 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 APOD: 2022 January 4 - Moons Beyond Rings at Saturn
APOD: 2022 January 4 - Moons Beyond Rings at Saturn
Explanation:
What's happened to that moon of Saturn?
Nothing -- Saturn's moon
Rhea is just partly hidden behind Saturn's rings.
In 2010, the robotic Cassini spacecraft then orbiting Saturn took
this narrow-angle view looking across the
Solar System's most
famous rings.
Rings visible in the foreground include the thin
F ring on the outside and the much wider
A and B rings just interior to it.
Although it seems to be hovering
over the rings, Saturn's moon
Janus is actually far behind them.
Janus is one of
Saturn's smaller
moons
and measures only about 180 kilometers across.
Farther out from the camera is the heavily cratered
Rhea, a much larger moon
measuring 1,500 kilometers across.
The top of Rhea is visible only through
gaps in the rings.
After more than a decade of exploration and discovery, the
Cassini spacecraft ran
low on fuel in 2017 and was directed to
enter Saturn's atmosphere,
where it surely
melted.
 APOD: 2020 August 8 - Crescent Saturn
APOD: 2020 August 8 - Crescent Saturn
Explanation:
From Earth, Saturn never shows a crescent phase.
But when viewed from a spacecraft the
majestic giant planet
can show just a sunlit slice.
This image of crescent Saturn
in natural color was taken by the robotic
Cassini spacecraft in 2007.
It captures
Saturn's
rings from the side of the ring plane opposite
the Sun -- the unilluminated side -- another
vista not visible from Earth.
Visible are
subtle colors of
cloud bands, the complex
shadows of the rings on the planet, and
the shadow of the planet
on the rings.
The moons Mimas, at 2 o'clock, and
Janus 4 o'clock, can be seen as specks of
light, but the real challenge is to find
Pandora (8 o'clock).
From Earth, Saturn's disk is nearly full now and
opposite the Sun.
Along with bright fellow giant planet Jupiter it
rises in the early evening.
 APOD: 2019 October 17 - Moons of Saturn
APOD: 2019 October 17 - Moons of Saturn
Explanation:
On July 29, 2011 the Cassini spacecraft's
narrow-angle camera
took
this snapshot and captured 5
of
Saturn's moons, from just above the ringplane.
Left to right are small moons Janus and Pandora respectively
179 and 81 kilometers across,
shiny 504 kilometer diameter Enceladus,
and Mimas, 396 kilometers across, seen just next to Rhea.
Cut off by the right edge of the frame, Rhea is Saturn's
second largest moon at 1,528 kilometers across.
So
how many moons
does Saturn have?
Twenty new found outer satellites bring its total to 82 known moons,
and since Jupiter's moon total stands at 79, Saturn is the Solar System's new
moon king.
The newly announced
Saturnian satellites are all very small, 5
kilometers or so in diameter, and most are in retrograde orbits inclined
to Saturn's ringplane.
You can help
name
Saturn's new moons, but you should
understand the rules.
Hint: A knowledge of Norse, Inuit, and Gallic mythology will help.
 APOD: 2019 July 7 - Crescent Saturn
APOD: 2019 July 7 - Crescent Saturn
Explanation:
Saturn never shows a crescent phase -- from Earth.
But when viewed from beyond, the
majestic
giant planet can show an unfamiliar diminutive sliver.
This image of crescent Saturn in natural color was taken by the robotic
Cassini spacecraft in 2007.
The featured image captures
Saturn's
majestic rings from the side of the ring plane opposite
the Sun -- the unilluminated side -- another
vista not visible from Earth.
Pictured are many of
Saturn's photogenic wonders, including the
subtle colors of
cloud bands, the complex
shadows of the rings on the planet, and
the shadow of the planet
on the rings.
A careful eye will find the moons
Mimas (2 o'clock) and
Janus (4 o'clock),
but the real challenge is to find
Pandora (8 o'clock).
Saturn is now nearly
opposite from the Sun in the Earth's sky and so
can be seen
in the evening starting just after sunset for the rest of the night.
 APOD: 2018 May 10 - Galaxies in the River
APOD: 2018 May 10 - Galaxies in the River
Explanation:
Large galaxies grow by eating small ones.
Even our own galaxy practices galactic
cannibalism, absorbing small galaxies that get too close and
are captured by
the Milky Way's gravity.
In fact, the
practice is common
in the universe and illustrated by this striking pair of interacting galaxies
from the banks of the southern constellation
Eridanus,
The River.
Located over 50 million light years away,
the large, distorted spiral NGC 1532 is seen locked in a
gravitational
struggle with dwarf galaxy NGC 1531 (right of center),
a struggle the smaller galaxy will
eventually lose.
Seen edge-on, spiral NGC 1532 spans about 100,000 light-years.
Nicely detailed in this sharp image, the
NGC 1532/1531 pair is thought to be similar
to the well-studied system of face-on spiral and small companion
known as M51.
 APOD: 2017 June 18 - Views from Cassini at Saturn
APOD: 2017 June 18 - Views from Cassini at Saturn
Explanation:
What has the Cassini orbiter seen at Saturn?
The featured music video
shows some of the early highlights.
In the first time-lapse sequence (00:07), a vertical line appears that is really Saturn's
thin rings seen nearly edge-on.
Soon some of
Saturn's
moon shoot past.
The next sequence (00:11) features Saturn's unusually
wavy F-ring that is constrained by the two
shepherd moons that are also continually perturbing it.
Soon much of Saturn's
extensive ring system flashes by, sometimes juxtaposed to the grandeur of the immense planet itself.
Cloud patterns on
Titan (00:39) and
Saturn (00:41) are highlighted.
Clips from flybys of several of Saturn's moon are then shown, including
Phoebe,
Mimas,
Epimetheus, and
Iapetus.
In other sequences, moons of Saturn
appear to pass each other as they orbit Saturn.
Background star fields seen by Cassini are sometimes intruded upon by bright passing moons.
The robotic Cassini spacecraft has been revolutionizing humanity's knowledge of Saturn and its moons since
2004.
In September,
Cassini's mission will be brought to a
dramatic conclusion as the spacecraft will be
directed to dive into ringed giant.
 APOD: 2014 November 2 - Titan Beyond the Rings
APOD: 2014 November 2 - Titan Beyond the Rings
Explanation:
When orbiting Saturn, be sure to watch for breathtaking superpositions of moons and rings.
One such picturesque vista was visible recently to the robot
Cassini spacecraft
now orbiting Saturn.
In 2006 April, Cassini
captured Saturn's
A and
F
rings stretching in front of
cloud-shrouded Titan.
Near the rings and appearing just above Titan was
Epimetheus, a moon which orbits just outside the
F ring.
The dark space in the
A ring is called the
Encke Gap, although several thin knotted ringlets and even the small moon
Pan orbit there.
 APOD: 2012 May 21 - A Close Pass of Saturn's Moon Dione
APOD: 2012 May 21 - A Close Pass of Saturn's Moon Dione
Explanation:
What's that past Dione?
When making its closest pass yet of Saturn's moon
Dione
late last year, the robotic Cassini spacecraft snapped this far-ranging picture featuring Dione, Saturn's rings, and the two small moons
Epimetheus and
Prometheus.
The above image
captures part of the heavily cratered snow-white surface of the 1,100 kilometer wide
Dione, the thinness of Saturn's rings, and the
comparative darkness
of the smaller moon Epimetheus.
The image was taken when Cassini was only about 100,000 kilometers from the
large icy moon.
Future events in Cassini's
continuing exploration of Saturn and its moons include tomorrow's
flyby of Titan
and imaging the distant Earth
passing behind Saturn in June.
 APOD: 2011 June 13 - Views from Cassini at Saturn
APOD: 2011 June 13 - Views from Cassini at Saturn
Explanation:
What has the Cassini orbiter seen since arriving at Saturn?
The above music video
shows some of the highlights.
In the first time-lapse sequence (00:07), a vertical line appears that is really Saturn's
thin rings seen nearly edge-on.
Soon some of
Saturn's
moon shoot past.
The next sequence (00:11) features Saturn's unusually
wavy F-ring that is constrained by the two
shepherd moons that are also continually perturbing it.
Soon much of Saturn's
extensive ring system flashes by, sometimes juxtaposed to the grandeur of the immense planet itself.
Cloud patterns on
Titan (00:39) and
Saturn (00:41) are highlighted.
Clips from flyby's of several of Saturn's moon are then shown, including
Phoebe,
Mimas,
Epimetheus, and
Iapetus.
In other sequences, moons of Saturn
appear to pass each other as they orbit Saturn.
Background star fields seen by Cassini are sometimes intruded upon by bright passing moons.
The robotic Cassini spacecraft has been revolutionizing humanity's knowledge of Saturn and its moons since
2004.
 APOD: 2010 July 12 - Moons Beyond the Rings of Saturn
APOD: 2010 July 12 - Moons Beyond the Rings of Saturn
Explanation:
What's happened to that moon of Saturn?
Nothing -- Saturn's moon Rhea is just partly hidden behind Saturn's rings.
In April, the robotic Cassini spacecraft now orbiting Saturn took this
narrow-angle view looking across the
Solar System's most
famous rings.
Rings visible in the foreground include the thin
F ring on the outside and the much wider
A and B rings just interior to it.
Although it seems to be hovering
over the rings, Saturn's moon
Janus is actually far behind them.
Janus is one of
Saturn's smaller
moons
and measures only about 180 kilometers across.
Farther out from the camera is the heavily cratered
Rhea, a much larger moon
measuring 1,500 kilometers across.
The top of Rhea is visible only through
gaps in the rings.
The Cassini mission around Saturn has
been extended to
2017
to better study the complex planetary system as its season changes from
equinox to
solstice.
 APOD: 2010 May 31 - Moons and Rings Before Saturn
APOD: 2010 May 31 - Moons and Rings Before Saturn
Explanation:
While cruising around Saturn,
be on the lookout for picturesque juxtapositions of moons and rings.
Another striking alignment occurred last March in the view of humanity's
Saturn-orbiting Cassini spacecraft.
Rhea, one of Saturn's larger moons,
was caught passing
Epimetheus, one of Saturn's smaller moons.
Epimetheus, as
pictured above, is actually well behind the heavily cratered Rhea.
Further back, several of the
complex rings of Saturn can be seen crossing the image horizontally.
Behind both the
moons and rings is giant Saturn itself,
showing expansive but featureless clouds in the
green light where the above image was taken.
The Cassini mission around Saturn has now
been extended to
2017
to better study the complex planetary system as its season changes from
equinox to
solstice.
 APOD: 2009 May 5 - Titan Beyond the Rings
APOD: 2009 May 5 - Titan Beyond the Rings
Explanation:
When orbiting Saturn, be sure to watch for breathtaking superpositions of moons and rings.
One such picturesque vista was visible recently to the robot
Cassini spacecraft
now orbiting Saturn.
In 2006 April, Cassini
captured Saturn's
A and
F
rings stretching in front of
cloud-shrouded Titan.
Near the rings and appearing just above Titan was
Epimetheus, a moon which orbits just outside the
F ring.
The dark space in the
A ring is called the
Encke Gap, although several thin knotted ringlets and even the small moon
Pan orbit there.
Cassini and
curious Earthlings await the coming
Saturnian equinox this summer when the
ring plane
will point directly at the Sun.
Mysterious spokes and telling
shadows are expected to become
visible
that might give away more clues about the nature of
Saturn's ring
particles.
 APOD: 2008 May 5 - A Persistent Electrical Storm on Saturn
APOD: 2008 May 5 - A Persistent Electrical Storm on Saturn
Explanation:
How do large storms evolve on Saturn?
On Earth, a
hurricane can persist for weeks, while the
Great Red Spot on
Jupiter has been in existence for
over 150 years.
On Saturn,
a storm system has now set a new endurance record,
now being discernable for greater than three months.
Electrical signals
were detected from the storm in late November of 2007, while the
above image
was taken in early March 2008.
The storm has roughly the width of planet Earth.
Planetary scientists hypothesize that the storm runs deep into Saturn's cloud tops.
The above image
is shown in exaggerated colors combining violet and green light with light normally
too red
for humans to see.
Visible on the upper right are shadows of
Saturn's
expansive ring system.
Careful inspection will reveal Saturn's small moon
Janus just below a ring shadow.
Understanding weather on other planets helps
atmospheric scientists better understand our Earth's weather.
Observers of our
Solar System's
huge ringed world will be tracking the storm to see how it evolves and how
long it will ultimately last.
 APOD: 2008 February 11 - Saturn's Moon Epimetheus from the Cassini Spacecraft
APOD: 2008 February 11 - Saturn's Moon Epimetheus from the Cassini Spacecraft
Explanation:
How did Epimetheus form?
No one is yet sure.
To help answer that question,
this small moon has recently been imaged again in great detail by the
robot spacecraft Cassini now orbiting
Saturn.
Epimetheus
sometimes
orbits Saturn in front of
Janus,
another small satellite, but sometimes behind.
The above image,
taken last December,
shows a surface covered with craters
indicating great age.
Epimetheus spans about 115 kilometers across.
Epimetheus
does not have enough
surface gravity to restructure itself into a
sphere.
The flattened face of
Epimetheus shown
above
might have been created by a
single large impact.
 APOD: 2007 October 23 - Crescent Saturn
APOD: 2007 October 23 - Crescent Saturn
Explanation:
Saturn never shows a crescent phase -- from Earth.
But when viewed from beyond, the
majestic giant planet
can show an unfamiliar diminutive sliver.
This image of crescent Saturn in natural color was
taken by the robotic
Cassini
spacecraft in May.
The image captures
Saturn's
majestic rings from the side of the ring plane opposite
the Sun -- the unilluminated side -- another
vista not visible from Earth.
Pictured are many of Saturn's photogenic wonders, including the
subtle colors of
cloud bands, the complex
shadows of the rings on the planet,
the shadow of the planet
on the rings, and the moons
Mimas (2 o'clock),
Janus (4 o'clock), and
Pandora (8 o'clock).
As Saturn moves towards
equinox in 2009,
the ring shadows are becoming smaller and moving toward the equator.
During equinox, the rings will be
nearly invisible
from Earth and project only an extremely
thin shadow line onto the planet.
 APOD: 2007 January 31 - Movie: Cassini Crosses Saturn's Ring Plane
APOD: 2007 January 31 - Movie: Cassini Crosses Saturn's Ring Plane
Explanation:
What would the rings of Saturn look like if you passed right through the ring plane?
To find out, NASA aimed cameras from the
Cassini spacecraft right at
Saturn's rings as the
robotic explorer passed from the sunlit side of the rings to the
shadowed side.
Resulting images from a vantage point outside the rings and most moons,
but inside the orbit of Titan,
have been gathered together in the
above time-lapse movie.
The dramatic movie
demonstrates that ring particle density and
reflectivity makes some parts of the shadowed side nearly the
photographic negative
of the sunlit side, but nearly empty regions remain continually dark.
Visible also are Saturn-orbiting moons
Enceladus,
Mimas,
Janus,
Epimetheus,
Prometheus, and
Pandora.
The extreme
thinness of Saturn's rings
can be appreciated from frames taken near the crossing time.
 APOD: 2006 November 7 - Janus: Potato Shaped Moon of Saturn
APOD: 2006 November 7 - Janus: Potato Shaped Moon of Saturn
Explanation:
Janus is one of the stranger moons of Saturn.
First, Janus
travels in an unusual orbit around Saturn where it periodically trades places with its sister moon
Epimetheus,
which typically orbits about 50 kilometers away.
Janus,
although slightly larger than
Epimetheus, is
potato-shaped and
has a largest diameter of about 190 kilometers.
Next, Janus is covered with large craters but strangely appears to lack small craters.
One possible reason for this is a fine dust that might cover the small moon,
a surface also hypothesized for
Pandora and
Telesto.
Pictured above,
Janus was captured in front of the
cloud tops of
Saturn in late September.
 APOD: 2005 November 2 - Epimetheus and Janus: Interchangeable Moons of Saturn
APOD: 2005 November 2 - Epimetheus and Janus: Interchangeable Moons of Saturn
Explanation:
These two moons change places.
Epimetheus and
Janus,
two small moons of
Saturn,
actually switch positions as they orbit their home planet.
The orbital radii of the moons are strangely separated by less than the
radii of the moons themselves: about 50 kilometers.
One moon orbits Saturn well ahead of the other, at first.
As the two moons gravitationally attract, they approach each other and, every few years, actually
pass and trade orbits.
This strange dance creates speculation that
Epimetheus and Janus were once joined and later split from each other.
Pictured above,
the two moons were photographed rounding their orbits just outside of
Saturn's F ring.
The above image was taken in early September by the robot
Cassini spacecraft,
also orbiting Saturn.
 APOD: 2005 August 24 - Epimetheus: A Small Moon of Saturn
APOD: 2005 August 24 - Epimetheus: A Small Moon of Saturn
Explanation:
How did Epimetheus form?
No one is yet sure.
To help answer that question,
this small moon has recently been imaged again in great detail by the
robot spacecraft Cassini now orbiting
Saturn.
Epimetheus
sometimes
orbits Saturn in front of
Janus,
another small satellite, but sometimes behind.
The above false-color image, taken during mid July,
shows a surface covered with craters
indicating great age.
Epimetheus spans about 115 kilometers across.
Epimetheus
does not have enough
surface gravity to restructure itself into a
sphere.
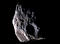 APOD: 2005 April 29 - Small Moon Epimetheus
APOD: 2005 April 29 - Small Moon Epimetheus
Explanation:
Small saturnian moon
Epimetheus
(ep-ee-MEE-thee-us)
is at most 116 kilometers across.
Its cratered surface and irregular shape are highlighted
by dramatic shadows in
this
composite close-up image from the Cassini spacecraft.
However, orbiting 91,000 kilometers above
Saturn's cloud tops,
Epimetheus
is not alone.
Similar in size, saturnian moon
Janus
occupies an orbit separated from
Epimetheus' by only about 50 kilometers.
The two actually approach each other once every four years,
but instead of colliding, the moons
deftly exchange orbits
and
move apart again!
In fact, co-orbiting Epimetheus and Janus both consist mostly of
porous
water ice and could have
formed from the breakup of a single parent body.
The small moons are also believed to play a role
in maintaining the outer edge of
Saturn's A ring.
 APOD: 2004 July 21 - A Shadow on the Rings of Saturn
APOD: 2004 July 21 - A Shadow on the Rings of Saturn
Explanation:
This picture of Saturn could not have been taken from Earth.
No Earth based picture could possibly view the
night side of Saturn
and the corresponding shadow cast across Saturn's rings.
Since Earth is much closer to the
Sun than
Saturn,
only the day side of the planet is visible from the Earth.
Rather, this picture was taken by the robot
Cassini spacecraft that began orbiting Saturn earlier this month.
The dark western limb of
Saturn
looms large on the image right, while complex concentrations of
small ring particles reflect sunlight on the image left.
Saturn's enigmatic F ring is visible around the outside, showing
mysterious knots.
The small moon
Epimetheus,
only about 100 kilometers across, can also been seen on the far left.
Cassini is scheduled to drop a
probe toward the largest moon
Titan in December.
 APOD: October 18, 1998 - Saturns Rings Seen Sideways
APOD: October 18, 1998 - Saturns Rings Seen Sideways
Explanation:
Saturn's rings
are actually very thin.
This picture
from the
Hubble Space Telescope
was taken on August 6, 1995 when the rings lined up sideways as seen from
Earth.
Saturn's largest moon
Titan is seen on the left, and Titan's
shadow can be seen on
Saturn's cloud tops!
Titan itself looks a brownish color because of its thick atmosphere. Four
other moons of Saturn can be seen just above the ring plane, which are,
from left to right:
Mimas,
Tethys,
Janus, and Enceladus. If you look
carefully, you will note that the dark band across the planet is actually
the shadow of the rings, and is slightly displaced from the real
rings - which are best seen away from the planet.
Saturn's
rings are not solid - they are composed of ice chunks which range
in size from a grain of sand to a house.
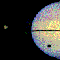 APOD: May 24, 1997 - Saturn's Rings Seen Sideways
APOD: May 24, 1997 - Saturn's Rings Seen Sideways
Explanation:
Saturn's rings
are actually very thin.
This picture
from the
Hubble Space Telescope
was taken on August 6, 1995 when the rings lined up sideways as seen from
Earth.
Saturn's largest moon
Titan is seen on the left, and Titan's
shadow can be seen on
Saturn's cloud tops!
Titan itself looks a brownish color because of its thick atmosphere. Four
other moon's of Saturn can be seen just above the ring plane, which are,
from left to right:
Mimas,
Tethys,
Janus, and Enceladus. If you look
carefully, you will note that the dark band across the planet is actually
the shadow of the rings, and is slightly displaced from the real
rings - which are best seen away from the planet.
Saturn's
rings are not solid - they are composed of ice chunks which range
in size from a grain of sand to a house.
 APOD: May 12, 1996 - Tracking Saturn's Moons
APOD: May 12, 1996 - Tracking Saturn's Moons
Explanation:
These five pairs of
Hubble Space Telescope images track some of
Saturn's moons as they orbit the ringed planet.
A pair of images was taken every 97 minutes on November 21, 1995 with
the Wide Field Planetary Camera-2, the normally bright ring system
appearing nearly edge-on. In the top pair, the large
bright moon Dione hangs above center while the smaller moons
Pandora, Prometheus,
and Mimas (top right image)
appear near the planet's disk close to the outer ring. By the second and third
pair of images, moons Rhea
and Epimetheus have joined the dance.
During the Saturn ring plane crossings, the reduction in light from
the edge-on rings provided an opportunity for astronomer's to
explore Saturn's complex moon system and search for elusive
undiscovered satellites.
 APOD: April 29, 1996 - Saturn's Rings Seen Sideways
APOD: April 29, 1996 - Saturn's Rings Seen Sideways
Explanation:
Saturn's rings
are actually very thin.
This picture
from the
Hubble Space Telescope
was taken on August 6, 1995 when the rings lined up sideways as seen from
Earth.
Saturn's largest moon
Titan is seen on the left, and Titan's
shadow can be seen on
Saturn's cloud tops!
Titan itself looks a brownish color because of its thick atmosphere. Four
other moon's of Saturn can be seen just above the ring plane, which are,
from left to right:
Mimas,
Tethys,
Janus, and Enceladus. If you look
carefully, you will note that the dark band across the planet is actually
the shadow of the rings, and is slightly displaced from the real
rings - which are best seen away from the planet.
Saturn's
rings are not solid - they are composed of ice chunks which range
in size from a grain of sand to a house.