 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 APOD: 2023 March 12 – Saturn's Hyperion: A Moon with Odd Craters
APOD: 2023 March 12 – Saturn's Hyperion: A Moon with Odd Craters
Explanation:
What lies at the bottom of
Hyperion's strange craters?
To help find out, the
robot Cassini spacecraft that once orbited
Saturn
swooped past the
sponge-textured moon and
took images of unprecedented detail.
A six-image mosaic from the 2005 pass,
featured here in scientifically assigned colors,
shows a remarkable world strewn with
strange craters and an
odd, sponge-like surface.
At the bottom of most craters lies some type of
unknown dark reddish material.
This material appears similar to that covering part of another of Saturn's moons,
Iapetus, and might sink into the
ice moon as it better
absorbs warming sunlight.
Hyperion
is about 250 kilometers across,
rotates chaotically,
and has a density so low that it
likely houses a vast system of
caverns inside.
 APOD: 2023 February 26 – Saturns Iapetus: Moon with a Strange Surface
APOD: 2023 February 26 – Saturns Iapetus: Moon with a Strange Surface
Explanation:
What would make a moon look like a walnut?
A strange ridge that circles
Saturn's moon
Iapetus's equator, visible near the bottom of the
featured image,
makes it appear similar to a popular
edible nut.
The origin of
the ridge remains unknown, though, with hypotheses including ice that welled up from below, a ring that crashed down from above,
and structure left over from its formation perhaps 100 million years ago.
Also strange is that about half of
Iapetus is so dark that it can
nearly disappear when viewed from Earth, while
the rest is, reflectively, quite bright.
Observations
show that the degree of darkness of the terrain is strangely uniform,
as if a dark coating was somehow recently applied to an ancient and highly cratered surface.
Last, several large impact basins occur around
Iapetus, with a 400-kilometer wide crater visible near the image center, surrounded by
deep cliffs that drop sharply to the crater floor.
The featured image was taken by the Saturn-orbiting
Cassini spacecraft during a
flyby of Iapetus at the end of 2004.
 APOD: 2021 July 13 - Saturn's Iapetus: Painted Moon in 3D
APOD: 2021 July 13 - Saturn's Iapetus: Painted Moon in 3D
Explanation:
What has happened to Saturn's moon Iapetus?
Vast sections of
this strange world are dark brown,
while others are as bright white.
The composition of the dark material is unknown, but
infrared spectra indicate that it possibly contains some dark form of
carbon.
Iapetus also has an unusual
equatorial ridge
that makes it appear like a walnut.
To help better understand this seemingly painted moon,
NASA directed the
robotic Cassini spacecraft orbiting Saturn to swoop
within 2,000 kilometers in 2007.
Iapetus is
pictured here in 3D.
A huge impact crater seen in the south spans a tremendous 450 kilometers
and appears superposed on an
older crater of similar size.
The dark material
is seen increasingly coating the easternmost part of
Iapetus, darkening craters and highlands alike.
Close inspection indicates that the dark coating typically faces the moon's equator and is less than a meter thick.
A leading hypothesis is that the dark material is mostly
dirt leftover when relatively warm but dirty ice
sublimates.
An initial coating of
dark material may have been effectively painted
on by the accretion of meteor-liberated debris from
other moons.
 APOD: 2021 July 6 - Saturn and Six Moons
APOD: 2021 July 6 - Saturn and Six Moons
Explanation:
How many moons does Saturn have?
So far 82 have been confirmed, the smallest being only a fraction
of a kilometer across.
Six of its largest satellites can be seen here
in a
composite image
with 13 short exposure of the bright planet, and
13 long exposures of the brightest of its faint moons,
taken over
two weeks last month.
Larger than Earth's Moon and even slightly larger than
Mercury,Saturn's largest moon
Titan has a diameter of 5,150 kilometers and was captured making
nearly a complete orbit around its
ringed parent planet.
Saturn's first known natural satellite, Titan was
discovered in 1655 by
Dutch astronomer
Christiaan Huygens, in contrast with several
newly discovered moons announced in 2019.
The trail on the far right belongs to
Iapetus, Saturn's third largest moon.
The radius of
painted Iapetus' orbit is so large
that only a portion of it was captured here.
Saturn leads Jupiter across the night sky
this month, rising soon after sunset toward the southeast,
and remaining visible until
dawn.
 APOD: 2018 June 3 - Saturn's Iapetus: Painted Moon
APOD: 2018 June 3 - Saturn's Iapetus: Painted Moon
Explanation:
What has happened to Saturn's moon Iapetus?
Vast sections of
this strange world are dark as
coal,
while others are as bright as ice.
The composition of the dark material is unknown, but
infrared spectra indicate that it possibly contains some dark form of
carbon.
Iapetus also has an unusual
equatorial ridge
that makes it appear like a walnut.
To help better understand this seemingly painted moon,
NASA directed the
robotic Cassini spacecraft orbiting Saturn to swoop
within 2,000 kilometers in 2007.
Pictured here,
from about 75,000 kilometers out, Cassini's trajectory allowed unprecedented imaging of the hemisphere of Iapetus that is
always trailing.
A huge impact crater seen in the south spans a tremendous 450 kilometers
and appears superposed on an
older crater of similar size.
The dark material
is seen increasingly coating the easternmost part of
Iapetus, darkening craters and highlands alike.
Close inspection indicates that the dark coating typically faces the moon's equator and is less than a meter thick.
A leading hypothesis is that the dark material is mostly
dirt leftover when relatively warm but dirty ice
sublimates.
An initial coating of
dark material may have been effectively painted on by the accretion of meteor-liberated debris from
other moons.
 APOD: 2018 May 14 - Saturn's Hyperion in Natural Color
APOD: 2018 May 14 - Saturn's Hyperion in Natural Color
Explanation:
What lies at the bottom of
Hyperion's strange craters?
To help find out, the
robot Cassini spacecraft that once orbited
Saturn
swooped past the
sponge-textured moon in 2005 and
2010 and took images of unprecedented detail.
A six-image mosaic from the 2005 pass,
featured here in natural color, shows a remarkable world strewn with
strange craters and an
odd sponge-like surface.
At the bottom of most craters lies some type of
unknown dark reddish material.
This material appears similar to that covering part of another of Saturn's moons,
Iapetus, and might sink into the
ice moon as it better
absorbs warming sunlight.
Hyperion
is about 250 kilometers across,
rotates chaotically,
and has a density so low that it
likely houses
a vast system of
caverns inside.
 APOD: 2017 June 18 - Views from Cassini at Saturn
APOD: 2017 June 18 - Views from Cassini at Saturn
Explanation:
What has the Cassini orbiter seen at Saturn?
The featured music video
shows some of the early highlights.
In the first time-lapse sequence (00:07), a vertical line appears that is really Saturn's
thin rings seen nearly edge-on.
Soon some of
Saturn's
moon shoot past.
The next sequence (00:11) features Saturn's unusually
wavy F-ring that is constrained by the two
shepherd moons that are also continually perturbing it.
Soon much of Saturn's
extensive ring system flashes by, sometimes juxtaposed to the grandeur of the immense planet itself.
Cloud patterns on
Titan (00:39) and
Saturn (00:41) are highlighted.
Clips from flybys of several of Saturn's moon are then shown, including
Phoebe,
Mimas,
Epimetheus, and
Iapetus.
In other sequences, moons of Saturn
appear to pass each other as they orbit Saturn.
Background star fields seen by Cassini are sometimes intruded upon by bright passing moons.
The robotic Cassini spacecraft has been revolutionizing humanity's knowledge of Saturn and its moons since
2004.
In September,
Cassini's mission will be brought to a
dramatic conclusion as the spacecraft will be
directed to dive into ringed giant.
 APOD: 2012 January 13 - Saturns Iapetus: Painted Moon
APOD: 2012 January 13 - Saturns Iapetus: Painted Moon
Explanation:
What has happened to Saturn's moon Iapetus?
Vast sections of
this strange world are dark as
coal,
while others are as bright as ice.
The composition of the dark material is unknown, but
infrared spectra indicate that it possibly contains some dark form of
carbon.
Iapetus also has an unusual
equatorial ridge
that makes it appear like a walnut.
To help better understand this seemingly painted moon,
NASA
directed the
robotic Cassini spacecraft orbiting Saturn to swoop
within 2,000 kilometers in 2007.
Pictured above,
from about 75,000 kilometers out, Cassini's trajectory allowed unprecedented imaging of the hemisphere of Iapetus that is
always trailing.
A huge impact crater seen in the south spans a tremendous 450 kilometers
and appears superposed on an
older crater of similar size.
The dark material
is seen increasingly coating the easternmost part of
Iapetus, darkening craters and highlands alike.
Close inspection indicates that the dark coating typically faces the moon's equator and is less than a meter thick.
A leading hypothesis is that the dark material is mostly
dirt leftover when relatively warm but dirty ice
sublimates.
An initial coating of
dark material may have been effectively painted on by the accretion of meteor-liberated debris from other moons.
This and other images from Cassini's
Iapetus flyby are being studied for even greater clues.
 APOD: 2011 June 13 - Views from Cassini at Saturn
APOD: 2011 June 13 - Views from Cassini at Saturn
Explanation:
What has the Cassini orbiter seen since arriving at Saturn?
The above music video
shows some of the highlights.
In the first time-lapse sequence (00:07), a vertical line appears that is really Saturn's
thin rings seen nearly edge-on.
Soon some of
Saturn's
moon shoot past.
The next sequence (00:11) features Saturn's unusually
wavy F-ring that is constrained by the two
shepherd moons that are also continually perturbing it.
Soon much of Saturn's
extensive ring system flashes by, sometimes juxtaposed to the grandeur of the immense planet itself.
Cloud patterns on
Titan (00:39) and
Saturn (00:41) are highlighted.
Clips from flyby's of several of Saturn's moon are then shown, including
Phoebe,
Mimas,
Epimetheus, and
Iapetus.
In other sequences, moons of Saturn
appear to pass each other as they orbit Saturn.
Background star fields seen by Cassini are sometimes intruded upon by bright passing moons.
The robotic Cassini spacecraft has been revolutionizing humanity's knowledge of Saturn and its moons since
2004.
 APOD: 2009 October 13 - Giant Dust Ring Discovered Around Saturn
APOD: 2009 October 13 - Giant Dust Ring Discovered Around Saturn
Explanation:
What has created a large dust ring around Saturn?
At over 200 times the radius of
Saturn
and over 50 times the radius of Saturn's expansive
E ring, the
newly discovered dust ring is the largest planetary ring yet imaged.
The ring was found in infrared light by the Earth-trailing
Spitzer Space Telescope.
A leading hypothesis for its origin is impact material ejected from Saturn's moon
Phoebe, which orbits right through the dust ring's middle.
An additional possibility is that the
dust ring supplies the
mysterious material that coats part of Saturn's moon
Iapetus, which orbits near the
dust ring's inner edge.
Pictured above in the inset, part of the dust ring
appears as false-color orange in front of numerous background stars.
 APOD: 2009 August 9 - Saturn's Iapetus: Painted Moon
APOD: 2009 August 9 - Saturn's Iapetus: Painted Moon
Explanation:
What has happened to Saturn's moon Iapetus?
Vast sections of
this strange world
are dark as
coal, while others are as bright as ice.
The composition of the dark material is unknown, but
infrared
spectra indicate that it possibly contains some dark form of
carbon.
Iapetus also has an unusual
equatorial ridge that makes it appear like a
walnut.
To help better understand this seemingly painted moon,
NASA
directed the
robotic Cassini spacecraft
orbiting Saturn to swoop
within 2,000 kilometers in 2007.
Pictured above,
from about 75,000 kilometers out, Cassini's trajectory allowed unprecedented imaging of the hemisphere of Iapetus that is
always trailing.
A huge impact crater seen in the south spans a tremendous 450 kilometers
and appears superposed on an
older crater of similar size.
The dark material
is seen increasingly coating the easternmost part of
Iapetus, darkening craters and highlands alike.
Close inspection indicates that the dark coating typically faces the moon's equator and is less than a meter thick.
A leading hypothesis is that the dark material is mostly
dirt leftover when relatively warm but dirty ice
sublimates.
An initial coating of
dark material may have been effectively painted on by the accretion of meteor-liberated debris from other moons.
This and other images from Cassini's
Iapetus flyby are being studied for even greater clues.
 APOD: 2007 October 10 - The Strange Trailing Side of Saturn's Iapetus
APOD: 2007 October 10 - The Strange Trailing Side of Saturn's Iapetus
Explanation:
What has happened to Saturn's moon Iapetus?
Vast sections of
this strange world
are dark as
coal, while others are as bright as ice.
The composition of the dark material is unknown, but
infrared
spectra indicate that it possibly contains some dark form of
carbon.
Iapetus also has an unusual
equatorial ridge that makes it appear like a
walnut.
To help better understand this mysterious moon,
NASA
directed the
robotic Cassini spacecraft
orbiting Saturn to swoop
within 2,000 kilometers just last month.
Pictured above,
from about 75,000 kilometers out, Cassini's trajectory allowed unprecedented imaging of the hemisphere of Iapetus that is
always trailing.
A huge impact crater seen in the south spans a tremendous 450 kilometers
and appears superposed on an
older crater of similar size.
The dark material
is seen increasingly coating the easternmost part of
Iapetus, darkening craters and highlands alike.
Close inspection indicates that the dark coating typically faces the moon's equator.
Whether Iapetus' colors are the result of
unusual episodes of internal
volcanism or
external splattering remains unknown.
This and other images from Cassini's
Iapetus flyby are being studied for even greater clues.
 APOD: 2007 September 19 - 4000 Kilometers Above Saturns Iapetus
APOD: 2007 September 19 - 4000 Kilometers Above Saturns Iapetus
Explanation:
What does the surface of Saturn's mysterious moon Iapetus look like?
To help find out, the robotic
Cassini spacecraft
now orbiting
Saturn was sent soaring last week just 2,000 kilometers from the unique equatorial ridge of the unusual
walnut-shaped
two-toned moon.
The
above image
from Cassini is from about 4,000 kilometers out and
allows objects under 100-meters across to be resolved.
Cassini found an
ancient and battered landscape of craters,
sloping hills, and mountains as high as 10 kilometers and so
rival the 8.8-kilometer height of
Mt. Everest on Earth.
Just above the center of
this image is a small bright patch where an impacting rock might have uncovered deep clean water ice.
Space scientists will be studying
flyby images like this for clues to the origin of
Iapetus' unusual shape and
coloring with particular emphasis because
no more close flybys
of the enigmatic world are planned.
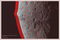 APOD: 2007 September 15 - Iapetus: 3D Equatorial Ridge
APOD: 2007 September 15 - Iapetus: 3D Equatorial Ridge
Explanation:
This bizarre, equatorial ridge
extending across and beyond
the dark, leading hemisphere
of Iapetus gives the
two-toned
Saturnian moon
a distinct walnut shape.
With red/blue glasses you can check out a
remarkable stereo composition of this extraordinary feature -- based on
close-up images from this week's Cassini
spacecraft flyby.
In fact, the ridge's combination of equatorial symmetry and scale,
about 20 kilometers wide and reaching up to 20 kilometers above
the surface, is not known to
be duplicated anywhere else in our solar system.
The unique feature was
discovered in Cassini images
from 2004.
It appears to be heavily cratered and therefore ancient,
but the origin of the
equatorial ridge on
Iapetus
remains a mystery.
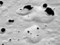 APOD: 2007 September 14 - Iapetus in Black and White
APOD: 2007 September 14 - Iapetus in Black and White
Explanation:
Iapetus, Saturn's
third largest moon, is a candidate for
the strangest moon of Saturn.
Tidally locked
in its orbit around the ringed gas giant,
Iapetus is sometimes called
the yin-yang moon
because
its leading hemisphere is very dark,
reflecting about 5 percent of the Sun's light,
while its trailing hemisphere is almost as bright as snow.
This recent Cassini spacecraft
flyby
image is one of the closest
views ever.
It spans about 35 kilometers across a cratered
transition
zone between bright and dark terrain.
Iapetus itself has a density close to that of water ice, but
the detailed reflective properties of the
dark material suggest an organic composition.
Honoring the moon's discoverer, the dark terrain is called
Cassini Regio.
 APOD: 2006 January 3 - Dark Terrain on Saturn s Iapetus
APOD: 2006 January 3 - Dark Terrain on Saturn s Iapetus
Explanation:
Why are vast sections of Iapetus as dark as
coal?
No one knows for sure.
Iapetus, the
third largest moon of
Saturn,
was inspected again as the Saturn-orbiting robot
Cassini spacecraft swooped past the
enigmatic world again late last year.
The dark material covers most of the surface visible in the
above image,
while the small portion near the top that appears almost white is of a
color and reflectance more typical of Saturn's other moons.
The unknown material covers about half of the 1,500 kilometer
wide moon.
The material is
so dark
that it reflects less than five percent of incident sunlight,
yet overlays craters indicating that it was spread after the
craters were formed.
Iapetus
has other unexplained features.
The bright part of
Iapetus
is covered with unexplained long thin streaks.
The orbit of
Iapetus is also unusual, being tilted to the plane of Saturn's
orbit by an unusually high fifteen degrees.
A strange ridge
about 13 kilometers high crosses much of Iapetus near the
equator and is visible
near
the bottom.
Oddly, this ridge is almost exactly parallel with Iapetus' equator.
The exact shape of Iapetus remains undetermined,
but images indicate that it is quite strange --
something like a
walnut.
Research into the formation and history of
mysterious Iapetus
is active and ongoing.
 APOD: 2005 February 1 - Saturn's Iapetus: Moon with a Strange Surface
APOD: 2005 February 1 - Saturn's Iapetus: Moon with a Strange Surface
Explanation:
What has happened to Saturn's moon Iapetus?
A strange ridge crosses the moon near the equator,
visible near the bottom of the above image, making
Iapetus
appear similar to the
pit of a peach.
Half of Iapetus
is so dark that it can nearly disappear when viewed from Earth.
Recent observations show that the degree of
darkness of the terrain is strangely uniform,
like a dark coating was somehow recently applied
to an ancient and highly cratered surface.
The other half of Iapetus is relatively bright but oddly covered with long and
thin streaks of dark.
A 400-kilometer wide impact basin is visible near the image center,
delineated by deep scarps
that drop sharply to the crater floor.
The above image was taken by the Saturn-orbiting
Cassini spacecraft during a
flyby of Iapetus at the end of last year.
 APOD: October 15, 1995 - Iapetus: Saturn's Disappearing Moon
APOD: October 15, 1995 - Iapetus: Saturn's Disappearing Moon
Explanation:
Iapetus has an unusual surface, one half of which is very dark, the other
half very light. This caused it's discoverer
Cassini to remark that
Iapetus could only be seen when on one side of Saturn but not the other.
The reason for the difference between hemispheres is presently unknown.
Iapetus is the third largest of
Saturn's moon behind
Titan and
Rhea. Iapetus
is composed predominantly of water ice.