 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 APOD: 2025 December 29 – M1: The Crab Nebula
APOD: 2025 December 29 – M1: The Crab Nebula
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The
Crab Nebula, the result of a
supernova
seen in
1054 AD,
is filled with
mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex but appear to have
less mass than expelled in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
The featured image was taken by an amateur astronomer in
Leesburg,
Florida,
USA over three nights last month.
It was captured in
three primary colors
but with extra detail provided by
specific emission
by hydrogen gas.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10
light years.
In the Nebula's very center lies a pulsar: a neutron star as massive as the Sun but
with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2025 August 24 – The Spinning Pulsar of the Crab Nebula
APOD: 2025 August 24 – The Spinning Pulsar of the Crab Nebula
Explanation:
At the core of the
Crab Nebula lies a city-sized, magnetized
neutron star spinning 30 times a second.
Known as the
Crab Pulsar, it is the bright spot
in the center of the gaseous swirl at the nebula's core.
About twelve light-years across, the spectacular picture frames
the glowing gas, cavities and swirling filaments near the
Crab Nebula's center.
The featured picture combines
visible light
from the
Hubble Space Telescope in purple,
X-ray light from the
Chandra X-ray Observatory in blue,
and infrared light from the
Spitzer Space Telescope in red.
Like a
cosmic
dynamo, the Crab pulsar powers the
emission from the nebula, driving a
shock wave through surrounding
material and accelerating the spiraling electrons.
With more mass than
the Sun
and the density of an atomic nucleus,the
spinning pulsar
is the collapsed core of a massive star that
exploded.
The outer parts of the Crab Nebula are the expanding
remnants of the star's component gases.
The supernova explosion was witnessed on planet Earth in
the year 1054.
 APOD: 2025 August 8 – Dawn of the Crab
APOD: 2025 August 8 – Dawn of the Crab
Explanation:
One of the all-time historic skyscapes occured in July 1054, when the
Crab Supernova
blazed into the dawn sky.
Chinese court astrologers
first saw the
Guest Star
on the morning of 4 July 1054
next to the star
Tianguan
(now cataloged as
Zeta Tauri).
The
supernova
peaked in late July 1054 a bit brighter than Venus,
and was visible in the daytime for 23 days.
The Guest Star was so bright that every culture around the world
inevitably discovered the supernova independently, although only nine
reports survive, including those from China,
Japan, and
Constantinople.
This iPhone picture is from
Signal Hill
near Tucson on the morning of 26 July 2025,
faithfully re-creates the year 1054 Dawn of the Crab,
showing the sky as seen by
Hohokam peoples.
The planet Venus, as a stand-in for the
supernova,
is close to the position of what is now the
Crab Nebula supernova remnant.
Step outside on a
summer dawn with bright Venus, and ask yourself "What would you have
thought in ancient times when suddenly seeing the Dawn of the Crab?"
 APOD: 2025 May 8 - M1: The Incredible Expanding Crab
APOD: 2025 May 8 - M1: The Incredible Expanding Crab
Explanation:
Cataloged as M1, the Crab Nebula is the first on
Charles Messier's famous list of things which are
not comets.
In fact, the Crab Nebula is
now known to be a supernova remnant, an expanding
cloud of debris from the death explosion of a massive star.
The violent birth of the Crab was
witnessed by astronomers
in the year 1054.
Roughly
10 light-years across,
the nebula is still expanding
at a rate
of about 1,500 kilometers per second.
You can see the expansion by
comparing these sharp images from the
Hubble Space Telescope and James Webb Space Telescope.
The Crab's dynamic, fragmented filaments were captured in visible
light by Hubble in 2005 and Webb in infrared light in 2023.
This cosmic crustacean
lies about 6,500 light-years away in the
constellation Taurus.
 APOD: 2024 December 19 - Messier 2
APOD: 2024 December 19 - Messier 2
Explanation:
After the Crab Nebula,
this giant star cluster is the second entry in
18th century astronomer Charles Messier's famous list of
things that are not comets.
M2 is one of the largest globular star clusters now known to
roam the halo of our Milky Way galaxy.
Though Messier originally described it as a nebula without stars, this
stunning
Hubble image resolves stars across the cluster's central 40
light-years.
Its population
of stars numbers close to 150,000, concentrated
within a total diameter of around 175 light-years.
About 55,000 light-years distant toward the constellation Aquarius,
this ancient denizen of the Milky Way, also
known as NGC 7089,
is 13 billion years old.
An extended
stellar debris stream, a signature of
past gravitational tidal disruption, was recently found to be
associated
with Messier 2.
 APOD: 2024 July 23 – The Crab Nebula from Visible to X Ray
APOD: 2024 July 23 – The Crab Nebula from Visible to X Ray
Explanation:
What powers the Crab Nebula?
A city-sized magnetized
neutron star spinning around 30 times a second.
Known as the Crab Pulsar, it is the bright spot in the center
of the gaseous swirl at the nebula's core.
About 10 light-years across, the
spectacular picture of the
Crab Nebula
(M1) frames a swirling central disk and complex filaments of surrounding and expanding glowing gas.
The picture combines
visible light from the
Hubble Space Telescope in red and blue with
X-ray light
from the
Chandra X-ray Observatory shown in white,
and diffuse X-ray emission detected by
Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) in diffuse purple.
The central pulsar
powers the
Crab Nebula's
emission and
expansion
by slightly slowing its spin rate,
which drives out a
wind of energetic
electrons.
The
featured image released today, the
25th Anniversary
of the
launch of NASA's
flagship-class X-ray Observatory:
Chandra.
 APOD: 2023 December 26 – IC 443: The Jellyfish Nebula
APOD: 2023 December 26 – IC 443: The Jellyfish Nebula
Explanation:
Why is this jellyfish swimming in a sea of stars?
Drifting near bright star
Eta Geminorum,
seen at the right, the
Jellyfish Nebula
extends its tentacles from the bright arcing ridge of emission left of center.
In fact, the cosmic
jellyfish
is part of bubble-shaped
supernova remnant IC 443,
the expanding debris cloud from a
massive star that exploded.
Light from the explosion first reached
planet Earth over
30,000 years ago.
Like its cousin in astronomical waters, the
Crab Nebula supernova remnant IC 443 is
known to harbor a
neutron star --
the remnant of the collapsed stellar core.
The Jellyfish Nebula is about 5,000
light-years away.
At that distance, the
featured image would
span about 140 light-years across.
 APOD: 2023 November 15 - M1: The Incredible Expanding Crab
APOD: 2023 November 15 - M1: The Incredible Expanding Crab
Explanation:
Cataloged as M1,
the Crab Nebula is the first on
Charles
Messier's famous list of things which are
not comets.
In fact, the Crab Nebula is
now known to be a supernova remnant, an expanding
cloud of debris from the death explosion of a massive star.
The violent birth of the Crab was
witnessed
by astronomers in the year 1054.
Roughly
10 light-years across,
the nebula is still expanding
at a rate
of about 1,500 kilometers per second.
You can see the expansion by
comparing these sharp images from the
Hubble Space Telescope and James Webb Space Telescope.
The Crab's dynamic, fragmented filaments were captured in visible
light by Hubble in 2005 and Webb in infrared light in 2023.
This cosmic crustacean
lies about 6,500 light-years away in the
constellation Taurus.
 APOD: 2023 November 9 - M1: The Crab Nebula
APOD: 2023 November 9 - M1: The Crab Nebula
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first object on
Charles Messier's
famous 18th century list of things which are not comets.
In fact,
the Crab
is now known to be a
supernova
remnant,
debris from the death explosion of a massive star
witnessed
by astronomers in the year 1054.
This sharp image from the
James Webb Space Telescope’s
NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) and
MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument)
explores the eerie glow and fragmented strands
of the still
expanding cloud of interstellar debris
in infrared light.
One of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers,
the Crab Pulsar,
a neutron star spinning 30 times a second,
is visible as a bright spot near
the nebula's center.
Like a cosmic dynamo,
this collapsed remnant of the stellar core
powers the Crab's emission across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spanning about 12 light-years, the Crab Nebula is a mere
6,500 light-years away in the head-strong
constellation Taurus.
 APOD: 2023 March 20 – M1: The Expanding Crab Nebula
APOD: 2023 March 20 – M1: The Expanding Crab Nebula
Explanation:
Are your eyes good enough to see the Crab Nebula expand?
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first on
Charles Messier's
famous
list of things which are
not comets.
In fact, the Crab is now known to be a
supernova remnant, an expanding
cloud of debris from the explosion of a massive star.
The violent birth of the Crab was
witnessed
by astronomers in the year 1054.
Roughly 10
light-years across today, the nebula is still
expanding
at a rate of over 1,000 kilometers per second.
Over the past decade, its expansion has been documented in this
stunning
time-lapse movie.
In each year from 2008 to 2022, an image was produced with the same
telescope and camera from a remote observatory in
Austria.
The sharp, processed frames even reveal the
dynamic energetic emission surrounding the rapidly
spinning pulsar at the center.
The Crab Nebula
lies about 6,500 light-years away
toward the constellation
of the Bull
(Taurus).
 APOD: 2023 January 15 – M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
APOD: 2023 January 15 – M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The Crab Nebula, the result of a supernova seen in
1054 AD, is filled with mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex, but appear to have
less mass than expelled in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
The featured image,
taken by the Hubble Space Telescope,
is presented in three colors chosen for
scientific interest.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light-years.
In the nebula's very center lies a
pulsar: a
neutron star as massive as the
Sun
but with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2022 August 21 - The Spinning Pulsar of the Crab Nebula
APOD: 2022 August 21 - The Spinning Pulsar of the Crab Nebula
Explanation:
At the core of the
Crab Nebula lies a city-sized, magnetized
neutron star spinning 30 times a second.
Known as the
Crab Pulsar, it is the bright spot
in the center of the gaseous swirl at the nebula's core.
About twelve light-years across, the spectacular picture frames
the glowing gas, cavities and swirling filaments near the
Crab Nebula's center.
The featured picture combines
visible light
from the
Hubble Space Telescope in purple,
X-ray light from the
Chandra X-ray Observatory in blue,
and infrared light from the
Spitzer Space Telescope in red.
Like a
cosmic
dynamo the Crab pulsar powers the
emission from the nebula, driving a
shock wave through surrounding
material and accelerating the spiraling electrons.
With more mass than
the Sun
and the density of an atomic nucleus,the
spinning pulsar
is the collapsed core of a massive star that
exploded.
The outer parts of the Crab Nebula are the expanding
remnants of the star's component gasses.
The supernova explosion was witnessed on planet Earth in
the year 1054.
 APOD: 2022 March 4 - The Multiwavelength Crab
APOD: 2022 March 4 - The Multiwavelength Crab
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first object on
Charles
Messier's famous list of things which are not comets.
In fact, the
Crab
is now known to be a
supernova
remnant, expanding debris from massive star's death explosion,
witnessed on planet Earth in 1054 AD.
This
brave new image offers a 21st century
view of the Crab Nebula by presenting image data from across the
electromagnetic
spectrum as wavelengths of visible light.
From space,
Chandra (X-ray)
XMM-Newton (ultraviolet),
Hubble (visible), and
Spitzer (infrared),
data are in purple, blue, green, and yellow hues.
From the ground,
Very Large Array
radio wavelength data is shown in red.
One of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers,
the Crab Pulsar,
a neutron star spinning 30 times a second,
is the bright spot near picture center.
Like a cosmic dynamo,
this collapsed remnant of the stellar core
powers the Crab's emission across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spanning about 12 light-years, the Crab Nebula is
6,500 light-years away in the constellation
Taurus.
 APOD: 2021 December 24 - M1: The Crab Nebula
APOD: 2021 December 24 - M1: The Crab Nebula
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first object on
Charles Messier's
famous 18th century list of things which are not comets.
In fact,
the Crab
is now known to be a
supernova remnant,
debris from the death explosion of a massive star,
witnessed
by astronomers in the year 1054.
This sharp, ground-based
telescopic view combines broadband color data with
narrowband data that tracks emission from ionized sulfur, hydrogen, and
oxygen atoms to explore the tangled filaments within
the still expanding cloud.
One of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers,
the Crab Pulsar,
a neutron star spinning 30 times a second,
is visible as a bright spot near
the nebula's center.
Like a cosmic dynamo,
this collapsed remnant of the stellar core
powers the Crab's emission across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spanning about 12 light-years, the Crab Nebula is a mere
6,500 light-years away in the
constellation Taurus.
 APOD: 2021 October 22 - A Comet and a Crab
APOD: 2021 October 22 - A Comet and a Crab
Explanation:
This pretty field of view spans over 2 degrees
or 4 full moons on the sky,
filled with stars toward the constellation Taurus, the Bull.
Above and right of center in the frame you can spot the faint fuzzy reddish
appearance of Messier 1 (M1),
also known as the Crab Nebula.
M1 is the first object in 18th century comet hunter
Charles Messier's famous catalog of things which are
definitely not comets.
Made from image data captured this October 11,
there is a comet in the picture though.
Below center and left lies the faint greenish coma and dusty
tail of periodic comet
67P Churyumov-Gerasimenko,
also known as Rosetta's comet.
In the 21st century, it became the
final resting place of
robots from planet Earth.
Rosetta's comet is
now returning to the inner solar system, sweeping
toward its next perihelion or closest approach to the Sun, on November 2.
Too faint to be seen
by eye alone, the comet's next perigee or closest
approach to Earth will be November 12.
 APOD: 2021 May 19 - The Jellyfish and Mars
APOD: 2021 May 19 - The Jellyfish and Mars
Explanation:
Normally faint and elusive, the Jellyfish Nebula is caught in
this alluring scene.
In the telescopic field of view two bright yellowish stars,
Mu and
Eta
Geminorum, stand just below and above the Jellyfish Nebula at the left.
Cool red giants, they lie at the foot of the
celestial
twin.
The Jellyfish Nebula itself floats below and left of center, a bright arcing
ridge of emission with dangling tentacles.
In fact, the cosmic jellyfish is part of bubble-shaped
supernova remnant IC 443, the expanding
debris cloud from a
massive star that exploded.
Light from that explosion first reached planet Earth over 30,000 years ago.
Like its cousin in
astrophysical waters the
Crab Nebula supernova remnant,
the Jellyfish Nebula is
known
to harbor a neutron star, the remnant of the collapsed stellar core.
Composed on April 30, this telescopic snapshot also captures Mars.
Now wandering
through early evening skies,
the Red Planet also shines with a yellowish glow on the
right hand side of the field of view.
Of course, the Jellyfish Nebula is about 5,000 light-years away, while
Mars is currently
almost 18 light-minutes from Earth.
 APOD: 2021 February 9 - Flashes of the Crab Pulsar
APOD: 2021 February 9 - Flashes of the Crab Pulsar
Explanation:
It somehow survived an explosion that would surely have destroyed our Sun.
Now it is spins 30 times a second and is famous for the its rapid flashes.
It is the
Crab Pulsar, the rotating
neutron star remnant of the supernova that created the
Crab Nebula.
A careful eye can spot the pulsar flashes in the
featured time-lapse video,
just above the image center.
The video was created by adding together images taken only when the pulsar was flashing,
as well as co-added images from other relative times.
The Crab Pulsar flashes may have been
first noted
by an unknown woman attending a
public observing night
at the University of Chicago in 1957 -- but who was not believed.
The progenitor supernova explosion was seen by many in the year 1054 AD.
The expanding Crab Nebula remains a
picturesque
expanding
gas cloud that
glows across the
electromagnetic spectrum.
The pulsar is now thought to have survived the
supernova explosion because it is composed of extremely-dense
quantum-degenerate matter.
 APOD: 2020 September 6 - M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
APOD: 2020 September 6 - M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The Crab Nebula, the result of a supernova seen in
1054 AD, is filled with mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex, but appear to have
less mass than expelled in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
The featured image,
taken by the Hubble Space Telescope,
is presentedi in three colors chosen for
scientific interest.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light-years.
In the nebula's very center lies a
pulsar: a
neutron star as massive as the
Sun
but with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2020 January 19 - M1: The Incredible Expanding Crab Nebula
APOD: 2020 January 19 - M1: The Incredible Expanding Crab Nebula
Explanation:
Are your eyes good enough to see the Crab Nebula expand?
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first on
Charles Messier's
famous
list of things which are
not comets.
In fact, the Crab is
now known to be a supernova remnant, an expanding
cloud of debris from the explosion of a massive star.
The violent birth of the Crab was
witnessed
by astronomers in the year 1054.
Roughly 10
light-years across today, the nebula is still
expanding
at a rate of over 1,000 kilometers per second.
Over the past decade, its expansion has been documented in
this stunning
time-lapse movie.
In each year from 2008 to 2017, an image was produced with the same
telescope and camera from a remote observatory in
Austria.
Combined in the
time-lapse movie,
the 10 images represent 32 hours of total
integration time.
The sharp, processed frames even reveal the
dynamic
energetic emission within the incredible expanding Crab.
The Crab Nebula
lies about 6,500 light-years away in the
constellation Taurus.
 APOD: 2019 April 24 - The Shape of the Southern Crab
APOD: 2019 April 24 - The Shape of the Southern Crab
Explanation:
The
symmetric, multi-legged appearance
of the Southern Crab Nebula is
certainly distinctive.
About 7,000 light-years distant toward the southern sky
constellation Centaurus, its glowing nested hourglass shapes
are produced by the remarkable symbiotic binary star system at its center.
The nebula's
dramatic stellar duo consists
of a hot white dwarf star and
cool, pulsating red giant star shedding outer layers
that fall onto the smaller, much hotter companion.
Embedded in a disk of material, outbursts from the white dwarf
cause an outflow of gas driven away both above and below the disk
resulting in the
bipolar hourglass shapes.
The bright central shape is about half a light-year across.
This
new Hubble Space Telescope image
celebrates the 29th anniversary
of Hubble's launch on April 24, 1990 on board the Space Shuttle
Discovery.
 APOD: 2019 April 4 - Messier 2
APOD: 2019 April 4 - Messier 2
Explanation:
After the Crab Nebula, M1,
this giant star cluster is the second entry in
18th century astronomer Charles Messier's famous list of
things that are not comets.
M2 is one of the largest globular star clusters now known to
roam the halo of our Milky Way galaxy.
Though Messier originally described it as a nebula without stars, this
stunning
Hubble image resolves stars across the central 40 light-years of M2.
Its population
of stars numbers close to 150,000, concentrated
within a total diameter of around 175 light-years.
About 55,000 light-years distant toward the constellation Aquarius,
this ancient denizen of the Milky Way, also
known as NGC 7089,
is 13 billion years old.
 APOD: 2019 March 7 - Sharpless 249 and the Jellyfish Nebula
APOD: 2019 March 7 - Sharpless 249 and the Jellyfish Nebula
Explanation:
Normally faint and elusive, the Jellyfish Nebula is caught in
this alluring
telescopic field of view.
The entire scene is a two panel mosaic constructed using narrowband
image data, with emission from sulfur, hydrogen and oxygen atoms
shown in red, green and blue hues.
It's anchored right and left by two bright stars,
Mu and
Eta
Geminorum, at the foot of the
celestial
twin.
The Jellyfish Nebula itself is right of center, the brighter arcing
ridge of emission with dangling tentacles.
In fact, the cosmic jellyfish is part of bubble-shaped
supernova remnant IC 443, the expanding
debris cloud from a
massive
star that exploded.
Light from the explosion first reached planet Earth over 30,000 years
ago.
Like its cousin in
astrophysical waters the
Crab Nebula
supernova remnant, the Jellyfish Nebula is
known
to harbor a neutron star, the remnant of the collapsed stellar core.
An emission nebula cataloged as
Sharpless 249
fills the field at the upper left.
The Jellyfish Nebula is about 5,000 light-years away.
At that distance, this image would be about 300 light-years across.
 APOD: 2018 September 9 - M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
APOD: 2018 September 9 - M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The Crab Nebula, the result of a supernova seen in
1054 AD, is filled with mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex, but appear to have
less mass than expelled in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
The featured image,
taken by the Hubble Space Telescope,
is presented in three colors chosen for
scientific interest.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light-years.
In the nebula's very center lies a
pulsar: a
neutron star as massive as the
Sun
but with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2018 March 23 - Sharpless 249 and the Jellyfish Nebula
APOD: 2018 March 23 - Sharpless 249 and the Jellyfish Nebula
Explanation:
Normally faint and elusive, the Jellyfish Nebula is caught in
this alluring telescopic image.
Centered in the scene it's anchored right and left by two bright stars,
Mu
and
Eta
Geminorum, at the foot of the
celestial
twin.
The Jellyfish Nebula is the brighter arcing
ridge of emission with dangling tentacles.
In fact, the cosmic jellyfish is part of bubble-shaped
supernova remnant IC 443, the expanding
debris cloud from a
massive
star that exploded.
Light from the explosion first reached planet Earth over 30,000 years
ago.
Like its cousin in
astrophysical waters the
Crab Nebula
supernova remnant, the Jellyfish Nebula is
known
to harbor a neutron star, the remnant of the collapsed stellar core.
An emission nebula cataloged as
Sharpless 249
fills the field at the upper left.
The Jellyfish Nebula is about 5,000 light-years away.
At that distance, this image would be about 300 light-years across.
 APOD: 2018 March 17 - The Crab from Space
APOD: 2018 March 17 - The Crab from Space
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first object on
Charles
Messier's famous list of things which are not comets.
In fact,
the
Crab is now known to be a
supernova remnant,
expanding debris from the death explosion of a massive star.
This
intriguing false-color image combines
data from space-based observatories,
Chandra,
Hubble, and
Spitzer,
to explore the debris cloud in X-rays (blue-white),
optical (purple), and infrared (pink) light.
One of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers,
the Crab Pulsar,
a neutron star spinning 30 times a second,
is the bright spot near picture center.
Like a cosmic dynamo,
this collapsed remnant of the stellar core
powers the Crab's emission across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spanning about 12 light-years, the Crab Nebula is
6,500 light-years away in the
constellation
Taurus.
 APOD: 2018 March 15 - Catalog Entry Number 1
APOD: 2018 March 15 - Catalog Entry Number 1
Explanation:
Every journey has a first step
and every catalog a first entry.
First entries in six well-known deep sky catalogs
appear in these panels, from upper left to lower right
in chronological order of original catalog publication.
From 1774,
Charles Messier's
catalog entry number 1 is M1, famous cosmic
crustacean and supernova remnant the Crab Nebula.
J.L.E. Dreyer's
(not so new) New General Catalog was published in 1888.
A spiral galaxy in Pegasus, his NGC 1 is centered in the next panel.
Just below it in the frame is another spiral galaxy
cataloged as NGC 2.
In Dreyer's follow-on Index Catalog (next panel), IC 1 is actually a
faint double star, though.
Now recognized as part of the Perseus molecular cloud complex,
dark nebula Barnard 1 begins the bottom row from
Dark
Markings of the Sky, a 1919 catalog by E.E. Barnard.
Abell 1 is a distant galaxy cluster in Pegasus, from
George Abell's 1958
catalog of Rich Clusters of Galaxies.
The final panel is centered on vdB 1, from Sidney
van den
Bergh's 1966 study.
The pretty, blue galactic reflection nebula
is found in the constellation Cassiopeia.
 APOD: 2018 January 4 - M1: The Incredible Expanding Crab
APOD: 2018 January 4 - M1: The Incredible Expanding Crab
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first on
Charles
Messier's famous list of things which are
not comets.
In fact, the Crab is
now known to be a supernova remnant, an expanding
cloud of debris from the explosion of a massive star.
The violent birth of the Crab was
witnessed
by astronomers in the year 1054.
Roughly 10 light-years across today, the nebula is still expanding
at a rate of over 1,000 kilometers per second.
Over the past decade, its expansion has been documented in
this stunning
time-lapse movie.
In each year from 2008 to 2017, an image was produced with the same
telescope and camera from a remote observatory in Austria.
Combined in the time-lapse movie, the 10 images represent 32 hours of total
integration time.
The sharp, processed frames even reveal the
dynamic
energetic emission within the incredible expanding Crab.
The Crab Nebula lies about 6,500 light-years away in the
constellation Taurus.
 APOD: 2017 May 11 - The Multiwavelength Crab
APOD: 2017 May 11 - The Multiwavelength Crab
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first object on
Charles
Messier's famous list of things which are not comets.
In fact, the Crab
is now known to be a
supernova
remnant, expanding debris from massive star's death explosion,
witnessed on planet Earth in 1054 AD.
This
brave new image offers a 21st century
view of the Crab Nebula by presenting image data from across the
electromagnetic
spectrum as wavelengths of visible light.
From space,
Chandra (X-ray)
XMM-Newton (ultraviolet),
Hubble (visible), and
Spitzer (infrared),
data are in purple, blue, green, and yellow hues.
From the ground,
Very Large Array
radio wavelength data is in shown in red.
One of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers,
the Crab Pulsar,
a neutron star spinning 30 times a second,
is the bright spot near picture center.
Like a cosmic dynamo,
this collapsed remnant of the stellar core
powers the Crab's emission across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spanning about 12 light-years, the Crab Nebula is
6,500 light-years away in the constellation
Taurus.
 APOD: 2017 January 7 - Sharpless 249 and the Jellyfish Nebula
APOD: 2017 January 7 - Sharpless 249 and the Jellyfish Nebula
Explanation:
Normally faint and elusive, the Jellyfish Nebula is caught in
this alluring telescopic mosaic.
The scene is anchored below by bright star
Eta
Geminorum, at the foot of the
celestial
twin, while
the Jellyfish Nebula is the brighter arcing
ridge of emission with tentacles dangling below and left of center.
In fact, the cosmic jellyfish is part of bubble-shaped
supernova remnant IC 443, the expanding
debris cloud from a
massive
star that exploded.
Light from the explosion first reached planet Earth over 30,000 years
ago.
Like its cousin in
astrophysical waters the
Crab Nebula supernova remnant,
the Jellyfish Nebula is
known
to harbor a neutron star, the remnant of the collapsed stellar core.
An emission nebula cataloged as
Sharpless 249
fills the field at the upper right.
The Jellyfish Nebula is about 5,000 light-years away.
At that distance,
this narrowband
composite image
presented in the Hubble Palette would be about 300 light-years across.
 APOD: 2016 September 18 - Starry Night Scavenger Hunt
APOD: 2016 September 18 - Starry Night Scavenger Hunt
Explanation:
Did you know that
van Gogh's painting
Starry Night includes Comet Hale-Bopp?
Hopefully not, because it doesn't.
But the featured image does.
Although today's picture may appear at first glance to be a faithful digital reproduction of the
original Starry Night,
actually it is a modern rendition meant not only to honor one of the most famous paintings of the second millennium, but to act as a
scavenger hunt.
Can you find, in the featured image, a
comet, a
spiral galaxy, an
open star cluster, and a
supernova remnant?
Too easy? OK, then find, the rings of
Supernova 1987A, the
NGC 2392, the
Crab Nebula,
Thor's Helmet, the
Cartwheel Galaxy, and the
Ant Nebula.
Still too easy? Then please identify any more hidden images not mentioned here -- and there are several -- on APOD's main discussion board:
The Asterisk.
Finally, the collagist has graciously hidden
APOD's 10th anniversary Vermeer photomontage
just to honor
APOD.
(Thanks!)
 APOD: 2016 July 8 - The Swirling Core of the Crab Nebula
APOD: 2016 July 8 - The Swirling Core of the Crab Nebula
Explanation:
At the core of the
Crab Nebula lies a city-sized, magnetized
neutron star spinning 30 times a second.
Known as the Crab Pulsar, it's actually the rightmost of two bright
stars, just below a central swirl in this
stunning Hubble snapshot of the nebula's core.
Some three light-years across, the spectacular picture frames
the glowing gas, cavities and swirling filaments bathed in
an eerie blue light.
The blue glow is visible radiation given off by electrons spiraling in a
strong magnetic field at nearly the speed of light.
Like a
cosmic
dynamo the pulsar powers the
emission from the nebula, driving a shock wave through surrounding
material and accelerating the spiraling electrons.
With more mass than
the Sun
and the density of an atomic nucleus,
the spinning pulsar is the collapsed core of a massive star
that exploded.
The Crab Nebula is the expanding remnant of the star's outer layers.
The supernova explosion was witnessed on planet Earth in
the year 1054.
 APOD: 2015 August 16 - M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
APOD: 2015 August 16 - M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The Crab Nebula, the result of a supernova seen in
1054 AD, is filled with mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex, but appear to have
less mass than expelled in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
The featured image,
taken by the Hubble Space Telescope,
is presented in three colors chosen for
scientific interest.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light-years.
In the nebula's very center lies a
pulsar: a
neutron star as massive as the
Sun
but with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2014 December 3 - Sharpless 249 and the Jellyfish Nebula
APOD: 2014 December 3 - Sharpless 249 and the Jellyfish Nebula
Explanation:
Normally faint and elusive, the Jellyfish Nebula is caught in
this alluring telescopic mosaic.
The scene is anchored right and left by two bright stars,
Mu
and
Eta
Geminorum, at the foot of the
celestial
twin while
the Jellyfish Nebula is the brighter arcing
ridge of emission with dangling tentacles below and right of center.
In fact, the cosmic jellyfish is part of bubble-shaped
supernova remnant IC 443, the expanding
debris cloud from a
massive
star that exploded.
Light from the explosion first reached planet Earth over 30,000 years
ago.
Like its cousin in
astrophysical waters the
Crab Nebula
supernova remnant, the Jellyfish Nebula is
known
to harbor a neutron star, the remnant of the collapsed stellar core.
An emission nebula cataloged as
Sharpless 249
fills the field at the upper left.
The Jellyfish Nebula is about 5,000 light-years away.
At that distance,
this narrowband composite image
would be about 300 light-years across.
 APOD: 2014 November 21 - M1: The Crab Nebula
APOD: 2014 November 21 - M1: The Crab Nebula
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first object on
Charles
Messier's famous 18th century list of things which are not comets.
In fact,
the
Crab is now known to be a
supernova remnant,
debris from the death explosion of a massive star,
witnessed
by astronomers in the year 1054.
This sharp,
ground-based telescopic view uses
narrowband data to track emission from ionized oxygen and hydrogen atoms
(in blue and red) and explore the tangled filaments within
the still expanding cloud.
One of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers,
the Crab Pulsar,
a neutron star spinning 30 times a second,
is visible as a bright spot near
the
nebula's center.
Like a cosmic dynamo,
this collapsed remnant of the stellar core
powers the Crab's emission across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spanning about 12 light-years, the Crab Nebula is a mere
6,500 light-years away in the
constellation
Taurus.
 APOD: 2014 July 25 - Cosmic Crab Nebula
APOD: 2014 July 25 - Cosmic Crab Nebula
Explanation:
The Crab Pulsar, a city-sized, magnetized
neutron star
spinning 30 times a second,
lies at the center of this tantalizing wide-field image of the
Crab Nebula.
A spectacular picture of one of
our Milky Way's supernova remnants, it
combines optical survey data with X-ray data from the orbiting
Chandra Observatory.
The composite was created as part of a celebration of
Chandra's 15
year long exploration of the
high energy cosmos.
Like a
cosmic
dynamo
the pulsar powers
the X-ray and optical emission from the nebula,
accelerating charged particles to extreme energies to
produce the jets and rings glowing in X-rays.
The innermost ring structure is about a light-year across.
With more mass than the Sun and the density of an
atomic nucleus, the spinning pulsar is the collapsed core of the
massive star that exploded, while the nebula is the
expanding remnant of the star's outer layers.
The supernova explosion was witnessed in
the year
1054.
 APOD: 2013 September 5 - M1: The Incredible Expanding Crab
APOD: 2013 September 5 - M1: The Incredible Expanding Crab
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first on
Charles
Messier's famous list of things which are
not comets.
In fact, the Crab is
now known to be a supernova remnant, an expanding
cloud of debris from the explosion of a massive star.
The violent birth of the Crab was
witnessed
by astronomers in the year 1054.
Roughly 10 light-years across today, the nebula is still expanding
at a rate of over 1,000 kilometers per second.
Want to watch the Crab Nebula expand?
Check out
this video (vimeo) animation
comparing an
image
of M1 taken in 1999 at the European Southern Observatory, with
this one, taken in 2012 at the Mt. Lemmon Sky Center.
Background stars were used to register the two images.
The Crab Nebula lies about 6,500 light-years away in the
constellation Taurus.
 APOD: 2013 January 9 - The Elusive Jellyfish Nebula
APOD: 2013 January 9 - The Elusive Jellyfish Nebula
Explanation:
Normally faint and elusive, the Jellyfish Nebula is caught in
this
alluring telescopic view.
Drifting near bright star
Eta
Geminorum, at the foot of a
celestial
twin, the Jellyfish Nebula is seen
dangling tentacles from the bright arcing ridge of emission
left of center.
In fact, the cosmic jellyfish is part of bubble-shaped
supernova remnant IC 443, the expanding
debris cloud from a
massive
star that exploded.
Light from the explosion first reached planet Earth over 30,000 years
ago.
Like its cousin in astrophysical waters the
Crab Nebula
supernova remnant, IC 443 is known to harbor
a neutron star, the remnant of the collapsed stellar core.
The Jellyfish Nebula is about 5,000 light-years away.
At that distance, this image would be about 100 light-years
across.
 APOD: 2011 December 25 - M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
APOD: 2011 December 25 - M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The Crab Nebula, the result of a supernova seen in
1054 AD, is filled with mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex, but appear to have
less mass than expelled in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
The above image,
taken by the Hubble Space Telescope,
is presented in three colors chosen for scientific interest.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light-years.
In the nebula's very center lies a
pulsar: a
neutron star as massive as the
Sun
but with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2011 May 23 - An Unexpected Flare from the Crab Nebula
APOD: 2011 May 23 - An Unexpected Flare from the Crab Nebula
Explanation:
Why does the Crab Nebula flare?
No one is sure.
The unusual behavior,
discovered
over the past few years, seems only to
occur in
very high energy light --
gamma rays.
As recently as one month ago, gamma-ray observations of the
Crab Nebula by the
Fermi Gamma Ray Space Telescope showed an
unexpected increase in gamma-ray brightness, becoming about five times the nebula's usual gamma-ray brightness, and
fading again in only a few days.
Now usually the faster the variability, the smaller the region involved.
This might indicate that the powerful pulsar at the
center of the Crab,
a compact neutron star rotating 30 times a second, is somehow involved.
Specifically,
speculation is centered on the changing
magnetic field
that surely surrounds the powerful
pulsar.
Rapid changes in this field might lead to waves of rapidly accelerated electrons which emit
the flares,
possibly in
ways similar to our
Sun.
The above image shows how the Crab Nebula normally
appears in gamma rays, as compared to the
Geminga pulsar, and how it then appeared during the recent brightening.
 APOD: 2011 April 18 - Visual Effects: Wonders of the Universe
APOD: 2011 April 18 - Visual Effects: Wonders of the Universe
Explanation:
What visual effects are depicted in this video?
The effects were created by
BDH for the
BBC television show
Wonders
of the Universe, but are unlabeled in this version.
Even so, some stills in the video are easily identified, such as the
Hubble image of the
Carina Nebula that occurs at about 2:22,
the Crab Nebula at about 7:45, and the
Cat's Eye Nebula that occurs at about 8:16.
A pan away from a spiral galaxy occurs at about 4:00, and breathtaking vistas of the spiral occur until past 5:00.
Pulsars and supernovas seem to take over at about 9:00 and are truly spectacular.
Binary star systems containing a pulsar and an
accretion disk occur beginning at about 14:30.
Past that, the entire computer animated video seems to sparkle with unknown stars, unknown planets, and sequences where unknown gas is flowing toward unknown places.
What, for example, is being depicted at 13:00?
Please help create a companion explanation for the video by
contributing to APOD's discussion page.
 APOD: 2010 December 20 - A Lunar Eclipse on Solstice Day
APOD: 2010 December 20 - A Lunar Eclipse on Solstice Day
Explanation:
Sometime after sunset tonight, the Moon will go dark.
This total lunar eclipse, where the entire Moon is engulfed in the shadow of the Earth, will be visible from all of
North America, while the partial phase of this eclipse will be visible throughout much of the rest of the world.
Observers on North America's east coast will have to wait until after midnight for totality to begin, while west coasters should be able to see a fully
darkened moon
before midnight.
Pictured above is a digital prediction, in image form, for how the
Moon and the surrounding sky could appear near maximum darkness.
Rolling your cursor over the image will bring up labels.
Parts of the Moon entering the circle labeled
umbra will appear the darkest since the Sun there will be completely blocked by the Earth.
Parts of the Moon entering the circle labeled
penumbra will be exposed to some direct sunlight, and so shine by some degree by reflected light.
The diminished glare of the normally full Moon will allow unusually good viewings of nearby celestial wonders such as the supernova remnant
Simeis 147, the open star cluster
M35, and the Crab Nebula
M1.
By coincidence this eclipse occurs on the day with the shortest amount of daylight in the northern hemisphere -- the Winter Solstice.
This solstice eclipse is the first in 456 years, although so far it appears that no one has
figured out when the next solstice eclipse will be.
 APOD: 2010 June 15 - Starry Night Scavenger Hunt
APOD: 2010 June 15 - Starry Night Scavenger Hunt
Explanation:
Did you know that
Van Gogh's painting
Starry Night includes Comet Hale-Bopp?
Hopefully not, because it doesn't.
But the above image does.
Although today's featured picture may appear at first glance to be a faithful digital reproduction of the
original Starry Night,
actually it is a modern rendition meant not only to honor one of the most famous paintings of the second millennium, but to act as a
scavenger hunt.
Can you find, in the above image, a comet, a spiral galaxy, an open star cluster, and a supernova remnant?
Too easy? OK, then find, the rings of
Supernova 1987A,
NGC 2392, the
Crab Nebula,
Thor's Helmet, the
Cartwheel Galaxy, and the
Ant Nebula.
Still too easy? Then please identify any more hidden images not mentioned here -- and there are several -- on APOD's main discussion board:
Starship Asterisk.
Finally, the collagist has graciously hidden
APOD's 10th anniversary Vermeer photomontage
to help honor
APOD
on its 15th anniversary tomorrow.
 APOD: 2010 May 15 - The Elusive Jellyfish Nebula
APOD: 2010 May 15 - The Elusive Jellyfish Nebula
Explanation:
Normally faint and elusive, the Jellyfish Nebula is caught in
this
alluring, false-color, telescopic view.
Flanked by two bright stars,
Mu
and
Eta
Geminorum,
at the foot of a
celestial
twin,
the Jellyfish Nebula is the brighter arcing
ridge of emission with dangling tentacles below and right of center.
In fact, the cosmic jellyfish is seen to be part of bubble-shaped
supernova remnant IC 443, the expanding
debris cloud from a
massive
star that exploded.
Light from the explosion first reached planet Earth over 30,000 years
ago.
Like its cousin in astrophysical waters the
Crab Nebula
supernova remnant, IC 443 is known to harbor
a neutron star, the remnant of the collapsed stellar core.
Emission nebula Sharpless 249 fills the field at the upper left.
The Jellyfish Nebula is about 5,000 light-years away.
At that distance, this image would be about 300 light-years
across.
The color scheme used in the narrowband composite was
made popular in Hubble Space Telescope images,
mapping emission
from oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur atoms to blue,
green and red colors.
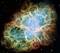 APOD: 2009 October 25 -M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
APOD: 2009 October 25 -M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The Crab Nebula, the result of a
supernova seen in
1054 AD,
is filled with
mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex, but appear to have
less mass than expelled in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
The above image,
taken by the Hubble Space Telescope,
is presented in three colors chosen for scientific interest.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light-years.
In the nebula's very center lies a
pulsar: a
neutron star as massive as the
Sun
but with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2009 May 14 - Elusive Jellyfish Nebula
APOD: 2009 May 14 - Elusive Jellyfish Nebula
Explanation:
Normally faint and elusive, the Jellyfish Nebula is caught in
this
alluring wide-field telescopic view.
Flanked by two yellow-tinted stars,
Mu
and
Eta
Geminorum,
at the foot of a
celestial
twin,
the Jellyfish Nebula is the brighter arcing
ridge of emission with dangling tentacles right of center.
In fact, the cosmic jellyfish is seen to be part of bubble-shaped
supernova remnant IC 443, the expanding
debris cloud from a
massive
star that exploded.
Light from the explosion first reached planet Earth over 30,000 years ago.
Like its cousin in astrophysical waters the
Crab Nebula
supernova remnant, IC 443 is known to harbor
a neutron star, the remnant of the collapsed stellar core.
Emission nebula Sharpless 249 fills the field at the upper left.
The Jellyfish Nebula is about 5,000 light-years away.
At that distance, this image would be almost 200 light-years
across.
 APOD: 2008 December 27 - Crab Pulsar Wind Nebula
APOD: 2008 December 27 - Crab Pulsar Wind Nebula
Explanation:
The Crab Pulsar, a city-sized, magnetized
neutron star spinning 30 times a second,
lies at the center of
this
remarkable image from
the orbiting Chandra Observatory.
The deep x-ray image gives the first
clear view of
the convoluted boundaries of the Crab's pulsar wind nebula.
Like a
cosmic
dynamo the pulsar powers the x-ray
emission.
The pulsar's energy accelerates
charged particles, producing eerie, glowing x-ray jets directed
away from the poles and an intense wind in the equatorial direction.
Intriguing edges are created as the charged
particles stream away, eventually losing energy as they interact
with the pulsar's strong magnetic field.
With more mass than the Sun and the density of an
atomic nucleus,
the spinning pulsar itself is the collapsed core of a
massive star.
The stellar core collapse resulted in a supernova explosion that
was witnessed in
the year
1054.
This Chandra image spans just under 9 light-years at the Crab's
estimated distance of 6,000 light-years.
 APOD: 2008 February 17 - M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
APOD: 2008 February 17 - M1: The Crab Nebula from Hubble
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The Crab Nebula, the result of a
supernova seen in
1054 AD,
is filled with
mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex, but appear to have
less mass than expelled in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
The above image,
taken by the Hubble Space Telescope,
is presented in three colors chosen for scientific interest.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light-years.
In the nebula's very center lies a
pulsar: a
neutron star as massive as the
Sun
but with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2006 October 26 - Composite Crab
APOD: 2006 October 26 - Composite Crab
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first object on
Charles
Messier's famous list of things which are not comets.
In fact,
the
Crab is now known to be a
supernova remnant,
expanding debris from the death explosion of a massive star.
This intriguing
false-color image combines
data from space-based observatories,
Chandra,
Hubble, and
Spitzer,
to explore the
debris cloud in x-rays (blue-purple),
optical (green), and infrared (red) light.
One of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers,
the Crab Pulsar,
a neutron star spinning 30 times a second,
is the bright spot near picture center.
Like a cosmic dynamo,
this collapsed remnant of the stellar core
powers the Crab's emission across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spanning about 12 light-years, the Crab Nebula is
6,500 light-years away in the
constellation
Taurus.
 APOD: 2005 December 2 - Crab Nebula Mosaic from HST
APOD: 2005 December 2 - Crab Nebula Mosaic from HST
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first object on
Charles
Messier's famous list of things which are not comets.
In fact, the
cosmic Crab
is now known to be a
supernova remnant,
an expanding cloud of debris from the death explosion of a massive star.
Light from that stellar catastrophe was first
witnessed
by astronomers on planet Earth in the year 1054.
Composed of 24
exposures taken in October 1999, January 2000,
and December 2000, this
Hubble Space Telescope mosaic spans about twelve light years.
Colors in the intricate filaments trace the light emitted from atoms
of hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur in the debris cloud.
The spooky blue interior glow is emitted by high-energy electrons
accelerated by the
Crab's central pulsar.
One of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers,
the pulsar is
a neutron star, the spinning remnant of the
collapsed stellar core.
The Crab Nebula lies about 6,500 light-years away in the
constellation
Taurus.
 APOD: 2005 September 20 - M1: The Crab Nebula from NOT
APOD: 2005 September 20 - M1: The Crab Nebula from NOT
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The Crab Nebula, the result of a
supernova seen in
1054 AD,
is filled with mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex, but appear to have
less mass than expelled
in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected
from a free explosion.
The above image, taken by the
Nordic Optical Telescope (NOT),
is in three colors chosen for scientific interest.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light-years.
In the nebula's very center lies a
pulsar: a
neutron star as massive as the
Sun
but with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar
rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2005 March 26 - Composite Crab
APOD: 2005 March 26 - Composite Crab
Explanation:
The Crab Pulsar, a city-sized, magnetized
neutron star
spinning 30 times a second,
lies at the center of this composite image of the inner region of
the well-known Crab
Nebula.
The spectacular picture combines optical data (red) from the
Hubble Space Telescope
and x-ray images (blue) from the
Chandra
Observatory, also used in the popular
Crab
Pulsar movies.
Like a
cosmic
dynamo the pulsar powers the x-ray
and optical emission from the nebula, accelerating
charged particles and producing the eerie, glowing x-ray jets.
Ring-like structures are x-ray emitting regions where
the high energy particles slam into the nebular material.
The innermost ring is about a light-year across.
With more mass than
the
Sun and the density of an
atomic nucleus,
the spinning pulsar is the collapsed core of a massive star
that exploded, while the nebula is the
expanding remnant of the star's outer layers.
The supernova explosion was witnessed in
the year 1054.
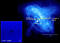 APOD: 2004 April 29 - Titan's X-Ray
APOD: 2004 April 29 - Titan's X-Ray
Explanation:
This June's rare and much heralded
transit of Venus will
feature our currently brilliant evening
star in silhouette,
as the inner planet glides across the face of the Sun.
But on January 5, 2003 an even rarer transit took place.
Titan, large moon
of ringed gas giant Saturn, crossed
in front of the Crab
Nebula, a supernova remnant some 7,000
light-years away.
During Titan's transit,
the orbiting Chandra Observatory's
x-ray detectors recorded the shadowing of cosmic x-rays generated
by the Crab's amazing pulsar
nebula, pictured above, in a situation analogous to a
medical
x-ray.
The resulting image (inset at left) probes the extent of
Titan's
atmosphere.
So, how rare was Titan's transit of the Crab?
While Saturn itself passes within a few degrees of the Crab
Nebula every 30 years, the next similar transit is reportedly
due in 2267.
And since the stellar explosion which gave birth to the Crab was
seen in 1054, the 2003 Titan transit may have been
the first to occur ... ever.
 APOD: 2004 April 8 - Elusive Jellyfish Nebula
APOD: 2004 April 8 - Elusive Jellyfish Nebula
Explanation:
Normally faint and elusive, the Jellyfish Nebula is caught in
the net of
this spectacular wide-field telescopic view.
Flanked by two yellow-tinted stars at the foot of a
celestial
twin - Mu and
Eta
Geminorum -
the Jellyfish Nebula is the brighter arcing
ridge of emission with dangling tentacles just right of center.
Here, the cosmic jellyfish is seen to be
part of bubble-shaped
supernova remnant
IC 443, the expanding
debris cloud from an exploded star some 5,000 light-years away.
Also in view, emission nebula IC 444 nearly fills the field to
the upper left, dotted with small blue reflection nebulae.
Like its cousin in astrophysical waters, the
Crab Nebula,
IC 443 is known to harbor
a neutron star, the collapsed core of the massive star that
exploded over 30,000 years ago.
 APOD: 2004 January 28 - The Crab Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2004 January 28 - The Crab Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The Crab Nebula, the result of a
supernova seen in
1054 AD,
is filled with mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex, but appear to have
less mass than expelled
in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected
from a free explosion.
The above image, taken by the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT),
is in three colors chosen for scientific interest.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light-years.
In the nebula's very center lies a
pulsar: a
neutron star as massive as the
Sun
but with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar
rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2003 September 14 - The Crab Nebula from VLT
APOD: 2003 September 14 - The Crab Nebula from VLT
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula, filled with mysterious filaments, is the result of a
star that was seen to explode in 1054 AD.
This spectacular supernova explosion was recorded by Chinese and (quite probably) Anasazi Indian astronomers.
The filaments are mysterious because they appear
to have less mass than expelled in the original supernova
and higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
In the above picture taken recently from a
Very Large Telescope,
the color indicates what is happening to the
electrons in differentparts of the
Crab Nebula.
Red indicates the electrons are recombining with protons to form neutral hydrogen,
while blue indicates the electrons are whirling around the magnetic field
of the inner nebula.
In the
nebula's very center lies a pulsar: a neutron star rotating, in this case, 30 times a second.
 APOD: 2003 September 4 - Composite Crab
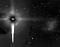
APOD: 2003 September 4 - Composite Crab
Explanation:
The Crab Pulsar, a city-sized, magnetized
neutron star
spinning 30 times a second,
lies at the center of this composite image of the inner region of
the well-known Crab
Nebula.
The spectacular picture combines optical data (red) from the
Hubble Space Telescope
and x-ray images (blue) from the
Chandra
Observatory, also used in the popular
Crab
Pulsar movies.
Like a
cosmic
dynamo the pulsar powers the x-ray
and optical emission from the nebula, accelerating
charged particles and producing the eerie, glowing x-ray jets.
Ring-like structures are x-ray emitting regions where
the high energy particles slam into the nebular material.
The innermost ring is about a light-year across.
With more mass than
the
Sun and the density of an
atomic nucleus,
the spinning pulsar is the collapsed core of a massive star
that exploded, while the nebula is the
expanding remnant of the star's outer layers.
The supernova explosion was witnessed in
the year 1054.
 APOD: 2003 January 10 - The Crab that Played with the Planet
APOD: 2003 January 10 - The Crab that Played with the Planet
Explanation:
Wandering
through the constellation Taurus,
Saturn
made its
closest approach to planet Earth last month, tilting its lovely rings
toward appreciative skygazers while rising high in midnight skies.
On January 4th and 5th, Saturn also crossed in front of the
high and far-off
Crab Nebula (M1), a cosmic cloud of
debris from a stellar explosion and first on the list of
astronomer Charles Messier's
celestial sights.
But Saturn
and the Crab made poor playmates,
as light from the bright planet overwhelmed the
the diffuse nebula, all but hiding the Crab
during the transit.
Taken on January 2nd,
a few days before their closest encounter,
this composite digital image illustrates the problem.
The subtle
nebula is just visible at the right,
while on the left, light from a drastically over-exposed Saturn
overflows its pixels.
Composited into the image is a correctly exposed picture of
ringed Saturn
with the Saturnian moons labeled.
The well-exposed Saturn image was also taken
on January 2nd, but captured with an exposure
lasting only a fraction of a second, in contrast with
the tens of seconds of exposure time required to
reveal the Crab.
 APOD: 2002 September 20 - The Crab Nebula Pulsar Shrugs
APOD: 2002 September 20 - The Crab Nebula Pulsar Shrugs
Explanation:
How does a city-sized neutron star power the vast
Crab Nebula?
The expulsion of wisps of hot gas at high speeds appears
to be at least part of the answer.
Yesterday
time-lapse movies taken from both the
Chandra X-ray Observatory
and the
Hubble Space Telescope
were released showing a wisp of gas moving
out at about half the speed of light.
Wisps like this likely result from tremendous
electric voltages created by the central pulsar, a rapidly rotating,
magnetized, central
neutron star.
The hot plasma strikes existing gas, causing it glow in colors
across the
electromagnetic spectrum.
Pictured above is a composite image of the
center of the Crab Nebula
where red represents
radio emission, green represents
visible emission,
and blue represents
X-ray emission.
The dot at the very center is the hot
pulsar
spinning 30 times per second.
 APOD: 2002 July 14 - The Crab Nebula from VLT
APOD: 2002 July 14 - The Crab Nebula from VLT
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula, filled with mysterious filaments, is the result of a
star that was seen to explode in 1054 AD.
This spectacular supernova explosion was recorded by Chinese and (quite probably) Anasazi Indian astronomers.
The filaments are mysterious because they appear
to have less mass than expelled in the original supernova
and higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
In the above picture taken recently from a
Very Large Telescope,
the color indicates what is happening to the electrons in different
parts of the Crab Nebula.
Red indicates the electrons are recombining with protons to form neutral hydrogen,
while blue indicates the electrons are whirling around the magnetic field
of the inner nebula.
In the
nebula's very center lies a pulsar: a neutron star rotating, in this case, 30 times a second.
 APOD: 2001 December 27 - The Incredible Expanding Crab
APOD: 2001 December 27 - The Incredible Expanding Crab
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is cataloged as M1, the first on
Charles Messier's
famous list of things which are not comets.
In fact, the Crab is
now known to be a supernova remnant, an expanding
cloud of debris from the explosion of a massive star.
The violent birth of the Crab was
witnessed
by astronomers in the year 1054.
Roughly 10 light-years across today, the nebula is still expanding
at a rate of over 1,000 kilometers per second.
Flipping between two images made nearly 30 years apart, this
animation clearly demonstrates the expansion.
The smaller Crab was recorded as a
photographic image made in 1973
using the Kitt Peak
National Observatory 4-meter telescope in 1973.
The
expanded Crab was made this year with the Kitt Peak
Visitor Center's
0.4-meter telescope and digital camera.
Background stars were used to register the two images.
 APOD: 2001 September 13 - X-Rays and the Circinus Pulsar
APOD: 2001 September 13 - X-Rays and the Circinus Pulsar
Explanation:
A bizarre
stellar
corpse 19,000 light-years from Earth,
pulsar
PSR B1509-58
beckons from the small southern constellation
of Circinus.
Like its cousin at the heart of the Crab nebula,
the Circinus pulsar is a rapidly spinning, magnetized
neutron star.
Seen in this false-color
Chandra Observatory
image, the environment
surrounding this cosmic powerhouse glows in high energy x-rays.
The Circinus
pulsar itself, thought to generate more than
7 quadrillion
volts (7 followed by 15 zeros), lies within the knot of bright
emission near the center of the picture.
Stretching toward the bottom left,
x-ray
emission traces a
jet of particles almost 20 light-years long
that seems to arise from the pulsar's south pole,
while the arc of bright emission
above the central knot is likely a shockwave produced by particles
driven from the pulsar's equator.
Near the top of the picture, lower energy x-ray emission shown in green
is from gas shock-heated to millions of degrees Celsius.
The shocked gas was produced by debris
blasted out from
the stellar explosion that
created the Circinus pulsar.
 APOD: 2001 June 2 - The Pulsar Powered Crab
APOD: 2001 June 2 - The Pulsar Powered Crab
Explanation:
In the Summer of 1054 A.D.
Chinese astronomers reported
that a star in the
constellation of Taurus suddenly became as bright as the full Moon.
Fading slowly, it remained visible for over a year.
It is now understood
that a spectacular supernova explosion -
the detonation of a massive star whose remains
are now visible as the Crab Nebula-
was responsible for the apparition.
The
core of the star collapsed to form a rotating
neutron
star or
pulsar,
one of the most exotic objects known to modern astronomers.
Like a cosmic lighthouse, the rotating Crab pulsar generates beams of
radio, visible, x-ray and
gamma-ray energy which, as the name
suggests, produce pulses as they sweep across our view.
Using a stunning series of
visible
light images taken with
the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in 1995, astronomers have discovered
spectacular pulsar powered motions within the Crab nebula.
Highlights of this
HST Crab "movie" show wisps of material moving
away from the pulsar at half the speed of light, a scintillating halo,
and an intense knot of emission dancing, sprite-like, above the pulsar's pole.
Only 10 kilometers wide but more
massive than the sun, the pulsar's energy drives the dynamics and emission
of the nebula itself which is more than 10 light-years across.
 APOD: 2001 March 25 - The Crab Nebula from VLT
APOD: 2001 March 25 - The Crab Nebula from VLT
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula, filled with mysterious filaments, is the result of a
star that was seen to explode in 1054 AD.
This spectacular supernova explosion was recorded by Chinese and (quite probably) Anasazi Indian astronomers.
The filaments are mysterious because they appear
to have less mass than expelled in the original supernova
and higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
In the above picture taken recently from a
Very Large Telescope,
the color indicates what is happening to the electrons in different
parts of the Crab Nebula.
Red indicates the electrons are recombining with protons to form neutral hydrogen,
while blue indicates the electrons are whirling around the magnetic field
of the inner nebula.
In the
nebula's very center lies a pulsar: a neutron star rotating, in this case, 30 times a second.
 APOD: 2000 July 11 - The Crab Nebula in Blue and White
APOD: 2000 July 11 - The Crab Nebula in Blue and White
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula is a complex shell of expanding gas.
The
Crab Nebula formed from a
star that was seen to explode in a
supernova about 1000 years ago.
This two color composite image taken with the
WIYN 3.5-meter telescope shows in great
detail filamentary structure of the glowing
hydrogen gas.
Also known as
M1, the center is home to a dense
neutron star, a star as massive as our
Sun but only the size of a
city.
The
neutron star is a
pulsar that spins thirty times a second and spits out
energy that powers the nebula.
The
nebula
is named from its likeness to a
crab in an early drawing.
The
Crab Nebula still
presents mysteries today as the total mass of the
nebula and
pulsar appears much less than the mass of the original
pre-supernova star!
 APOD: 2000 June 9 - Vela Pulsar: Neutron Star-Ring-Jet
APOD: 2000 June 9 - Vela Pulsar: Neutron Star-Ring-Jet
Explanation:
This
stunning image from the orbiting
Chandra X-ray
Observatory is centered on the Vela pulsar -- the collapsed
stellar core within
the Vela supernova remnant
some 800 light-years distant.
The Vela pulsar is a
neutron star.
More massive than the Sun, it has the density of an atomic nucleus.
About 12 miles in diameter it
spins 10 times a second as it hurtles through the
supernova debris cloud.
The pulsar's electric and magnetic fields accelerate
particles to nearly the speed of light, powering the compact
x-ray emission nebula revealed
in the Chandra picture.
The cosmic crossbow shape is over 0.2 light-years across,
composed of an arrow-like jet emanating from the polar region of
the
neutron star and bow-like inner and outer arcs believed
to be the edges of tilted rings of x-ray
emitting high energy particles.
Impressively, the swept back compact nebula indicates the
neutron star is moving up and to the right in this
picture, exactly along the direction of the x-ray jet.
The Vela pulsar (and
associated
supernova remnant) was created by a massive
star which exploded over 10,000 years ago.
Its awesome x-ray rings and jet are reminiscent of another
well-known pulsar powered system,
the Crab Nebula.
 APOD: 2000 June 5 - In the Heart of the Crab
APOD: 2000 June 5 - In the Heart of the Crab
Explanation:
The supernova explosion that formed the
Crab Nebula was
first seen on the year 1054.
Last week, astronomers
released a new image of the
still-evolving center of the explosion.
The above representative-color photograph
was taken in colors emitted by specific
elements including
hydrogen (orange),
nitrogen (red),
sulfur (pink), and
oxygen (green), with the result appearing oddly similar to a
Jackson Pollock painting.
Visible is a complex array of gas
filaments rushing out at
over 5 million kilometers per hour.
Even at these tremendous speeds, though, it takes a
filament over 600 years to cross the 3
light year wide frame.
The rapidly spinning
neutron star
remnant of this
ancient cataclysm is visible as the lower of the
two bright stars just above the
photograph center.
The
Crab Nebula
(M1) is located 6,500 light-years
away towards the
constellation of
Taurus.
 APOD: 2000 March 11 - Messier Marathon
APOD: 2000 March 11 - Messier Marathon
Explanation:
Gripped by an
astronomical spring fever,
it's once again time for
many amateur stargazers to embark on
a Messier Marathon!
The Vernal Equinox
occurs March 20, marking the
first day of Spring for the Northern Hemisphere.
It also marks a favorable
celestial situation for
potentially viewing all the objects in 18th century French astronomer
Charles Messier's catalog
in one
glorious dusk to dawn observing run.
This year a bright full moon will interfere with dark skies near
the actual equinox, so good nights near new moon for weekend
marathoners are March 11/12 and April 1/2.
(As an added bonus all the
planets in the solar system can be viewed
on these dates.)
Astronomer Paul Gitto has created this
masterful Messier Marathon grid with 11 rows
and 10 columns of
Messier catalog objects.
In numerical order, the grid begins with
M1, the Crab Nebula,
at upper left
and ends
with M110, a small elliptical galaxy in Andromeda
(lower right).
Gitto's images were made with a digital camera and a 10-inch diameter
reflecting telescope.
 APOD: November 22, 1999 - The Crab Nebula from VLT
APOD: November 22, 1999 - The Crab Nebula from VLT
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula, filled with mysterious filaments, is the result of a
star that was seen to explode in 1054 AD.
This spectacular supernova explosion was recorded by Chinese and (quite probably) Anasazi Indian astronomers.
The filaments are mysterious because they appear
to have less mass than expelled in the original supernova
and higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
In the above picture taken recently from a
Very Large Telescope,
the color indicates what is happening to the electrons in different
parts of the Crab Nebula.
Red indicates the electrons are recombining with protons to form neutral hydrogen,
while blue indicates the electrons are whirling around the magnetic field
of the inner nebula.
In the
nebula's very center lies a pulsar: a neutron star rotating, in this case, 30 times a second.
 APOD: September 29, 1999 - The Crab Nebula in X Rays
APOD: September 29, 1999 - The Crab Nebula in X Rays
Explanation:
Why does the Crab Nebula
still glow? In the year 1054 A.D. a
supernova
was observed that left a nebula that even today
glows brightly in every color possible, across the entire electromagnetic spectrum.
At the nebula's center is an ultra-dense
neutron star
that rotates 30 times a second.
The power liberated as this
neutron star slows its rotation matches
the power radiated by the
Crab Nebula.
The above picture by the recently launched
Chandra X-Ray Observatory
shows new details of the nebula's center in X-ray light, yielding important clues to how the
neutron star powers the nebula.
Visible are rings of
high-energy particles that are being flung outward near
light-speed from the center, and powerful
jets emerging from the poles.
Astrophysicists continue to study and learn from this
unusual engine
which continually transfers 30 million times more power than
lightning
at nearly perfect
efficiency.
 APOD: March 18, 1999 - Messier Marathon
APOD: March 18, 1999 - Messier Marathon
Explanation:
Gripped by an
astronomical spring fever, this week
many amateur stargazers embark on
a Messier Marathon.
The Vernal Equinox
occurs Saturday, March 20, marking the
first day of Spring for the Northern Hemisphere.
It also marks a favorable celestial situation for
potentially viewing all the objects in 18th century French astronomer
Charles Messier's catalog
in one
glorious dusk to dawn observing run.
This year, interference from bright moonlight will be minimal as
the the moon is near its dark or new phase.
Astronomer Paul Gitto has created this
masterful Messier Marathon grid with 11 rows
and 10 columns of
Messier catalog objects.
In numerical order, the grid begins with
M1, the Crab Nebula,
at upper left and ends
with M110, a small elliptical galaxy in Andromeda
(lower right).
Gitto's images were made with a digital camera and a 10-inch diameter
reflecting telescope.
 APOD: November 22, 1998 - The High Energy Crab Nebula
APOD: November 22, 1998 - The High Energy Crab Nebula
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes. The
Crab Nebula
is so energetic that it glows in
every kind of light known.
Shown above are images of the
Crab Nebula from visible light to the
X-ray band.
NUV stands for "near
ultraviolet" light, FUV means "far
ultraviolet" light, and VIS means visible light. In the center of the
Crab Nebula lies the powerful
Crab pulsar - a spinning
neutron star with mass comparable to our
Sun but with the diameter of only a
small town.
The pulsar expels particles and radiation in a beam that sweeps past the
Earth 30 times a second. The
supernova that created the
Crab Nebula was seen by
ancient
Chinese astronomers and possibly even the
Anasazi Indians -- in 1054 AD, perhaps glowing for a
week as bright as the
full moon. The
Crab
still presents mysteries today as the total mass of the nebula and pulsar appears much less than the mass of the original pre-supernova star!
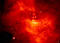 APOD: September 5, 1998 - The Pulsar Powered Crab
APOD: September 5, 1998 - The Pulsar Powered Crab
Explanation:
In the Summer of 1054 A.D.
Chinese astronomers reported
that a star in the
constellation of Taurus suddenly became as bright as the full Moon.
Fading slowly, it remained visible for over a year.
It is now understood
that a spectacular supernova explosion -
the detonation of a massive star whose remains
are now visible as the Crab Nebula-
was responsible for the apparition.
The core of the star collapsed to form a rotating
neutron star or
pulsar,
one of the most exotic objects known to 20th century astronomy.
Like a cosmic lighthouse, the rotating Crab pulsar generates beams of
radio, visible, x-ray and gamma-ray energy which, as the name
suggests, produce pulses as they sweep across our view.
Using a stunning series of
visible light images taken with
the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), astronomers have discovered
spectacular pulsar powered motions within the Crab nebula.
Highlights of this
HST Crab "movie" show wisps of material moving
away from the pulsar at half the speed of light, a scintillating halo,
and an intense knot of emission dancing, sprite-like, above the pulsar's pole.
Only 6 miles wide but more
massive than the sun, the pulsar's energy drives the dynamics and emission
of the nebula itself which is more than 10 lightyears across.
In this HST image,
the pulsar is the left most of the two bright central stars.
 APOD: February 11, 1998 - Ultra Fast Pulsar
APOD: February 11, 1998 - Ultra Fast Pulsar
Explanation:
Pulsars are rotating
neutron stars, born in the violent
crucibles of supernova explosions.
Like cosmic lighthouses, beams of radiation from surface hotspots sweep
past our viewpoint creating pulses which reveal the rotation rates
of these incredibly dense stellar corpses.
The most famous pulsar of all is found in the nearby supernova
remnant, the Crab Nebula.
The Crab's young pulsar is fast.
Rotating at 33 times a second,
its radiation energizes the surrounding
gaseous stellar debris.
But using
archival observations from orbiting X-ray telescopes,
astronomers have recently identified another "Crab-like" pulsar
that is even faster.
Located in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC),
X-ray pulses from this newly discovered pulsar,
in the supernova remnant N157B,
indicate an even faster rotation rate - 62 times a second -
making it
the fastest known pulsar associated with a supernova remnant.
This contoured, false color X-ray image of
a portion of the LMC
shows the location of N157B along with
the core of the nearby
hot star cluster R136,
and the site of another Crab-like pulsar in SNR 0540-69.3
(rotating a mere 20 times a second).
The image is about 1,500 light-years across.
 APOD: February 8, 1998 - M1: Filaments of the Crab Nebula
APOD: February 8, 1998 - M1: Filaments of the Crab Nebula
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula, filled with mysterious filaments, is the result of a
star that exploded in 1054 AD.
This spectacular supernova
explosion was recorded by Chinese and (quite probably) Anasazi Indian astronomers.
The filaments are mysterious because they appear
to have less mass than expelled in the original supernova
and higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
In the above picture, the color indicates what is
happening to the electrons in different
parts of the Crab Nebula.
Red indicates the electrons are recombining with protons to form neutral hydrogen,
while green indicates the electrons are whirling around the magnetic field
of the inner nebula. In the nebula's
very center lies a pulsar: a neutron star rotating, in this case, 30 times a second.
 APOD: February 7, 1997 - M1: Filaments of the Crab Nebula
APOD: February 7, 1997 - M1: Filaments of the Crab Nebula
Explanation: The Crab Nebula is filled with mysterious
filaments. The Crab Nebula
is the result of a star that exploded in 1054 AD.
This spectacular supernova
explosion was recorded by Chinese
and (quite probably) Anasazi Indian
astronomers. The filaments are mysterious because they appear
to have less mass than expelled in the original supernova
and higher speed than expected from a free explosion.
In the above picture,
the color indicates what is happening to the electrons in different
parts of the Crab Nebula.
Red indicates the electrons are recombining with protons to form neutral hydrogen,
while green indicates the electrons are whirling around the magnetic field
of the inner nebula. In the nebula's
very center lies a pulsar:
a neutron star
rotating, in this case, 30 times a second.
 APOD: September 9, 1996 - The High Energy Crab Nebula
APOD: September 9, 1996 - The High Energy Crab Nebula
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes. The
Crab Nebula
is so energetic that it glows in
every kind of light known.
Shown above are images of the
Crab Nebula from visible light to the
X-ray band.
NUV stands for "near
ultraviolet" light, FUV means "far
ultraviolet" light, and VIS means visible light. In the center of the
Crab Nebula lies the powerful
Crab pulsar - a spinning
neutron star
with mass comparable to our
Sun but with the diameter of only a
small town.
The pulsar expels particles and radiation in a beam that sweeps past the
Earth 30 times a second. The
supernova that created the
Crab Nebula was seen by
ancient
Chinese astronomers and possibly even the
Anasazi Indians
-- in 1054 AD, perhaps glowing for a week as bright as the
full moon. The Crab
still presents mysteries today as the total mass of the nebula and pulsar appears much less than the mass of the original pre-supernova star!
 APOD: June 26, 1996 - Happy Birthday Charles Messier: M1
APOD: June 26, 1996 - Happy Birthday Charles Messier: M1
Explanation:
French astronomer
Charles Messier was born on June 26, 1730.
Inspired by childhood sightings of comets and a solar eclipse visible
from his home town of Badonvillier, he became an astronomer
and comet hunter
who kept careful records of his observations.
While
hunting for comets in the skies above France
he made
a now famous list of the positions of about 100 fuzzy,
diffuse looking objects which appeared at fixed positions in the sky.
Although these objects looked like comets,
Messier knew that since they
did not move with respect to the background stars they could not be the
comets he was searching for. These objects are now well
known to modern astronomers to be among the brightest and most striking
nebulae, star clusters, and galaxies.
Objects on Messier's list are still
referred to by their "Messier number".
The first object in his catalog,
M1 pictured above - also known as
the Crab Nebula,
was recorded during his search for
the return of comet Halley in 1758.
Messier died in his home in Paris in 1817.
 APOD: May 31, 1996 - The Pulsar Powered Crab
APOD: May 31, 1996 - The Pulsar Powered Crab
Explanation:
In the Summer of 1054 A.D. Chinese astronomers reported
that a star in the
constellation of Taurus suddenly became as bright as the full Moon.
Fading slowly, it remained visible for over a year. It is now understood
that a spectacular supernova explosion -
the detonation of a massive star whose remains
are now visible as the Crab Nebula-
was responsible for the apparition.
The core of the star collapsed to form a rotating
neutron star or
pulsar,
one of the most exotic objects known to 20th century astronomy.
Like a cosmic lighthouse, the rotating Crab pulsar generates beams of
radio, visible, x-ray and gamma-ray energy which, as the name
suggests, produce pulses as they sweep across our view.
Using a stunning series of
visible light images taken with
the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), astronomers have recently discovered
spectacular pulsar powered motions within the Crab nebula.
Highlights of this
HST Crab "movie" show wisps of material moving
away from the pulsar at half the speed of light, a scintillating halo,
and an intense knot of emission dancing, sprite-like, above the pulsar's pole.
Only 6 miles wide but more
massive than the sun, the pulsar's energy drives the dynamics and emission
of the nebula itself which is more than 10 lightyears across.
In the HST image above,
the pulsar is the left most of the two bright central stars.
 APOD: November 23, 1995 - M1: Polarization of the Crab
APOD: November 23, 1995 - M1: Polarization of the Crab
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula resulted from a star that
exploded - a
supernova. Although the stellar explosion
that caused the
Crab Nebula was seen over 900 years ago, the
nebula itself still expands and shines. Much of the emitted light has been
found to be
polarized.
Light waves with the same polarization vibrate in the same plane.
Light waves can be polarized by reflection from a surface, an effect familiar
to sunglass wearing fishermen and skiers.
Polarized light can also be emitted by
regions that contain strong magnetic fields.
Areas of different polarization above are
highlighted by different colors.
Mapping the
polarization helps astronomers decipher which
physical processes create the
observed light.
 APOD: November 22, 1995 - M1: The Exploding Crab Nebula
APOD: November 22, 1995 - M1: The Exploding Crab Nebula
Explanation:
The Crab Nebula resulted from a star that
exploded - a
supernova. The outer
layers of the star were thrown violently into space, while the inner core
collapsed to form a
neutron star. This
neutron star is visible to us today as a
pulsar - a rotating star
at the center of the nebula that emits
visible flashes of light. The
Crab Pulsar flashes about 30 times every
second. Although the stellar explosion that caused the Crab Nebula was
seen over 900 years ago, the nebula itself still expands and shines. How
the nebula obtains the energy needed to shine was a mystery eventually
solved by noting that this energy could be released by the slowing of the
pulsar's rotation.
 APOD: July 25, 1995 - M1: The Crab Nebula
APOD: July 25, 1995 - M1: The Crab Nebula
Explanation:
In the year 1054 a star in the constellation of Taurus exploded in a
spectacular
supernova so bright it appeared to
dominate the sky except for the Sun and Moon for many days.
It left behind one of the most
brilliant nebulae, listed first in
Charles Messier's list of nebulous sky
objects. Today we know that the center of the nebula houses the remnant
of the explosion: a spinning
neutron star called a pulsar.
The Crab pulsar
is visible in almost every part of the electromagnetic spectrum, and has
been a useful astronomical tool. It is still unclear how the the pulsar
emits the light that we see.
 APOD: June 24, 1995 - Gamma Ray Crab, Geminga
APOD: June 24, 1995 - Gamma Ray Crab, Geminga
Explanation:
What if you could "see" in gamma-rays? If you could, these two
spinning
neutron stars
or pulsars
would be among the brightest objects in the sky. This computer processed
image shows the Crab Nebula pulsar (below and right of center)
and the Geminga pulsar (above and left of center) in the "light" of
gamma-rays. Gamma-ray photons are more than 10,000 times more
energetic than visible light photons and are blocked from the
Earths's surface by the atmosphere. This image was produced by
the high energy gamma-ray telescope "EGRET" on board NASA's orbiting
Compton Observatory satellite.