difficult target for Earth bound observers.
The only spacecraft to explore
Mercury close-up was
Mariner 10 which
executed 3 flybys of Mercury in 1974 and 1975,
surveying approximately 45 percent of its surface.
Mariner 10 deftly manuevered to photograph part of the sunlit
hemisphere during each approach, passed behind the planet,
and continued to image the sun-facing side as the spacecraft receded.
Its highest resolution
photographs recorded features
approximately a mile across.
A recent reprocessing
of the Mariner 10 data has resulted in this dramatic mosaic.
Like the
Earth's Moon,
Mercury's surface shows
the scars of impact cratering -
the smooth vertical band and patches visible above represent
regions where no image information is available.
 APOD: July 24, 1998 - Alan B. Shepard Jr. 1923 1998
APOD: July 24, 1998 - Alan B. Shepard Jr. 1923 1998
Explanation:
On another Friday (May 5, 1961),
at the dawn of the space age,
NASA controllers "lit the candle" and sent
Alan B. Shepard Jr. arcing into space atop
a Redstone rocket.
The picture shows the pressure-suited Shepard before the launch
in his
cramped space capsule dubbed
"Freedom 7" .
This
historic flight - the first spaceflight by an American -
made Shepard
a national hero.
Born in East Derry, New Hampshire on November 18, 1923,
Shepard graduated from the United States Naval Academy
in 1944 and went on to train and serve as a Naval Aviator.
Chosen as one of the original seven
Mercury Program astronauts,
he considered
this first flight the greatest
challenge and actively sought the assignment.
Shepard's accomplishments in his career as an astronaut
spanned a remarkable
period in human achievement and in 1972
he walked on the moon as commander of the Apollo 14 mission.
A true pioneer and intrepid explorer,
Alan Shepard died Tuesday at age 74
after a lengthy illness.
 APOD: July 2, 1998 - X-ray Transit of Mercury
APOD: July 2, 1998 - X-ray Transit of Mercury
Explanation:
This sequence of
false color X-ray images captures a rare event -
the passage or
transit of planet Mercury in front of the Sun.
Mercury's small disk is
silhouetted against the bright background of X-rays from the hot
Solar Corona.
It appears just to the right of center in the
top frame and moves farther right as the sequence progresses toward
the bottom.
The dark notch is
a coronal hole near
the Solar South Pole, while
a flaring coronal bright point can be seen to the left of the notch
in the top frames.
The frames were recorded on November 6, 1993 by the
Soft X-ray Telescope
on board
the orbiting Yohkoh satellite.
Transits of Mercury (and Venus) were historically used to discover
the geometry of the solar system and to
map planet Earth itself.
 APOD: May 12, 1998 - Callisto Enhanced
APOD: May 12, 1998 - Callisto Enhanced
Explanation:
Callisto
is half rock and half ice. This moon of
Jupiter is approximately the size of the planet Mercury, making it the third largest moon in the
Solar System, after
Ganymede and Titan.
Callisto's icy surface is
billions of years old, lacks any sign of
volcanic activity,
and is densely covered with rifts and craters.
These features are particularly apparent in this contrast-enhanced image
taken by the
Galileo spacecraft, and released last week.
Visible near the image center is Valhalla, one of the largest impact craters in the
Solar System, measuring about 4,000 kilometers across.
The rings and size of Valhalla make its appearance similar to the
Caloris Impact Basin on Mercury.
 APOD: April 4, 1998 - Mercury Astronauts and a Redstone
APOD: April 4, 1998 - Mercury Astronauts and a Redstone
Explanation:
Space suited
project Mercury astronauts
John H. Glenn,
Virgil I. Grissom, and
Alan B. Shepard Jr.
(left to right) are posing in front of a
Redstone rocket
in this vintage 1961 NASA publicity photo.
Project Mercury was the
first U.S. program designed to put humans in space.
It resulted in 6 flights
using one-man capsules and
Redstone and
Atlas rockets.
Shortly after the
first U.S. manned flight on May 5, 1961, a suborbital flight piloted
by Alan Shepard, President Kennedy announced
the goal of a manned lunar landing by 1970.
This goal was achieved by NASA's
Apollo program and Shepard himself
walked on the moon
as commander of the Apollo 14 mission.
Virgil Grissom died in a tragic fire
during an Apollo launch pad test in 1967.
Senator John Glenn will fly again on the 25th voyage of the
Space Shuttle Discovery.
 APOD: December 4, 1997 - A Sky Full Of Planets
APOD: December 4, 1997 - A Sky Full Of Planets
Explanation:
Look up tonight.
Just after sunset, the crescent moon and
all five "naked-eye" planets
(Mercury,
Venus,
Mars,
Jupiter,
and Saturn)
will be visible (depending on your latitude), lying near
our solar system's ecliptic plane.
Venus and Jupiter will shine brilliantly as the brightest "stars"
in the sky, but Mercury will be near the horizon and hard to see.
A pair of binoculars will also reveal Uranus and Neptune and
observers with a telescope and a good site may even be able
to glimpse faint Pluto just above the
Western horizon in the fading twilight (not shown on the chart above).
Enjoy this lovely spectacle
any clear night through about December 8.
A similar gathering is expected in May 2000
but the planets will be hidden from view by the solar glare.
A night sky as full of planets as this one will occur
again though ... in about 100 years.
 APOD: November 30, 1997 - Mercury: A Cratered Inferno
APOD: November 30, 1997 - Mercury: A Cratered Inferno
Explanation:
Mercury's surface looks similar to our Moon's. Each is heavily
cratered and made of rock.
Mercury's diameter is about 4800 km, while the
Moon's is slightly less at about 3500 km (compared with about 12,700 km for the
Earth). But
Mercury is unique in many ways.
Mercury is the closest planet to the
Sun, orbiting at about 1/3 the radius of the
Earth's orbit. As
Mercury slowly rotates, its surface temperature varies from an unbearably cold -180 degrees
Celsius to an unbearably hot 400 degrees
Celsius. The place nearest the
Sun in
Mercury's orbit changes slightly each orbit - a fact used by
Albert Einstein to help verify the correctness of his then newly discovered theory of gravity:
General Relativity.
The above picture was taken by the only spacecraft ever to pass
Mercury:
Mariner 10 in 1974.
 APOD: April 6, 1997 - Mercury Astronauts and a Redstone
APOD: April 6, 1997 - Mercury Astronauts and a Redstone
Explanation:
Space suited
project Mercury astronauts
John H. Glenn,
Virgil I. Grissom, and
Alan B. Shepard Jr.
(left to right) are pictured here posing in front of a
Redstone rocket
in this vintage 1961 NASA publicity photo.
Project Mercury was the
first U.S. program designed to put humans in space.
It resulted in 6 flights
using one-man capsules and
Redstone and
Atlas rockets.
Shortly after the
first U.S. manned flight on May 5, 1961, a suborbital flight piloted
by Alan Shepard, President Kennedy announced
the goal of a manned lunar landing by 1970. This goal was achieved by NASA's
Apollo program
and Shepard himself walked on the moon
as commander of the Apollo 14 mission.
 APOD: January 12, 1997 - Mercury in Stereo: Craters Within Craters
APOD: January 12, 1997 - Mercury in Stereo: Craters Within Craters
Explanation:
This Stereo image pair of craters on
on Mercury was
produced using data from NASA's robot explorer
Mariner 10 which performed three close flybys of
the Sun's closest companion,
two in 1974 and one in 1975.
However, the spacecraft was not equipped with a Stereo camera!
Instead,
the Stereo pair was created using two images of the same region each
recorded from a slightly different angle.
The image on the left was actually taken during the first flyby,
the one on the right during the second.
A crater within a crater is visible at the upper left, the outer one
is about 70 miles in diameter.
The embedded craters themselves are within the
230 mile wide Dostoevsky crater - a segment of Dostoevsky's
rim runs through the lower half of the image.
To get the 3D Stereo effect, your left eye should see only the left image
and your right eye only the right one.
(Try placing one edge of a piece of paper on the screen between the
pictures and touching your nose to the other edge while viewing.)
 APOD: December 17, 1996 - Mariner's Mercury
APOD: December 17, 1996 - Mariner's Mercury
Explanation:
Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun,
remains the most mysterious of the Solar System's inner planets.
Hiding in the Sun's glare it is
a difficult target for Earth bound observers.
The only spacecraft to explore Mercury close-up was Mariner 10 which
executed 3 flybys of Mercury in 1974 and 1975,
surveying approximately 45 percent of its surface.
Mariner 10 deftly manuevered to photograph part of the sunlit
hemisphere during each approach, passed behind the planet,
and continued to image the sun-facing side as the spacecraft receded.
Its highest resolution
photographs recorded features
approximately a mile across.
A recent reprocessing
of the Mariner 10 data has resulted in this dramatic mosaic. Like
the Earth's Moon, Mercury's surface shows
the scars of impact cratering -
the smooth vertical band and patches visible above represent
regions where no image information is available.
 APOD: December 8, 1996 - Degas Ray Crater on Mercury
APOD: December 8, 1996 - Degas Ray Crater on Mercury
Explanation:
Like the Earth's Moon,
Mercury is scarred with craters,
testifying to an intense bombardment during the early history of
the Solar System.
In 1974,
the Mariner 10 spacecraft
surveyed this innermost planet up close,
producing the only detailed images of its tortured surface.
In the above mosaic the bright rays
emanating from the 27 mile wide
Degas crater almost appear to be painted on.
The rays consist of light colored material blasted out during the
crater's formation. Numerous smaller, younger craters are seen
superposed on the Degas crater itself.
 APOD: September 23, 1996 - Venus: Earth's Cloudy Twin
APOD: September 23, 1996 - Venus: Earth's Cloudy Twin
Explanation: If Venus weren't so cloudy it would be more
similar to Earth. This picture by the Galileo spacecraft
shows just how cloudy Venus
is. Venus
is very similar to Earth in size
and mass - and so is sometimes referred to as Earth's sister planet
- but Venus
has a quite different climate. Venus'
thick clouds and closeness to the Sun
(only Mercury is closer) make it
the hottest planet - much hotter than the Earth. Humans could
not survive there, and no life of any sort has ever been found.
When Venus is visible
it is usually the brightest object in the sky after the Sun and
the Moon. More than 20 spacecraft
have visited Venus
including Venera 9,
which landed on the surface, and Magellan,
which used radar to peer through the clouds and make a map of
the surface. This visible light picture of Venus
was taken by the Galileo spacecraft now
in orbit around Jupiter. Many things about Venus remain unknown,
including the cause of mysterious bursts of radio waves.
 APOD: September 13, 1996 - Southwest Mercury
APOD: September 13, 1996 - Southwest Mercury
Explanation:
The planet Mercury resembles a moon.
Mercury's
old surface is heavily
cratered like many moons.
Mercury is larger than most moons but smaller than
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede and
Saturn's moon
Titan. Mercury is much denser and more massive than any moon, though, because it is made mostly of iron. In fact, the
Earth is the only planet more dense. A visitor to
Mercury's surface would see some strange sights. Because
Mercuryrotates exactly three times every two orbits around the
Sun, and because
Mercury's orbit is so elliptical, a visitor to
Mercury might see the
Sun rise, stop in the sky, go back toward the rising
horizon, stop again, and then set quickly over the other horizon. From
Earth, Mercury's proximity to the
Sun cause it to be
visible only for a short time just after sunset or just before sunrise.
 APOD: September 12, 1996 - Mercury: A Cratered Inferno
APOD: September 12, 1996 - Mercury: A Cratered Inferno
Explanation:
Mercury's surface looks similar to our Moon's. Each is heavily
cratered and made of rock.
Mercury's diameter is about 4800 km, while the
Moon's is slightly less at about 3500 km (compared with about 12,700 km for the
Earth). But
Mercury is unique in many ways.
Mercury is the closest planet to the
Sun, orbiting at about 1/3 the radius of the
Earth's orbit. As
Mercury slowly rotates, its surface temperature varies from an unbearably cold -180 degrees
Celsius to an unbearably hot 400 degrees
Celsius. The place nearest the
Sun in
Mercury's orbit changes slightly each orbit - a fact used by
Albert Einstein to help verify the correctness of his then newly discovered theory of gravity:
General Relativity.
The above picture was taken by the only spacecraft ever to pass
Mercury:
Mariner 10 in 1974.
 APOD: May 1, 1996 - Comet Hyakutake and a Cactus
APOD: May 1, 1996 - Comet Hyakutake and a Cactus
Explanation:
Comet Hyakutake is shown photographed the night of March 27 in Arizona,
USA, with a cactus in the foreground.
Polaris, the north star, is the
bright star seen just to the upper right of the comet's head. Today Comet
Hyakutake reaches its closest approach to the
Sun. Comet Hyakutake is now
at its intrinsic brightest, but because of its distance from the
Earth, it
will appear less bright to us than it did during its closest approach to
the Earth in late March. In fact, due to the comet's angular proximity to
the Sun, it will difficult to see at all from the Earth! Comet Hyakutake
will reach less than one quarter of the Earth-Sun distance - inside the
orbit of Mercury.
Comet Hyakutake will
not venture near the Sun again for
another about 15,000 years.
 APOD: January 21, 1996 - Mercury's Faults
APOD: January 21, 1996 - Mercury's Faults
Explanation:
The
surface of the planet
Mercury is not without fault. In this case,
however, "fault" refers to unusual surface features that are the topic of
much speculation. The above fault line is called Santa Maria Rupes, and
runs through many prominent craters. The meandering feature is thought to
be the result of huge forces of compression on
Mercury's surface. Such rupes probably originate from
large impacts
and a general shrinking of
Mercury's crust,
which in turn causes parts of the crust to push above other parts.
 APOD: January 20, 1996 - Mercury's Caloris Basin
APOD: January 20, 1996 - Mercury's Caloris Basin
Explanation:
Mercury, the closest planet to the
Sun, has a surface with so many craters
it resembles the
Earth's
Moon. The largest surface feature on
Mercury is the Caloris Basin, which resulted from a collision with an
asteroid.
The basin, which is more that 1000 kilometers across, is visible
as the large circular feature at the bottom of the above photograph.
Similar features, such as the Mare Orientale,
are seen on the Moon.
The Caloris Basin gets very hot because it is near the "sub-solar point" - the
point on
Mercury's surface
that is directly under the
Sun when
Mercury
is closest to the Sun.
 APOD: January 7, 1996 - Mercury Astronauts and a Redstone
APOD: January 7, 1996 - Mercury Astronauts and a Redstone
Explanation: Space suited
project Mercury astronauts
John H. Glenn,
Virgil I. Grissom, and
Alan B. Shepard Jr.
(left to right) are pictured here posing in front of a
Redstone rocket
in this 1961 NASA publicity photo.
Project Mercury was the
first U.S. program designed to put humans in space.
It resulted in 6 manned flights
using one-man capsules and
Redstone and
Atlas rockets.
Shortly after the
first U.S. manned flight on May 5, 1961, a suborbital flight piloted
by Alan Shepard, President Kennedy announced
the goal of a manned lunar landing by 1970. This goal was achieved by NASA's
Apollo program
and Shepard himself walked on the moon
as a member of the Apollo 14 mission.
 APOD: August 14, 1995 - Mercury: Closest Planet to the Sun
APOD: August 14, 1995 - Mercury: Closest Planet to the Sun
Explanation:
This picture was compiled from images
taken by the NASA spacecraft Mariner 10 which flew by the
planet three times in 1974.
Mercury is the closest planet to the
Sun, the
second hottest planet (Venus
gets hotter), and the second smallest planet (Pluto is smaller).
Mercury rotates so slowly that one day there - "day" meaning the
normal time it takes from sunset to sunset - lasts 176 days on
Earth. It is
difficult to see
Mercury not because it is dim but because it always
appears near the Sun, and is therefore only visible for a short time just
after sunset or just before sunrise. Mercury is made of rocky material
like Earth. No one knows why Mercury has the magnetic field that it does.