 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 APOD: 2025 December 14 – Juno Flyby of Ganymede and Jupiter
APOD: 2025 December 14 – Juno Flyby of Ganymede and Jupiter
Explanation:
What would it be like to fly over the
largest moon in the
Solar System?
In 2021, the robotic
Juno spacecraft
flew past
Jupiter's
huge moon
Ganymede and took images that have been digitally
constructed into a detailed flyby.
As the featured video begins,
Juno swoops over the two-toned surface of the 5,000-km wide moon, revealing an icy alien landscape filled with grooves and craters.
The grooves are likely caused by shifting surface plates, while the craters are caused by
violent impacts.
Continuing on in its orbit, Juno then performed its 34th
close pass over Jupiter's clouds.
The digitally-constructed video shows numerous
swirling clouds in the north,
colorful planet-circling zones and bands across the middle -- featuring several
white-oval clouds from the
String of Pearls, and finally more
swirling clouds in the south.
 APOD: 2025 November 11 – Jupiter in Ultraviolet from Hubble
APOD: 2025 November 11 – Jupiter in Ultraviolet from Hubble
Explanation:
Jupiter looks a bit different in ultraviolet light.
To better interpret
Jupiter's cloud motions and to help NASA's robotic
Juno spacecraft understand the
planetary context of the small fields that it sees, the
Hubble Space Telescope was being directed to
regularly image the entire Jovian giant.
The colors of Jupiter
being monitored go beyond the normal human visual range to include both
ultraviolet and
(not pictured) infrared light.
Featured from 2017, Jupiter appears different
in near ultraviolet light, partly because the amount of sunlight
reflected back is distinct, giving differing cloud heights and latitudes
discrepant brightnesses.
In the
near UV, Jupiter's poles appear relatively dark, as does its
Great Red Spot and a smaller (optically)
white oval to the right.
The String of Pearl storms farther to the right, however, are brightest in near ultraviolet, and so here appear (false-color) pink.
Jupiter's largest moon
Ganymede appears on the upper left.
Juno continues on a looping 33-day orbit around Jupiter,
while Earth-orbiting Hubble is aging and now relies on a
single stabilizing gyroscope.
 APOD: 2025 September 1 – Callisto: Dirty Battered Iceball
APOD: 2025 September 1 – Callisto: Dirty Battered Iceball
Explanation:
Its surface is the most densely cratered in the Solar System -- but what's inside?
Jupiter's moon
Callisto is a battered ball of dirty ice
that is slightly smaller than the planet
Mercury.
It was visited by NASA's
Galileo spacecraft in the 1990s and 2000s, but the recently reprocessed
featured image
is from a flyby of NASA's
Voyager 2 in 1979.
The moon would appear darker if it weren't for the tapestry of light-colored
fractured surface ice created by eons of impacts.
The interior of Callisto
is potentially even more interesting because therein might lie an internal layer of liquid water.
This potential
underground sea is a candidate to
harbor life -- similar with sister moons
Europa and
Ganymede.
Callisto is larger than
Luna,
Earth's Moon, and even with its high ice content is still more massive.
ESA's
JUICE and NASA's
Europa Clipper missions are now headed
out to Jupiter
to better investigate its
largest moons.
 APOD: 2025 August 23 – Fishing for the Moon
APOD: 2025 August 23 – Fishing for the Moon
Explanation:
How big is planet Earth's Moon?
Compared to other moons of the Solar System,
it's number 5 on the
largest to smallest ranked list,
following
Jupiter's moon Ganymede,
Saturn's moon Titan,
and
Jovian moons Callisto and
Io.
Continuing the list, the Moon comes before
Jupiter's Europa and
Neptune's Triton.
It's also larger than
dwarf planets
Pluto and Eris.
With a diameter of 3,475 kilometers the Moon is about 1/4
the size of Earth though, and that does make it the largest
moon when compared to the size of its parent Solar System planet.
Of course in this
serene, twilight sea and skyscape,
August's rising Full Moon still appears small enough
to be caught in the nets of an ancient fishing rig.
The telephoto snapshot was taken along the Italian Costa dei
Trabocchi,
on the Adriatic Sea.
 APOD: 2023 November 28 – Ganymede from Juno
APOD: 2023 November 28 – Ganymede from Juno
Explanation:
What does the largest moon in the Solar System look like?
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede, larger than even
Mercury and
Pluto,
has an icy surface speckled with bright young craters overlying a mixture of
older, darker, more cratered terrain laced with
grooves and ridges.
The cause of the grooved terrain remains a
topic of research,
with a leading hypothesis relating it to shifting ice plates.
Ganymede is thought to have an
ocean layer that contains more water than Earth -- and
might contain life.
Like Earth's Moon, Ganymede keeps the
same face towards
its central planet, in this case Jupiter.
The
featured image was captured in 2021 by NASA's robotic Juno spacecraft when it passed by the immense moon.
The close pass reduced Juno's orbital period around Jupiter from 53 days to 43 days.
Juno continues to study the
giant planet's high gravity,
unusual magnetic field, and
complex cloud structures.
 APOD: 2023 August 8 – Moon Meets Jupiter
APOD: 2023 August 8 – Moon Meets Jupiter
Explanation:
What's that below the Moon?
Jupiter -- and its largest moons.
Many
skygazers across planet Earth enjoyed the close conjunction of
Earth's Moon passing nearly in front of Jupiter in mid-June.
The featured image is a single exposure of the event taken from
Morón de la Frontera,
Spain.
The sunlit lunar crescent on the left is overexposed, while the Moon's night side,
on the right, is only faintly illuminated by Earthshine.
Lined up diagonally below the Moon, left to right, are
Jupiter's bright Galilean satellites:
Callisto,
Ganymede,
Io
(hard to see as it is very near to Jupiter), and
Europa.
In fact, Callisto, Ganymede, and Io are larger than Earth's Moon, while
Europa is only slightly smaller.
NASA's robotic spacecraft
Juno
is currently orbiting Jupiter and made a
close pass near Io only a week ago.
If you
look up in the
night sky tonight, you will again see two of the brightest
objects angularly close together -- because
tonight is another
Moon-Jupiter conjunction.
 APOD: 2022 October 25 - Jupiter Rotates as Moons Orbit
APOD: 2022 October 25 - Jupiter Rotates as Moons Orbit
Explanation:
Jupiter and its moons move like our Sun and its planets.
Similarly,
Jupiter spins while
its moons circle around.
Jupiter’s rotation can be observed by tracking
circulating dark belts and light zones.
The Great Red Spot, the largest storm known,
rotates to become visible after about 15 seconds in the 48-second time lapse video.
The video
is a compilation of shorts taken over several nights
last month and combined into a digital recreation of how
24-continuous hours would appear.
Jupiter's brightest moons always orbit in the plane of the planet's rotation,
even as Earth’s spin
makes the whole system appear to
tilt.
The moons
Europa,
Ganymede, and
Io are
all visible, with Europa's
shadow appearing as the icy
Galilean moon
crosses Jupiter's disk.
Jupiter remains
near opposition this month,
meaning that it is unusually bright,
near to its closest to the Earth,
and visible nearly all night long.
 APOD: 2022 October 7 - In Ganymede's Shadow
APOD: 2022 October 7 - In Ganymede's Shadow
Explanation:
At opposition,
opposite the Sun in Earth's sky,
late last month Jupiter is also approaching perihelion,
the closest point to the Sun in its elliptical orbit,
early next year.
That makes
Jupiter exceptionally close
to our fair planet,
currently resulting in excellent views of the
Solar System's ruling gas giant.
On September 27, this
sharp image of Jupiter
was recorded with a small telescope from a backyard in Florence, Arizona.
The stacked video frames reveal the massive world
bounded by
planet girdling winds.
Dark belts and light zones span the gas giant, along with rotating
oval storms and its signature
Great Red Spot.
Galilean moon Ganymede is below and right in the frame.
The
Solar System's largest moon
and its shadow are in transit across the southern
Jovian cloud tops.
 APOD: 2022 April 27 - Moon Shadow on Jupiter
APOD: 2022 April 27 - Moon Shadow on Jupiter
Explanation:
What is that large dark spot on Jupiter?
It's the shadow of
Ganymede,
Jupiter's largest moon.
When Jupiter's moons cross between the Jovian giant and the Sun, they
created shadows
just like when the
Earth's moon crosses between the Earth and the Sun.
Also like on Earth, if you were in a
dark shadow on Jupiter,
you would see a moon completely
eclipse the Sun.
Unlike on Earth,
moon shadows
occur most days on Jupiter -- what's
more unusual is that a spacecraft was close enough to record one with a
high-resolution
image.
That spacecraft, Juno, was passing so close to
Jupiter
in late February that nearby clouds and the dark eclipse shadow appear
relatively large.
Juno has made many discoveries about our
Solar System's largest planet, including, recently,
rapidly expanding circular auroras.
 APOD: 2022 February 4 - Moons at Twilight
APOD: 2022 February 4 - Moons at Twilight
Explanation:
Even though Jupiter
was the only planet visible in the evening sky on February 2, it
shared the twilight
above the western horizon with the Solar System's
brightest moons.
In a single exposure made just after sunset, the Solar System's
ruling gas giant is at the upper right in
this telephoto field-of-view from Cancun, Mexico.
The snapshot also captures our fair planet's own natural satellite
in its young crescent phase.
The Moon's disk looms large, its
familiar face illuminated
mostly by
earthshine.
But the four points of light lined-up with Jupiter are Jupiter's
own large
Galilean moons.
Top to bottom are Ganymede, [Jupiter], Io, Europa, and Callisto.
Ganymede, Io, and Callisto are physically larger than Earth's Moon while
water world Europa
is only slightly smaller.
 APOD: 2021 October 11 - Juno Flyby of Ganymede and Jupiter
APOD: 2021 October 11 - Juno Flyby of Ganymede and Jupiter
Explanation:
What would it be like to fly over the
largest moon in the
Solar System?
In June, the robotic
Juno spacecraft
flew past
Jupiter's
huge moon
Ganymede and took images that have been digitally constructed into a detailed flyby.
As the featured video begins,
Juno swoops over the two-toned surface of the 2,000-km wide moon, revealing an icy alien landscape filled with grooves and craters.
The grooves are likely caused by shifting surface plates, while the craters are caused by
violent impacts.
Continuing on in its orbit, Juno then performed its 34th
close pass over Jupiter's clouds.
The digitally-constructed video shows numerous
swirling clouds in the north,
colorful planet-circling zones and bands across the middle -- featuring several
white-oval clouds from the
String of Pearls, and finally more
swirling clouds in the south.
Next September, Juno is
scheduled to make a close pass over another of Jupiter's large moons:
Europa.
 APOD: 2021 August 21 - Triple Transit and Mutual Events
APOD: 2021 August 21 - Triple Transit and Mutual Events
Explanation:
These three panels feature the Solar System's ruling
gas giant Jupiter
on August 15 as seen from Cebu City, Philippines, planet Earth.
On that date the
well-timed telescopic views
detail some remarkable performances,
transits and mutual events, by Jupiter's Galilean moons.
In the top panel,
Io
is just disappearing into Jupiter's shadow at
the far right, but the three other large Jovian moons appear against the
planet's banded disk.
Brighter
Europa
and darker
Ganymede
are at the far left, also casting
their two shadows on the gas giant's cloud tops.
Callisto
is below and right near the planet's edge, the three moons in
a triple transit across the face of Jupiter.
Moving to the middle panel, shadows
of Europa and Ganymede are still visible near center
but Ganymede has occulted or passed in front of Europa.
The bottom panel captures a rare view of Jovian moons in eclipse
while transiting Jupiter, Ganymede's shadow falling on Europa itself.
From planet Earth's perspective, similar mutual events,
when Galilean moons occult and eclipse each other,
can be seen every six years or so when
Jupiter is near its own equinox.
 APOD: 2021 June 14 - Ganymede from Juno
APOD: 2021 June 14 - Ganymede from Juno
Explanation:
What does the largest moon in the Solar System look like?
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede, larger than even
Mercury and
Pluto,
has an icy surface speckled with bright young craters overlying a mixture of
older, darker, more cratered terrain laced with
grooves and ridges.
The cause of the grooved terrain remains a
topic of research,
with a leading hypothesis relating it to shifting ice plates.
Ganymede is thought to have an
ocean layer that contains more water than Earth -- and
might contain life.
Like Earth's Moon, Ganymede keeps the
same face towards
its central planet, in this case Jupiter.
The
featured image was captured last week by NASA's robotic Juno spacecraft as it passed only about 1000 kilometers above the immense moon.
The close pass reduced Juno's orbital period around Jupiter from 53 days to 43 days.
Juno continues to study the
giant planet's high gravity,
unusual magnetic field, and
complex cloud structures.
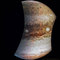 APOD: 2021 June 8 - A Face in the Clouds of Jupiter from Juno
APOD: 2021 June 8 - A Face in the Clouds of Jupiter from Juno
Explanation:
What do you see in the clouds of Jupiter?
On the largest scale, circling the planet,
Jupiter
has alternating
light zones and reddish-brown belts.
Rising zone gas,
mostly hydrogen and helium, usually swirls around regions of high pressure.
Conversely, falling belt gas usually
whirls around regions of low pressure,
like cyclones and
hurricanes on Earth.
Belt storms can form into large and long-lasting
white ovals and
elongated
red spots.
NASA's robotic
Juno spacecraft
captured most of these cloud features in 2017 during
perijove 6, its
sixth pass over the giant planet in its looping 2-month orbit.
But it is surely not these clouds themselves that
draws your attention to the
displayed image,
but rather their
arrangement.
The face that stands out, nicknamed
Jovey McJupiterFace,
lasted perhaps a few weeks before the neighboring storm clouds rotated away.
Juno has now completed 33 orbits
around Jupiter and just yesterday made a
close pass near
Ganymede,
our Solar System's
largest moon.
 APOD: 2020 December 23 - Jupiter Meets Saturn: A Red Spotted Great Conjunction
APOD: 2020 December 23 - Jupiter Meets Saturn: A Red Spotted Great Conjunction
Explanation:
It was time for their
close-up.
Two days ago
Jupiter and
Saturn
passed a tenth of
a degree
from each other in what is known a
Great Conjunction.
Although the
two planets pass each other on the sky every 20 years,
this was the closest pass in nearly four centuries.
Taken early in day of the
Great Conjunction, the
featured multiple-exposure combination
captures not only both giant planets in a single frame,
but also Jupiter's four largest moons (left to right)
Callisto,
Ganymede,
Io, and
Europa --
and Saturn's largest moon
Titan.
If you look very closely, the clear
Chilescope image even captures Jupiter's
Great Red Spot.
The now-separating planets can still be seen
remarkably close -- within about a degree -- as they set just after the
Sun,
toward the west,
each night for the remainder of the year.
 APOD: 2020 May 19 - Posters of the Solar System
APOD: 2020 May 19 - Posters of the Solar System
Explanation:
Would you like a NASA astronomy-exploration poster?
You are just one page-print away.
Any of the panels you see on
the featured image can appear on your
wall.
Moreover,
this NASA page has, typically,
several more posters of each of the
Solar System objects depicted.
These posters highlight many of the places humanity, through
NASA, has explored in the past 50 years,
including our
Sun, and planets
Mercury,
Venus,
Earth,
Mars,
Jupiter,
Saturn,
Uranus, and
Neptune.
Moons of Jupiter that have been posterized include
Europa,
Ganymede,
Callisto, and
Io,
while moons of Saturn that can be framed include
Enceladus and
Titan.
Images of
Pluto,
Ceres,
comets and asteroids are also presented, while six deep space scenes --
well beyond
our Solar System -- can also be prominently displayed.
If you
lack wall space or blank poster sheets don't despair --
you can still print many of these out as
trading cards.
 APOD: 2019 October 5 - Jupiter and the Moons
APOD: 2019 October 5 - Jupiter and the Moons
Explanation:
After sunset on October 3, some of the Solar System's largest moons
stood low along the western horizon with
the largest planet.
Just after nightfall, a pairing of the Moon approaching first quarter
phase and Jupiter was captured in this telephoto field of view.
A blend of short and long exposures, it reveals
the familiar face
of our fair planet's own large natural satellite in stark sunlight and
faint earthshine.
At lower right are the ruling gas giant and its four Galilean moons.
Left to right, the tiny pinpricks of light are
Ganymede, [Jupiter], Io, Europa, and Callisto.
Our own natural satellite appears to loom large because it's close,
but Ganymede, Io, and Callisto are actually larger than Earth's Moon.
Water world Europa
is only slightly smaller.
Of the Solar System's six
largest planetary satellites,
only Saturn's moon Titan, is missing from this scene.
But be sure
to check for large moons
in your sky tonight.
 APOD: 2019 May 23 - Moons Near Jupiter
APOD: 2019 May 23 - Moons Near Jupiter
Explanation:
On May 20, a nearly Full Moon and Jupiter shared this telephoto field of
view.
Captured when a passing cloud bank dimmed the moonlight,
the single exposure reveals the familiar
face of our fair planet's own large natural satellite, along
with bright Jupiter (lower right) and some of its
Galilean moons.
Lined up left to right the tiny pinpricks of light near Jupiter are
Ganymede,
Europa,
[Jupiter] and
Callisto.
(That's not just dust on your screen ...)
Closer and brighter, our own natural satellite appears to loom large.
But Ganymede, and Callisto are physically larger than Earth's Moon,
while water
world Europa is only slightly smaller.
In fact, of the Solar System's six
largest
planetary satellites, Saturn's moon Titan is missing
from the scene and a fourth Galilean moon, Io, is hidden by our
ruling gas giant.
 APOD: 2018 October 16 - Jupiter in Ultraviolet from Hubble
APOD: 2018 October 16 - Jupiter in Ultraviolet from Hubble
Explanation:
Jupiter looks a bit different in ultraviolet light.
To better interpret
Jupiter's cloud motions and to help NASA's robotic
Juno spacecraft understand the
planetary context of the small fields that it sees, the
Hubble Space Telescope is being directed to
regularly image the entire Jovian giant.
The colors of Jupiter
being monitored go beyond the normal human visual range to include both
ultraviolet and
(not pictured) infrared light.
Featured from 2017, Jupiter appears different in near ultraviolet light, partly because the amount of sunlight reflected back is distinct, giving differing cloud heights and latitudes
discrepant brightnesses.
In the
near UV, Jupiter's poles appear relatively dark, as does its
Great Red Spot and a smaller (optically)
white oval to the right.
The String of Pearl storms farther to the right, however, are brightest in near ultraviolet, and so here appear (false-color) pink.
Jupiter's largest moon
Ganymede appears on the upper left.
Juno continues on its looping 53-day orbits around Jupiter, while Earth-orbiting
Hubble is now recovering from the loss of a
stabilizing gyroscope.
 APOD: 2018 May 3 - Opposite the Setting Sun
APOD: 2018 May 3 - Opposite the Setting Sun
Explanation:
On April 30, a
Full Moon
rose opposite the setting Sun.
Its yellowish moonglow silhouettes a low tree-lined ridge
along Lewis Mountain in this northeastern Alabama skyscape.
Sharing
the telephoto field-of-view opposite the Sun
are Earth's grey shadow, the pinkish Belt of Venus, and bright
planet Jupiter.
Nearing its own 2018 opposition on
May 8,
Jupiter is
flanked by tiny pinpricks of light, three of its large Galilean moons.
Europa lies just below Jupiter, and Ganymede and Callisto are
just above.
Closer and brighter, our own natural satellite appears to loom large
but the Moon is physically a little smaller
than Ganymede and
Callisto, and
slightly larger than
water
world Europa.
Sharp eyes will also spot the trails of two jets across the clear evening
sky.
 APOD: 2017 May 14 - Ganymede: The Largest Moon
APOD: 2017 May 14 - Ganymede: The Largest Moon
Explanation:
What does the largest moon in the
Solar System look like?
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede, larger than even
Mercury and
Pluto, has an icy surface speckled with bright young craters overlying a mixture of older, darker, more cratered terrain laced with grooves and ridges.
The large circular feature on the upper right, called
Galileo Regio,
is an ancient region of
unknown origin.
Ganymede is thought to have an
ocean layer that contains
more water than Earth and
might contain life.
Like Earth's Moon, Ganymede keeps the
same face towards
its central planet, in this case Jupiter.
The featured image was taken about 20 years ago by NASA's
Galileo probe,
which ended its mission by diving into Jupiter's atmosphere in 2003.
Currently, NASA's
Juno spacecraft orbits Jupiter and is
studying the giant planet's internal structure, among many other attributes.
 APOD: 2017 April 13 - Moons and Jupiter
APOD: 2017 April 13 - Moons and Jupiter
Explanation:
On April 10, a Full Moon and Jupiter shared this telephoto field of view.
Both were near opposition, opposite the Sun in Earth's night sky.
Captured when a passing cloud bank dimmmed the bright moonlight,
the single exposure reveals the familiar
face of our fair planet's own large natural satellite, along
with a line up of the ruling gas giant's four Galilean moons.
Labeled top to bottom,
the tiny pinpricks of light above bright Jupiter are
Callisto,
Europa,
Ganymede, and
Io.
Closer and brighter, our own natural satellite appears to loom large.
But Callisto, Ganymede, and Io are physically larger than Earth's Moon,
while water
world Europa is only slightly smaller.
In fact, of the Solar System's six
largest
planetary satellites, only Saturn's moon Titan is missing
from the scene.
 APOD: 2017 March 25 - Ganymede's Shadow
APOD: 2017 March 25 - Ganymede's Shadow
Explanation:
Approaching
opposition
early next month, Jupiter is offering
some of its best telescopic views from planet Earth.
On March 17, this impressively sharp image of the solar system's
ruling gas giant was taken from a remote observatory in Chile.
Bounded by
planet girdling winds, familiar dark belts and light zones
span the giant planet spotted with rotating
oval storms.
The solar system's
largest moon Ganymede is above and left in the frame,
its shadow seen in transit across the northern
Jovian
cloud tops.
Ganymede itself is seen in remarkable detail along with bright
surface features on fellow Galilean moon Io,
right of Jupiter's looming disk.
 APOD: 2016 July 10 - Moon Meets Jupiter
APOD: 2016 July 10 - Moon Meets Jupiter
Explanation:
What's that next to the Moon?
Jupiter -- and its four largest moons.
Skygazers
around planet Earth enjoyed the close encounter of planets and
Moon in 2012 July 15's predawn skies.
And while many saw bright Jupiter next to the slender, waning crescent,
Europeans also had the opportunity to watch the
ruling gas giant pass
behind the lunar disk, occulted by the Moon as it slid through the
night.
Clouds threaten in this telescopic view from
Montecassiano,
Italy, but
the frame still captures Jupiter after it emerged from the occultation
along with all four of its large Galilean moons.
The sunlit crescent is overexposed with the Moon's night side faintly
illuminated by Earthshine.
Lined up left to right beyond the dark lunar limb are Callisto,
Ganymede, Jupiter, Io, and Europa.
In fact,
Callisto, Ganymede, and Io are larger than Earth's Moon, while
Europa is only slightly smaller.
Last week,
NASA's Juno became the second
spacecraft ever to orbit Jupiter.
 APOD: 2016 March 3 - Moons and Jupiter
APOD: 2016 March 3 - Moons and Jupiter
Explanation:
Some of the Solar System's largest moons rose together
on February 23.
On that night, a twilight pairing of a waning gibbous Moon
and Jupiter was captured in this sharp
telescopic field of view.
The composite of short and long exposures reveals the familiar
face of our fair planet's own large natural satellite, along
with a line up of the ruling gas giant's four Galilean moons.
Left to right, the tiny pinpricks of light are
Callisto,
Io,
Ganymede, [Jupiter], and
Europa.
Closer and brighter, our own natural satellite appears to loom large.
But Callisto, Io, and Ganymede are actually larger than Earth's Moon,
while water
world Europa is only slightly smaller.
In fact, of the Solar System's six
largest
planetary satellites, only Saturn's moon Titan is missing
from the scene.
(Editor's note: Composite corrected for orientation and field of
view posted on March 7.)
 APOD: 2015 May 15 - Jupiter, Ganymede, Great Red Spot
APOD: 2015 May 15 - Jupiter, Ganymede, Great Red Spot
Explanation:
In this sharp snapshot,
the Solar System's
largest moon Ganymede poses next to Jupiter,
the largest planet.
Captured on March 10 with a small telescope from
our fair planet Earth, the scene also includes Jupiter's
Great Red Spot, the Solar System's largest storm.
In fact,
Ganymede is about 5,260 kilometers in diameter.
That beats out
all three of its other fellow Galilean
satellites,
along with
Saturn's Moon Titan at 5,150 kilometers and Earth's own Moon at
3,480 kilometers.
Though its been
shrinking
lately, the Great Red Spot's diameter is
still around 16,500 kilometers.
Jupiter, the Solar System's ruling gas giant, is about
143,000 kilometers in
diameter
at its equator.
That's nearly 10 percent the diameter of the Sun.
 APOD: 2014 September 19 - Potentially Habitable Moons
APOD: 2014 September 19 - Potentially Habitable Moons
Explanation:
For astrobiologists,
these may be the four most
tantalizing moons in our Solar System.
Shown at the same scale, their exploration by interplanetary
spacecraft has launched the idea that moons, not just
planets, could have environments supporting life.
The Galileo mission to Jupiter discovered
Europa's global subsurface ocean of liquid water
and indications of
Ganymede's
interior seas.
At Saturn, the Cassini probe detected erupting fountains of water ice
from Enceladus indicating warmer subsurface water on
even that small moon, while finding surface lakes
of frigid but still liquid hydrocarbons beneath the dense atmosphere
of large moon Titan.
Now looking beyond the Solar System,
new
research suggests that sizable exomoons,
could actually outnumber
exoplanets in stellar
habitable zones.
That would make moons the most common type of habitable world
in the Universe.
 APOD: 2013 February 15 - Shadows Across Jupiter
APOD: 2013 February 15 - Shadows Across Jupiter
Explanation:
Two dark shadows loom across the banded and mottled
cloud tops of Jupiter in this
sharp telescopic view.
In fact, captured on January 3rd, about a month after the ruling gas giant
appeared at opposition in planet Earth's sky,
the scene includes the shadow casters.
Visible in remarkable
detail at the left are the large
Galilean moons Ganymede (top)
and Io.
With the two moon shadows still in transit, Jupiter's
rapid rotation has
almost carried its famous
Great Red Spot
(GRS) around the planet's limb from the right.
The pale GRS was preceded by the smaller but similar hued
Oval
BA, dubbed Red Spot Jr., near top center.
North is down in the
inverted image.
 APOD: 2012 July 20 - Moon Meets Jupiter
APOD: 2012 July 20 - Moon Meets Jupiter
Explanation:
Skygazers
around planet Earth enjoyed the close encounter of planets and
Moon in July 15's predawn skies.
And while many saw bright Jupiter next to the slender, waning crescent,
Europeans also had the
opportunity to watch the
ruling gas giant pass
behind the lunar disk, occulted by the Moon as it slid through the
night.
Clouds threaten in this telescopic view from Montecassiano, Italy, but
the frame still captures Jupiter after it emerged from the occultation
along with all four of its large Galilean moons.
The sunlit crescent is overexposed with the Moon's night side faintly
illuminated by Earthshine.
Lined up left to right beyond the dark lunar limb are Callisto,
Ganymede, Jupiter, Io, and Europa.
In fact,
Callisto, Ganymede, and Io are larger than Earth's Moon, while
Europa is only slightly smaller.
 APOD: 2012 March 2 - Jupiter Unplugged
APOD: 2012 March 2 - Jupiter Unplugged
Explanation:
Five hand drawn sketches of Jupiter were used to create this
beautifully detailed flat map of the ruling gas giant's
turbulent cloud tops.
Made with colored pencils at the eyepiece of a 16 inch diameter
telescope, the original drawings are about 5 inches (12.5 cm) in
diameter.
The drawn
planisphere
map dimensions are 16x8 inches (40x20 cm).
Observing on different dates in November and December of 2011,
astronomical artist Fred Burgeot has relied
on
Jupiter's rotation to
cover the planet's complete circumference.
Digital animator Pascal Chauvet has also translated Burgeot's drawings
into an intriguing video (vimeo),
synthesizing a telescopic view of the rotating planet
with a tilt and phase appropriate for the observing dates.
The video includes the Galilean moons
moving along their orbits,
beginning with Ganymede and Io casting shadows as they
glide in front of Jupiter, followed
by Europa and Callisto passing behind the planet's banded disk.
 APOD: 2011 October 22 - Jupiter Near Opposition
APOD: 2011 October 22 - Jupiter Near Opposition
Explanation:
On
October 29 (UT), Jupiter,
the
solar system's largest planet, will be at opposition,
opposite the Sun in planet Earth's sky,
shining brightly and rising as the Sun sets.
That
configuration results in Jupiter's almost annual
closest approach to planet Earth, so near opposition
the gas giant offers earthbound telescopes stunning views of its
stormy, banded atmosphere and large
Galilean moons.
This sharp snapshot of Jupiter was captured on October 13 with the
1 meter telescope
at the Pic Du Midi
mountain top observatory in the
French Pyrenees.
North is up in the image that shows off oval shaped vortices
and planet girdling
dark belts
and light zones.
Also seen in remarkable detail, Jupiter's
icy Ganymede,
the solar system's largest moon, is emerging from
behind the planet (top) while
volcanic Io
enters the frame near the lower left edge.
 APOD: 2010 October 8 - Two Planet Opposition
APOD: 2010 October 8 - Two Planet Opposition
Explanation:
In late September, two planets were
opposite the Sun in Earth's
sky, Jupiter and Uranus.
Consequently closest to Earth,
at a distance of only 33 light-minutes
and 2.65 light-hours respectively,
both were good targets for telescopic observers.
Recorded on September 27, this well-planned composite of
consecutive multiple exposures captured both gas giants
in their remarkable celestial line-up accompanied by their brighter
moons.
The faint greenish disk of distant planet Uranus is near the upper
left corner.
Of the tilted planet's 5
larger moons, two
can be spotted
just above and left of the planet's disk.
Both discovered by 18th century British astronomer Sir William Herschel
and later named for characters in Shakespeare's
A Midsummer Night's Dream,
Oberon
is farthest left, with Titania
closer in.
At the right side of the frame is ruling gas giant Jupiter, flanked
along a line by all four of its
Galilean satellites.
Farthest from Jupiter is
Callisto, with
Europa and
Io all left of the planet's disk, while
Ganymede
stands alone at the right.
 APOD: 2009 September 20 - Ganymede Enhanced
APOD: 2009 September 20 - Ganymede Enhanced
Explanation:
What does the largest moon in the Solar System look like?
Ganymede,
larger than even
Mercury and
Pluto,
has a surface speckled with bright young craters overlying a mixture of
older, darker, more cratered
terrain laced with
grooves and ridges.
Like Earth's Moon,
Ganymede keeps the same face towards its central planet, in this case Jupiter.
In this historic and
detailed image mosaic taken by the
Galileo
spacecraft
that orbited Jupiter from 1995 to 2003,
the colors of this planet-sized moon have been enhanced to
increase surface contrasts.
The violet shades extending from the top and bottom are likely due
to frost particles in Ganymede's polar regions.
Possible future missions to Jupiter are being proposed that can search
Europa and
Ganymede for deep oceans that may harbor elements thought important for
supporting life.
 APOD: 2009 January 6 - Jupiter Eclipsing Ganymede
APOD: 2009 January 6 - Jupiter Eclipsing Ganymede
Explanation:
How hazy is Jupiter's upper atmosphere?
To help find out, astronomers deployed the
Hubble Space Telescope to watch Jupiter eclipse its moon
Ganymede.
Although
Ganymede circles Jupiter
once a week, a particularly useful occultation occurs more rarely.
Such an occultation
was captured in great visual detail in April 2007.
When near Jupiter's limb,
Ganymede reflects sunlight though Jupiter's upper atmosphere, allowing astronomers to search for haze by
noting
a slight dimming at different colors.
One result of this investigation was the
above spectacular image, where bands of clouds that circle Jupiter are clearly visible, as well as magnificent swirling storm systems such as the
Great Red Spot.
Ganymede, at the image bottom, also shows noticeable detail on its
dark icy surface.
Since Jupiter and Ganymede are so bright, many eclipses can be
seen right here on Earth with a small telescope.
 APOD: 2007 August 24 - Astronomer's Moon
APOD: 2007 August 24 - Astronomer's Moon
Explanation:
Jupiter is
an astronomer's planet --
its large size and contrasting global
cloud belts and zones
allow detailed studies with a range of
earthbound telescopes.
On the other hand, most telescopic views
of Jupiter's moons usually
show only featureless, tantalizing points of light hovering near
the ruling gas giant.
But this impressive picture from a small, ground-based
telescope reveals a
stunning
amount of detail on Ganymede,
a jovian moon about the same size as Earth's moon but at least 1,500
times farther away.
The image was carefully constructed by combining and processing
only the 409 sharpest frames from a total of 10,000 recorded
at 30 frames per second by a digital camera.
Ganymede's
radius is about 2,600 kilometers indicating that the
surface markings visible are as small
as around 900 kilometers across.
 APOD: 2007 March 29 - Jupiter Moon Movie
APOD: 2007 March 29 - Jupiter Moon Movie
Explanation:
South is toward the top in this frame from a stunning movie featuring
Jupiter and moons recorded last Thursday from the Central Coast
of New South Wales, Australia.
In fact, three jovian moons and
two red spots are ultimately seen in the full video as
they glide around
the solar system's ruling gas giant.
In the early frame above,
Ganymede,
the largest moon in the solar system, is
off the lower right limb of the planet, while intriguing
Europa
is visible against
Jupiter's cloud tops, also near the lower right.
Jupiter's new red spot junior
is just above the broad white band
in the planet's southern (upper) hemisphere.
In later frames, as planet and moons rotate (right to left), red spot junior
moves behind Jupiter's left edge while the
Great Red Spot
itself comes into view from the right.
Also finally erupting into view at the right, is Jupiter's
volcanic moon, Io.
To download the full 2 megabyte movie as an animated gif file, click
on the picture.
 APOD: 2004 December 9 - Jupiter and the Moon's Shadowed Horizon
APOD: 2004 December 9 - Jupiter and the Moon's Shadowed Horizon
Explanation:
Early Tuesday
morning, December 7th, June Croft thought the
southeastern sky above Atmore, Alabama, USA was beautiful.
Watching
the Moon rise through gossamer clouds, she
noted, " ... the crescent Moon looked like it was held in
the sky by a star just off its shadowed horizon."
What was that star?
Bright Jupiter of course, and
some watched as the Moon actually
occulted or passed in front of
the Solar System's reigning gas
giant planet.
For astronomer Jimmy Westlake in Colorado, Jupiter was
already hidden at moonrise that morning,
but later he was able to record this lovely image,
not unlike the view that inspired Croft.
Seen through gossamer clouds, Jupiter along with large
Jovian satellites
Ganymede and Callisto (bottom to top) has emerged from
behind the crescent Moon's
shadowed horizon.
 APOD: 2004 November 11 - Pastel Planet, Triple Eclipse
APOD: 2004 November 11 - Pastel Planet, Triple Eclipse
Explanation:
This false-color
image of banded gas giant Jupiter
shows a triple eclipse in progress on March 28 - a relatively
rare
event, even for a large planet with many moons.
Captured by the Hubble Space Telescope's near-infrared camera are
shadows of
Jupiter's moons Ganymede (left edge), Callisto (right
edge) and Io, three black spots crossing the sunlit Jovian cloud tops.
In fact, Io itself is
visible as a white spot
near picture center with a bluish Ganymede above and to the right,
but Callisto is off the right hand edge of the scene.
Viewed from Jupiter's perspective, these
shadow crossings would be
seen as solar eclipses, analogous to the
Moon's shadow crossing
the sunlit face of planet Earth.
Historically,
timing the eclipses of Jupiter's moons allowed
astronomer Ole Roemer
to make the first accurate
measurement of
the speed of light in 1676.
 APOD: 2003 February 27 - When Moons and Shadows Dance
APOD: 2003 February 27 - When Moons and Shadows Dance
Explanation:
It's no wonder Jupiter is a favorite
target
for even modest earthbound telescopes.
The most massive planet
in the solar system with
four of the largest moons also boasts the famous
Great Red Spot,
a giant hurricane-like storm system over three hundred years old.
Recorded on December 15, 2002 between 7:19 and 8:40 UT,
over a thousand digital images were processed and stacked to
create this spectacular 21 frame animation of the
Jovian system.
South is up and as the Great Red Spot tracks across the face of Jupiter,
innermost Galilean
moon Io enters the scene at the far right.
Io occults (passes in front of) the edge of the more
sedately orbiting Ganymede with
Io's shadow moving quickly across the gas giant's
cloud tops, just below the Red Spot.
While the moon Callisto is outside the field of view, its large,
dark shadow is also
visible crossing the Jovian disk at the upper left.
Viewed from Earth, the orbits of the Galilean moons presently
lie nearly edge-on, offering many chances to observe similar
dances of Jupiter's moons.
 APOD: 2003 February 16 - Southwest Mercury
APOD: 2003 February 16 - Southwest Mercury
Explanation:
The planet Mercury resembles a moon. Mercury's old surface is heavily cratered like many moons.
Mercury is larger than most moons but smaller than
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede and
Saturn's moon
Titan.
Mercury is much denser and more massive than any moon,
though, because it is made mostly of iron. In fact, the
Earth is the only planet more dense.
A visitor to Mercury's surface
would see some strange sights.
Because
Mercury rotates exactly three times every two orbits around the
Sun, and because
Mercury's orbit is so elliptical, a visitor to
Mercury might see the
Sun rise, stop in the sky, go back toward the rising
horizon,
stop again, and then set quickly over the
other horizon.
From Earth, Mercury's proximity to the
Sun causes it to be
visible only for a short time just after
sunset or just before sunrise.
 APOD: 2001 December 15 - Ganymede: Torn Comet Crater Chain
APOD: 2001 December 15 - Ganymede: Torn Comet Crater Chain
Explanation:
This striking line of 13 closely spaced craters
on Jupiter's moon
Ganymede
was photographed by the Galileo spacecraft in 1997.
The picture covers an area about 120 miles wide and
the chain of craters cuts across a sharp boundary between
dark and light terrain.
What caused this crater chain?
Remarkably, the
exploration
of the Solar System, has shown that
crater chains like this one are
not
unique, though
they
were considered mysterious until a
dramatic object lesson was offered by comet Shoemaker-Levy 9.
In 1994 many denizens of planet Earth
watched as huge pieces of
this torn comet
slammed into Jupiter itself in a spectacular series of
sequential impacts.
It is very likely that similar torn comets from the early history
of the Solar System are responsible for this and
other crater chains.
 APOD: 2001 July 31 - Oceans Under Jupiters Callisto
APOD: 2001 July 31 - Oceans Under Jupiters Callisto
Explanation:
Why does
Jupiter's moon
Callisto alter the
magnetic field of Jupiter in its vicinity?
Callisto itself does not have a strong magnetic field.
One possible answer is that
Callisto harbors sub-surface oceans of
electrically conducting salt-water.
This hypothesis was
bolstered recently by a new analysis of how
Callisto creates and dissipates heat.
Callisto is thought to create heat by the
radioactive decay of internal rock -- a process that keeps the
Earth's mantle molten.
Callisto may not be able to dissipate this heat very efficiently,
however, as it has thick layers of ice and rock on its surface.
Perhaps this heat is enough to keep sub-surface water from
freezing into ice.
With this hypothesis, Callisto joins two other of
Jupiter's moons,
Europa and
Ganymede,
in candidates for sub-surface oceans.
Callisto's oceans, however,
might prove too hostile to support
Earth-like life.
 APOD: 2001 January 16 - Europa Rotating
APOD: 2001 January 16 - Europa Rotating
Explanation:
Evidence has been mounting that beneath the
vast planes of ice that cover
Europa lies water --
liquid oceans that might be home to
alien life.
The smallest of
Jupiter's
Galilean Moons
(which include
Io,
Ganymede, and
Callisto), Europa's deep interior is composed of mostly of
silicate rock.
Upon close inspection, many
surface cracks
stop abruptly only to continue on somewhere else -- indicating
surface plates that might be sliding.
The
above time-lapse sequence is a composite of images
taken during the
Voyager spacecraft flyby of the moon twenty years ago.
Not all regions are resolved in high detail.
The movie shows
Europa during a complete rotation,
which corresponds to a complete revolution around
Jupiter since
Europa always keeps the same face toward the giant planet.
The cause of many of the surface colors on
Europa also remains a
topic of research.
 APOD: 2001 January 2 - Jupiter, Europa, and Callisto
APOD: 2001 January 2 - Jupiter, Europa, and Callisto
Explanation:
As the
robot Cassini spacecraft rounds
Jupiter on its way toward
Saturn, it has taken a
sequence of images
of the gas giant with its
four largest moons.
Previously released images have highlighted
Ganymede and
Io.
Pictured above are the two remaining
Galilean satellites:
Europa and
Callisto.
Europa is the bright moon superposed near
Jupiter's Great Red Spot,
while Callisto is the dark moon near the frame edge.
Callisto is so dark that it would be hard to see
here if its brightness was not digitally enhanced.
Recent evidence indicates that both moons hold salt-water seas under surface ice that might be home to extra-terrestrial life.
By noting the times that moons disappeared and
reappeared behind Jupiter in 1676,
Ole Roemer was able to make the
first accurate estimation of the speed of light.
 APOD: 2000 December 19 - A Close Up of Aurora on Jupiter
APOD: 2000 December 19 - A Close Up of Aurora on Jupiter
Explanation:
Jupiter has
aurorae.
Like Earth, the
magnetic field of the gas giant funnels
charged particles released from the Sun
onto the poles.
As these particles strike the atmosphere,
electrons are temporarily knocked away from existing gas
molecules.
Electric force attracts these electrons back.
As the
electrons recombine to remake neutral molecules,
auroral light is emitted.
In the
above recently released photograph by the
Hubble Space Telescope taken in
ultraviolet light, the
aurorae
appear as annular sheets around the pole.
Unlike
Earth's aurorae,
Jupiter's aurorae include
several bright streaks and dots.
These marks are caused by magnetic flux tubes connecting
Jupiter to its
largest moons.
Specifically,
Io
caused the bright streak on the far left,
Ganymede
caused the bright dot below center, and
Europa caused the dot to its right.
 APOD: 2000 December 18 - Oceans Under Jupiter's Ganymede
APOD: 2000 December 18 - Oceans Under Jupiter's Ganymede
Explanation:
The
search for extraterrestrial life
came back into our own
Solar System last week with the
announcement that there may be
liquid oceans under the surface of
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede.
Ganymede now joins
Callisto and
Europa as moons of
Jupiter that may harbor seas of liquid water under
layers of surface ice.
The ocean hypothesis surfaced as an explanation for
Ganymede's unusually strong magnetic field.
Ganymede, the largest moon in the Solar System,
also has the largest measured
magnetic field of any moon.
Some
exobiologists hypothesize that
life may be able to emerge in such an ocean,
much as it did in the
oceans of ancient Earth.
Above, a frame from a
computer simulation shows what it would look like to
fly over the surface of Ganymede,
as extrapolated from photographs of the
grooved moon taken by the
robot spacecraft Galileo currently orbiting Jupiter.
 APOD: 2000 December 12 - Jupiter Eyes Ganymede
APOD: 2000 December 12 - Jupiter Eyes Ganymede
Explanation:
Who keeps an eye
on the largest moon in the
Solar System?
This moon, visible on the lower right, is
Ganymede, and the planet it orbits,
Jupiter,
seems to be keeping a watchful eye, as its
Great Red Spot
appears serendipitously nearby.
This recently released enhanced-contrast image from the
robot spacecraft Cassini captures new details of the
incredible intricacies of
Jupiter's complex cloud patterns.
Features as small as 250 kilometers can be seen.
Counter-clockwise rotating high-pressure
white ovals that are similar to the
Great Red Spot
appear in the red band below the spot.
Between these spots are darker
low-pressure systems that rotate clockwise.
The hydrogen and
helium that compose most of
Jupiter's clouds is nearly invisible -
the trace chemicals that give Jupiter these colors
remain unknown.
The Cassini spacecraft is using
Jupiter to
pull it toward
Saturn, where it is
scheduled to arrive in 2004.
 APOD: 2000 November 18 - Jupiter And Family
APOD: 2000 November 18 - Jupiter And Family
Explanation:
This composite image features classic portraits of members of one of
the Solar System's
most prominent families -
Jupiter and its four large
"Galilean" moons.
Starting from the top the moons are
Io,
Europa,
Ganymede, and
Callisto.
The top-to-bottom order is also the order of increasing distance from
Jupiter.
These are big moons indeed which attend
the largest planet.
The smallest of the lot, Europa, is the size of
Earth's moon while
Ganymede is the largest moon in the Solar System.
In fact, Ganymede with a diameter of 3,100 miles, is larger
than the planets Mercury and
Pluto.
The swirling
Great Red Spot appears at the edge of Jupiter.
A hurricane-like storm system that has persisted for over 300 years,
two to three earths could fit inside it.
Battered Callisto's
image was recorded during the 1979 flyby
of Voyager.
The other portraits were taken by
the
Galileo spacecraft which began
exploring the Jovian system in 1995.
 APOD: 2000 October 24 - Io Rotating
APOD: 2000 October 24 - Io Rotating
Explanation:
The surface of Io is continually changing.
Jupiter's moon
is the home to many powerful
volcanoes so active
they are effectively turning the moon inside out.
The above time-lapse sequence is a composite of images
taken during two space missions that approached the violent moon:
Voyager and
Galileo.
The sequence shows
Io during a complete rotation,
which corresponds to a complete revolution around
Jupiter since
Io always keeps the same face toward the giant planet.
The rampant volcanism is thought to be caused by
Jupiter's more distant
Galilean Moons
(Europa,
Ganymede, and
Callisto) pulling on Io and continually distorting its shape,
causing internal
frictional heating.
Io is composed mostly of rock, with the yellow color originating from
sulfur.
The causes of many of the other colors remain a
topic of research.
 APOD: 2000 June 20 - Ganymede: The Largest Moon in the Solar System
APOD: 2000 June 20 - Ganymede: The Largest Moon in the Solar System
Explanation:
If Ganymede orbited the Sun, it would be considered a planet.
The reason is that
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede is not only the largest moon in the
Solar System, it is larger than planets
Mercury and
Pluto.
The
robot spacecraft Galileo currently orbiting
Jupiter has been able to zoom by
Ganymede several times and snap many close-up pictures.
Ganymede,
shown above in its natural colors, sports a
large oval dark region known as
Galileo Regio.
In general, the dark regions on
Ganymede are heavily cratered,
implying they are very old, while the light regions
are younger and dominated by
unusual grooves.
The origin of the
grooves is still
under investigation.
 APOD: 2000 May 8 - Jupiters Moons Thebe, Amalthea, and Metis
APOD: 2000 May 8 - Jupiters Moons Thebe, Amalthea, and Metis
Explanation:
The robot
spacecraft Galileo in orbit around
Jupiter has recently photographed the
inner moons of Jupiter in greater detail than ever before.
These pictures of
Thebe,
Amalthea,
and
Metis
are shown to scale, and reveal details as
small as three kilometers across.
Amalthea, by contrast, has a
total length of about 200 kilometers.
The
moons are composed
mostly of ice, are much smaller than Jupiter's
more famous
Galilean satellites
(Io,
Europa,
Ganymede, and
Callisto), and orbit between Io and
Jupiter's rings.
Thebe appears dominated by a huge
impact crater
40 kilometers across.
Astronomers are uncertain of the
origin of the unusual white gash at the bottom of
Amalthea.
 APOD: 2000 February 13 - Southwest Mercury
APOD: 2000 February 13 - Southwest Mercury
Explanation:
The planet Mercury resembles a moon. Mercury's old surface is heavily cratered like many moons.
Mercury is larger than most moons but smaller than
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede and
Saturn's moon
Titan.
Mercury is much denser and more massive than any moon,
though, because it is made mostly of iron. In fact, the
Earth is the only planet more dense.
A visitor to Mercury's surface
would see some strange sights.
Because
Mercury rotates exactly three times every two orbits around the
Sun, and because
Mercury's orbit is so elliptical, a visitor to
Mercury might see the
Sun rise, stop in the sky, go back toward the rising
horizon,
stop again, and then set quickly over the other horizon.
From
Earth, Mercury's proximity to the
Sun cause it to be
visible only for a short time just after sunset or just before sunrise.
 APOD: March 4, 1999 - Ganymede Mosaic
APOD: March 4, 1999 - Ganymede Mosaic
Explanation:
Ganymede, one of
the four Galilean moons of Jupiter, is the largest moon
in the Solar System.
With a diameter of 5,260 kilometers it is even
larger than planets Mercury and Pluto
and just over three quarters the size of Mars.
Ganymede is locked in
synchronous rotation with Jupiter.
This detailed mosaic
of images from the Galileo spacecraft
shows the trailing hemisphere of this planet-sized moon.
Speckled with bright young craters, Ganymede's
surface shows a mixture of
old, dark, cratered
terrain and lighter regions laced with
grooves and ridges.
Ganymede's true colors tend toward subtle browns and grays, but
this mosaic's colors have been enhanced to increase surface contrasts.
The violet shades extending from the top and bottom are likely due
to frost particles in Ganymede's polar regions.
 APOD: August 5, 1998 - Ganymede: Torn Comet Crater Chain
APOD: August 5, 1998 - Ganymede: Torn Comet Crater Chain
Explanation:
This remarkable line of 13 closely spaced craters
on Jupiter's moon
Ganymede
was photographed by the Galileo spacecraft in 1997.
The picture covers an area about 120 miles wide and
the chain of craters cuts across a sharp boundary between
dark and light terrain.
What caused this crater chain?
During the
exploration of the Solar System,
crater chains like this one
have been discovered
in several places
and were considered mysterious until a
dramatic object lesson was offered by
comet Shoemaker-Levy 9.
In 1994
many denizens of planet Earth
watched as huge pieces of
this torn comet
slammed into Jupiter itself in a spectacular series of
sequential impacts.
It is very likely that
similar torn comets from the early history
of the Solar System are responsible for this and
other crater chains.
 APOD: July 22, 1998 - Dark Craters on Ganymede
APOD: July 22, 1998 - Dark Craters on Ganymede
Explanation:
Ganymede has
craters within
craters within
craters.
The old surface of the largest moon in the Solar System shows its
age
by the large amount of these impact features. The above picture released last week
shows two old craters with dark floors located
in a relatively bright region known as
Memphis Facula,
a region itself thought created by an ancient collision.
The strange dark floors of these craters were
themselves created long ago and now house craters
of their own.
Crater Chrysor, on the left, spans about 6000 meters,
about half that of crater Aleyn on the right. The
robot spacecraft Galileo took the
above photograph
during a flyby of this moon of Jupiter in June 1996.
 APOD: May 13, 1998 - Occultations and Rising Moons
APOD: May 13, 1998 - Occultations and Rising Moons
Explanation:
On April 23, the rising crescent Moon
occulted (passed in front of) Venus and Jupiter.
The double occultation was a rare event
and only visible from certain
locations tracing a path across Earth's surface.
This dramatic telephoto picture was
taken at one such location,
Ascension Island in the South Atlantic.
The sunlit crescent is over-exposed revealing the rest of the lunar surface
illuminated by faint earthshine.
Venus is emerging just beyond the crescent's tip
and Jupiter is trailing above the dark lunar edge with a spot of light,
Jupiter's moon Ganymede, between the lunar limb and the planet's disk.
Look closely at Jupiter and you can see yet another
Jovian moon,
Io, just visible against Jupiter's glare!
 APOD: May 12, 1998 - Callisto Enhanced
APOD: May 12, 1998 - Callisto Enhanced
Explanation:
Callisto
is half rock and half ice. This moon of
Jupiter is approximately the size of the planet Mercury, making it the third largest moon in the
Solar System, after
Ganymede and Titan.
Callisto's icy surface is
billions of years old, lacks any sign of
volcanic activity,
and is densely covered with rifts and craters.
These features are particularly apparent in this contrast-enhanced image
taken by the
Galileo spacecraft, and released last week.
Visible near the image center is Valhalla, one of the largest impact craters in the
Solar System, measuring about 4,000 kilometers across.
The rings and size of Valhalla make its appearance similar to the
Caloris Impact Basin on Mercury.
 APOD: February 2, 1998 - A Triple Eclipse on Jupiter
APOD: February 2, 1998 - A Triple Eclipse on Jupiter
Explanation:
Part of Jupiter is missing.
Actually, three parts appear to be missing.
In reality though, the three dark spots seen in the above photograph are only shadows. The
unusual alignment of three of Jupiter's moons between the
Jovian giant and the Sun was imaged last November 10th.
The shadows of
Io,
Callisto, and
Ganymede move across
Jupiter as these moons progress in their orbits.
It was by noting the times of eclipse
of Jupiter's moons in 1675 that Ole Roemer became the first person to measure the
speed of light.
When a shadow from
Earth's Moon
crosses the Earth's surface, the people inside the shadow see an
eclipse of the Sun.
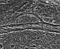 APOD: December 9, 1997 - Mysterious Features on Ganymede
APOD: December 9, 1997 - Mysterious Features on Ganymede
Explanation:
Where is the rest of the circle? Jupiter's largest moon
Ganymede has some truly unusual terrain,
including the pictured half circle above cut by nearly parallel curves.
Full circles can be easily explained by
impact craters,
but partial circles imply that some resurfacing has
occurred since the original impact.
The diameter of the half circle is about 32 kilometers.
Also of interest is a dense linear
crater chain
that cuts across the top of the half-circle.
Mysteries like these are typically solved by the
hard work of reconstructing a sequence of natural occurrences,
which in this case may yield a better understanding of
Ganymede's interesting past.
 APOD: September 29, 1997 - Jupiter And Family
APOD: September 29, 1997 - Jupiter And Family
Explanation:
This composite image features classic portraits of members of one of
the Solar System's most prominent families -
Jupiter and its four large
"Galilean" moons.
Starting from the top the moons are
Io,
Europa,
Ganymede, and
Callisto.
The top-to-bottom order is also the order of increasing distance from
Jupiter.
These are big moons indeed which attend
the largest planet.
The smallest of the lot, Europa, is the size of
Earth's moon while
Ganymede is the largest moon in the Solar System.
In fact, Ganymede with a diameter of 3,100 miles, is larger
than the planets Mercury and
Pluto.
The swirling
Great Red Spot appears at the edge of Jupiter.
A hurricane-like storm system that has persisted for over 300 years,
two to three earths could fit inside it.
Battered Callisto's
image was recorded during the 1979 flyby
of Voyager.
The other portraits were taken by
the Galileo spacecraft which began
exploring the Jovian system in 1995.
 APOD: June 12, 1997 - Jupiter's Dry Spots
APOD: June 12, 1997 - Jupiter's Dry Spots
Explanation:
Known for its spectacular images of Jupiter's moons,
Io,
Ganymede,
Callisto,
and Europa,
the robot spacecraft Galileo has also aggressively explored the Jovian
atmosphere.
In December of 1995,
Galileo's atmospheric probe descended into
Jupiter's clouds and reported
a surprising absence of water.
It is now believed that the probe entered through one of
Jupiter's dry spots,
similar to the dark region in
this image of the swirling Jovian cloud deck.
The smallest features visible here are tens of miles in size.
These dry regions appear to correspond to locations where
winds converge creating downdrafts. The downdrafts generate
local cloudless clearings through which
Jupiter's deeper warmer layers can be glimpsed.
Just as the dark areas are extremely dry, the surroundings are
full of moisture. The contrast is analogous to
the desert and tropics of Earth.
 APOD: December 23, 1996 - The Hills of Ganymede
APOD: December 23, 1996 - The Hills of Ganymede
Explanation:
This computer generated 3D close-up view of Jupiter's
large moon Ganymede
was created using image data from
NASA's Galileo spacecraft.
Simulating stereo vision by
combining two recent images recorded from different angles,
3 dimensional information was reconstructed for a section
of Ganymede's surface.
The result shows the furrows, craters, and hills in the
region appropriately known as "Galileo Regio" with a resolution
of about 250 feet.
Currently exploring
the Jovian System,
the Galileo spacecraft
just completed a flyby of Europa.
It is scheduled to return to Ganymede in April next year.
 APOD: November 7, 1996 - Fields of Minerals on Ganymede
APOD: November 7, 1996 - Fields of Minerals on Ganymede
Explanation: What treasures lie on the surface of Ganymede?
Last week, NASA released a map of Jupiter's largest moon made
by the Galileo Orbiter
highlighting ice and minerals deposits. The leftmost photograph
by Voyager
shows surface features in visible light, but the rightmost photograph,
taken in
infrared light
by Galileo, shows the locations of minerals in red and ice
grains in blue. The NIMS team
is working to identify these minerals with preliminary hopes
of finding emission indicative of montmorillonite
and alunite
 APOD: October 25, 1996 - A Flyby View of Ganymede
APOD: October 25, 1996 - A Flyby View of Ganymede
Explanation: This is what it would look like to fly over
the surface of Jupiter's moon Ganymede. NASA's robot spacecraft Galileo
recently approached only 6000 miles from this frozen ice-ball
of a moon. The above image
is a digital reconstruction from two images taken during this
flyby. The blue color of the sky is artificial. Deep furrows
cover Ganymede's surface, and several
impact craters are also present. Galileo continues to orbit Jupiter
and send back breathtaking photos of Ganymede,
Io, Europa,
Callisto, and, of course, Jupiter
itself.
 APOD: October 22, 1996 - The Cracked Ice Plains of Europa
APOD: October 22, 1996 - The Cracked Ice Plains of Europa
Explanation: What caused the cracks in this giant ice-ball?
Jupiter's moon Europa
has smoothest surface in the solar system and is composed mostly
of cracked water-ice. In the above false-colored picture
released last week by the NASA team
in charge of the Galileo mission,
blue hues represent ice plains divided by dirty red and brown
bands of mottled terrain. As the robot Galileo spacecraft orbits
Jupiter, it sends back revealing pictures of Jupiter and
its large moons
including Europa, Io,
Ganymede, and Callisto.
The region of Europa
highlighted above is known as Minos Linea. The cause for many
of the cracks remains unknown but may involve shifting stresses
from gravity and temperature variations. The new Galileo pictures
have increased evidence that liquid oceans may indeed exist
under these giant ice-sheets, a place possibly ripe for the development of life.
 APOD: September 13, 1996 - Southwest Mercury
APOD: September 13, 1996 - Southwest Mercury
Explanation:
The planet Mercury resembles a moon.
Mercury's
old surface is heavily
cratered like many moons.
Mercury is larger than most moons but smaller than
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede and
Saturn's moon
Titan. Mercury is much denser and more massive than any moon, though, because it is made mostly of iron. In fact, the
Earth is the only planet more dense. A visitor to
Mercury's surface would see some strange sights. Because
Mercuryrotates exactly three times every two orbits around the
Sun, and because
Mercury's orbit is so elliptical, a visitor to
Mercury might see the
Sun rise, stop in the sky, go back toward the rising
horizon, stop again, and then set quickly over the other horizon. From
Earth, Mercury's proximity to the
Sun cause it to be
visible only for a short time just after sunset or just before sunrise.
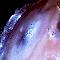 APOD: August 5, 1996 - Erupting Volcanoes on Io
APOD: August 5, 1996 - Erupting Volcanoes on Io
Explanation:
Jupiter's moon Io has active volcanoes. The
Voyager spacecraft
caught several erupting when they passed the energetic moon in 1979. In the
above picture, several of
Io's volcanoes are visible and one is seen
actually
erupting. Debris from this explosive event can be seen on the upper left of
the photo, just beyond Io's edge.
Io's volcanism is thought to be caused
by the large tidal distortions raised by
Jupiter,
Europa, and
Ganymede.
These tides stretch
Io, cause internal friction, and thus heat the
interior. The hot interior then expands and forces its
way out through volcanoes. Currently, the
spacecraft Galileo is orbiting
Jupiter and
photographing Jupiter's Galilean moons.
 APOD: July 19, 1996 - Galileo's First Color Image of Io
APOD: July 19, 1996 - Galileo's First Color Image of Io
Explanation:
Above is
the first color image
of
Jupiter's volcanic moon Io released by the Galileo Project.
(Io sounds like "eye-oh".)
The image was made on June 25 when the
Galileo spacecraft approached within 1.4 million miles.
It reveals features as small as 14 miles across - comparable to the resolution
of the best 1979 vintage
Voyager images.
The Voyager flybys discovered
active volcanos on Io's mottled surface
and this image indicates that
dramatic changes have occurred since, notably in the region of
the Masubi volcano located in Io's southern hemisphere.
This region, apparently covered with new deposits
of sulfur and sulfur dioxide frost deposited by volcanic eruption,
is seen as the pronounced white area at the bottom of the picture.
While scientists continue to analyze this image and
other recent Galileo data the robot spacecraft will continue
to explore Jupiter's moons.
Its next scheduled
close encounter is set for September 6th with
the moon Ganymede.
Higher resolution images of Io are also expected during the ongoing
mission.
 APOD: July 12, 1996 - Ancient Cratered Plains on Ganymede
APOD: July 12, 1996 - Ancient Cratered Plains on Ganymede
Explanation:
The largest moon in the Solar System shows regions that are ancient and
battered. The high density of craters demonstrate that patches of
Ganymede
are indeed billions of years old.
This photo is
one of a series
released by
NASA two days ago from the
Galileo spacecraft orbiting
Jupiter.
The large impact crater on the left is 19 kilometers across, while dark
indentations in
Ganymede's crusty surface-ice run diagonally.
Ganymede is composed of
half rock and half water-ice. The
Galileo
spacecraft will continue to orbit
Jupiter
over the next 16 months and send back data about
Jupiter and its
four largest moons:
Io,
Europa,
Ganymede, and
Callisto.
 APOD: July 11, 1996 - Ganymede: A Really Groovy Moon
APOD: July 11, 1996 - Ganymede: A Really Groovy Moon
Explanation:
Ganymede's surface is a wrinkled mess. As large ice-sheets shift on
the
moon's surface, parts of the surface buckle causing high ridges, deep
furrows, and parallel grooves.
This photo,
taken by the
Galileo
spacecraft
currently orbiting
Jupiter, was
released yesterday.
The large circular feature near the picture bottom is a large impact
crater. The impact that caused this large crater also caused the strange
dark ejecta seen to the crater's right. The Sun illuminates the scene from
the lower left. The
Galileo spacecraft
has also just discovered that
Ganymede
has a region of orbiting charged particles called a magnetosphere -
a first for any moon. How
Ganymede
is able to generate a
magnetosphere
is a mystery.
 APOD: July 10, 1996 - Galileo Photographs Ganymede
APOD: July 10, 1996 - Galileo Photographs Ganymede
Explanation:
Ganymede's surface is slowly being pulled apart.
This photo of Ganymede was
released earlier today by the Galileo team at NASA. The
Galileo Spacecraft arrived at
Jupiter
in December 1995. In late June, the spacecraft passed
within 10,000 kilometers of
Ganymede's icy surface, and took pictures
showing complex surface details for the first time. The
line-like features in this photo are sunlit ridges rising above
Ganymede's ice-plains.
The circular features are impact craters.
Ganymede
is the largest moon of
Jupiter and hence the largest of
the four Galilean satellites:
Io,
Europa,
Ganymede, and
Callisto.
 APOD: June 27, 1996 - Voyager's Preview of Galileo at Ganymede
APOD: June 27, 1996 - Voyager's Preview of Galileo at Ganymede
Explanation:
NASA's robot spacecraft Galileo
began its long voyage to Jupiter in October of 1989.
In December of last year it arrived in the Jovian system, beginning
its unprecedented, detailed exploration
by dropping a probe
into the gas giant's atmosphere.
By early this morning it will have accomplished
another milestone in its ambitious mission.
Now in orbit around Jupiter,
Galileo will make its first close
flyby of Ganymede,
Jupiter's (and the solar system's) largest moon
at 2:29 a.m. EDT.
As planned,
approaching to within 524 miles, it will make a series
of high resolution images of the surface which will reveal features
as small as 33 feet across.
This close-up color image from the Voyager 2 flyby in 1979
previews sights
Galileo will see in greater detail.
Showing features
as small as 3 miles across, it reveals a variety of terrain on
Ganymede's icy surface, including impact craters with bright rays
and long strips of light grooved structures suggesting large scale
motions of the frozen crust.
Galileo's flyby images will be stored onboard for playback
and should be available during the week of July 10.
 APOD: December 24, 1995 - Uranus' Moon Miranda
APOD: December 24, 1995 - Uranus' Moon Miranda
Explanation:
NASA's robot spacecraft Voyager 2 passed the planet
Uranus and its moons in
1986. While the cloud tops of
Uranus proved to be rather featureless, the surface of
Miranda, the
innermost of
Uranus' large moons, showed several interesting features.
Voyager 2 passed closer to
Miranda than to any
Solar System body and hence
photographed it with the clearest resolution. Miranda's heavily cratered
terrain shows grooves like
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede and
several valleys and cliffs. Miranda is made of a roughly equal mix of ice
and rock. Miranda was discovered by Gerard Kuiper in 1948.
 APOD: November 25, 1995 - Saturn's Cleanest Moon: Enceladus
APOD: November 25, 1995 - Saturn's Cleanest Moon: Enceladus
Explanation:
Enceladus orbits
Saturn between the smaller
Mimas and the larger
Tethys.
Enceladus is composed mostly of water ice and has the cleanest and purest
ice surface in the
Solar System. It's surface therefore appears
nearly white. The surface also has many unusual groves and relatively few
craters, like
Jupiter's moon
Ganymede. This indicates that the surface is young
and/or newly reformed. To explain this, some astronomers speculate that
Enceladus is susceptible to some sort of
volcanic activity. Enceladus was
originally discovered in 1789 by
William Herschel.
 APOD: November 3, 1995 - Jupiter's Moon Amalthea
APOD: November 3, 1995 - Jupiter's Moon Amalthea
Explanation:
Amalthea is
Jupiter's fifth largest moon, much smaller than
the four
Galilean
satellites
Io,
Europa,
Ganymede, and
Callisto.
The orbit of
Amalthea is inside of these moons, and with its long axis always
pointing toward
Jupiter. It's dark surface color is
probably due to sulfur being
expelled from Io.
Amalthea is not massive enough for its internal
gravity to make it spherical.
Amalthea was discovered in 1892 by Edward Barnard.
 APOD: October 13, 1995 - Jupiter, Io, and Ganymede's Shadow
APOD: October 13, 1995 - Jupiter, Io, and Ganymede's Shadow
Explanation:
Jupiter, the
solar system's largest planet,
is seen here next to
Io, its closest
Galilean moon.
On the cloud tops of
Jupiter
near the left edge of the picture can be seen a dark circular spot which is
caused by the shadow of
Jupiter's largest moon
Ganymede.
Jupiter's cloud tops show light bands
and dark belts. The clouds are primarily composed of
hydrogen and
helium,
but their intense colors are probably caused by very small amounts of
heavier elements such as sulfur or organic (carbon-containing) compounds.
 APOD: September 6, 1995 - Callisto: Dark Smashed Iceball
APOD: September 6, 1995 - Callisto: Dark Smashed Iceball
Explanation:
Callisto is a dirty battered world, showing the most beaten surface of
Jupiter's major moons. Made of a rocky core
covered by fractured ice,
Callisto's past collisions with large meteors are evident as large
craters surrounded by concentric rings. The four largest moons of Jupiter:
Io,
Europa,
Ganymede, and
Callisto were all discovered by
Galileo
and
Marius in 1610 with early telescopes and are now known as the
Galilean satellites. The
NASA spacecraft Galileo
is scheduled to arrive at Jupiter is December of 1995.
 APOD: September 4, 1995 - Ganymede: Moonquake World
APOD: September 4, 1995 - Ganymede: Moonquake World
Explanation:
Ganymede probably undergoes frequent ground shaking events not unlike
terrestrial earthquakes.
Ganymede, the largest moon of
Jupiter and the
Solar System,
has a thick outer coating of water ice. Passing Voyager spacecraft
found a large number of cracks and grooves in the ice so it is
thought that Ganymede, like the
Earth, has large shifting surface
masses called tectonic plates. Ganymede was discovered by
Galileo and
Marius in 1610, and is larger than the planets Mercury and Pluto. The
NASA spacecraft Galileo
is scheduled to arrive at Jupiter is December of 1995.