 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 APOD: 2024 April 25 - NGC 604: Giant Stellar Nursery
APOD: 2024 April 25 - NGC 604: Giant Stellar Nursery
Explanation:
Located some 3 million light-years away in the arms of nearby spiral
galaxy M33,
giant stellar nursery
NGC 604 is
about 1,300 light-years across.
That's nearly 100 times the size of the Milky Way's
Orion Nebula, the closest large star forming
region to planet Earth.
In fact, among the star forming regions within the Local Group of
galaxies, NGC 604 is second in size only to 30 Doradus,
also known as
the Tarantula Nebula in the
Large Magellanic Cloud.
Cavernous bubbles and cavities in NGC 604
fill this stunning infrared image from the
James Webb Space Telescope's NIRCam.
They are carved out by energetic stellar winds
from the region's
more than 200 hot, massive, young stars, all still in early
stages of their lives.
 APOD: 2024 March 8 - The Tarantula Zone
APOD: 2024 March 8 - The Tarantula Zone
Explanation:
The Tarantula Nebula,
also known as 30 Doradus, is more than a thousand light-years in diameter,
a giant star forming region within nearby satellite galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud.
About 180 thousand light-years away, it's the largest,
most violent star forming region known in the whole Local
Group of galaxies.
The cosmic arachnid sprawls across
this magnificent view,
an assembly of image data from large space- and ground-based telescopes.
Within the Tarantula (NGC 2070),
intense radiation, stellar winds, and supernova shocks
from the central young cluster of massive stars cataloged as R136
energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
Around the
Tarantula are other star forming regions with
young star clusters, filaments, and blown-out
bubble-shaped clouds.
In fact, the frame includes the site of the closest supernova in
modern times, SN 1987A,
at lower right.
The rich field of view spans about 2 degrees
or 4 full moons in the southern
constellation Dorado.
But were the Tarantula Nebula closer, say 1,500 light-years distant like
the Milky Way's own star forming Orion Nebula,
it would take up half the sky.
 APOD: 2023 September 7 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
APOD: 2023 September 7 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
Explanation:
The 16th century Portuguese navigator
Ferdinand Magellan and his crew had plenty of time to study the
southern sky during the
first circumnavigation of planet Earth.
As a result, two fuzzy cloud-like
objects easily visible to southern hemisphere
skygazers are known as the
Clouds of Magellan, now understood to be
satellite galaxies of our much larger, spiral Milky Way galaxy.
About 160,000 light-years distant in the constellation
Dorado, the
Large Magellanic Cloud
is seen in this
sharp galaxy portrait.
Spanning about 15,000 light-years or so, it is
the most massive of the Milky Way's
satellite galaxies
and is the home of the
closest supernova in modern times,
SN 1987A.
The prominent patch above center is 30 Doradus,
also known as the magnificent
Tarantula Nebula, a giant
star-forming region about 1,000 light-years across.
 APOD: 2023 April 27 - The Tarantula Nebula from SuperBIT
APOD: 2023 April 27 - The Tarantula Nebula from SuperBIT
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula, also known as 30 Doradus,
is more than a thousand light-years in diameter,
a giant star forming region within nearby satellite galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud.
About 160 thousand light-years away, it's the largest,
most violent star forming region known in the whole Local
Group of galaxies.
The cosmic arachnid is near the center of this spectacular image
taken during the
flight of SuperBIT
(Super Pressure Balloon Imaging Telescope),
NASA's balloon-borne 0.5 meter telescope
now floating near the edge of space.
Within the well-studied Tarantula (NGC 2070),
intense radiation,
stellar winds and supernova shocks from the central young cluster of
massive stars, cataloged as R136,
energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
Around the Tarantula
are other star forming regions with
young star clusters, filaments, and blown-out
bubble-shaped clouds.
SuperBIT's field of view spans about 1/3 of a degree
in the southern
constellation Dorado.
 APOD: 2022 September 16 - The Tarantula Zone
APOD: 2022 September 16 - The Tarantula Zone
Explanation:
The Tarantula Nebula,
also known as 30 Doradus, is more than a thousand light-years in diameter,
a giant star forming region within nearby satellite galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud.
About 180 thousand light-years away, it's the largest,
most violent star forming region known in the whole Local
Group of galaxies.
The cosmic arachnid sprawls across
this magnificent view,
an assembly of image data from large space- and ground-based telescopes.
Within the Tarantula (NGC 2070),
intense radiation, stellar winds, and supernova shocks
from the central young cluster of massive stars cataloged as R136
energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
Around the
Tarantula are other star forming regions with
young star clusters, filaments, and blown-out
bubble-shaped clouds.
In fact, the frame includes the site of the closest supernova in modern times,
SN 1987A,
at lower right.
The rich field of view spans about 2 degrees
or 4 full moons, in the southern
constellation Dorado.
But were the Tarantula Nebula closer, say 1,500 light-years distant like
the Milky Way's own star forming Orion Nebula,
it would take up half the sky.
 APOD: 2020 November 13 - The Tarantula Zone
APOD: 2020 November 13 - The Tarantula Zone
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula, also known as 30 Doradus,
is more than a thousand light-years in diameter,
a giant star forming region within nearby satellite galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud.
About 180 thousand light-years away, it's the largest,
most violent star forming region known in the whole Local
Group of galaxies.
The cosmic arachnid sprawls across the top of
this spectacular view,
composed with narrowband filter data centered on emission
from ionized hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
Within the Tarantula
(NGC 2070), intense radiation,
stellar winds and supernova shocks from the central young cluster of
massive stars, cataloged as R136,
energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
Around the Tarantula
are other star forming regions with
young star clusters, filaments, and blown-out
bubble-shaped clouds.
In fact, the frame includes the site of the closest supernova
in modern times,
SN 1987A,
right of center.
The rich field of view spans about 2 degrees
or 4 full moons, in the southern
constellation Dorado.
But were the Tarantula Nebula closer, say 1,500 light-years distant like
the local star forming Orion Nebula,
it would take up half the sky.
 APOD: 2019 September 5 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
APOD: 2019 September 5 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
Explanation:
The 16th century Portuguese navigator
Ferdinand
Magellan and his crew had plenty of time to study the
southern sky during the
first
circumnavigation of planet Earth.
As a result, two fuzzy cloud-like
objects easily visible to southern hemisphere
skygazers are known as the
Clouds of Magellan, now understood to be
satellite galaxies of our much larger, spiral Milky Way galaxy.
About 160,000 light-years distant in the constellation
Dorado, the Large
Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is seen here in a remarkably
deep,
colorful, image.
Spanning about 15,000 light-years or so, it is
the most massive of the Milky Way's
satellite
galaxies and is the home of the
closest
supernova in modern times,
SN 1987A.
The prominent patch below center is 30 Doradus,
also known as the magnificent
Tarantula Nebula, a giant
star-forming region about 1,000 light-years across.
 APOD: 2018 November 17 - The Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2018 November 17 - The Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula, also known as 30 Doradus,
is more than a thousand light-years in diameter,
a giant star forming region within nearby satellite galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud.
About 180 thousand light-years away, it's the largest,
most violent star forming region known in the whole Local
Group of galaxies.
The cosmic arachnid sprawls across this spectacular view,
composed with narrowband filter data centered on emission
from ionized hydrogen atoms.
Within the Tarantula (NGC 2070), intense radiation,
stellar winds and supernova shocks from the central young cluster of
massive stars, cataloged as R136,
energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
Around
the Tarantula are other star forming regions with
young star clusters, filaments, and blown-out
bubble-shaped clouds.
In fact, the frame includes the site of the closest supernova
in modern times,
SN 1987A,
left of center.
The rich field of view spans about 1 degree
or 2 full moons, in the southern
constellation
Dorado.
But were the Tarantula Nebula closer, say 1,500 light-years distant like
the local star forming Orion Nebula,
it would take up half the sky.
 APOD: 2018 May 20 - In the Heart of the Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2018 May 20 - In the Heart of the Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
In the heart of monstrous
Tarantula Nebula lies huge bubbles of energetic gas,
long filaments of dark dust, and unusually massive stars.
In the center of this heart, is a
knot of stars so dense that it was once thought to be a single star.
This star cluster, labeled as
R136 or NGC 2070,
is visible just above the center of the
featured image and home to a great number of hot young stars.
The energetic light from these stars continually ionizes nebula gas,
while their energetic particle wind blows
bubbles and defines intricate filaments.
The
representative-color picture, a digital synthesis of images from the
NASA/ESA orbiting
Hubble Space Telescope and
ESO's ground-based
New Technology Telescope, shows great details of the
LMC nebula's tumultuous center.
The Tarantula Nebula, also known as the
30 Doradus nebula, is one of the
largest
star-formation regions known, and has been creating
unusually strong episodes of
star formation every few million years.
 APOD: 2017 November 16 - The Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2017 November 16 - The Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula is more than a thousand light-years in diameter,
a giant star forming region within nearby satellite galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud,
about 180 thousand light-years away.
The largest, most violent star forming region known in the whole Local
Group of galaxies, the cosmic arachnid sprawls across
this spectacular view
composed with narrowband data centered on emission
from ionized hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
Within the Tarantula (NGC 2070), intense radiation,
stellar winds and supernova shocks from the central young cluster of
massive stars, cataloged as R136,
energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
Around
the Tarantula are other star forming regions with
young star clusters, filaments, and blown-out
bubble-shaped clouds.
In fact, the frame includes the site of the closest supernova in modern times,
SN 1987A,
right of center.
The rich field of view spans about 1 degree
or 2 full moons, in the southern
constellation
Dorado.
But were the Tarantula Nebula closer, say 1,500 light-years distant like
the local star forming Orion Nebula,
it would take up half the sky.
 APOD: 2016 February 26 - The Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2016 February 26 - The Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula is more than a thousand light-years in diameter,
a giant star forming region within nearby satellite galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud,
about 180 thousand light-years away.
The largest, most violent star forming region known in the whole Local
Group of galaxies, the cosmic arachnid sprawls across
this
spectacular composite view constructed with space- and ground-based
image data.
Within the Tarantula (NGC 2070), intense radiation,
stellar winds and supernova shocks from the central young cluster of
massive stars, cataloged as R136,
energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
Around
the Tarantula are other star forming regions with
young star clusters, filaments, and blown-out
bubble-shaped clouds
In fact, the frame includes the
site of the closest supernova in modern times,
SN
1987A, at the lower right.
The rich field of view spans about 1 degree
or 2 full moons, in the southern
constellation Dorado.
But were the Tarantula Nebula closer, say 1,500 light-years distant like
the local star forming Orion Nebula,
it would take up half the sky.
 APOD: 2016 January 24 - Star Cluster R136 Bursts Out
APOD: 2016 January 24 - Star Cluster R136 Bursts Out
Explanation:
In the center of star-forming region 30 Doradus lies a huge cluster
containing some of the largest, hottest, and most massive stars known.
These stars, known collectively as
star cluster R136, were captured in the
featured image in
visible light by the
Wide Field Camera 3 in 2009 peering through the
Hubble Space Telescope.
Gas and dust clouds in
30 Doradus, also known as the
Tarantula Nebula,
have been sculpted into elongated shapes by powerful
winds and
ultraviolet radiation
from these hot cluster stars.
The 30 Doradus Nebula
lies within a neighboring galaxy known as the
Large Magellanic Cloud and is located a mere 170,000
light-years away.
 APOD: 2015 August 27 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
APOD: 2015 August 27 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
Explanation:
The 16th century Portuguese navigator
Ferdinand
Magellan and his crew had plenty of time to study the
southern sky during the
first
circumnavigation of planet Earth.
As a result, two fuzzy cloud-like
objects easily visible to southern hemisphere
skygazers are known as the
Clouds of Magellan, now understood to be
satellite galaxies of our much larger, spiral Milky Way galaxy.
About 160,000 light-years distant in the constellation
Dorado, the Large
Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is seen here in a remarkably
deep, colorful, image.
Spanning about 15,000 light-years or so, it is
the most massive of the Milky Way's
satellite
galaxies and is the home of the
closest
supernova in modern times,
SN 1987A.
The prominent patch below center is 30 Doradus,
also known as the magnificent
Tarantula Nebula, is a giant
star-forming region about 1,000 light-years across.
 APOD: 2014 June 12 - The Tarantula Zone
APOD: 2014 June 12 - The Tarantula Zone
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula is more than 1,000 light-years in diameter,
a giant star forming region within our neighboring galaxy
the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC).
That cosmic arachnid lies toward the upper left in this deep and
colorful
telescopic view made through broad-band and
narrow-band filters.
The image spans nearly 2 degrees (4 full moons) on the sky and
covers a part of the LMC over 8,000 light-years across.
Within the Tarantula (NGC 2070), intense radiation,
stellar winds and supernova shocks from the central young cluster of massive
stars, cataloged as R136,
energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
Around the Tarantula
are other violent star-forming regions with
young star clusters, filaments, and
bubble-shaped clouds
In fact, the frame includes the
site of the closest supernova in modern times,
SN 1987A,
just above center.
The rich field of view is located in the southern
constellation
Dorado.
 APOD: 2013 May 28 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
APOD: 2013 May 28 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
Explanation:
The 16th century Portuguese navigator
Ferdinand
Magellan and his crew had plenty of time to study the
southern sky during the
first
circumnavigation of planet Earth.
As a result, two fuzzy cloud-like
objects easily visible to southern hemisphere
skygazers are known as the
Clouds of Magellan, now understood to be
satellite galaxies of our much larger, spiral Milky Way galaxy.
About 160,000 light-years distant in the constellation
Dorado,
the Large
Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is seen here in a remarkably deep, colorful,
and annotated composite image.
Spanning about 15,000 light-years or so, it is
the most massive of the Milky Way's
satellite
galaxies and is the home of the
closest
supernova in modern times,
SN 1987A.
The prominent patch just left of center is 30 Doradus,
also known as the magnificent
Tarantula Nebula, is a giant
star-forming region about 1,000
light-years
across.
 APOD: 2013 February 11 - N11: Star Clouds of the LMC
APOD: 2013 February 11 - N11: Star Clouds of the LMC
Explanation:
Massive stars, abrasive
winds, mountains of
dust, and
energetic light
sculpt one of the largest and most picturesque regions of
star formation in the
Local Group of Galaxies.
Known as N11, the region is
visible on the upper right of many images of its home galaxy, the
Milky Way neighbor known as the
Large Magellanic Clouds (LMC).
The above image was taken for scientific purposes by the Hubble Space Telescope and
reprocessed for artistry by an amateur to win the
Hubble's Hidden Treasures
competition.
Although the section imaged above is known as
NGC 1763,
the entire N11 emission nebula is second in LMC size only to
30 Doradus.
Studying the stars in N11
has shown that it actually houses three successive generations of star formation.
Compact globules of dark dust
housing emerging young stars are also visible around the image.
 APOD: 2012 July 30 - Ash and Lightning Above an Icelandic Volcano
APOD: 2012 July 30 - Ash and Lightning Above an Icelandic Volcano
Explanation:
Why did the picturesque
2010 volcanic eruption in Iceland create so much ash?
Although the large
ash plume was not unparalleled in its abundance, its location was particularly
noticeable because it
drifted across such well-populated areas.
The
Eyjafjallajökull
volcano in southern Iceland began erupting on 2010 March 20,
with a second eruption starting under the center of a small glacier on 2010 April 14.
Neither eruption was unusually powerful.
The second eruption, however, melted a large amount of
glacial ice which then cooled and fragmented lava into gritty
glass particles that were carried up with the
rising volcanic plume.
Pictured above
during the second eruption,
lightning bolts illuminate
ash pouring out of the Eyjafjallajökull volcano.
 APOD: 2012 July 29 - Star Cluster R136 Bursts Out
APOD: 2012 July 29 - Star Cluster R136 Bursts Out
Explanation:
In the center of star-forming region
30 Doradus lies a
huge cluster
of the largest, hottest, most massive stars known.
These stars, known collectively as
star cluster R136,
were captured above in
visible light by the
Wide Field Camera
peering through the refurbished
Hubble Space Telescope.
Gas and dust clouds in
30 Doradus, also known as the
Tarantula Nebula,
have been sculpted into elongated shapes by powerful
winds and
ultraviolet radiation
from these hot cluster stars.
The 30 Doradus Nebula
lies within a neighboring galaxy known as the
Large Magellanic Cloud and is located a mere 170,000
light-years away.
 APOD: 2012 May 16 - Star Formation in the Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2012 May 16 - Star Formation in the Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
The largest, most violent star forming region known in the whole
Local Group of galaxies
lies in our neighboring galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC).
Were the Tarantula Nebula at the distance of the
Orion Nebula -- a local star forming region --
it would take up fully half the sky.
Also called
30 Doradus, the red and pink gas indicates a massive
emission nebula, although
supernova remnants and
dark nebula also exist there.
The bright knot of stars
left of center
is called R136 and contains many of the most
massive, hottest, and brightest stars known.
The
above image is one of the largest mosaics ever created by
observations of the
Hubble Space Telescope and has revealed unprecedented details of this enigmatic star forming region.
The image is being released to celebrate the
22nd anniversary of Hubble's launch.
 APOD: 2010 October 16 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
APOD: 2010 October 16 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
Explanation:
The 16th century Portuguese navigator
Ferdinand
Magellan and his crew had plenty of time to study the
southern sky during the
first
circumnavigation of planet Earth.
As a result, two fuzzy cloud-like
objects easily visible to southern hemisphere skygazers are known as the
Clouds of Magellan,
now understood to be
satellite galaxies of our much larger, spiral Milky Way galaxy.
About 160,000 light-years distant in the constellation
Dorado,
the Large
Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is seen here in a remarkably
deep, colorful composite image, starlight from the
central bluish bar
contrasting with the telltale reddish glow of
ionized atomic hydrogen gas.
Spanning about 15,000 light-years or so, it is
the most massive of the Milky Way's
satellite
galaxies and is the home of the
closest
supernova in modern times, SN 1987A.
The prominent patch at top left is 30 Doradus,
also known as the magnificent
Tarantula Nebula.
The giant star-forming region is about 1,000 light-years across.
 APOD: 2010 May 18 - Tentacles of the Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2010 May 18 - Tentacles of the Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
The largest, most violent star forming region known in the whole
Local Group of galaxies
lies in our neighboring galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC).
Were the Tarantula Nebula at the distance of the
Orion Nebula -- a local star forming region --
it would take up fully half the sky.
Also called
30 Doradus, the red and pink gas indicates a massive
emission nebula, although
supernova remnants and
dark nebula also exist there.
The bright knot of stars
left of center
is called R136 and contains many of the most
massive, hottest, and brightest stars known.
The
above image taken
with the
European Southern Observatory's (ESO's)
Wide Field Imager
is one of the
most detailed ever of this vast star forming region.
A recent
Hubble image of part of the nebula has uncovered a very massive
star escaping
from the region.
 APOD: 2009 December 21 - Star Cluster R136 Bursts Out
APOD: 2009 December 21 - Star Cluster R136 Bursts Out
Explanation:
In the center of star-forming region
30 Doradus lies a
huge cluster
of the largest, hottest, most massive stars known.
These stars, known collectively as
star cluster R136,
were captured above in
visible light by the newly installed
Wide Field Camera
peering though the recently refurbished
Hubble Space Telescope.
Gas and dust clouds in
30 Doradus, also known as the
Tarantula Nebula,
have been sculpted into elongated shapes by powerful
winds and
ultraviolet radiation
from these hot cluster stars.
The 30 Doradus Nebula
lies within a neighboring galaxy known as the
Large Magellanic Cloud and is located a mere 170,000
light-years away.
 APOD: 2009 September 16 - The Tarantula Zone
APOD: 2009 September 16 - The Tarantula Zone
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula is more than 1,000 light-years in diameter --
a giant star forming region within our neighboring galaxy
the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC).
That cosmic arachnid lies left of center
in this sharp, colorful telescopic image taken through
narrow-band filters.
It covers a part of the LMC
over 2,000 light-years across.
Within the Tarantula (NGC 2070), intense radiation, stellar winds and
supernova shocks from the central young cluster of massive
stars, cataloged as R136,
energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
Around the Tarantula are other violent star-forming regions with
young star clusters, filaments and
bubble-shaped clouds.
The rich field is about as wide
as the full Moon on the sky, located in the southern
constellation
Dorado.
 APOD: 2009 March 31 - In the Heart of the Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2009 March 31 - In the Heart of the Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
In the heart of monstrous
Tarantula Nebula lies huge bubbles of energetic gas,
long filaments of dark dust, and unusually massive stars.
In the center of this heart, is a
knot of stars so dense that it was once thought to be a single star.
This star cluster, labeled as
R136 or NGC 2070,
is visible just above the center of the
above image and home to a great number of hot young stars.
The energetic light from these stars continually ionizes nebula gas,
while their energetic particle wind blows
bubbles and defines intricate filaments.
The
above representative-color picture of this great
LMC nebula details its tumultuous center.
The Tarantula Nebula, also known as the
30 Doradus nebula, is one of the
largest
star-formation regions known, and has been creating
unusually strong episodes of star formation every few million years.
 APOD: 2009 February 5 - NGC 604: X-rays from a Giant Stellar Nursery
APOD: 2009 February 5 - NGC 604: X-rays from a Giant Stellar Nursery
Explanation:
Some 3 million light-years distant in nearby spiral
galaxy M33,
giant stellar nursery
NGC 604 is
about 1,300 light-years across,
or nearly 100 times the size of the
Orion Nebula.
In fact, among the star forming regions within the Local Group of
galaxies, NGC 604 is second in size only to 30 Doradus,
also known as
the Tarantula Nebula in the
Large Magellanic Cloud.
This space-age
color composite of X-ray data (in blue hues)
from the Chandra Observatory, and
Hubble optical data
shows that NGC 604's cavernous bubbles and cavities are filled with a
hot, tenuous,
X-ray
emitting gas.
Intriguingly, NGC 604 itself is divided by
a wall of relatively cool gas.
On the western (right) side of the nebula,
measurements
indicate that material is likely
heated to X-ray temperatures by the energetic winds
from a cluster of about 200 young, massive stars.
On the eastern side the X-ray filled cavities seem to be older,
suggesting
supernova explosions from the end of
massive star evolution contribute to their formation.
 APOD: 2008 December 19 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
APOD: 2008 December 19 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
Explanation:
The 16th century Portuguese navigator
Ferdinand
Magellan and his crew had plenty of time to study the
southern sky during the first circumnavigation of planet Earth.
As a result, two fuzzy cloud-like
objects easily visible to southern hemisphere skygazers are known as the
Clouds of Magellan,
now understood to be
satellite galaxies of our much larger, spiral Milky Way galaxy.
About 160,000 light-years distant in the constellation
Dorado,
the Large
Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is seen here in a remarkably detailed,
10
frame mosaic image.
Spanning about 30,000 light-years or so, it is
the most massive of the Milky Way's
satellite
galaxies and is the site of the
closest
supernova in modern times, SN 1987A.
The prominent reddish knot near the bottom is 30 Doradus, or the
Tarantula Nebula, a giant star-forming
region in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
To identify the location of the supernova and navigate your way
around the many star clusters and nebulae of the LMC, just consult this
well-labeled view.
 APOD: 2008 November 11 - The Cosmic Web of the Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2008 November 11 - The Cosmic Web of the Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
First
cataloged as a star, 30 Doradus is actually an
immense star forming region in nearby galaxy
The Large Magellanic Cloud.
The region's spidery appearance is responsible for its popular name,
the Tarantula
nebula, except that this tarantula is about 1,000
light-years across, and 180,000 light-years
away in the southern constellation
Dorado.
If the Tarantula
nebula were at the distance of the
Orion Nebula
(1,500 light-years), the nearest stellar nursery to Earth, it
would appear to cover about 30 degrees (60
full moons)
on the sky.
The spindly arms of the
Tarantula nebula
surround
NGC 2070,
a star cluster that contains some of the brightest,
most massive stars known.
Intriguing details of the nebula are visible in
this
scientifically-colored image.
The cosmic Tarantula
also lies near the site of the closest
recent supernova.
 APOD: 2008 April 26 - The Tarantula Zone
APOD: 2008 April 26 - The Tarantula Zone
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula is more than 1,000 light-years in diameter --
a giant star forming region within our neighboring galaxy
the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC).
That cosmic arachnid lies at the upper left of
this
expansive mosiac covering a part of the LMC
over 6,000 light-years across.
Within the Tarantula (NGC 2070), intense radiation, stellar winds and
supernova shocks from the central young cluster of massive
stars, cataloged as R136,
energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
Around the Tarantula are other violent star-forming regions with
young star clusters, filaments and
bubble-shaped clouds.
The small but expanding remnant of
supernova 1987a, the closest supernova
in modern history, is located near the center of the view.
The rich field is about as wide
as four full moons on the sky, located in the southern
constellation
Dorado.
 APOD: 2007 August 22 - Tentacles of the Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2007 August 22 - Tentacles of the Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
The largest, most violent star forming region known in the whole
Local Group of galaxies
lies in our neighboring galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC).
Were the Tarantula Nebula at the distance of the
Orion Nebula -- a local star forming region --
it would take up fully half the sky.
Also called
30 Doradus, the red and pink
gas indicates a massive
emission nebula, although
supernova remnants and
dark nebula also exist there.
The bright knot of stars left of center is called
R136 and contains many of the most
massive, hottest, and brightest stars known.
The
above image taken with the
European Southern Observatory's (ESO's)
Wide Field Imager
is one of the
most detailed ever of this vast star forming region.
ESO has made it possible to fly around and into this detailed image by
clicking here.
 APOD: 2007 May 6 - Star Cluster R136 Bursts Out
APOD: 2007 May 6 - Star Cluster R136 Bursts Out
Explanation:
In the center of star-forming region
30 Doradus lies a
huge cluster of the largest, hottest, most massive stars known.
These stars, known as the
star cluster R136,
and part of the surrounding nebula are captured here in
this gorgeous visible-light image from the
Hubble Space Telescope.
Gas and dust clouds in
30 Doradus, also known as the
Tarantula Nebula,
have been sculpted into elongated shapes by powerful
winds and
ultraviolet radiation
from these hot cluster stars.
The 30 Doradus Nebula lies within a neighboring galaxy, the
Large Magellanic Cloud, located a mere 170,000
light-years away.
 APOD: 2006 May 10 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
APOD: 2006 May 10 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
Explanation:
Portuguese navigator
Fernando
de Magellan and his crew had plenty of time to study the
southern sky during the first circumnavigation of planet Earth.
As a result, two fuzzy cloud-like
objects easily visible for southern hemisphere
skygazers are known as the
Clouds of Magellan.
Of course, these star clouds are now understood to be
dwarf irregular galaxies, satellites of our larger spiral
Milky Way galaxy.
The Large
Magellanic Cloud (LMC)
pictured above is only about 180,000 light-years distant in
the constellation
Dorado.
Spanning about 15,000 light-years or so, it is
the most massive of the
Milky Way's satellite galaxies
and is the site of the
closest
supernova in modern times.
The prominent red knot on the left is 30 Doradus, or the
Tarantula Nebula, a giant star-forming
region in the
Large
Magellanic Cloud.
 APOD: 2006 January 6 - The Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2006 January 6 - The Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
First
cataloged as a star, 30 Doradus is actually an
immense star forming region in nearby galaxy
The Large Magellanic Cloud.
The region's spidery appearance is responsible for its popular name,
the Tarantula
Nebula, except that this tarantula is about
1,000 light-years across, and 180,000 light-years away in
the southern constellation
Dorado.
If the Tarantula Nebula were at the distance of the
Orion Nebula
(1,500 light-years), the nearest stellar nursery to Earth, it
would appear to cover about 30 degrees
on the sky or 60 full moons.
The spindly arms of the
Tarantula Nebula surround
NGC 2070, a cluster
that contains some of the intrinsically brightest,
most massive stars known.
Intriguing details of the nebula's core can be seen in
this
remarkable skyscape, a composite
of 31 hours of exposure time.
This cosmic Tarantula
also lies near the site of the closest
recent supernova.
 APOD: 2005 December 12 - 30 Doradus: The Tarantula Zone
APOD: 2005 December 12 - 30 Doradus: The Tarantula Zone
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula is more than 1,000 light-years across -
a giant emission nebula within our
neighboring galaxy
the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Inside this cosmic
arachnid
lies a central young cluster of massive stars, cataloged as
R136, whose intense radiation and strong winds
have helped energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
In this impressive color mosaic of images from the
Curtis Schmidt telescope at
Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory
(CTIO) in Chile,
other young star clusters can be seen still within the nebula's grasp.
Also notable among the denizens
of the Tarantula zone are several
dark clouds, sprawling wispy filaments of gas,
compact emission nebula,
nearly spherical supernova remnants,
and areas surrounding hot stars known as superbubbles.
The rich mosaic's field of view covers an area on the sky
about the size of the full moon in the southern
constellation Dorado.
 APOD: 2005 December 11 - R136: The Massive Stars of 30 Doradus
APOD: 2005 December 11 - R136: The Massive Stars of 30 Doradus
Explanation:
In the center of star-forming region
30 Doradus lies a
huge cluster of the largest, hottest, most massive stars known.
These stars, known as the
star cluster R136,
and part of the surrounding nebula are captured here in
this gorgeous visible-light image from the
Hubble Space Telescope.
Gas and dust clouds in
30 Doradus, also known as the
Tarantula Nebula,
have been sculpted into elongated shapes by powerful
winds and
ultraviolet radiation
from these hot cluster stars.
The 30 Doradus Nebula lies within a neighboring galaxy, the
Large Magellanic Cloud, located a mere 170,000
light-years away.
 APOD: 2004 December 28 - Tentacles of the Tarantula Nebula
APOD: 2004 December 28 - Tentacles of the Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
The Tarantula Nebula is a giant
emission nebula
within our neighboring galaxy the
Large Magellanic Cloud.
Inside this cosmic
arachnid lies a huge central young cluster of massive stars,
cataloged as R136
and partially visible on the upper right.
The energetic light and
winds from this cluster light up the nebula and sculpt
the surrounding gas and dust into vast
complex filaments.
These "tentacles" give the
Tarantula Nebula its name.
In this impressive color image from the
Wide-Field Imager camera on ESO's
2.2-meter telescope at
La Silla Observatory,
intricacies of the nebula's complex array of
dust and gas
are visible.
A 300 light-year portion of the Tarantula Nebula is imaged.
The Tarantula Nebula, also dubbed 30 Doradus, lies 170,000 light years away toward the constellation of Dorado.
 APOD: 2004 September 2 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
APOD: 2004 September 2 - The Large Cloud of Magellan
Explanation:
Portuguese navigator
Fernando
de Magellan and his crew had plenty
of time to study the southern sky during the
first circumnavigation of planet Earth.
As a result, two fuzzy cloud-like
objects easily visible for southern hemisphere skygazers
are known as the
Clouds of Magellan.
Of course, these star clouds are now understood to be dwarf
irregular galaxies,
satellites of our larger spiral
Milky Way galaxy.
The Large
Magellanic Cloud (LMC)
pictured above is only about 180,000 light-years distant in
the constellation
Dorado.
Spanning about 15,000 light-years or so, it is
the most massive of the Milky Way's satellite galaxies
and is the site of the
closest
supernova in modern times.
The prominent red knot on the right is 30 Doradus, or the
Tarantula Nebula, a giant star-forming
region in the
Large Magellanic Cloud.
 APOD: 2004 July 7 - N11B: Star Cloud of the LMC
APOD: 2004 July 7 - N11B: Star Cloud of the LMC
Explanation:
Massive stars, abrasive
winds, mountains of
dust, and
energetic light
sculpt one of the largest and most picturesque regions of
star formation in the
Local Group of Galaxies.
Known as N11, the region is
visible on the upper right of many images of its home galaxy, the
Milky Way neighbor known as the
Large Magellanic Clouds (LMC).
The above image actually highlights
N11B, part of the nebula that spans about 100 light years and is particularly active.
The entire emission nebula N11 is second in LMC size only to
30 Doradus.
Studying the stars in N11B has shown that it actually houses three successive
generations of star formation.
Compact globules of dark dust
housing emerging young stars are also visible on the upper right.
 APOD: 2004 February 2 - The Tarantula Nebula from Spitzer
APOD: 2004 February 2 - The Tarantula Nebula from Spitzer
Explanation:
In the heart of monstrous
Tarantula Nebula lies one of the most unusual
star clusters.
Known as NGC 2070 or
R136,
it is home to a great number of
hot young stars.
The energetic light from these stars continually
ionizes nebula gas, while their energetic particle
wind blows
bubbles and defines intricate
filaments.
The new
Spitzer Space Telescope took the
above representative-color infrared image of this great
LMC
cluster. The image details the cluster's tumultuous center in gas,
dust and young stars.
The 30 Doradus nebula is one of the
largest star-formation regions known, and has been creating
unusually strong episodes of
star formation every few million years.
In the heart of this heart is a
central knot of stars
that is so dense
it was once thought to be a single star.
 APOD: 2003 August 23 - The Tarantula Zone
APOD: 2003 August 23 - The Tarantula Zone
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula is more than 1,000 light-years across -
a giant emission nebula within our
neighboring galaxy
the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Inside this cosmic arachnid lies a central young cluster of massive
stars, cataloged as
R136, whose intense radiation and strong winds
have helped energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
In this
impressive color mosaic
of images from the
Wide-Field Imager
camera on ESO's 2.2 meter telescope at La Silla Observatory, other
young star clusters can be seen still within the
nebula's grasp.
Also notable among the denizens
of the Tarantula zone are several
dark clouds
invading the nebula's outer limits as well as
the dense cluster
of stars NGC 2100 at the extreme left edge of the
picture.
The small but expanding remnant of
supernova 1987a, the closest supernova
in modern history,
lies just off the lower right corner of the field.
The rich mosaic's field of view covers an area on the sky
about the size of
the full moon in the southern
constellation Dorado.
 APOD: 2003 June 22 - Massive Stars of 30 Doradus
APOD: 2003 June 22 - Massive Stars of 30 Doradus
Explanation:
In the center of star-forming region
30 Doradus lies a huge cluster of the largest, hottest,
most massive stars known.
These stars and part of the surrounding nebula are captured here in
this gorgeous visible-light
Hubble Space Telescope image.
Gas and dust clouds in 30 Doradus, also known as the
Tarantula Nebula,
have been sculpted into elongated shapes by
powerful winds and ultraviolet radiation from these
hot cluster stars.
Insets in the picture represent corresponding views from the
Hubble's infrared camera
where each square measures 15.5
light-years across.
Penetrating the obscuring
dust, these infrared images themselves
offer detailed pictures of
star formation within
the nebula's collapsing clouds, revealing
the presence of newborn massive stars.
The 30 Doradus Nebula
lies within a neighboring galaxy,
the Large Magellanic Cloud,
located a mere 170,000 light-years away.
 APOD: 2002 June 13 - The Tarantula Zone
APOD: 2002 June 13 - The Tarantula Zone
Explanation:
The
Tarantula Nebula is more than 1,000 light-years across -
a giant emission nebula within our neighboring galaxy
the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Inside this cosmic arachnid lies a central young cluster of massive
stars, cataloged as
R136, whose intense radiation and strong winds
have helped energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments.
In this
impressive color mosaic
of images from the
Wide-Field Imager
camera on ESO's 2.2 meter telescope at La Silla Observatory, other
young star clusters can be seen still within the
nebula's grasp.
Also notable among the denizens
of the Tarantula zone are several
dark clouds
invading the nebula's outer limits as well as
the dense cluster
of stars NGC 2100 at the extreme left edge of the
picture.
The small but expanding remnant of
supernova 1987a, the closest supernova
in modern history,
lies just off the lower right corner of the field.
The rich mosaic's field of view covers an area on the sky
about the size of
the full moon in the southern
constellation Dorado.
 APOD: 2001 July 30 - Star Cluster R136 Bursts Out
APOD: 2001 July 30 - Star Cluster R136 Bursts Out
Explanation:
In the center of star-forming region
30 Doradus
lies a huge cluster of the largest, hottest,
most massive stars known.
Known as
R136, the cluster's
energetic stars are breaking out of the
cocoon of gas and dust from which they formed.
This disintegrating cocoon, which fills the rest of the recently released
above picture by the
Hubble Space Telescope,
is predominantly
ionized hydrogen from 30 Doradus.
R136 is composed of thousands of
hot blue stars,
some about 50 times more massive than our
Sun.
R136, also known as
NGC 2070, lies in the
LMC - a satellite galaxy to our own
Milky Way Galaxy.
Although the young ages of stars in R136 make it
similar to a Milky Way
open cluster,
its high density of stars will likely turn it into a low mass
globular cluster
in a few billion years.
 APOD: October 27, 1999 - In the Heart of the Tarantula Nebula
APOD: October 27, 1999 - In the Heart of the Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
In the heart of monstrous
Tarantula Nebula
lies one of the most unusual star clusters.
Known as
NGC 2070 or R136,
it is home to a great number of hot young stars.
The energetic light from these stars continually ionizes nebula gas,
while their energetic particle wind blows bubbles and defines intricate filaments.
The
above representative-color picture of this great
LMC cluster details
its tumultuous center in gas,
dust and young stars.
The
30 Doradus nebula is one of the largest
star-formation regions known, and has been creating
unusually strong episodes of star formation
every few million years.
In the heart of this heart is a
central knot of stars
that is so dense it was once thought to be a single star.
 APOD: October 26, 1999 - 30 Doradus: The Tarantula Nebula
APOD: October 26, 1999 - 30 Doradus: The Tarantula Nebula
Explanation:
30 Doradus is an immense star forming region in a nearby galaxy known
as the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Its
spidery appearance is responsible for its popular name, the
Tarantula Nebula, except that
this tarantula is about 1,000 light-years across, and
165,000 light-years away in the southern constellation
Dorado.
If it were at the distance of the
Orion Nebula,
the nearest stellar nursery to Earth, it
would appear to cover about 30 degrees
on the sky or about 60
full moons.
The
above image was taken with the
Big Throughput Camera
and is shown in representative colors.
The spindly arms of the
Tarantula Nebula surround the
NGC 2070 star cluster
which contains some of the intrinsically brightest,
most massive stars known.
This celestial
Tarantula is also seen near the site of the
closest recent Supernova.
 APOD: October 1, 1999 - New Stars In 30 Doradus
APOD: October 1, 1999 - New Stars In 30 Doradus
Explanation:
Compare these
matched Hubble Space Telescope views
(visible-light on top; infrared on bottom) of a region
in the star-forming
30 Doradus Nebula.
Find the numbered
arrows in the infrared image which
identify newborn massive stars.
For example,
arrows 1 and 5 both point to compact clusters of
bright young stars.
Formed within
collapsing gas and dust clouds, the winds and radiation
from these hot stars have cleared away the remaining obscuring material
making the clusters easily apparent in both visible and infrared images.
But still shrouded in dust and readily seen only in the penetrating infrared
view are
newborn stars and star systems
indicated by arrows 2, 3, and 4.
Perhaps even more remarkable are the infrared bright spots indicated
by arrows 6 and 7.
Exactly in a line on opposite sides of the bright cluster at arrow 5,
they may actually be caused by
symmetric jets of material produced
by one of the young cluster stars.
These luminous spots are each about 5 light-years from the
cluster and would
correspond to points at which the
energetic jet material impacts
the surrounding dust clouds.
 APOD: September 30, 1999 - Massive Stars Of 30 Doradus
APOD: September 30, 1999 - Massive Stars Of 30 Doradus
Explanation:
This gorgeous visible-light
Hubble Space Telescope image shows a
young
cluster of massive stars at the center of the
30 Doradus Nebula.
Gas and dust clouds in 30 Doradus, also known as the
Tarantula Nebula,
have been sculpted into elongated shapes by
powerful winds and ultraviolet radiation from these
hot cluster stars.
Insets in the picture represent corresponding views from the
Hubble's infrared camera
where each square measures 15.5 light-years across.
Penetrating the obscuring dust, these infrared images themselves
offer detailed pictures of
star formation within
the nebula's collapsing clouds, revealing
the presence of newborn massive stars.
The 30 Doradus Nebula lies within a neighboring galaxy,
the Large Magellanic Cloud,
located a mere 170,000 light-years away.
 APOD: February 21, 1999 - In the Center of 30 Doradus
APOD: February 21, 1999 - In the Center of 30 Doradus
Explanation:
In the center of
30 Doradus
lies a huge cluster of the largest, hottest,
most massive stars known. The center of this cluster, known as
R136, is
boxed in the upper right portion of the above picture. The gas and
dust
filling the rest of the picture is predominantly ionized
hydrogen from the
emission nebula
30
Doradus. R136 is composed of thousands of hot blue
stars, some about 50 times more massive than our
Sun.
30 Doradus and R136 lie in the
LMC - a satellite galaxy to our own
Milky Way Galaxy. Although
the ages of stars in R136 cause it to be best described as an
open cluster,
R136's density will likely make it a low mass
globular cluster in a
few billion years.
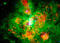 APOD: December 24, 1997 - 30 Doradus Across the Spectrum
APOD: December 24, 1997 - 30 Doradus Across the Spectrum
Explanation:
30 Doradus is lit up like a Christmas tree.
Shining in light across the electromagnetic spectrum,
30 Doradus glows because of all the energetic processes that go on there.
A distinctive region visible in a
Milky Way satellite galaxy
called the
Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), 30 Doradus is a hotbed of
star formation,
supernova explosions, and
ionized plasma. The
above image
is a composite of three pictures taken in three different wavelength bands of light.
Red represents
X-ray emission created by
gas as hot as 1 million degrees Kelvin. Green represents emission from
ionized hydrogen gas, and blue represents
ultraviolet
radiation primarily emitted by hot stars.
At the conclusion of this symphony of star formation and
light in a few million years,
astronomers expect that a new
globular cluster will have formed.
 APOD: October 4, 1997 - In the Center of 30 Doradus
APOD: October 4, 1997 - In the Center of 30 Doradus
Explanation:
In the center of
30 Doradus
lies a huge cluster of the largest, hottest,
most massive stars known. The center of this cluster, known as
R136, is
boxed in the upper right portion of the above picture. The gas and
dust
filling the rest of the picture is predominantly ionized
hydrogen from the
emission nebula
30
Doradus. R136 is composed of thousands of hot blue
stars, some about 50 times more massive than our
Sun. 30 Doradus and R136
lie in the
LMC - a satellite galaxy to our own
Milky Way Galaxy. Although
the ages of stars in R136 cause it to be best described as an
open cluster,
R136's density will likely make it a low mass
globular cluster in a
few billion years.
 APOD: June 4, 1997 - Tarantula
APOD: June 4, 1997 - Tarantula
Explanation:
NGC 2070 is an immense star forming region in a nearby galaxy known
as the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Its spidery appearance is responsible for its popular name,
"The Tarantula Nebula", except that
this tarantula is about 1,000 light-years across, and
165,000 light-years away in
the southern constellation Dorado.
If it were at the distance of
the Orion Nebula,
the nearest stellar nursery to Earth, it
would appear to cover about 30 degrees on the sky or about 60 full moons.
The spindly arms of
the Tarantula Nebula
surround the 30 Doradus Star Cluster
which contains some of the intrinsically brightest, most massive stars known.
This celestial Tarantula is also seen near the site of
the closest recent Supernova.
 APOD: March 5, 1997 - In the Center of NGC 604
APOD: March 5, 1997 - In the Center of NGC 604
Explanation: Stars are sometimes born in the midst of chaos.
About 3 million years ago in the nearby galaxy M33,
a large cloud of gas spawned dense internal knots which gravitationally
collapsed to form stars. But NGC 604
was so large, it could form enough stars to make a globular cluster.
Many young stars from this cloud
are visible above, along with what is left of the initial gas
cloud. Some stars were so massive they have already evolved and
exploded in a
supernova.
The brightest stars that are left emit
light so energetic that they create one of the largest cloud of ionized hydrogen gas known,
second only to the 30 Doradus Cluster
in Milky Way's close neighbor,
the Large Magellanic Cloud.
 APOD: May 24, 1996 - In the Center of 30 Doradus
APOD: May 24, 1996 - In the Center of 30 Doradus
Explanation:
In the center of
30 Doradus
lies a huge cluster of the largest, hottest,
most massive stars known. The center of this cluster, known as
R136, is
boxed in the upper right portion of the above picture. The gas and
dust
filling the rest of the picture is predominantly ionized
hydrogen from the
emission nebula
30
Doradus. R136 is composed of thousands of hot blue
stars, some about 50 times more massive than our
Sun. 30 Doradus and R136
lie in the
LMC - a satellite galaxy to our own
Milky Way Galaxy. Although
the ages of stars in R136 cause it to be best described as an
open cluster,
R136's density will likely make it a low mass
globular cluster in a
few billion years.
 APOD: May 23, 1996 - The Violent Star Cluster 30 Doradus
APOD: May 23, 1996 - The Violent Star Cluster 30 Doradus
Explanation:
The largest, most violent star forming region known in the whole
Local
Group of galaxies lies in our neighboring galaxy the
LMC. Were 30 Doradus
at the distance of the
Orion Nebula -- a local star forming region -- it
would take up fully half the sky. Also called the
Tarantula Nebula, the red gas indicates a massive
emission nebula, although
supernova remnants and
dark nebula
also exist in
30
Doradus. The bright knot of stars just below
center is called R136 and contains many of the most massive, hottest, and
brightest stars known.
 APOD: October 27, 1995 - The Tarantula and the Supernova
APOD: October 27, 1995 - The Tarantula and the Supernova
Explanation:
In this close-up of the Large Magellanic Cloud,
the spidery looking nebula on the left is fittingly known as
as the Tarantula nebula. It is an
emission nebula
surrounding a cluster of hot, young stars
called the 30 Doradus super cluster. This
cluster may contain the most massive stars known (about 50 times
the mass of the Sun). Such massive stars put out
more than 100 times as much energy as our Sun.
The bright "star" (lower right) is actually
Supernova 1987a
and is a harbinger of things to come for the stars
within the Tarantula. Massive stars
burn their nuclear fuel at drastically enhanced rates to support
their high energy output. As a result their lives
last only a few million years compared to the Sun's few billions of years.
They end in a spectacular death explosion, a
supernova,
like the star which exploded in 1987 as seen above.
Supernovae may leave behind imploded stellar cores which
form neutron stars or
black holes.